

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 1357.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210013
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
XUE Linlin, LYU Ruijing, WANG Aoxuan, LUO Jiayan( )
)
Received:2021-01-05
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-08
Contact:
LUO Jiayan
E-mail:jluo@tju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XUE Linlin, LYU Ruijing, WANG Aoxuan, LUO Jiayan. Strategies Concerning Anode Modification in Rechargeable Magnesium Batteries[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1357.
| Metal anode | Electrode potential/V | Gravimetric capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Volumetric capacity/(mA·h·cm-3) | Cost/(USD·kg-1) | Abundance rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | -3.04 | 3862 | 2066 | 19.2 | 33rd |
| Na | -2.71 | 1166 | 1128 | 0.2 | 6th |
| K | -2.93 | 685 | 591 | 1.0 | 7th |
| Mg | -2.37 | 2205 | 3832 | 2.2 | 8th |
| Zn | -0.76 | 820 | 5854 | 2.2 | 25th |
| Ca | -2.87 | 1337 | 2072 | 2.4 | 5th |
| Al | -1.66 | 2980 | 8046 | 1.9 | 3rd |
Table 1 Different properties of various metal anodes
| Metal anode | Electrode potential/V | Gravimetric capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Volumetric capacity/(mA·h·cm-3) | Cost/(USD·kg-1) | Abundance rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | -3.04 | 3862 | 2066 | 19.2 | 33rd |
| Na | -2.71 | 1166 | 1128 | 0.2 | 6th |
| K | -2.93 | 685 | 591 | 1.0 | 7th |
