

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (11): 2018.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160449
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Bingxing1,2, YE Liping1,2,*( ), GU Huijie1,2, XU Huasheng2,3, LUO Yong1,2, LI Huiying4
), GU Huijie1,2, XU Huasheng2,3, LUO Yong1,2, LI Huiying4
Received:2016-06-22
Online:2016-11-10
Published:2016-10-18
Contact:
YE Liping
E-mail:ylp_by@126.com
TrendMD:
YANG Bingxing, YE Liping, GU Huijie, XU Huasheng, LUO Yong, LI Huiying. Theoretical Studies on the Structure and Adsorption Properties of Isomorphously Substituted FAU Zeolite†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2018.
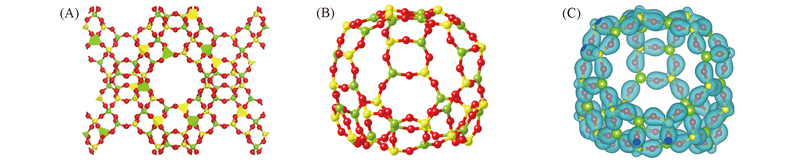
Fig.1 Calculated structure of FAU zeolite(A), β cage(B) and the isosurface(50 e/nm3) of calculated spin charge densities(C) The Si, Al and O atoms are represented by balls in yellow, green and red, respectively.
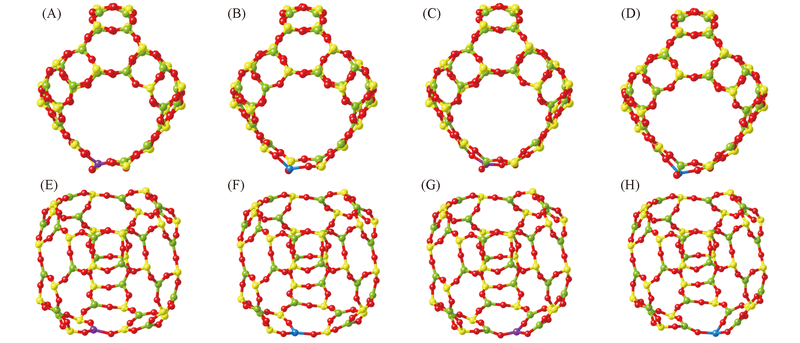
Fig.2 Calculated structures of Al(A, B), Si(C, D), Al'(E, F) and Si'(G, H) atoms substituted by Zn(A, C, E, G) and Ca(B, D, F, H) atoms The Zn and Ca atoms are represented by balls in purple and blue, respectively.
| Defect | Substitution atom | d(Al/Si/Zn/Ca—O)/nm | rRMS/nm | Esub/eV | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Al | 0.1701, 0.1698, 0.1701 | 1(B) | ||
| Si | 0.1641, 0.1647, 0.1643 | 1(B) | |||
| Al' | 0.1685, 0.1699, 0.1696 | 1(B) | |||
| Si' | 0.1646, 0.1629, 0.1641 | 1(B) | |||
| Zn doped | Al | 0.1842, 0.1999, 0.1863 | 0.0213 | 4.89 | 2(A) |
| Si | 0.1888, 0.1860, 0.1929 | 0.0250 | 5.67 | 2(C) | |
| Al' | 0.1975, 0.1852, 0.1859 | 0.0211 | 5.05 | 2(E) | |
| Si' | 0.1900, 0.1833, 0.1909 | 0.0244 | 5.72 | 2(G) | |
| Ca doped | Al | 0.2133, 0.2112, 0.2254 | 0.0470 | 0.92 | 2(B) |
| Si | 0.2147, 0.2129, 0.2169 | 0.0505 | 1.86 | 2(D) | |
| Al' | 0.2103, 0.2141, 0.2254 | 0.0477 | 1.00 | 2(F) | |
