

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 20220627.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220627
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHEN Xinyi1,2, ZHANG Sen1,2, WANG Shutao1,2,3, SONG Yongyang1,2( )
)
Received:2022-09-21
Online:2023-01-10
Published:2022-11-26
Contact:
SONG Yongyang
E-mail:yysong@mail.ipc.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SHEN Xinyi, ZHANG Sen, WANG Shutao, SONG Yongyang. Synthesis Strategies for Polymer Hollow Particles[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220627.
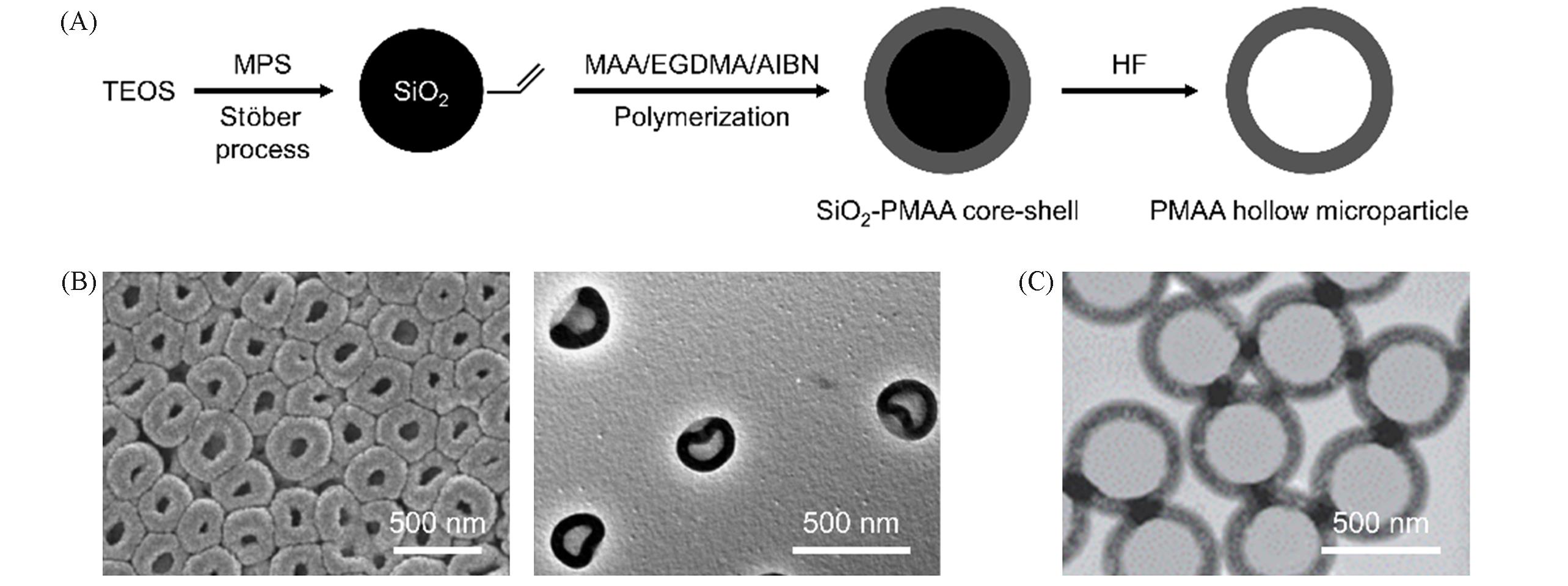

Fig.1 Hard template strategy for the synthesis of polymer hollow microparticles(A) Preparation of PMAA microparticles using SiO2 microspheres as hard template. The process includes synthesis of SiO2 microspheres with vinyl groups on the surface, in situ polymerization of MAA on SiO2 microspheres and etching of SiO2 microspheres by HF. (B) Scanning electron microscopy(SEM) image and transmission electron microscope(TEM) image of PMAA hollow particles[24]. (C) TEM image of PMMA hollow microspheres[26].(A, B) Copyright 2008, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2006, Wiley-VCH.
