

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 1221.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20141027
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Dong1, HAN Na1,*( ), ZHANG Xingxiang1,*(
), ZHANG Xingxiang1,*( ), WANG Lejun2, WANG Ning1, LI Wei1, YU Wanyong1, LI Zhinan1
), WANG Lejun2, WANG Ning1, LI Wei1, YU Wanyong1, LI Zhinan1
Received:2014-11-21
Online:2015-06-10
Published:2015-05-06
Contact:
HAN Na,ZHANG Xingxiang
E-mail:hanna@tjpu.edu.cn;zhangxingxing@tipu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Dong, HAN Na, ZHANG Xingxiang, WANG Lejun, WANG Ning, LI Wei, YU Wanyong, LI Zhinan. Preparation and Characterization of Cellulose Propionate-g-diethylene Glycol Hexadecyl Ether Solid-solid Phase Change Material†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(6): 1221.
| Sample | n(Prepolymer)∶n(CP) | n(CP2O)∶n(CELL) | m(CELL)/g | m(AmimCl)/g | V(CP2O)/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 4∶1 | 2∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 1.6 |
| b | 4∶1 | 4∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 3.2 |
| c | 4∶1 | 6∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 4.8 |
| d | 4∶1 | 8∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 6.4 |
| e | 6∶1 | 2∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 1.1 |
| f | 6∶1 | 4∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 2.2 |
| g | 6∶1 | 6∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 3.2 |
| h | 6∶1 | 8∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 4.3 |
| i | 8∶1 | 2∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 0.8 |
| j | 8∶1 | 4∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 1.6 |
| k | 8∶1 | 6∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 2.4 |
| l | 8∶1 | 8∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 3.2 |
Table 1 Feeding ratio and composition of raw materials
| Sample | n(Prepolymer)∶n(CP) | n(CP2O)∶n(CELL) | m(CELL)/g | m(AmimCl)/g | V(CP2O)/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 4∶1 | 2∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 1.6 |
| b | 4∶1 | 4∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 3.2 |
| c | 4∶1 | 6∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 4.8 |
| d | 4∶1 | 8∶1 | 1.0 | 19.2 | 6.4 |
| e | 6∶1 | 2∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 1.1 |
| f | 6∶1 | 4∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 2.2 |
| g | 6∶1 | 6∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 3.2 |
| h | 6∶1 | 8∶1 | 0.7 | 12.8 | 4.3 |
| i | 8∶1 | 2∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 0.8 |
| j | 8∶1 | 4∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 1.6 |
| k | 8∶1 | 6∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 2.4 |
| l | 8∶1 | 8∶1 | 0.5 | 9.6 | 3.2 |
| Sample | b | c | d | f | g | h | j | k | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19.4 | 17.1 | 25.9 | 32.2 | 25.9 | 33.4 | 31.3 | 24.8 | 32.2 | |
| 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.18 | |
| 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.33 |
Table 2 1H NMR analysis of CP-g-E2C16 samples
| Sample | b | c | d | f | g | h | j | k | l |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19.4 | 17.1 | 25.9 | 32.2 | 25.9 | 33.4 | 31.3 | 24.8 | 32.2 | |
| 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.31 | 0.15 | 0.21 | 0.18 | |
| 0.14 | 0.12 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.22 | 0.37 | 0.31 | 0.21 | 0.33 |
| Sample | n(Prepolymer)∶n(CP) | n(CP2O)∶n(CELL) | Heating | Cooling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tonset/℃ | Tp/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Tonset/℃ | Tp/℃ | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | |||
| E2C16 | 28 | 35 | 94 | 19 | 25 | 93 | ||
| CP | 6∶1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| c | 4∶1 | 6∶1 | 28 | 35 | 45 | 13 | 23 | 45 |
| g | 6∶1 | 6∶1 | 27 | 35 | 48 | 11 | 22 | 48 |
| k | 8∶1 | 6∶1 | 25 | 36 | 52 | 11 | 23 | 52 |
Table 3 DSC data of CP-g-E2C16 copolymers and native materials
| Sample | n(Prepolymer)∶n(CP) | n(CP2O)∶n(CELL) | Heating | Cooling | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tonset/℃ | Tp/℃ | ΔHm/(J·g-1) | Tonset/℃ | Tp/℃ | ΔHc/(J·g-1) | |||
| E2C16 | 28 | 35 | 94 | 19 | 25 | 93 | ||
| CP | 6∶1 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| c | 4∶1 | 6∶1 | 28 | 35 | 45 | 13 | 23 | 45 |
| g | 6∶1 | 6∶1 | 27 | 35 | 48 | 11 | 22 | 48 |
| k | 8∶1 | 6∶1 | 25 | 36 | 52 | 11 | 23 | 52 |
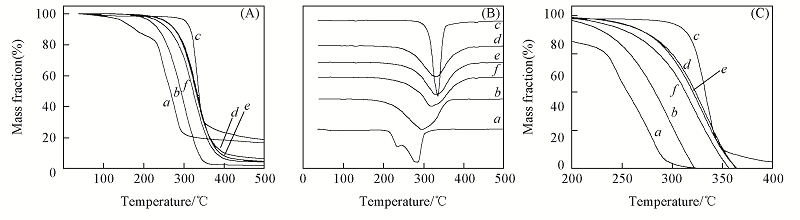
Fig.4 TG(A) and DTG(B) curves of CP(a), E2C16(b),CEll(c) and CP-g-E2C16 copolymersPpartly enlarge TG curve of (A). d. sample c; e. sample g; f. sample k.
