

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 215.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130931
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WENG Qiang1, CHEN Pei1,*( ), ZHAO Fengqi2, GAO Hongxu2, CHEN Xinbing1, AN Zhongwei1,2
), ZHAO Fengqi2, GAO Hongxu2, CHEN Xinbing1, AN Zhongwei1,2
Received:2013-09-22
Online:2014-02-10
Published:2013-12-30
Contact:
CHEN Pei
E-mail:chenpei@snnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WENG Qiang, CHEN Pei, ZHAO Fengqi, GAO Hongxu, CHEN Xinbing, AN Zhongwei. Synthesis and Characterization of Hierarchical Aluminum Free Beta Zeolite†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(2): 215.
| Sample | Molar compositiona | Stateb | Seedc | Td/℃ | te/d | Heat sourcef | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | m | ||||||
| H7.5-150/11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 | S | N | 150 | 11 | H |
| H7.5-150/8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 | S | N | 150 | 8 | H |
| C9H7.5-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 7.5 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H10-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H10-150/4-s | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | S | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H20-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H20-150/4-s | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | S | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H30-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H30-150/4-s | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G1C9H30-150/4 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G1C9H30-150/4-s | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G2C9H30-150/4 | 0.2 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G2C9H30-150/4-s | 0.2 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H30-150/4 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H30-150/4-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H20-150/4 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H20-150/4-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | L | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H10-150/4-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | G | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H30-150/0.5-m | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-150/0.5-m-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 150 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-160/0.5-m | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 160 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-160/0.5-m-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 160 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-170/0.5-m | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 170 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-170/0.5-m-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 170 | 0.5 | M |
| P3H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.03 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P9H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P23H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P28H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.28 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P33H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 | 10 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P48H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.48 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P23H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.23 | 10 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P28H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.28 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P33H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.33 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P48H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.48 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P48H20-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.48 | 20 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P48H30-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.48 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
Table 1 Synthesis parameters of aluminum free Beta zeolite
| Sample | Molar compositiona | Stateb | Seedc | Td/℃ | te/d | Heat sourcef | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | m | ||||||
| H7.5-150/11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 | S | N | 150 | 11 | H |
| H7.5-150/8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7.5 | S | N | 150 | 8 | H |
| C9H7.5-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 7.5 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H10-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H10-150/4-s | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | S | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H20-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H20-150/4-s | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | S | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H30-150/4 | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| C9H30-150/4-s | 0 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G1C9H30-150/4 | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G1C9H30-150/4-s | 0.1 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | G | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G2C9H30-150/4 | 0.2 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G2C9H30-150/4-s | 0.2 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H30-150/4 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H30-150/4-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H20-150/4 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H20-150/4-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 20 | L | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H10-150/4-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 10 | G | Y | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3C9H30-150/0.5-m | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-150/0.5-m-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 150 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-160/0.5-m | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 160 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-160/0.5-m-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 160 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-170/0.5-m | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | N | 170 | 0.5 | M |
| G3C9H30-170/0.5-m-s | 0.3 | 0.09 | 0 | 30 | L | Y | 170 | 0.5 | M |
| P3H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.03 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P9H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.09 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P23H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.23 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P28H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.28 | 10 | S | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P33H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.33 | 10 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| P48H10-150/4 | 0 | 0 | 0.48 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P23H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.23 | 10 | G | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P28H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.28 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P33H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.33 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P48H10-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.48 | 10 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P48H20-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.48 | 20 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
| G3P48H30-150/4 | 0.3 | 0 | 0.48 | 30 | L | N | 150 | 4 | H |
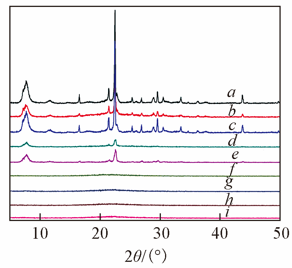
Fig.2 XRD patterns of samplesa. H7.5-150/11; b. H7.5-150/8; c. C9H7.5-150/4; d. C9H10-150/4; e. C9H10-150/4-s; f. C9H20-150/4; g. C9H20-150/4-s; h. C9H30-150/4; i. C9H30-150/4-s.
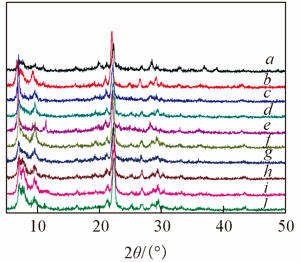
Fig.4 XRD patterns of the samplesa. G1C9H30-150/4; b. G1C9H30-150/4-s; c. G2C9H30-150/4; d. G2C9H30-150/4-s; e. G3C9H30-150/4; f. G3C9H30-150/4-s; g. G3C9H20-150/4; h. G3C9H20-150/4-s; i. G3C9H10-150/4; j. G3C9H10-150/4-s.