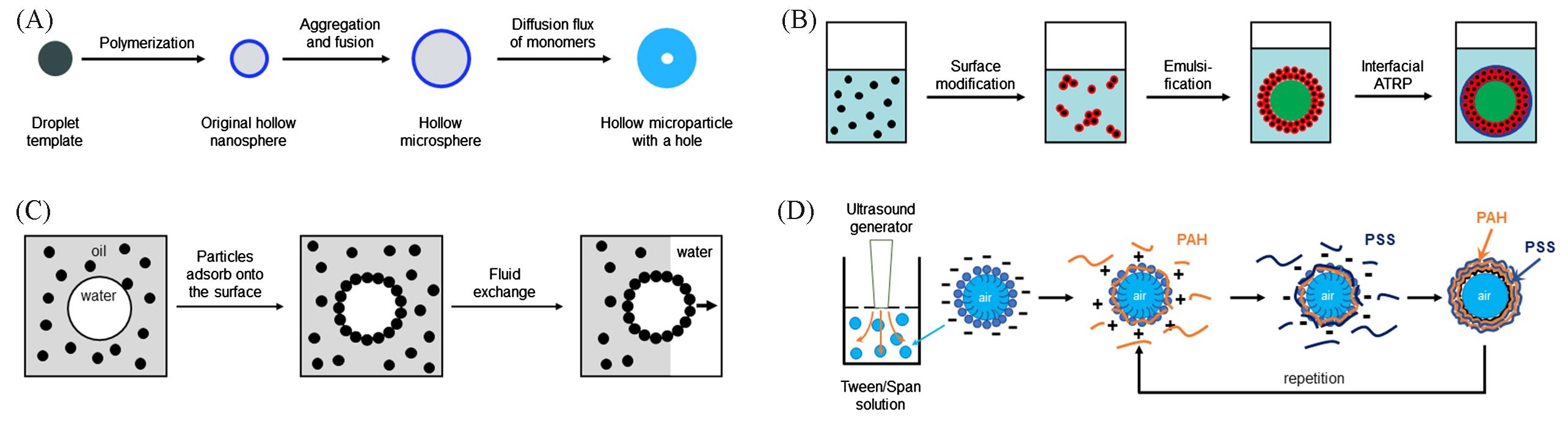
Fig.2 Soft template strategy for the synthesis of polymer hollow particles(A) Oil (o-methoxyaniline) droplets stabilized by molecular surfactants as soft template[30]. (B) Oil droplets stabilized by nanoparticles as soft template[32]. (C) Water droplets stabilized by colloidal particles as soft template[35]. (D) Air bubbles as soft template stabilized by Tween/Span mixture[29].(A) Copyright 2007, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2010, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2002, American Association for the Advancement of Science; (D) Copyright 2005, Wiley-VCH.
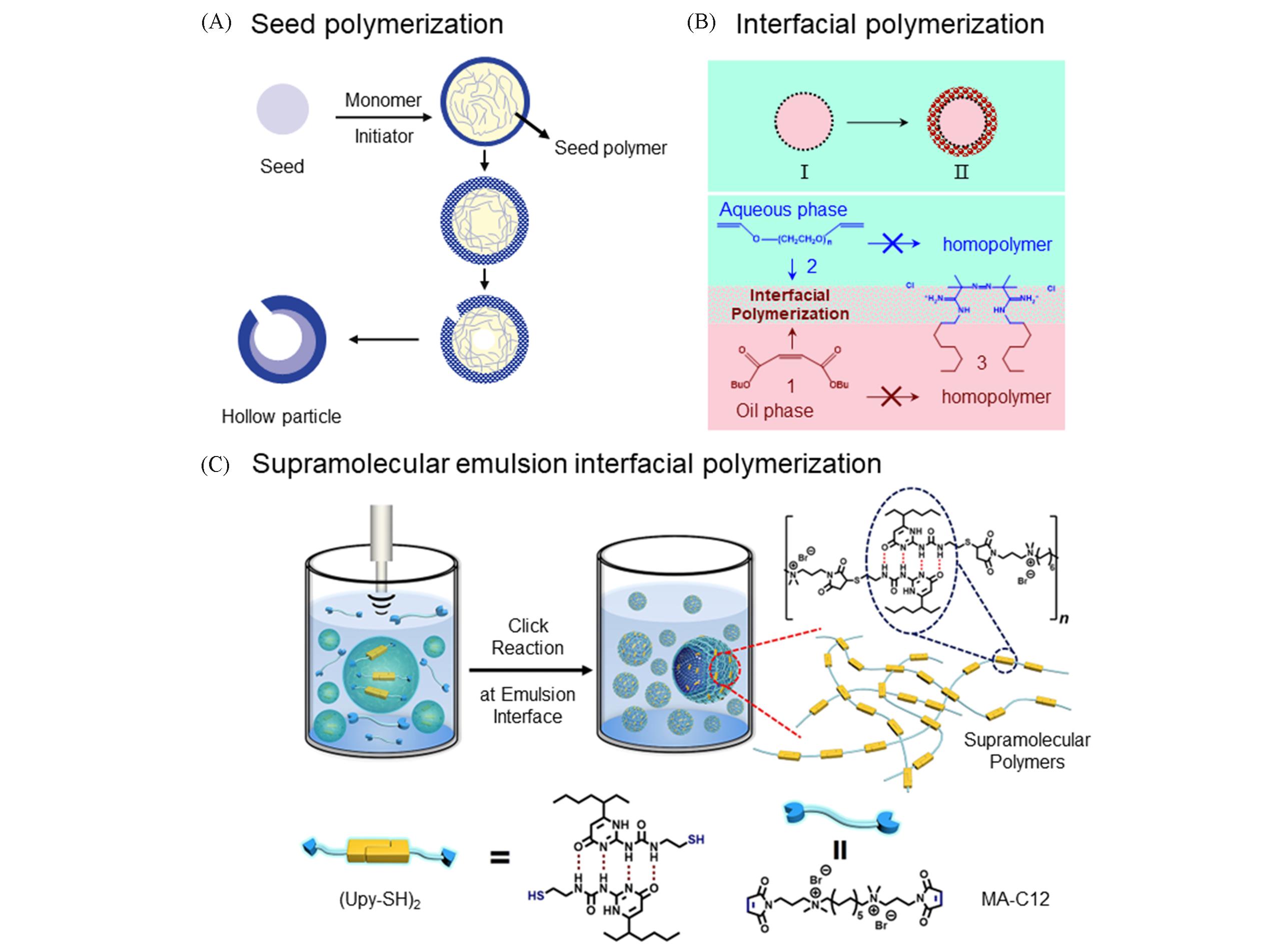
Fig.3 Emulsion polymerization strategy for the synthesis of polymer hollow particles(A) Seed polymerization. Seed polymer particles are first swollen by monomers and initiators, and then phase separation occurs upon the polymerization of monomers, resulting in hollow particles