

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1784.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160402
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MI Xiaolong, JIAO Xiaojie, LIU Chang, HE Song*( ), ZENG Xianshun*(
), ZENG Xianshun*( )
)
Received:2016-06-06
Online:2016-10-10
Published:2016-09-18
Contact:
HE Song,ZENG Xianshun
E-mail:hesong@tjut.edu.cn;xshzeng@tjut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MI Xiaolong, JIAO Xiaojie, LIU Chang, HE Song, ZENG Xianshun. Rhodamine-based Cell Permeable Fluoresecent Turn-on Probes for Cupric Ion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1784.
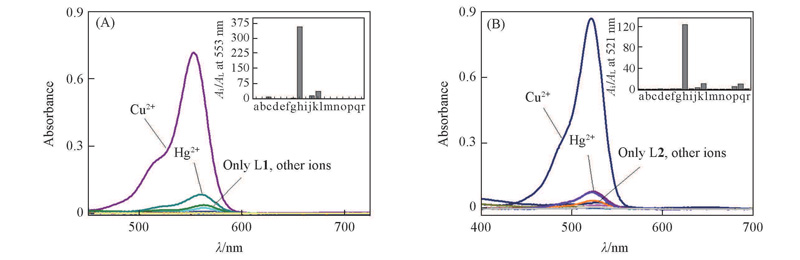
Fig.1 UV-Vis spectra of probes L1(A) and L2(B)(1×10-5 mol/L) in the presence of nitrate salts of metal ions(5×10-5 mol/L ) in MeCN/H2O(volume ratio 1∶5) solventInset: histogram representing the absorbance enhancement of probe L1 at 553 nm and probe L2 at 521 nm, respectively, in the presence of different metal ions. a. No other ions; b. Ag+; c. Al3+; d. Ca2+; e. Cd2+; f. Co2+; g. Cr3+; h. Cu2+; i. Fe2+; j. Fe3+; k. Hg2+; l. K+; m. Mg2+; n. Na+; o. NH4+; p. Ni2+; q. Pb2+; r. Zn2+.
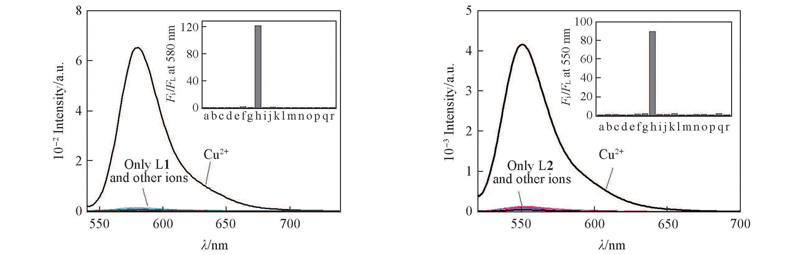
Fig.2 Fluorescence emission spectra of probes L1(A) and L2(B)(1×10-6 mol/L) in the presence of nitrate salts of metal ions(5×10-6 mol/L) in MeCN/H2O(volume ratio 1∶5)Inset: histogram representing the fluorescence enhancement of probe L in the presence of different metal ions. a. No other ions; b. Ag+; c. Al3+; d. Ca2+; e. Cd2+; f. Co2+; g. Cr3+; h. Cu2+; i. Fe2+; j. Fe3+; k. Hg2+; l. K+; m. Mg2+; n. Na+; o. NH4+; p. Ni2+; q. Pb2+; r. Zn2+. Excitation was performed at 520 nm(A) and 500 nm(B). Excitation/emission slit width: 2.5 nm/5 nm.
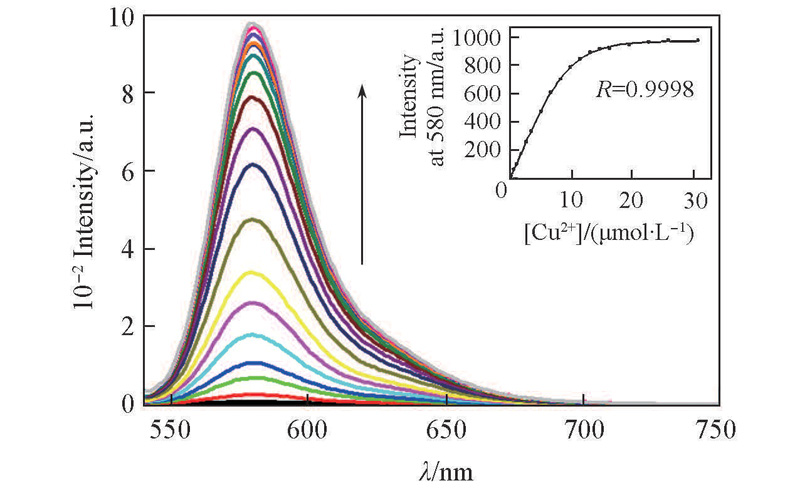
Fig.3 Fluorescent titration spectra of probes L1(1×10-6 mol/L) in the presence of different concentrations of Cu2+ in MeCN/H2O(volume ratio 1∶5)[Cu2+]/(μmol·L-1): 0, 0.2, 0.6, 1.0, 1.8, 2.6, 3.4, 5.0, 6.6, 8.2, 9.8, 11.4, 13.0, 14.6, 16.2, 19.4, 22.6, 25.8, 30.6. Excitation was performed at 520 nm. Excitation/emission slit width: 2.5 nm/5 nm. Inset: plot of fluorescent intensity of L1 at 580 nm versus [Cu2+].