| Sample | T5%/℃ | Tonset/℃ | Tp/℃ | Mass fraction(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CELL | 321 | 317 | 335 | 75.6 |
| E2C16 | 256 | 246 | 295 | 98.0 |
| CP | 171 | 138 | 285 | 82.8 |
| c | 298 | 289 | 332 | 92.1 |
| g | 296 | 285 | 329 | 93.0 |
| k | 287 | 276 | 319 | 94.2 |
Table 4 Thermogravimetic analysis of CP-g-E2C16 copolymers
| Sample | T5%/℃ | Tonset/℃ | Tp/℃ | Mass fraction(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CELL | 321 | 317 | 335 | 75.6 |
| E2C16 | 256 | 246 | 295 | 98.0 |
| CP | 171 | 138 | 285 | 82.8 |
| c | 298 | 289 | 332 | 92.1 |
| g | 296 | 285 | 329 | 93.0 |
| k | 287 | 276 | 319 | 94.2 |
| [1] | Tzvetkov G., Fink R. H., Scripta Mater., 2008, 59, 348—351 |
| [2] | You M., Zhang X. X., Li W., Wang X. C., Thermochim Acta, 2008, 472(1/2), 20—24 |
| [3] | Bryant Y. G., David C. P., Fabric with Reversible Enhanced Thermal Properties, WO 9324241, 1992-12-09 |
| [4] | Nihal S., Emel O., Thermochimica Acta, 2007, 454(2), 90—98 |
| [5] | Hawes D. W., Banu D., Sol. Energ. Mater., 1990, 21(1), 61—80 |
| [6] | Jiang Y., Ding E. Y., Li G. K., Polym. Mater. Sci. & Eng., 2001, 17(3), 173—175 |
| (姜勇, 丁恩勇, 黎国康.高分子材料科学与工程, 2001,17(3), 173—175) | |
| [7] | Jiang Y., Ding E. Y., Yang Y.Q., Li Y. K., J. Cellulose Sci. & Technol., 2000, 8(2), 17—24 |
| (姜勇, 丁恩勇, 杨玉芹, 黎国康.纤维素科学与技术, 2000,8(2), 17—24) | |
| [8] | Jiang Y., Ding E.Y., Li G. K.,Guangzhou Chem., 1999, (3), 48—54 |
| (姜勇, 丁恩勇, 黎国康.广州化学, 1999, (3), 48—54) | |
| [9] | Guo Y. Q., Lv S. H., Ye S. H., He T., Chen M. C., Polym. Mater. Sci. & Eng., 2005, 21(1), 176—179 |
| (郭元强, 吕社辉, 叶四化, 何涛, 陈鸣才.高分子材料科学与工程, 2005,21(1), 176—179) | |
| [10] | Crépy L., Miri V., Joly N., Martin P., Lefebvre J. M., Carbohyd. Polym., 2011, 83(4), 1812—1820 |
| [11] | Li Y. X., Wu M., Liu R. G., Huang Y., Sol. Energ. Mater. Sol. C, 2009, 93(8), 1321—1328 |
| [12] | Meng J. Y., Tang X. F., Zhang Z. L., Zhang X. X., Shi H. F., Thermochimica Acta, 2013, 574, 116—120 |
| [13] | Meng J.Y., Zhang X. X., Li W., Yuan W. J., Wu X. M., Zhang Z. L., Shi H. F., Sci. Adv. Mater., 2014, 6(12), 2640—2645 |
| [14] | Zhang Z. L., Tang X. F., Meng J. Y., Zhang X. X., Shi H. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1), 175—179 |
| (张智力, 唐孝芬, 孟洁云, 张兴祥, 石海峰.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(1), 175—179) | |
| [15] | Luan Y. H., Wu J., Zhan M. S., Zhang J. M., Zhang J., He J. S., Cellulose, 2013, 20(1), 327—337 |
| [16] | Luan Y. H., Zhang J. M., Zhan M. S., Wu J., Zhang J., He J. S., Carbohyd. Polym., 2013, 92(1), 307—311 |
| [17] | Wang D. S., Huang Y., Shen J. R., J. South China Univ. Technol., 2001, 29(12), 26—30 |
| (王东山, 黄勇, 沈家瑞.华南理工大学学报, 2001,29(12), 26—30) | |
| [18] | Ren Q., Wu J., Zhang J., He J.S., Guo M. L.,Acta Polym. Sin., 2003, (3), 448—451 |
| (任强, 武进, 张军, 何嘉松, 过梅丽. 高分子学报, 2003, (3), 448—451) | |
| [19] | Zhang H., Wu J., Zhang J., He J. S., Macromolecules, 2005, 38(20), 8272—8277 |
| [20] | Wang M. L., Zang H. J., Cai B. X., Cheng B. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(7), 1469—1472 |
| (王美玲, 臧洪俊, 蔡白雪, 程博闻.高等学校化学学报, 2009,30(7), 1469—1472) | |
| [21] | Tang X. F., Meng J. Y., Zhang X. X., Shi H. F., Li W., Funct. Mater., 2014, 15(45), 15027—15030 |
| (唐孝芬, 孟洁云, 张兴祥, 石海峰, 李伟.功能材料, 2014,15(45), 15027—15030) | |
| [22] | Ulrich N., Berthold W., Siegfried W., Starch, 2002, 54, 449—453 |
| [23] | Bhanu V. A., Rangarajan P., Wiles K., Bortner M., Sankarpandian M., Godshall D., Glass T. E., Banthia A.K., Yang J., Wilkes G., Baird D., McGrath J. E., Polymer, 2002, 43, 4841—4850 |