with a hole[40]. (B) Interfacial polymerization. Hydrophilic and hydrophobic monomers are confined to the O/W emulsion interface for polymerization[42]. (C) Supramolecular emulsion interfacial polymerization[45]. Supramonomers(UPy-SH)2 are dissolved in oil, and MA-C12 are dissolved in water, respec- tively. (UPy-SH)2 first aggregate at the interface of emulsion to form nanospheres, and stable nanospheres can be fabricated through polymerization at emulsion interface.(A) Copyright 2008, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2005, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
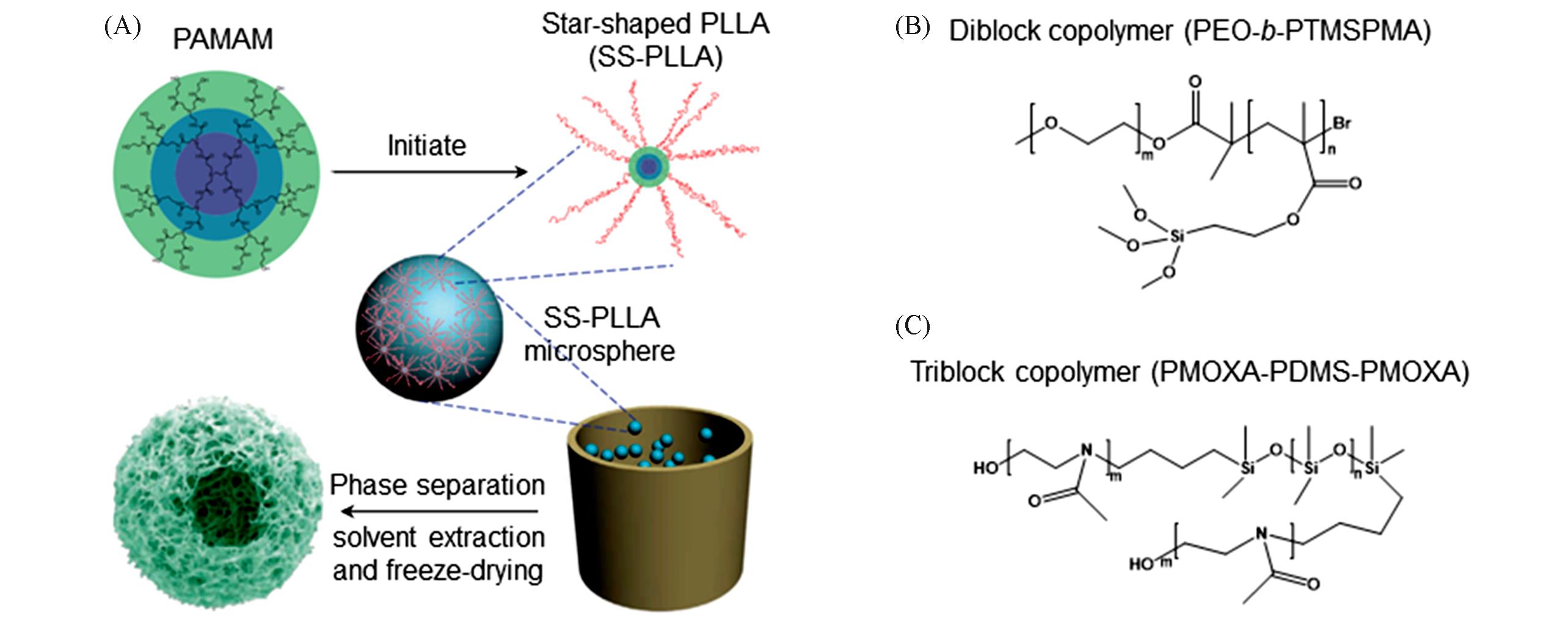
Fig.4 Self⁃assembly strategy for the synthesis of polymer hollow particles(A) Nanofiber hollow spheres are fabricated by self-assembly of star-shaped PLLA[48]. (B) Diblock copolymer that can be used for the preparation of polymer hollow microspheres via self-assembly[50]. (C) Triblock copolymer that can be used for the preparation of polymer hollow microspheres via self-assembly[51].