

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1776.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160284
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Yong, LI Xiangzhi, LI Yongtao, LIU Dongming, ZHANG Qing’an, SI Tingzhi*( )
)
Received:2016-04-25
Online:2016-10-10
Published:2016-09-23
Contact:
SI Tingzhi
E-mail:tzsiahut@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MA Yong, LI Xiangzhi, LI Yongtao, LIU Dongming, ZHANG Qing’an, SI Tingzhi. Phase Structures and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Mg2Ni1-xCox Alloys Prepared by Solid Solution Sintering†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1776.
| Atom | Site | g | Coordinate | B/nm2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| Mg | 1a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.026(1) |
| Ni | 3c | 1 | 0 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0.016(8) |
| Co | 1b | 1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0.022(3) |
Table 1 Atomic coordinates, occupation factors(g) and isotropic thermal parameters(B) of MgNi3Co refined from X-ray powder diffraction data
| Atom | Site | g | Coordinate | B/nm2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x | y | z | ||||
| Mg | 1a | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.026(1) |
| Ni | 3c | 1 | 0 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0.016(8) |
| Co | 1b | 1 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 1/2 | 0.022(3) |
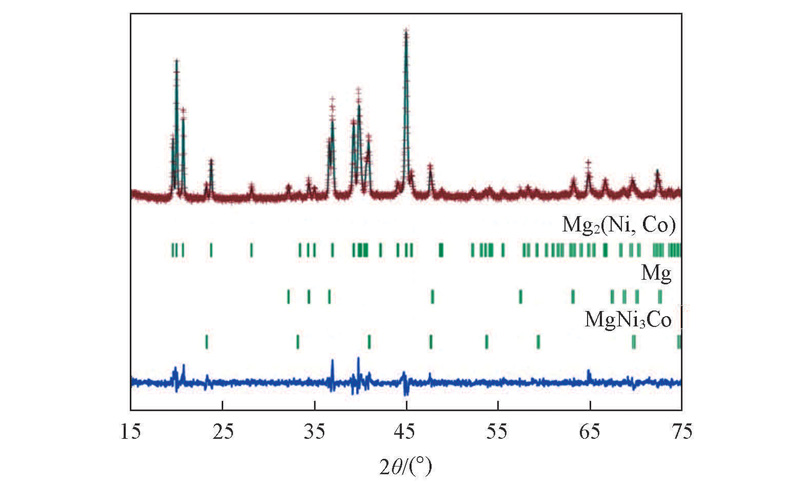
Fig.3 Rietveld refinement of the observed XRD pattern for the sintered Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15 alloyThe calculated(line) and observed(+) X-ray diffraction patterns for sintered Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15 alloy are displayed above the vertical bars, below which shows the difference between the observed and calculated patters.
| Sample | Phase | Space group | RI(%) | Lattice parameter/nm | Abundance(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | c | |||||
| Mg2Ni0.9Co0.1 | Mg2(Ni, Co) | P6222 | 3.43 | 0.5216(1) | 1.3283(2) | 91 |
| Rwp=6.58% | Mg | P63/mmc | 3.99 | 0.3207(2) | 0.5208(2) | 4 |
| S=1.8 | MgNi3Co | Pm | 2.80 | 0.3810(1) | 5 | |
| Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15 | Mg2(Ni, Co) | P6222 | 4.84 | 0.5218(1) | 1.3284(2) | 90 |
| Rwp=7.00% | Mg | P63/mmc | 4.29 | 0.3208(2) | 0.5209(2) | 4 |
| S=1.9 | MgNi3Co | Pm | 7.63 | 0.3813(1) | 6 | |
| Mg2Ni0.8C | Mg2(Ni, Co) | P6222 | 4.68 | 0.5218(1) | 1.3291(1) | 89 |
| Rwp=6.54% | Mg | P63/mmc | 4.83 | 0.3207(1) | 0.5207(2) | 5 |
| S=1.4 | MgNi3Co | Pm | 5.59 | 0.3811(1) | 6 | |
Table 2 Structural parameters and phase abundance of the sintered Mg2Ni1-xCox (x=0.10, 0.15, 0.20) alloys
| Sample | Phase | Space group | RI(%) | Lattice parameter/nm | Abundance(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | c | |||||
| Mg2Ni0.9Co0.1 | Mg2(Ni, Co) | P6222 | 3.43 | 0.5216(1) | 1.3283(2) | 91 |
| Rwp=6.58% | Mg | P63/mmc | 3.99 | 0.3207(2) | 0.5208(2) | 4 |
| S=1.8 | MgNi3Co | Pm | 2.80 | 0.3810(1) | 5 | |
| Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15 | Mg2(Ni, Co) | P6222 | 4.84 | 0.5218(1) | 1.3284(2) | 90 |
| Rwp=7.00% | Mg | P63/mmc | 4.29 | 0.3208(2) | 0.5209(2) | 4 |
| S=1.9 | MgNi3Co | Pm | 7.63 | 0.3813(1) | 6 | |
| Mg2Ni0.8C | Mg2(Ni, Co) | P6222 | 4.68 | 0.5218(1) | 1.3291(1) | 89 |
| Rwp=6.54% | Mg | P63/mmc | 4.83 | 0.3207(1) | 0.5207(2) | 5 |
| S=1.4 | MgNi3Co | Pm | 5.59 | 0.3811(1) | 6 | |
| Sample | Mg2Ni0.9Co0.1 | Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15 | Mg2Ni0.8Co0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| g(Ni/Co) | 0.84/0.16(2) | 0.72/0.28(5) | 0.64/0.36(3) |
Table 3 Occupation factor(g) of Co atoms in Ni(3d) sites of the Mg2(Ni, Co) phases
| Sample | Mg2Ni0.9Co0.1 | Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15 | Mg2Ni0.8Co0.2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| g(Ni/Co) | 0.84/0.16(2) | 0.72/0.28(5) | 0.64/0.36(3) |
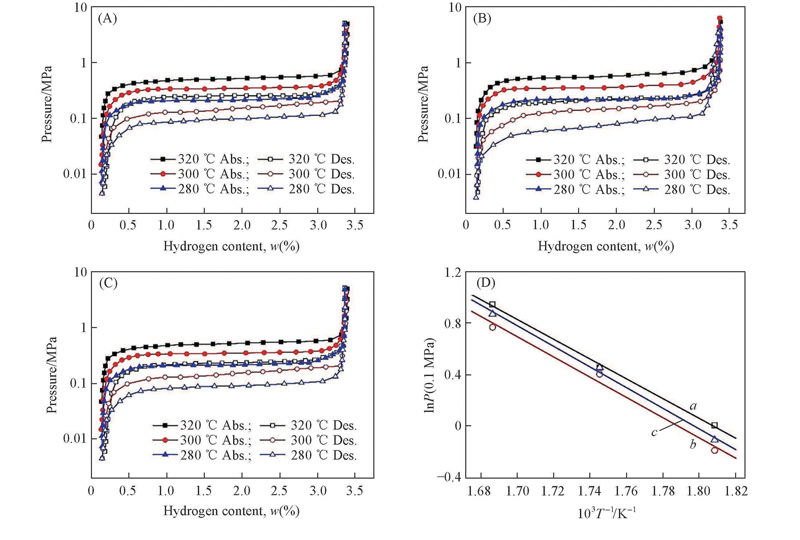
Fig.5 P-C isotherms of hydrogen absorption/desorption for the Mg2Ni1-xCox (x =0.10, 0.15, 0.20) alloys(A)—(C) and van’t Hoff plots in dehydriding process(D)(A) x =0.10; (B) x =0.15; (C) x =0.20. a. Mg2Ni0.9Co0.1-H2; b. Mg2Ni0.85Co0.15-H2; c. Mg2Ni0.8Co0.2-H2.
| [1] | Ma J. L., Wang Y., Tao Z. L., Chen J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(3), 536—540 |
| (马建丽, 王艳, 陶占良, 陈军.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(3), 536—540) | |
| [2] | Zhu M., Lu Y., Ouyang L., Wang H., Materials, 2013, 6(10), 4654—4674 |
| [3] | Jain I., Lal C., Jain A., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35(10), 5133—5144 |
| [4] | Huo L., Shi H. C., Xu B. E., Li X. Y., Meng L. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(8), 1799—1806 |
| (霍亮, 史洪存, 许保恩, 李晓艳, 孟令鹏.高等学校化学学报, 2011,32(8), 1799—1806) | |
| [5] | Liang G., Huot J., Boily S., Schulz R., J. Alloys Compd., 2000, 305(1), 239—245 |
| [6] | Jeon K. J., Moon H. R., Ruminski A. M., Jiang B., Kisielowski C., Bardhan R., Urban J. J., Nat. Mater., 2011, 10(4), 286—290 |
| [7] | Jung H., Yuh J., Cho S., Lee W., J. Alloys Compd., 2014, 601,63—66 |
| [8] | Reilly Jr. J. J., Wiswall Jr. R. H., Inorg. Chem., 1968, 7(11), 2254—2256 |
| [9] | Shao H., Xu H., Wang Y., Li X., J. Solid State Chem., 2004, 177(10), 3626—3632 |
| [10] | Yang H., Yuan H., Ji J., Sun H., Zhou Z., Zhang Y., J. Alloys Compd., 2002, 330,640—644 |
| [11] | Palade P., Sartori S., Maddalena A., Principi G., Russo S. L., Lazarescu M., Schinteie G., Kuncser V., Filoti G., J. Alloys Compd., 2006, 415(1), 170—176 |
| [12] | Wang X. L., Tu J. P., Zhang X. B., Gao R. G., Chen C. P., Chin. J. Nonferrous Met., 2002, 12(5), 907—911 |
| (王秀丽, 涂江平, 张孝彬, 高嵘岗, 陈长聘.中国有色金属学报, 2002,12(5), 907—911) | |
| [13] | Zhang Y. H., Li B. W., Ren H. P., Ding X. X., Liu X. G., J. Alloys Compd., 2011, 509(6), 2808—2814 |
| [14] | Xie L., Shao H., Wang Y., Li Y., Li X., J. Hydrogen Energy, 2007, 32(12), 1949—1953 |
| [15] | Izumi F., Ikeda T., Mater. Sci. Forum, 2000, 321,198—205 |
| [16] | Simiic' M. , Zdujic' M., Dimitrijevic' R., Nikolic'-Bujanovic' L., Popovic' N., J. Power Sources, 2006, 158(1), 730—734 |