| [1] | FU Jinzhou, WANG Hanwei, LI Yingying, WANG Chao, LI Caicai, SUN Qingfeng, LI Huiqiao. Micro/Nanocellulose Functional Membranes for Energy and Environment [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1407. |
| [2] | ZHAO Ziyi,ZHENG Hongzhi,XU Yan. Multi-color Circularly Polarized Luminescence Properties of Cellulose Nanocrystal † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1120. |
| [3] | KONG Jinfeng, ZHU Yuzhang, JIN Jian. Sulfonated Cellulose Nanofibers Film Supported Nanofiltration Membrane for High-flux and High-rejection Desalination † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 690. |
| [4] | WU Rong, DONG Qihui, SUN Yiyi, SU Erzheng. Efficient Enzyme Immobilization by Combining Adsorption and Cellulose Membrane Coating † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1888. |
| [5] | HU Xueyi, CHEN Miaomiao, FANG Yun, FENG Ruiqin, HAN Huihui. Investigation on Pseudo-polyanions of Cationic Cellulose-Sodium Dodecylbenzenesulfonate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1464. |
| [6] | WANG Wenliang,SHI Yujie,WANG Shaohua,DANG Zepan,LI Xinping. Pyrolysis Behavior and Product Characteristics of Microwave co-Pyrolysis of Cellulose and Waste Tire† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 964. |
| [7] | LIU Gang, ZHANG Heng, SUN Heng, ZHU Hongxia, ZHANG Yuhan, ZHU Qingzeng, YUAN Shiling. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on the Structure of Cellulose Inclusion Complexes and Interactions Between Cellulose Chains and Solvent Molecules in Alkali/urea Aqueous Solution† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 714. |
| [8] | LIU Xing, WANG Wenjun, SHAO Ziqiang, LI Lei. Preparation and Characterization of Nanocellulose/Polylactide Fully Green Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 373. |
| [9] | LIU Yu,CHEN Gang,ZHU Jiatian,CHEN Wenjin,HU Wen,LIU Yingyao,FANG Zhiqiang. Preparation, Structure and Properties of Strong, Transparent Cellulose Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2298. |
| [10] | LI Caixin, LIANG Xiaorong, GU Ju. Preparation and Characterization of Bagasse Nanocellulose† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1286. |
| [11] | HAN Na, WANG Xiufang, QU Tingsi, QIAN Yongqiang, LU Yahong. Preparation and Properties of Cellulose Benzoate and Preliminary Exploration About Cellulose Benzoate-g-polyoxyethylene(2) Hexadecyl Ether† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 1099. |
| [12] | ZHANG Sihang, HE Yongfeng, FU Runfang, JIANG Jie, LI Qingbi, GU Yingchun, CHEN Sheng. Preparation and Electrochromic Properties of Nano Cellulose/Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) Composite Films† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 1090. |
| [13] | WANG Shaojun, LUO Ting, ZHANG Xiaomin, SHU You, ZHU Jin, SU Shengpei. Manipulation of Native Cellulose Eletrospinning from LiCl-DMAc System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 990. |
| [14] | FU Ranran, JI Xiujie, LIU Chao, REN Yanfei, WANG Gang, CHENG Bowen. Fabrication of Cellulose/Nano Lamellar ZnO Composite Antibacterial Fibers Using Ionic Liquid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2344. |
| [15] | KONG Xuelin, LU Yun, YE Guichao, LI Daohao, SUN Jin, YANG Dongjiang, YIN Yafang. Nanofibrillated Cellulose Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels: Efficient Anode Material for Lithium Ion Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1941. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||