| Si' | 0.2181, 0.2096, 0.2162 | 0.0509 | 1.90 | 2(H) |
Table 1 Calculated lengths of Al/Si/Zn/Ca-O bonds, rRMS of different substituted atoms and substitution energies of Zn/Ca doped β cage
| Defect | Substitution atom | d(Al/Si/Zn/Ca—O)/nm | rRMS/nm | Esub/eV | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Al | 0.1701, 0.1698, 0.1701 | 1(B) | ||
| Si | 0.1641, 0.1647, 0.1643 | 1(B) | |||
| Al' | 0.1685, 0.1699, 0.1696 | 1(B) | |||
| Si' | 0.1646, 0.1629, 0.1641 | 1(B) | |||
| Zn doped | Al | 0.1842, 0.1999, 0.1863 | 0.0213 | 4.89 | 2(A) |
| Si | 0.1888, 0.1860, 0.1929 | 0.0250 | 5.67 | 2(C) | |
| Al' | 0.1975, 0.1852, 0.1859 | 0.0211 | 5.05 | 2(E) | |
| Si' | 0.1900, 0.1833, 0.1909 | 0.0244 | 5.72 | 2(G) | |
| Ca doped | Al | 0.2133, 0.2112, 0.2254 | 0.0470 | 0.92 | 2(B) |
| Si | 0.2147, 0.2129, 0.2169 | 0.0505 | 1.86 | 2(D) | |
| Al' | 0.2103, 0.2141, 0.2254 | 0.0477 | 1.00 | 2(F) | |
| Si' | 0.2181, 0.2096, 0.2162 | 0.0509 | 1.90 | 2(H) |
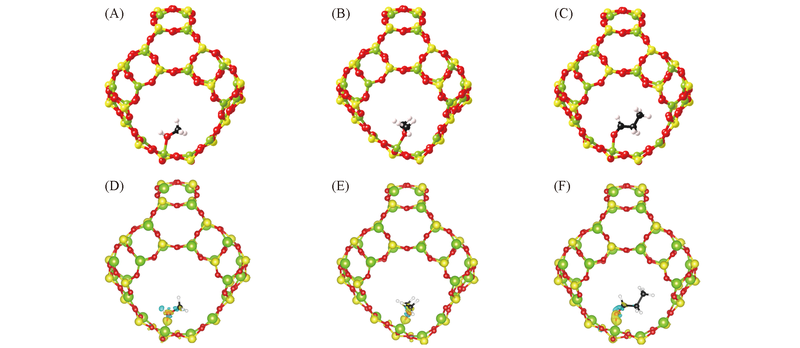
Fig.3 Calculated structures of methanol(A), dimethyl ether(B) and propionaldehyde adsorption(C) at Al site of β cage and isosurfaces(6 e/nm3)(D—F) of charge redistribution of (A—C), respectively The yellow and blue isosurfaces denote charge gain and miss, repectively. The C and H atoms are represented by balls in black and white, respectively.
| Defect | Adsorption molecular | Before adsorption Al/Si—O/nm | After adsorption Al/Si—O/nm | rRMS/nm | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Ethanol | 0.1701, 0.1698, 0.1701 | 0.1726, 0.1736, 0.1718 | 0.0028 | 3(A) |
| Dimethylether | 0.1727, 0.1728, 0.1707 | 0.0023 | 3(B) | ||
| Propionaldehyde | 0.1733, 0.1737, 0.1727 | 0.0033 | 3(C) | ||
| Zn doped | Ethanol | 0.1550, 0.1590, 0.1589 | 0.1614, 0.1618, 0.1640 | 0.005 | 4(G) |
| Dimethyl ether | 0.1592, 0.1612, 0.1631 | 0.0037 | 4(H) | ||