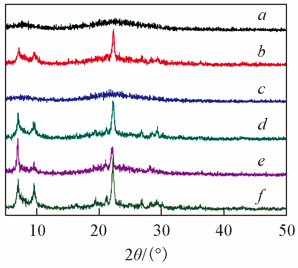
Fig.6 XRD patterns of the samplesa. G3C9H30-150/0.5-m; b. G3C9H30-150/0.5-m-s;c. G3C9H30-160/0.5-m; d. G3C9H30-160/0.5-m-s;e. G3C9H30-170/0.5-m; f. G3C9H30-170/0.5-m-s.
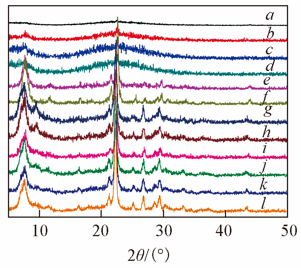
Fig.7 XRD patterns of the samplesa. P3H10-150/4; b. P9H10-150/4; c. P23H10-150/4; d. P28H10-150/4; e. P33H10-150/4; f. P48H10-150/4; g. G3P23H10-150/4; h. G3P28H10-150/4; i. G3P33H10-150/4; j. G3P48H10-150/4; k. G3P48H20-150/4; l. G3P48H30-150/4.
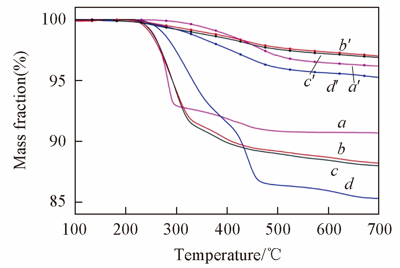
Fig.9 TG curves of four samples before(a—d) and after(a'—d') being calcineda, a'. C9H7.5-150/4; b, b'. G3P48H20-150/4; c, c'. G3P48H30-150/4; d, d'. G3C9H30-150/4-s.
| Sample | N/Si | O/Si | F/Si | Al/Si | Cl/Si | P/Si | Ge/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9H7.5-150/4 | 0.14 | 2.06 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0 |
| G3C9H30-150/4-s | 0.14 | 2.30 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.003 | 0 | 0.19 |
| G3P48H20-150/4 | 0.14 | 2.03 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.13 |
| G3P48H30-150/4 | 0.19 | 2.04 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.12 |
Table 2 Atom ratio calculated from EDS data for four samples before calcined
| Sample | N/Si | O/Si | F/Si | Al/Si | Cl/Si | P/Si | Ge/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9H7.5-150/4 | 0.14 | 2.06 | 0.07 | 0 | 0.001 | 0 | 0 |
| G3C9H30-150/4-s | 0.14 | 2.30 | 0.02 | 0.07 | 0.003 | 0 | 0.19 |
| G3P48H20-150/4 | 0.14 | 2.03 | 0.03 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.13 |
| G3P48H30-150/4 | 0.19 | 2.04 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.12 |
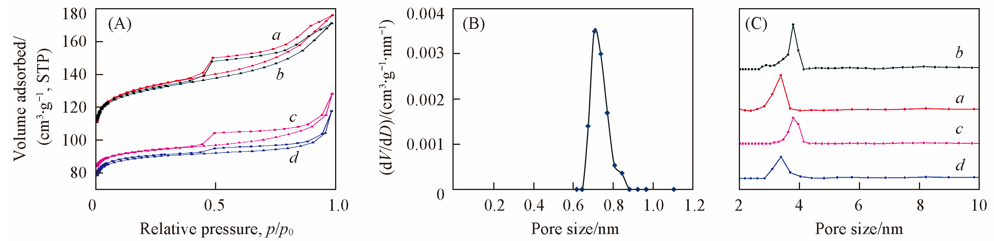
Fig.10 Isotherms(A), micropore(B) and mesopore(C) size distribution of four samplesa. G3P48H20-150/4; b. G3P48H30-150/4; c. C9H7.5-150/4; d. G3C9H30-150/4-s.