(A) Copyright 2011, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2003, American Chemlical Society; (C) Copyright 2000, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
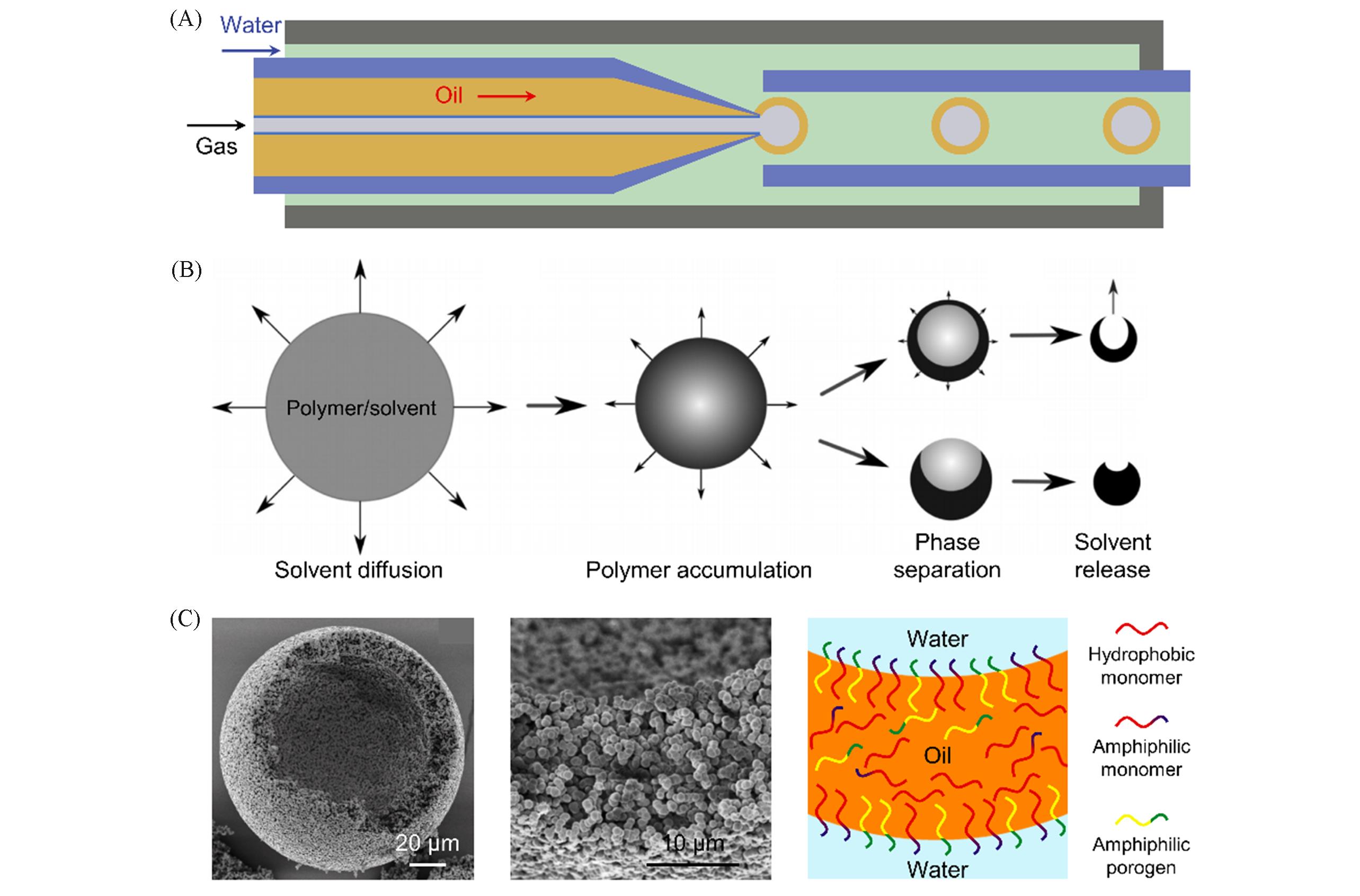
Fig.5 Microfluidic strategy for the synthesis of polymer hollow microspheres(A) A typical capillary microfluidic device for the preparation of G/O/W emulsion[62]. (B) Phase separation occurs in the polymer-solvent droplet prepared by microfluidic strategy, obtaining hollow microspheres[64]. (C) SEM images and scheme of hollow polymer particles with interconnected shell[66].(A) Copyright 2012, the Royal Society of Chemistry; (B) Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society; (C) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
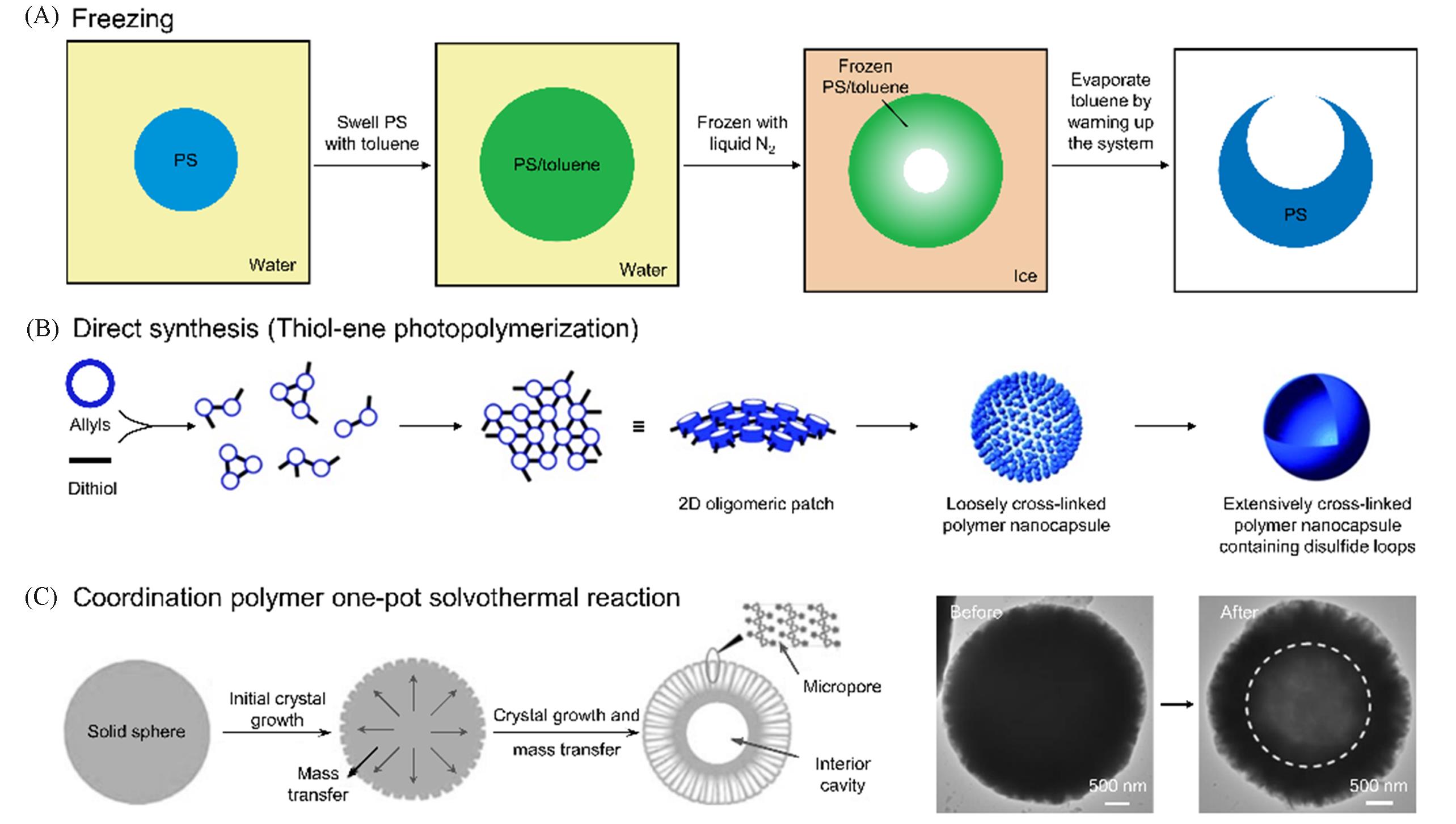
Fig.6 Other strategies for the synthesis of hollow polymer particles(A) Freezing strategy. This strategy includes swelling of the polymer(PS) microparticles by solvent(toluene), freezing, and evaporation of the solvent by warming up[67]. (B) Direct synthesis strategy[68]. Allyls(disk-shaped monomers) are linked by dithiol, forming 2D dimer or trimer oligomeric patches, then loosely cross-linked polymer nanocapsules, and finally extensively cross-linked polymer nanocapsules. (C) Coordination polymer one-pot solvothermal reaction strategy[74]. Initial solid spheres are composed of smaller polymer crystallites. Mass transfer from interior to exterior by a dissolution-outmigration process, constructing coordination polymer hollow particles with interior cavity and surface micropores. Formation process and TEM images of the initial solid microspheres and resultant hollow coordination polymer microspheres.(A) Copyright 2005, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2007, Wiley-VCH; (C) Copyright 2010, Wiley-VCH.