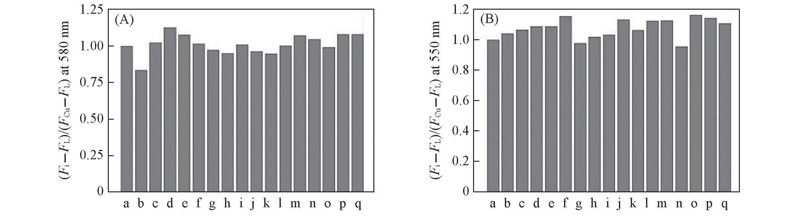
Fig.4 Relative fluorescent intensity change ratios[(Fi-FL)/(FCu2+-FL)] of probes L1(A) and L2(B)(1×10-6 mol/L) upon addition of Cu2+(5×10-6 mol/L) in the presence of metal ions(5×10-6 mol/L) in MeCN/H2O(volume ratio 1∶5)a. Cu2+; b. Cu2++Ag+; c. Cu2++Al3+; d. Cu2++Ca2+; e. Cu2++Cd2+; f. Cu2++Co2+; g. Cu2++Cr3+; h. Cu2++Fe2+; i. Cu2++Fe3+; j. Cu2++Hg2+; k. Cu2++K+; l. Cu2++Mg2+; m. Cu2++Na+; n. Cu2++NH4+; o. Cu2++Ni2+; p. Cu2++Pb2+; q. Cu2++Zn2+. Excitation was performed at 520 nm(A) and 500 nm(B). Excitation/emission slit width: 2.5 nm/5 nm.
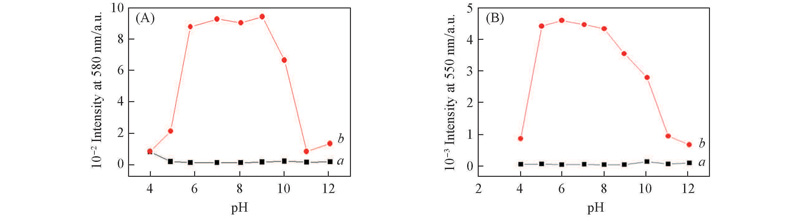
Fig.5 Profile of pH dependence of the fluorescence intensity of probes L1(A)(1×10-6 mol/L) at 580 nm and L2(B)(1×10-6 mol/L) at 550 nm in the absence(a) and presence(b) of Cu2+(5×10-6 mol/L) in MeCN/H2O(volume ratio 1∶5)Excitation was performed at 520 nm(A) and 500 nm(B). Excitation/emission slit width: 2.5 nm/5 nm.
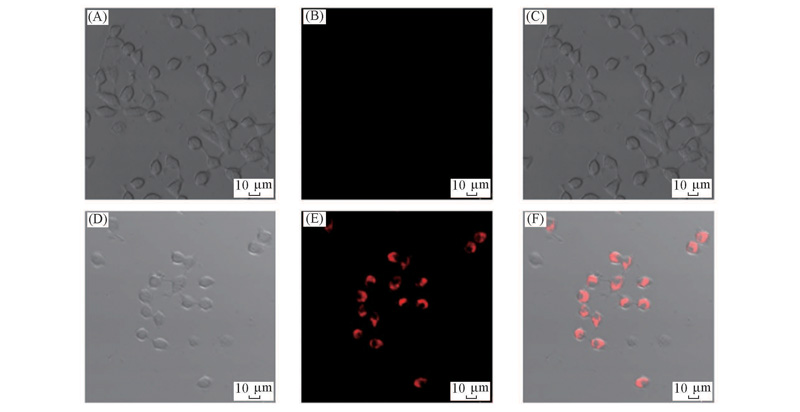
Fig.6 Bright field images(A, D), fluorescence images(B, E) and overlay images(C, F) of INS-1 cells incubated with L1(A—C) as well as L1 and Cu2+(D—F) Excitation wavelength: 559 nm.