| Propionaldehyde | 0.1619, 0.1625, 0.1665 | 0.0063 | 4(I) | ||
| Ca doped | Ethanol | 0.1595, 0.1602, 0.1552 | 0.1620, 0.1622, 0.1557 | 0.0019 | 4(D) |
| Dimethyl ether | 0.1625, 0.1626, 0.1559 | 0.0023 | 4(E) | ||
| Propionaldehyde | 0.1629, 0.1630, 0.1579 | 0.003 | 4(F) |
Table 2 Calculated lengths of Al/Si—O bonds, rRMS of methanol, dimethyl ether and propionaldehyde adsorption at Al/Si site of β cage
| Defect | Adsorption molecular | Before adsorption Al/Si—O/nm | After adsorption Al/Si—O/nm | rRMS/nm | Figure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Ethanol | 0.1701, 0.1698, 0.1701 | 0.1726, 0.1736, 0.1718 | 0.0028 | 3(A) |
| Dimethylether | 0.1727, 0.1728, 0.1707 | 0.0023 | 3(B) | ||
| Propionaldehyde | 0.1733, 0.1737, 0.1727 | 0.0033 | 3(C) | ||
| Zn doped | Ethanol | 0.1550, 0.1590, 0.1589 | 0.1614, 0.1618, 0.1640 | 0.005 | 4(G) |
| Dimethyl ether | 0.1592, 0.1612, 0.1631 | 0.0037 | 4(H) | ||
| Propionaldehyde | 0.1619, 0.1625, 0.1665 | 0.0063 | 4(I) | ||
| Ca doped | Ethanol | 0.1595, 0.1602, 0.1552 | 0.1620, 0.1622, 0.1557 | 0.0019 | 4(D) |
| Dimethyl ether | 0.1625, 0.1626, 0.1559 | 0.0023 | 4(E) | ||
| Propionaldehyde | 0.1629, 0.1630, 0.1579 | 0.003 | 4(F) |
| Site | Eads/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Dimethyl ether | Propionaldehyde | |
| Al | 0.83 | 0.97 | 0.76 |
| Si | 0.54 | ||
Table 3 Calculated adsorption energies of ethanol, dimethyl ether and propionaldehyde at Al and Si sites
| Site | Eads/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Dimethyl ether | Propionaldehyde | |
| Al | 0.83 | 0.97 | 0.76 |
| Si | 0.54 | ||
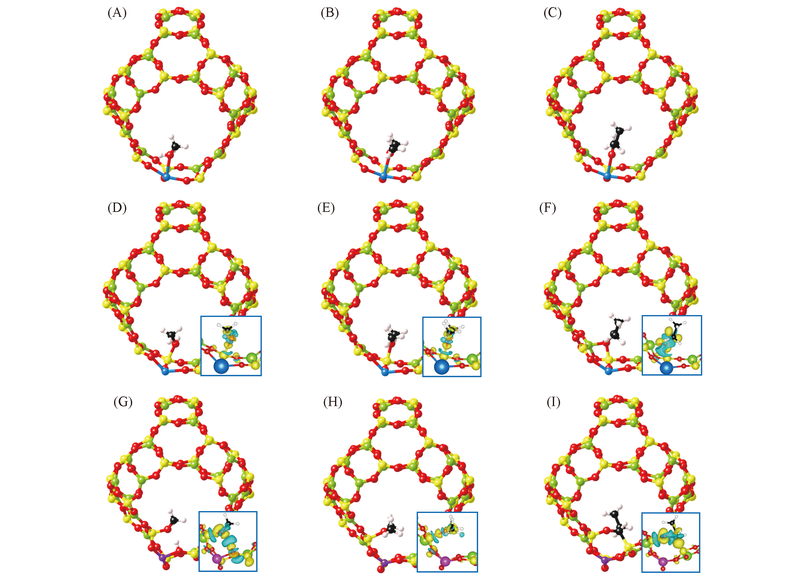
Fig.4 Calculated structures of ethanol(A, D, G), dimethyl ether(B, E, H) and propionaldehyde(C, F, I) adsorption in Ca-doped(D—F) and Zn-doped(G—I) β cageThe insets denote the isosurfaces(6 e/nm3) of charge redistribution.