| 1 | Mohseni⁃Vadeghani E., Karimi⁃Soflou R., Khorshidi S., Karkhaneh A., Colloids Surf. B, 2021, 197, 111376 |
| 2 | Zhou L., Xu Z., Hua C., Cao H., Qin B., Zhao H., Xie Y., Chemosphere, 2022, 287, 131982 |
| 3 | Qin J., Su Z., Mao Y., Liu C., Qi B., Fang G., Wang S., Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf., 2021, 208, 111729 |
| 4 | Lou X. W., Archer L. A., Yang Z., Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 3987—4019 |
| 5 | Song Y., Li X., Fan J. B., Kang H., Zhang X., Chen C., Liang X., Wang S., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1803299 |
| 6 | Song Y., Fan J. B., Li X., Liang X., Wang S., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1900391 |
| 7 | Cui J., Wang Y., Postma A., Hao J., Hosta⁃Rigau L., Caruso F., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20, 1625—1631 |
| 8 | Song Y., Zhou J., Fan J. B., Zhai W., Meng J., Wang S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1802493 |
| 9 | Xie L., Yan M., Liu T., Gong K., Luo X., Qiu B., Zeng J., Liang Q., Zhou S., He Y., Zhang W., Jiang Y., Yu Y., Tang J., Liang K., Zhao D., Kong B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 1634—1646 |
| 10 | White S. R., Sottos N. R., Geubelle P. H., Moore J. S., Kessler M. R., Sriram S., Brown E. N., Viswanathan S., Nature, 2001, 409, 794—797 |
| 11 | Su D., Zhang J., Dou S., Wang G., Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 16092—16095 |
| 12 | Li D., Zhang J., Zhan W., Cai G., Li L., Zuo W., Wang Q., Tian Y., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10, 13936—13945 |
| 13 | Bao Y., Chang J., Zhang Y., Chen L., Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 446, 136959 |
| 14 | Lai X., Halpert J. E., Wang D., Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5, 5604—5618 |
| 15 | Shi X., Shen M., Möhwald H., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2004, 29, 987—1019 |
| 16 | Caruso F., Chem. Eur. J., 2000, 6, 413—419 |
| 17 | Wang X., Feng J., Bai Y., Zhang Q., Yin Y., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 10983—11060 |
| 18 | Chen P. W., Erb R. M., Studart A. R., Langmuir, 2012, 28, 144—152 |
| 19 | Zha L., Zhang Y., Yang W., Fu S., Adv. Mater., 2002, 14, 1090—1092 |
| 20 | Xu X., Asher S. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126, 7940—7945 |
| 21 | Ko J. H., Kang N., Park N., Shin H. W., Kang S., Lee S. M., Kim H. J., Ahn T. K., Son S. U., ACS Macro Lett., 2015, 4, 669—672 |
| 22 | Feng X., Mao C., Yang G., Hou W., Zhu J. J., Langmuir, 2006, 22, 4384—4389 |
| 23 | Nandiyanto A. B. D., Ogi T., Okuyama K., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 4418—4427 |
| 24 | Li G., Liu G., Kang E., Neoh K., Yang X., Langmuir, 2008, 24, 9050—9055 |
| 25 | Guan G., Zhang Z., Wang Z., Liu B., Gao D., Xie C., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 2370—2374 |
| 26 | Kida T., Mouri M., Akashi M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45, 7534—7536 |
| 27 | Cui J., Wang Y., Postma A., Hao J., Hosta‐Rigau L., Caruso F., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2010, 20, 1625—1631 |
| 28 | Grigoriev D., Bukreeva T., Möhwald H., Shchukin D., Langmuir, 2008, 24, 999—1004 |
| 29 | Shchukin D. G., Köhler K., Möhwald H., Sukhorukov G. B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 3310—3314 |
| 30 | Han J., Song G., Guo R., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19, 973—975 |
| 31 | Han J., Song G., Guo R., Adv. Mater., 2006, 18, 3140—3144 |
| 32 | Li J., Hitchcock A. P., Stoever H. D. H., Langmuir, 2010, 26, 17926—17935 |
| 33 | Rossier⁃Miranda F. J., Schroen C. G. P. H., Boom R. M., Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2009, 343, 43—49 |