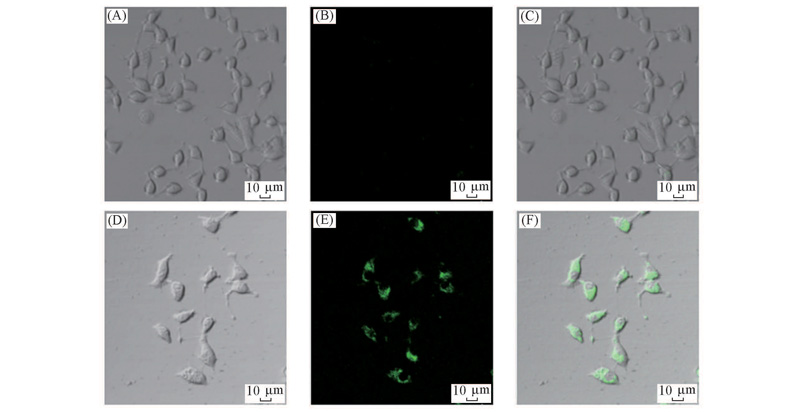
Fig.7 Bright field images(A, D), fluorescence images(B, E) and overlay images(C, F) of INS-1 cells incubated with L2(A—C) as well as L2 and Cu2+(D—F) Excitation wavelength: 488 nm.
| [1] | Cowan J.A., Inorganic Biochemistry: An Introduction, Wiley-VCH, New York, 1997, 133—134 |
| [2] | High B., Bruce D., Richter M. M., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2001, 449,17—22 |
| [3] | Tapia L., Suazo M., Hodar C., Cambiazo V., Gonzalez M., Bio. Metals, 2003, 16,169—174 |
| [4] | Barnham K. J., Masters C. L., Bush A. I., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2004, 3,205—214 |
| [5] | Gorell J. M., Johnson C. C., Rybicki B. A., Peterson E. L., Kortsha G. X., Brown G. G., Richardson R. J., Neurotoxicology, 1999, 20,239—247 |
| [6] | Waggoner D. J., Bartnikas T. B., Gitlin J. D., Neurobiol. Dis., 1999, 6,221—230 |
| [7] | Georgopoulos P. G., Roy A., Yonone-Lioy M. J., Opiekun R. E., Lioy P. J., J. Toxicol. Environ. Health, Part B, 2001, 4,341—394 |
| [8] | Zhao Y., Zhang X., Han Z., Qiao L., Li C., Jian L., Shen G., Yu R., Anal. Chem., 2009, 81(16), 7022—7030 |
| [9] | de Silva A. P., Gunaratne H. Q. N., Gunnlaugsson T., Huxley A. J. M., McCoy C. P., RademacherJ. T., Rice T. E., Chem. Rev., 1997, 97,1515—1566 |
| [10] | Prodi L., Bolletta F., Montalti M., Zaccheroni N., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2000, 205,59—83 |
| [11] | Grandini P., Mancin P., Tecilla P., Scrimin P., Tonellato U., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 1999, 38(20), 3061—3064 |
| [12] | Lee Y. H., Park N., Park Y. B., Hwang Y. J., Kang C., Kim J. S., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50,3197—3200 |
| [13] | Xue X., Fang H., Chen H., Zhang C., Zhu C., Bai Y., He W., Guo Z., Dyes and Pigments, 2016, 130,116—121 |
| [14] | Wang X., Ma X., Yang Z., Zhang Z., Wen J., Geng Z., Wang Z., Chem. Commun., 2013, 49,11263—11265 |
| [15] | Fan J., Zhan P., Hu M., Sun W., Tang J., Wang J., Sun S., Song F., Peng X., Org. Lett., 2013, 15,492—495 |
| [16] | Swamy K.M. K., Ko S. K., Kwon S. K., Lee H. N., Mao C., Kim J. M., Lee K. H., Kim J., Shin I., Yoon J.,Chem. Commun., 2008, 5915—5917 |
| [17] | Zhou Z., Li N., Tong A., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2011, 702,81—86 |
| [18] | Andréasson J., Kodis G., Terazono Y., Liddell P. A., Bandyopadhyay S., Mitchell R. H., Moore A. L., Gust D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(49), 15926—15927 |
| [19] | Malkondu S., Turhan D., Kocak A., Tetrahedron Lett., 2015, 56,162—167 |
| [20] | Liu Z., Zhang C., Wang X., He W., Guo Z., Org. Lett., 2012, 14,378—4381 |
| [21] | Wang H., Yang L., Zhang W., Zhou Y., Zhao B., Li X., Inorg. Chimica Acta, 2012, 381,111—116 |
| [22] | Li C., Liu Z., Miao Y., Zhou X., Wu X., Dyes and Pigments, 2016, 125,292—298 |
| [23] | Kim M.H., Jang H. H., Yi S., Chang S. K., Han M. S.,Chem. Commun., 2009, 4838—4840 |
| [24] | Wu C., Bian Q. N., Zhang B. G., Cai X., Zhang S. D., Zheng H., Yang S. Y., Jiang Y. B., Org. Lett., 2012, 14,4198—4201 |
| [25] | Wang D., Shirashi Y., Hirai T., Chem. Commun., 2011, 47,2673—2675 |
| [26] | Liang L., Zhao L., Zeng X., J. Fluoresc., 2014, 24,1671—1677 |
| [27] | Dujols V., Ford F., Czarnik A. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1997, 119, 7386—7387 |
| 28 | [28] Kwon J. Y., Jang Y. J., Lee Y. J., Kim K. M., Seo M. S., Nam W., Yoon J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127,10107—10111 |
| [29] | Cao L., Jia C., Zhang Q., Chen D., Zhang C., Qian Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(3), 362—367 |
| [30] | Bender M. L., Turnquest B. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1957, 79,1889—1893 |
| [31] | Liu K., Shang H., Meng F., Liu Y., Lin W., Talanta, 2016, 147,193—198 |