| Mg | -2.37 | 2205 | 3832 | 2.2 | 8th |
| Zn | -0.76 | 820 | 5854 | 2.2 | 25th |
| Ca | -2.87 | 1337 | 2072 | 2.4 | 5th |
| Al | -1.66 | 2980 | 8046 | 1.9 | 3rd |
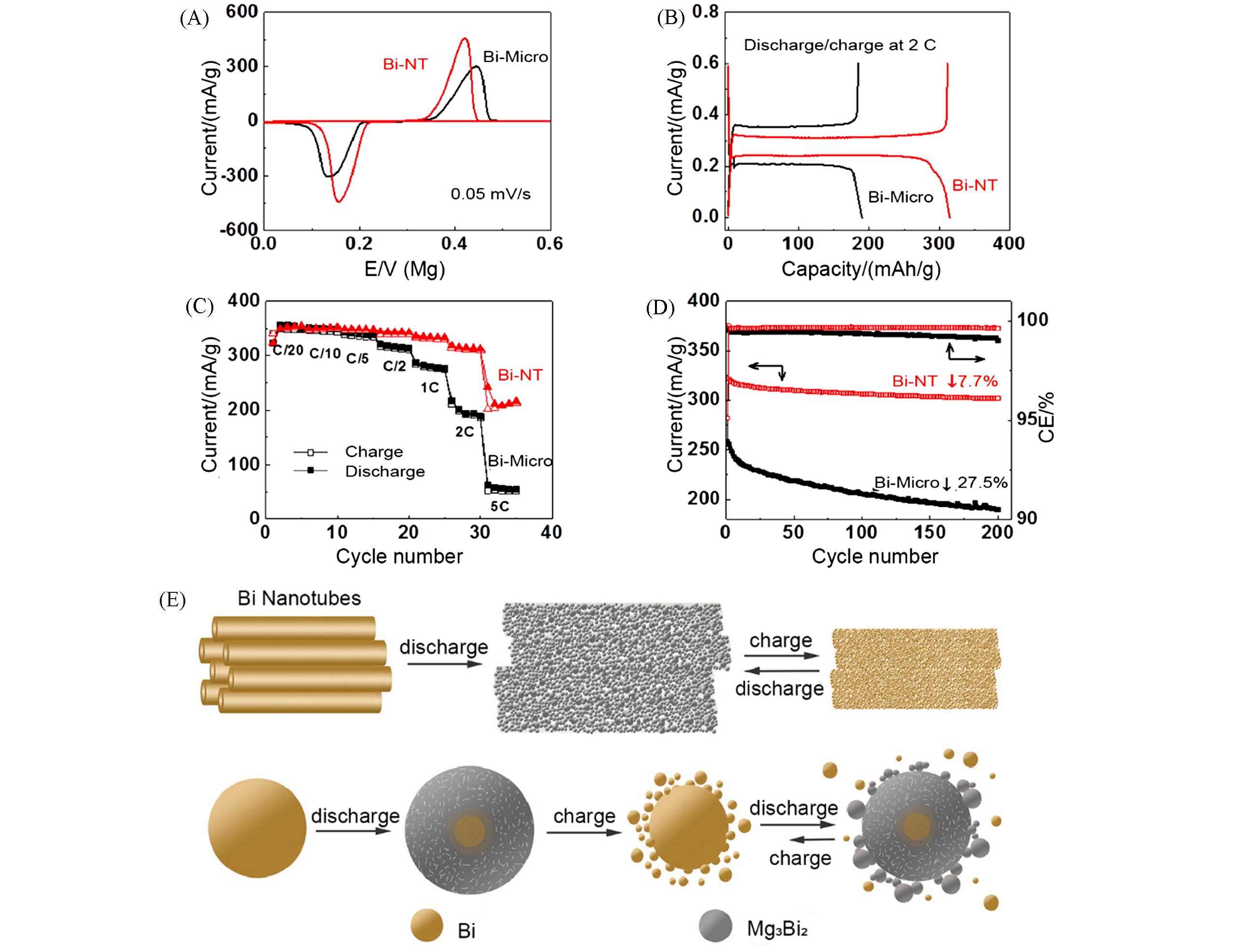
Fig.3 Electrochemical performance and illustration of structural transformation for Bi?Mg alloy anode[41](A) Cyclic voltammograms of Mg2+ insertion/deinsertion in Bi?NT and Bi?micro; (B) discharge/charge profile of a Mg?Bi cell; (C) rate performance of a Mg?Bi cell; (D) cycling stability and Coulombic efficiency of Bi electrode; (E) schematic illustration of the structural transformations of Bi?NT and Bi?micro during the discharge/charge process.Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
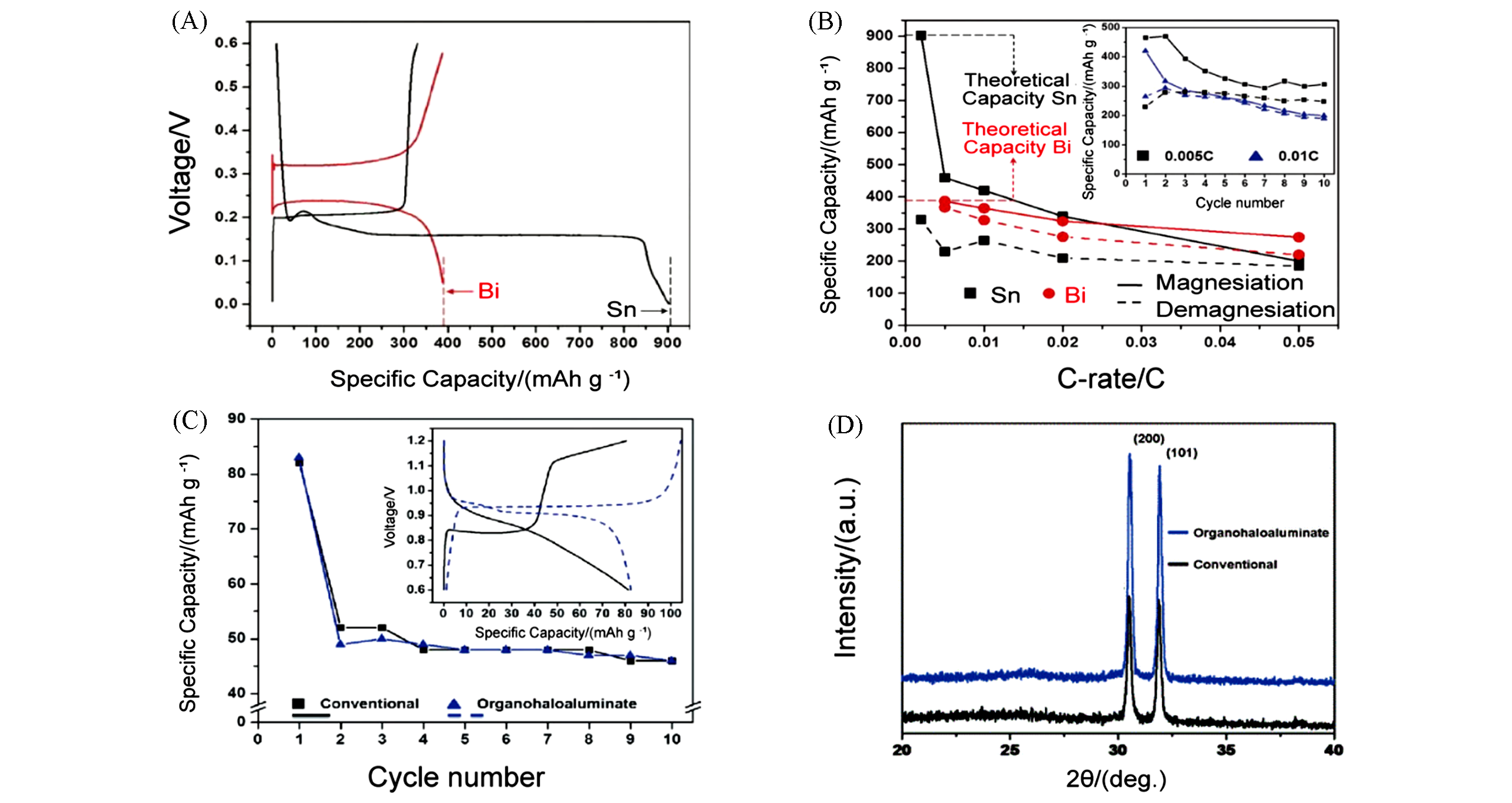
Fig.4 Electrochemical performance and XRD patterns of Sn?Mg alloy anode[48](A) 1st cycle galvanostatic magnesiation/demagnesiation curves for Sn/Mg and Bi/Mg half cells at 0.002C rate(using organohaloaluminate electrolyte); (B) magnesiation/demagnesiation capacities for Sn/Mg and Bi/Mg half?cells at various rates. Inset of (B): 10 cycles of a Sn/Mg half?cell at 0.005C and 0.01C rates in the same electrolyte; (C) the first 10 cycles for [Mo6S8/conventional electrolyte/Mg2Sn] and [Mo6S8/organohaloaluminate electrolyte/Mg2Sn] full?cell. Inset of (C): 1st cycle voltage profiles for each full?cell; (D) XRD patterns of demagnesiated Mg2Sn from organohaloaluminate and conventional electrolytes.Copyright 2013, The Royal Society of Chemistry.