| 34 | Whitesides G. M., Grzybowski B., Science, 2002, 295, 2418—2421 |
| 35 | Dinsmore A., Hsu M. F., Nikolaides M., Marquez M., Bausch A., Weitz D., Science, 2002, 298, 1006—1009 |
| 36 | Wang Z., van Oers M. C. M., Rutjes F. P. J. T., van Hest J. C. M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 10746—10750 |
| 37 | Wang Y., Angelatos A. S., Caruso F., Chem. Mater., 2008, 20, 848—858 |
| 38 | Hata Y., Suzuki T., Minami H., Okubo M., Colloid Polym. Sci., 2008, 286, 1561—1567 |
| 39 | Suzuki T., Mizowaki T., Okubo M., Polymer, 2016, 106, 182—188 |
| 40 | Lv H., Lin Q., Zhang K., Yu K., Yao T., Zhang X., Zhang J., Yang B., Langmuir, 2008, 24, 13736—13741 |
| 41 | Nuasaen S., Tangboriboonrat P., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2013, 396, 75—82 |
| 42 | Scott C., Wu D., Ho C. C., Co C. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 4160—4161 |
| 43 | Sun Q., Deng Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 8274—8275 |
| 44 | Wei Z. X., Wan M. X., Adv. Mater., 2002, 14, 1314 |
| 45 | Zhang S., Qin B., Huang Z., Xu J. F., Zhang X., ACS Macro Lett., 2019, 8, 177—182 |
| 46 | Luo Y. W., Gu H. Y., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2006, 27, 21—25 |
| 47 | Utama R. H., Guo Y., Zetterlund P. B., Stenzel M. H., Chem. Commun., 2012, 48, 11103—11105 |
| 48 | Liu X., Jin X., Ma P. X., Nat. Mater., 2011, 10, 398—406 |
| 49 | Li C., Li Q., Kaneti Y. V., Hou D., Yamauchi Y., Mai Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49, 4681—4736 |
| 50 | Du J., Chen Y., Zhang Y., Han C. C., Fischer K., Schmidt M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 14710—14711 |
| 51 | Nardin C., Thoeni S., Widmer J., Winterhalter M., Meier W., Chem. Commun., 2000, 1433—1434 |
| 52 | Nardin C., Hirt T., Leukel J., Meier W., Langmuir, 2000, 16, 1035—1041 |
| 53 | Wu D., Xu F., Sun B., Fu R., He H., Matyjaszewski K., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 3959—4015 |
| 54 | Geng Y., Ling S., Huang J., Xu J., Small, 2020, 16, 1906357 |
| 55 | Castro⁃Hernandez E., van Hoeve W., Lohse D., Gordillo J. M., Lab Chip, 2011, 11, 2023—2029 |
| 56 | Xu J., Li S., Chen G., Luo G., AIChE J., 2006, 52, 2254—2259 |
| 57 | Xu J., Luo G., Li S., Chen G., Lab Chip, 2006, 6, 131—136 |
| 58 | Xu J., Li S., Tan J., Wang Y., Luo G., Langmuir, 2006, 22, 7943—7946 |
| 59 | Okushima S., Nisisako T., Torii T., Higuchi T., Langmuir, 2004, 20, 9905—9908 |
| 60 | Chu L. Y., Utada A. S., Shah R. K., Kim J. W., Weitz D. A., Angew. Chem., 2007, 119, 9128—9132 |
| 61 | Wang W., Xie R., Ju X. J., Luo T., Liu L., Weitz D. A., Chu L. Y., Lab Chip, 2011, 11, 1587—1592 |
| 62 | Chen R., Dong P. F., Xu J. H., Wang Y. D., Luo G. S., Lab Chip, 2012, 12, 3858—3860 |
| 63 | Hung L. H., Teh S Y., Jester J., Lee A. P., Lab Chip, 2010, 10, 1820—1825 |
| 64 | Vasiliauskas R., Liu D., Cito S., Zhang H., Shahbazi M. A., Sikanen T., Mazutis L., Santos H. A., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7, 14822—14832 |
| 65 | Utada A. S., Lorenceau E., Link D. R., Kaplan P. D., Stone H. A., Weitz D., Science, 2005, 308, 537—541 |
| 66 | Loiseau E., Niedermair F., Albrecht G., Frey M., Hauser A., Rühs P. A., Studart A. R., Langmuir, 2017, 33, 2402—2410 |
| 67 | Im S. H., Jeong U. Y., Xia Y. N., Nat. Mater., 2005, 4, 671—675 |
| 68 | Kim D., Kim E., Kim J., Park K. M., Baek K., Jung M., Ko Y. H., Sung W., Kim H. S., Suh J. H., Park C. G., Na O. S., Lee D. K., Lee K. E., Han S. S., Kim K., Angew. Chem., 2007, 119, 3541—3544 |
| 69 | Zlotnick A., Stray S. J., Trends Biotechnol., 2003, 21, 536—542 |
| 70 | Zlotnick A., Johnson J. M., Wingfield P. W., Stahl S. J., Endres D., Biochemistry, 1999, 38, 14644—14652 |
| 71 | Kitagawa S., Kitaura R., Noro S. I., Angew. Chem., 2004, 116, 2388—2430 |