| [32] | Zhang X. F., Zhang Y., Liu L., J. Lumin.2014, 145,448—453 |
| [33] | Du P., Lippard S. J., Inorg. Chem., 2010, 49,10753—10755 |
| [34] | World Health Organization, Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality,Geneva, 1996 |
| [1] | LIU Miao, LIU Ruibo, LIU Badi, QIAN Ying. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Lysosome-targeted Indole-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [2] | CHEN Shaoyun, ZHANG Xingying, LIU Ben, TIAN Du, LI Qi, CHEN Fang, HU Chenglong, CHEN Jian. Controllable Growth of Silver Nanoparticles on TiO2 Tetragonal Prism Nanarrays and Its SERS Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2381. |
| [3] | LI Qi, TIAN Du, CHEN Shaoyun, ZHONG Min, HU Chenglong, CHEN Jian. Controllable Assembling of Silver Nanosheets on Non-woven Fabric Fibers and Its SERS Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 736. |
| [4] | CHEN Hongda, ZHANG Hua, WANG Zhenxin. Development of Small Animals in vivo Fluorescence-photothermal Dual Mode Imaging System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 725. |
| [5] | WANG Mengmeng, LUAN Tianjiao, YANG Mingyan, LYU Jiajia, GAO Jie, LI Hongyu, WEI Gang, YUAN Zeli. Rhodamine Fluorescent Probe for Tumor Targeted Hypoxia-imaging as Intra-operative Navigators [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3071. |
| [6] | LI Xiaoqian, ZHANG Hua, LU Haijian, LIU Chang, LIU Qinglong, MA Xiayu, FANG Yuanping, LIANG Dapeng. Mechanism of Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B by TiO2 Nanowire Array with Internal Extraction Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2003. |
| [7] | LIANG Yuxin, ZHAO Rong, LIANG Xinyue, FANG Xiaohong. Single-molecule Imaging and Analysis of Signal Transduction Proteins on Cell Membranes † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1127. |
| [8] | BAI Cuiting, YUE Renye, LUO Liegao, MA Nan. Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNA Content by Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer Cells Using Dual-color Fluorescence Nanosensor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1252. |
| [9] | SHAO Wei, LEE Jiyoung, LI Fangyuan, LING Daishun. Organic Small Molecule Nanoparticles for Phototheranostics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2356. |
| [10] | TANG Yucai,QU Huang,ZHANG Wenxi,WANG Feifei,WANG Gang. Synthesis of α-Sulfonyl Ketones via I2/TBHP Promoted Radical Sulfonylation of Silyl Enol Ethers with Sulfohydrazides under Mild Conditions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 118. |
| [11] | Yong ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN. Benzimidazole-Derived Fluorescence Enhancement Probe for Visual Detection of HClO † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2480. |
| [12] | Yingying ZHANG,Yiwen HUANG,Bing ZHAO,Liyan WANG,Bo SONG. Synthesis of a Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe of Cr 3+ and Its Application in Cell Imaging † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2486. |
| [13] |
YU Zhaochuan, MA Wenhui, WU Tao, WEN Jing, ZHANG Yong, WANG Liyan, CHU Hongtao.
Preparation of B, N, S co-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Fluorescence Detection of Fe 3+ and H2P |
| [14] | LIU Meihong, TAO Ran, LI Bing, LI Xinghua, HAN Chaohan, LI Xiaowei, SHAO Changlu. Controllable Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Three-dimensional Porous Zinc-tungsten Oxide Heterojunctions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2367. |
| [15] | LIU Dahai, ZHANG Xueyan, FENG Yusha, DU Xianlong, XUE Longqi, DU Jianshi, ZHANG Guirong, YANG Qingbiao, LI Yaoxian. Synthesis of Novel Fluorescein-Thiospirolactams Hg2+ Fluorescent Probes and Its Application in vivo† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1412. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||