| Sample | Sa/(m2·g-1) | Smic/(m2·g-1) | Sext/(m2·g-1) | Vp/(cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9H7.5-150/4 | 373 | 350 | 23 | 0.135 | 0.198 |
| G3C9H30-150/4-s | 356 | 338 | 18 | 0.132 | 0.181 |
| G3P48H20-150/4 | 490 | 435 | 54 | 0.172 | 0.259 |
| G3P48H30-150/4 | 511 | 458 | 53 | 0.179 | 0.267 |
Table 3 Textural properties of four samples*
| Sample | Sa/(m2·g-1) | Smic/(m2·g-1) | Sext/(m2·g-1) | Vp/(cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C9H7.5-150/4 | 373 | 350 | 23 | 0.135 | 0.198 |
| G3C9H30-150/4-s | 356 | 338 | 18 | 0.132 | 0.181 |
| G3P48H20-150/4 | 490 | 435 | 54 | 0.172 | 0.259 |
| G3P48H30-150/4 | 511 | 458 | 53 | 0.179 | 0.267 |
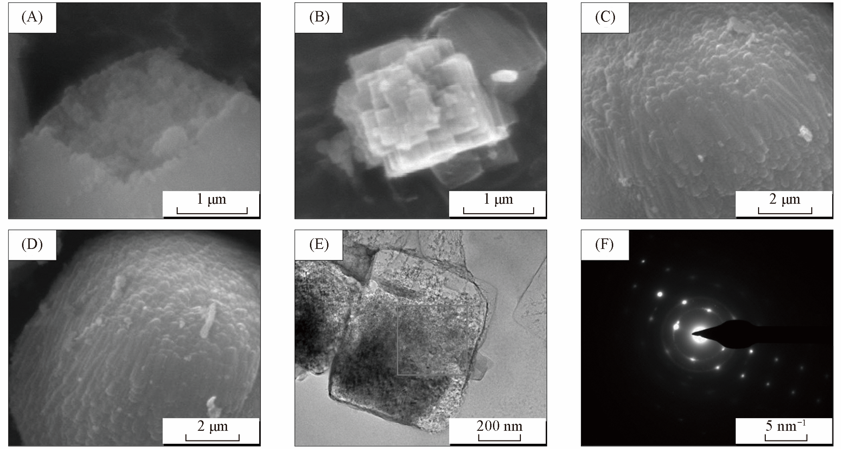
Fig.11 High-magnification SEM images of four samples(A—D) and TEM image(E) and selected area electron diffraction spectrum(F) of zeolite fragment(A) C9H7.5-150/4; (B) G3C9H30-150/4-s; (C) G3P48H20-150/4; (D) G3P48H30-150/4.
| [1] | Serrano D. P., Escola J. M., Pizarro P., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 4004—4035 |
| [2] | Na K., Choi M., Ryoo R., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2013, 166, 3—19 |
| [3] | Janssen A. H., Koster A. J., de Jong K. P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40(6), 1102—1104 |
| [4] | Sashkina K. A., Labko V. S., Rudina N. A., Parmon V. N., Parkhomchuk E. V., J. Catal., 2013, 299, 44—52 |
| [5] | Kore R., Sridharkrishna R., Srivastava R., RSC Adv., 2013, 3, 1317—1322 |
| [6] | Larlus O., Mintova S., Wilson S. T., Willis R. R., Abrevaya H., Bein T., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2011, 142(1), 17—25 |
| [7] | Taborda F., Willhammar T., Wang Z., Montes C., Zou X., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2011, 143(1), 196—205 |
| [8] | Serrano D. P., Grieken R. V., Sánchez P., Sanz R., Rodríguez L., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2001, 46(1), 35—46 |
| [9] | Camblor M. A., Villaescusa L. A., Díaz-Cabañas M. J., Top. Catal., 1999, 9, 59—76 |
| [10] | Kumar R., Bhaumik A., Ahedi R. K., Ganapathy S., Nature, 1996, 381, 298—300 |
| [11] | Kadgaonkar M. D., Kasture M. W., Bhange D. S., Joshi P. N., Ramaswamy V., Kumar R., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2007, 101(1/2), 108—114 |
| [12] | Corma A., Navarro M.T., Rey F., Valencia S.,Chem. Commun., 2001, 1486—1487 |
| [13] | Na K., Jo C., Kim J., Cho K., Jung J., Seo Y., Messinger R. J., Chmelka B. F., Ryoo R., Science, 2011, 333, 328—332 |
| [14] | Wang Y., Min E., Mu X., Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., 2004, 154(Part A), 241—249 |
| [15] | Newsam J. M., Treacy M. M. J., Koetsier W. T., Gruyter C. B., Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A, 1988, 420, 375—405 |
| [16] | Cheng C. H., Juttu G., Mitchell S. F., Shantz D. F., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(45), 22488—22495 |
| [17] | Cheng C. H., Juttu G., Mitchell S. F., Shantz D. F., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(43), 21430—21437 |
| [18] | Ghosh A., Vargas N. G., Mitchell S. F., Stevenson S., Shantz D. F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113(28), 12252—12259 |
| [19] | Corma A., Navarro M.T., Rey F., Rius J., Valencia S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2001, 40(12), 2277—2280 |
| [20] | Camblor M. A., Corma A., Valencia S., J. Mater. Chem., 1998, 8(9), 2137—2145 |
| [21] | Xu R.R., Pang W. Q.,Chemistry Zeolites and Porous Materials, 2004, 146—147 |
| (徐如人, 庞文琴. 分子筛与多孔材料化学, 北京: 科学出版社, 2004, 146—147) |