| 72 | Eddaoudi M., Moler D. B., Li H., Chen B., Reineke T. M., O'keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Acc. Chem. Res., 2001, 34, 319—330 |
| 73 | Lan A., Li K., Wu H., Olson D. H., Emge T. J., Ki W., Hong M., Li J., Angew. Chem., 2009, 121, 2370—2374 |
| 74 | Huo J., Wang L., Irran E., Yu H., Gao J., Fan D., Li B., Wang J., Ding W., Amin A. M., Li C., Ma L., Angew. Chem., 2010, 122, 9423—9427 |
| 75 | Pan J., Li L., Hang H., Wu R., Dai X., Shi W., Yan Y., Langmuir, 2013, 29, 8170—8178 |
| 76 | Song Y., Bao H., Shen X., Li X., Liang X., Wang S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2022, 32, 2113153 |
| 77 | Song Y., Dong X., Shang D., Zhang X., Li X., Liang X., Wang S., Small, 2021, 17, 2102802 |
| 78 | Ramli R. A., RSC Adv., 2017, 7, 52632—52650 |
| [1] | WANG Pengfei, FU Wenhao, SUN Shaoni, CAO Xuefei, YUAN Tongqi. Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Materials Using Cellulose Nanocrystals as Templates and Their Electrochemical Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(2): 20220497. |
| [2] | DUAN Yixiong, YANG Bai, LI Yunfeng. Self-assembly of Cellulose Nanocrystals in Spatial Confinement: from Colloidal Liquid Crystals to Functional Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(2): 20220474. |
| [3] | LIU Shuanghong, XIA Siyu, LIU Shiqi, LI Min, SUN Jiajie, ZHONG Yong, ZHANG Feng, BAI Feng. Current Advances of Hollow All-solid-state Z-Scheme Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220512. |
| [4] | WANG Sijia, HOU Lu, LI Chenglong, LI Wencui, LU Anhui. Recent Advances in Synthesis and Applications of Hollow Nano-carbons [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220637. |
| [5] | YANG Qingfeng, LYU Liang, LAI Xiaoyong. Progress on Preparation and Electrocatalytic Application of Hollow MOFs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220666. |
| [6] | YANG Jiye, SUN Dayin, WANG Yan, GU Anqi, YE Yilan, DING Shujiang, YANG Zhenzhong. Progresses in Template Synthesis and Applications of Hollow Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220665. |
| [7] | YE Zuyang, YIN Yadong. Etching-based Hollowing of Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220656. |
| [8] | ZHU Kerun, REN Wenxuan, ZHANG Wei, LI Wei. Salt-templated Synthesis and Morphological Control of Monodisperse Hollow Mesoporous Structures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220607. |
| [9] | LI Ziruo, ZHANG Hongjuan, ZHU Guoxun, XIA Wei, TANG Jing. Iron Phthalocyanine Coated Nitrogen-doped Hollow Carbon Spheres for Efficient Catalysis of Oxygen Reduction Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220677. |
| [10] | WU Yucai, DU Huan, ZHU Jiexin, XU Nuo, ZHOU Liang, MAI Liqiang. Intricate Hollow Structured Materials: Synthesis and Energy Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220689. |
| [11] | WANG Hui, ZHAO Decai, YANG Nailiang, WANG Dan. Gate Keeper in the Smart Hollow Drug Carrier [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(1): 20220237. |
| [12] | LI Lin, QI Fenglian, QIU Lili, MENG Zihui. Dynamic Amorphous Photonic Structure Patterns Assembled by Hexagonal Magnetic Nanosheets [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220123. |
| [13] | WU Yushuai, SHANG Yingxu, JIANG Qiao, DING Baoquan. Research Progress of Controllable Self-assembled DNA Origami Structure as Drug Carrier [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220179. |
| [14] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [15] | LI Bo, MENG Yuxi, WANG Wenwen, ZANG Hongying. Synthesis and Proton Conductivity of Polynuclear Polyoxothiomolybdate Compound [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210657. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||