| Site | Eads/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Dimethyl ether | Propionaldehyde | |
| Zn | |||
| Si(Zn) | 2.28 | 1.08 | 3.93 |
| Ca | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Si(Ca) | 0.77 | 0.68 | 2.29 |
| Site | Eads/eV | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethanol | Dimethyl ether | Propionaldehyde | |
| Zn | |||
| Si(Zn) | 2.28 | 1.08 | 3.93 |
| Ca | 0.45 | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Si(Ca) | 0.77 | 0.68 | 2.29 |
| Si number | Charge/e | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Ca-doped | Zn-doped | |
| 1 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.76 |
| 3 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
Table 5 Calculated Bader charge of different Si sites
| Si number | Charge/e | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Clean | Ca-doped | Zn-doped | |
| 1 | 0.83 | 0.76 | 0.00 |
| 2 | 0.82 | 0.00 | 0.76 |
| 3 | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.78 |
| [1] | 夏思奇, 王鹏飞, 徐华胜, 胡杰, 吕待清. 精细化工, 2014, 31( 12), 1476- 1479 |
| Xia S., Q. , Wang P., F. , Xu H., S. , Hu, J. , Lv D., Q. , Fine Chem., 2014, 31( 12), 1476- 1479 ( | |
| [2] | Luiz K., C. , Juliana J., R. , Jose R., Z. , Geraldo, N. , Cristiano M., B. , Romulo S., A. , Carlos E., F. , Powder Techn., 2012, 229, 1- 6 |
| [3] | Sheng X., L. , Zhou Y., M. , Duan Y., Z. , Xue M., W. , J. Porous Mat., 2011, 18( 6), 677- 683 |
| [4] | Yan, B. , Mahmood, A. , Liang, Y. , Xu B., Q. , Catal. Today, 2016, 269( 1), 65- 73 |
| [5] | 张艳青, 郑华艳, 章日光, 李忠, 王宝俊, 赵秋勇. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36( 10), 1945- 1953 |
| Zhang Y., Q. , Zheng H., Y. , Zhang R., G. , Li, Z. , Wang B., J. , Zhao Q., Y. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36( 10), 1945- 1953 ( | |
| [6] | Popovych N., O. , Kyriienko P., I. , Soloviev S., O. , Orlyk S., M. , Dzwigaj, S. , Microp. Mesop. Mater., 2016, 226( 15), 10- 18 |
| [7] | Najar, H. , Zina M., S. , Ghorbel, A. , React Kinet. Mech. Catal., 2010, 100( 2), 385- 398 |
| [8] | Lim W., T. , Seo S., M. , Lee O., S. , Wang L., Z. , Lu G., Q. , J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem., 2010, 67( 3), 261- 269 |
| [9] | Li H., C. , Zhou D., H. , Tian D., X. , Shi, C. , Muller, U. , Feyen, M. , Yilmaz, B. , Gies, H. , Xiao F., S. , de Vos, D. , ChemPhysChem, 2014, 15( 8), 1700- 1707 |
| [10] | Meeprasert, J. , Jungsuttiwong, S. , Namuangruk, S. , Microp. Mesop. Mater., 2013, 175, 99- 106 |
| [11] | Ma, J. , Qiang L., S. , Wang J., F. , Tang X., B. , Tang D., Y. , J. Porous Mat., 2011, 18( 5), 607- 614 |
| [12] | Wang, Q. , Wu Y., J. , Wang, J. , Lin, X. , Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2012, 28( 9), 2108- 2114 |
| [13] | Hernandez-Morales, V. , Nava, R. , Acosta-Silva Y., J. , Pawelec, B. , Microp. Mesop. Mater., 2012, 160, 133- 142 |
| [14] | Tao, L. , Li G., S. , Yin S., F. , Au C., T. , React Kinet. Mech. Catal., 2011, 103( 1), 191- 207 |
| [15] | 张瑞珍, 王翠, 邢普, 温少波, 王剑, 赵亮富, 李玉平. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36( 4), 725- 732 |
| Zhang R., Z. , Wang, C. , Xing, P. , Wen S., B. , Wang, J. , Zhao L., F. , Li Y., P. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36( 4), 725- 732 ( | |
| [16] | Su X., F. , Wang G., L. , Bai X., F. , Wu, W. , Xiao L., F. , Fang Y., J. , Zhang J., W. , Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 293, 365- 375 |
| [17] | Jin Y., J. , Asaoka, S. , Zhang S., D. , Li, P. , Zhao S., L. , Fuel Proc. Techn., 2013, 115, 34- 41 |
| [18] | Omata, K. , Yamazaki, Y. , Watanabe, Y. , Kodama, K. , Yamada, M. , Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2009, 48( 13), 6256- 6261 |
| [19] | 王瑜, 吴伟, 李程, 杨杰, 周亚静. 石油学报, 2011, 27( 5), 682- 686 |
| Wang, Y. , Wu, W. , Li, C. , Yang, J. , Zhou Y., J. , Acta Petrolei Sin., 2011, 27( 5), 682- 686 ( | |
| [20] | Geraldo, E. , Stevie H., L. , Ana C., R. , Antonio S., A. , Valter, J. , J. Mater. Sci., 2010, 45( 4), 1117- 1122 |
| [21] | Shamzhy, M. , Shvets, O. , Opanasenko, M. , Cejka, J. , J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22( 31), 15793- 15803 |