| [1] | CHEN Weiqin, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Preparation of Organic Hybrid Mesoporous Beta Zeolite for Alkylation of Mesitylene with Benzyl Alcohol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220086. |
| [2] | FAN Juanjuan, HAN Yuanyuan, CUI Jie. Monte Carlo Simulation of the Transformation Control of ABC Triblock Copolymer Micelles from Multicompartment Structure to Multicore Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 857. |
| [3] | WANG Yuyao, ZHANG Qiang, YU Jihong. Synthesis of Hierarchical NaX Zeolite and Its CO2 Adsorption Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 616. |
| [4] | JI Yuchun,MAO Wenhui,LIAO Hejie,WANG Jilin,LONG Fei,GU Yunle. Boron Nitride Nanotube-nanosheet Hierarchical Structures andIts Optical/adsorption Properties† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 216. |
| [5] | CUI Yan, ZHANG Kai, CHEN Yixin, SUN Hongchen, HUANG Yang, WANG Dandan. In situ Biomimetic Remineralization of Enamel-like Hierarchical Structures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1121. |
| [6] | KONG Xuelin, LU Yun, YE Guichao, LI Daohao, SUN Jin, YANG Dongjiang, YIN Yafang. Nanofibrillated Cellulose Derived Hierarchical Porous Carbon Aerogels: Efficient Anode Material for Lithium Ion Battery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1941. |
| [7] | SHI Gang, BAI Huiyu, WANG Likui, SANG Xinxin, YANG Jingguo, NI Caihua, LI Ying. Fabrication of Hierarchical Hemisphere Ag Substrate Using Transfer Imprinting with No Pressure Under Ambient Temperature† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1719. |
| [8] | ZHANG Fan, WANG Bin, WANG Jiaona, LI Xiuyan, LI Congju. Preparation of Hierarchically Structured AOPAN@Mg(OH)2 Composite Nanofibrous Membrane and Cr(Ⅵ)-removal Capacity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2117. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xiao, XIE Yingjuan, MA Peijun, WU Zhijiao, ZHAO Suling, PIAO Lingyu. Photocatalytic Performances for Mixed-phase Hierarchical Structure TiO2 Prepared by Physical Mixing† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1977. |
| [10] | HUANG Jianye, WANG Fenghui, HOU Shaohang, ZHAO Xiang. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Hierarchical Structures by an Ultrasonic Etch Method† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 1968. |
| [11] | SHEN Junhai, LI Jiajia, LI Liangchao, LI Juanbi, DING Yan. Fabrication and Morphological Control of Hierarchical-structure ZnO† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1135. |
| [12] | JING Weixuan, ZHOU Fan, CHEN Lujia, QI Han, JIANG Zhuangde, WANG Bing, NIU Lingling. Glucose Sensor of Spirally Hierarchical Structure with ZnO Nanowires Synthesized on a Spiralled Au Fiber† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 493. |
| [13] | WEI Yi, PENG Jun, YU Xia, DING Yanhong, LU Haiyang, REN Zixing, XU Min, LI Guangzhe. Synthesis of Polyoxometalate Microtubes with Hierarchical Structure and the Adsorption of Doxorubicin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11): 2291. |
| [14] | CHEN Zhong-Xin, LU Hong-Bin. Overview of Graphene/Polyaniline Composite for High-performance Supercapacitor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(9): 2020. |
| [15] | JING Wei-Xuan, NIU Ling-Ling, WANG Bing, CHEN Lu-Jia, QI Han, ZHOU Fan, JIANG Zhuang-De. Preparation and Characterization of a ZnO Nanowires-based Cylindrical Hierarchical Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7): 1585. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||