| [17] | Altomare A., Burla M., Cascarano G., Giacovazzo C., Guagliardi A., Moliterni A., Polidori G., J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1995, 28(6), 842—846 |
| [18] | Chen J. S., Zeng H., Wang L., Lan Z. Q., Guo J., Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2012, 22(1), 216—223 |
| (陈捷狮, 曾含, 王路, 蓝志强, 郭进.中国有色金属学报, 2012,22(1), 216—223) | |
| [19] | Deledda S., Hauback B., Nanotechnology, 2009, 20(20), 259—265 |
| [20] | Mendoza-Zélis L., Meyer M., Baum L., J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(1), 600—605 |
| [21] | Parker S. F., Deledda S., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(48), 25206—25212 |
| [22] | Shelyapina M., Pinyugzhanin V., Skryabina N., Hauback B., Phys. Solid State, 2013, 55(1), 12—20 |
| [23] | Verbovytskyy Y., Zhang J., Cuevas F., Paul-Boncour V., Zavaliy I., J. Alloys Compd., 2015, 645,S408—S411 |
| [24] | Hayakawa H., Ishido Y., Nomura K., Uruno H., Ono S., J. Less-Common Met., 1984, 103(2), 277—283 |
| [25] | Darnaudery J., Darriet B., Pezat M., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 1983, 8(9), 705—708 |
| [26] | Van Setten M. J., de Wijs G. A., Brocks G., Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 76(7), 075125 |
| [27] | Takahashi Y., Yukawa H., Morinaga M., J. Alloys Compd., 1996, 242(1), 98—107 |
| [28] | Xie D. H., Li P., Zeng C. X., Sun J. W., Qu X. H., J. Alloys Compd., 2009, 478(1/2), 96—102 |
| [29] | Gu R., Zhang M., Wang C. Y., Huang W. J., Liu D. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(4), 688—692 |
| (顾润, 张明, 王春阳, 黄维军, 柳东明.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(4), 688—692) | |
| [30] | Li Q., Lin Q., Chou K. C., Jiang L., J. Mater. Sci., 2004, 39(1), 61—65 |
| [31] | Barkhordarian G., Klassen T., Bormann R., J. Alloys Compd., 2006, 407(1), 249—255 |
| [32] | Ouyang L., Cao Z., Wang H., Liu J., Sun D., Zhang Q., Zhu M., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38(21), 8881—8887 |
| [33] | Liang G., Huot J., Boily S., van Neste A., Schulz R., J. Alloys Compd., 1999, 282(1), 286—290 |
| [34] | Jia Y., Sun C., Cheng L., Wahab M. A., Cui J., Zou J., Zhu M., Yao X., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(16), 5814—5820 |
| [35] | Jia Y., Sun C., Shen S., Zou J., Mao S. S., Yao X., Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev., 2015, 44,289—303 |
| [36] | Lv P., Wang Z., Zhou H., Deng J., Yao Q., Zhang H., Mater. Sci. Technol., 2014, 30(2), 176—182 |
| [1] | LIU Hai-Zhen, WANG Xin-Hua, LIU Yong-An, YAN Mi. Preparations and Dehydriding Properties of AlH3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(10): 2274. |
| [2] | DENG Shuai-Shuai, XIAO Xue-Zhang, CHEN Li-Xin, HAN Le-Yuan, LI Shou-Quan, GE Hong-Wei, WANG Qi-Dong. Effects of Stoichiometry and Dehydrogenation Back-pressure on the Dehydrogenation Behavior of LiBH4+xMg2NiH4 Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(09): 2030. |
| [3] | MA Jian-Li, WANG Yan, TAO Zhan-Liang, CHEN Jun. Preparation and Hydrogen Storage Properties of Mg2FeH6 Nanocrystals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(03): 536. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||