| [22] | Ahmed, S. , J. Porous Mat., 2012, 19( 1), 111- 117 |
| [23] | Wang J., H. , Xie J., Y. , Zhou, Y. , Wang, J. , Microp. Mesop. Mater., 2013, 171, 87- 93 |
| [24] | Yang C., G. , Qiu M., H. , Hu S., W. , Chen X., Q. , Zeng G., F. , Liu Z., Y. , Sun Y., H. , Microp. Mesop. Mater., 2016, 231, 110- 116 |
| [25] | Zhou, Y. , Jin Y., H. , Wang, M. , Zhang, W. , Xie J., Y. , Gu, J. , Wen H., M. , Wang, J. , Peng L., M. , Chem. Eur. J., 2015, 21( 43), 15412- 15420 |
| [26] | Kang L., H. , Zhang, T. , Liu Z., M. , Han K., L. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112( 14), 5526- 5532 |
| [27] | Kresse, G. , Furthmü, ller J. , Comp. Mater. Sci., 1996, 6, 15- 50 |
| [28] | Kresse, G. , Furthmü, ller J. , Phys. Rev. B, 1996, 54( 16), 11169- 11186 |
| [29] | Perdew J., P. , Burke, K. , Ernzerhof, M. , Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77( 18), 3865- 3868 |
| [30] | Kresse, G. , Joubert, D. , Phys. Rev. B, 1999, 59( 3), 1758- 1775 |
| [31] | Blö, chl P. E. , Phys. Rev. B, 1994, 50( 24), 17953- 17979 |
| [32] | Monkhorst H., J. , Pack J., D. , Phys. Rev. B, 1976, 13, 5188- 5192 |
| [33] | Wang H., F. , Gong X., Q. , Guo Y., L. , Guo, Y. , Lu G., Z. , Hu, P. , J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113( 23), 10229- 10232 |
| [34] | Li H., Y. , Wang H., F. , Gong X., Q. , Guo Y., L. , Guo, Y. , Lu G., Z. , Hu, P. , Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 79( 19), 193401- 193405 |
| [1] | CHENG Qian, YANG Bolong, WU Wenyi, XIANG Zhonghua. S-doped Fe-N-C as Catalysts for Highly Reactive Oxygen Reduction Reactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220341. |
| [2] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [3] | SONG Youwei, AN Jiangwei, WANG Zheng, WANG Xuhui, QUAN Yanhong, REN Jun, ZHAO Jinxian. Effects of Ag,Zn,Pd-doping on Catalytic Performance of Copper Catalyst for Selective Hydrogenation of Dimethyl Oxalate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210842. |
| [4] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [5] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [6] | SUN Xuefeng, RENAGUL Abdurahman, YANG Tongsheng, YANG Qianting. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Cr,In Co-doped Small Size MgGa2O4 Near-infrared Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210850. |
| [7] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, JIANG Wei, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Activation of Biochar from Cattail and the VOCs Adsorption Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [8] | CHEN Xiaolu, YUAN Zhenyan, ZHONG Yingchun, REN Hao. Preparation of Triphenylamine Based PAF-106s via Mechanical Ball Milling and C2 Hydrocarbons Adsorption Property [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [9] | MENG Xianglong, YANG Ge, GUO Hailing, LIU Chenguang, CHAI Yongming, WANG Chunzheng, GUO Yongmei. Synthesis of Nano-zeolite and Its Adsorption Performance for Hydrogen Sulfide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [10] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [11] | WANG Zumin, MENG Cheng, YU Ranbo. Doping Regulation in Transition Metal Phosphides for Hydrogen Evolution Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220544. |
| [12] | ZHENG Meiqi, MAO Fangqi, KONG Xianggui, DUAN Xue. Layered Double Hydroxides as Sorbent for Remediation of Radioactive Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [13] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [14] | TIAN Xiaokang, ZHANG Qingsong, YANG Shulin, BAI Jie, CHEN Bingjie, PAN Jie, CHEN Li, WEI Yen. Porous Materials Inspired by Microbial Fermentation: Preparation Method and Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| [15] | MA Jianxin, LIU Xiaodong, XU Na, LIU Guocheng, WANG Xiuli. A Multi-functional Zn(II) Coordination Polymer with Luminescence Sensing, Amperometric Sensing, and Dye Adsorption Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210585. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||