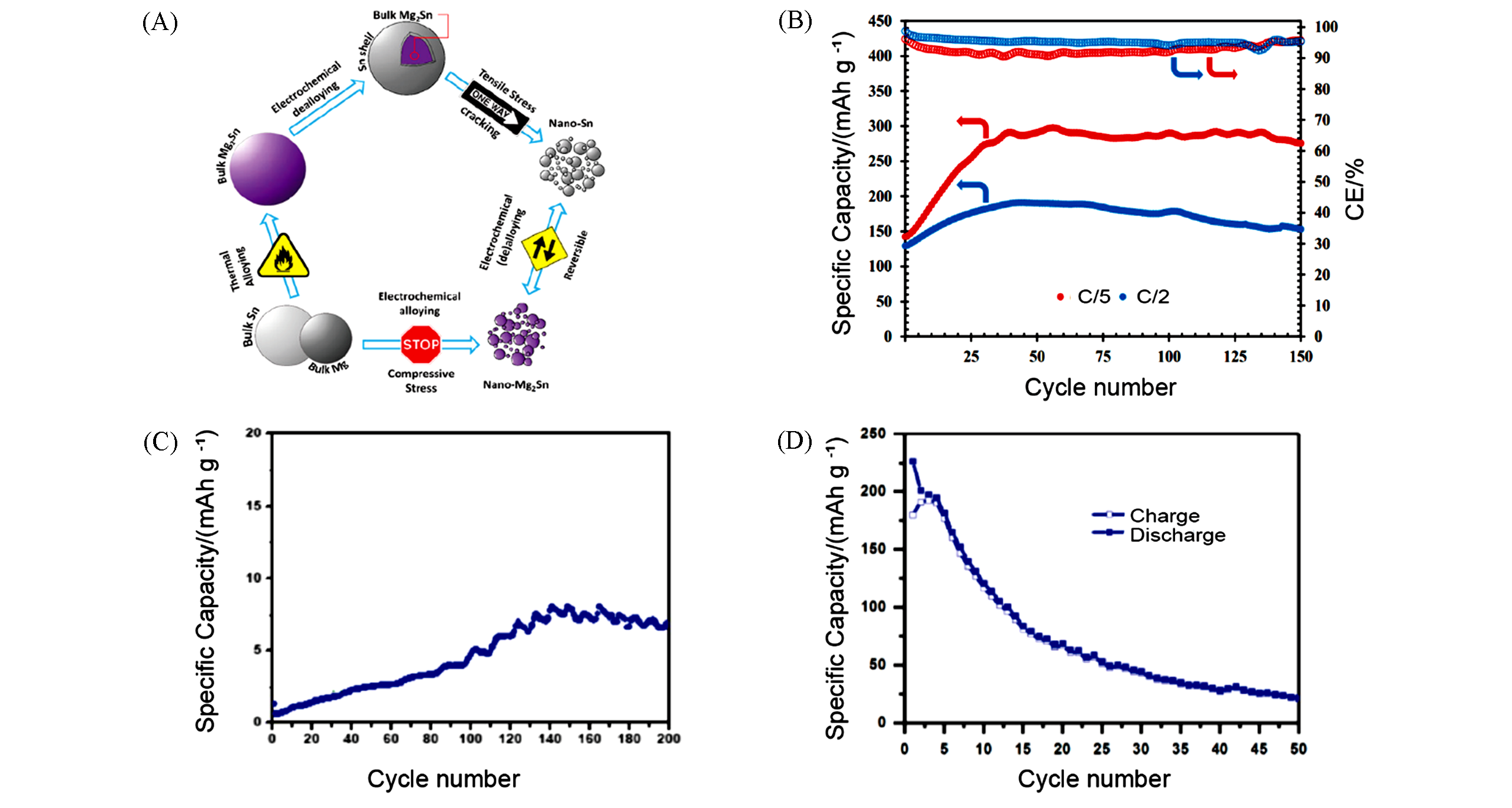
Fig.5 Synthesis process and electrochemical performance of Sn based anode(A) Schematic illustration of process producing nanostructured Sn[50]; (B) capacity retention of Mg2Sn/APC/Mg cells following application of oxidative pulses and past the preconditioning steps at C/5 and C/2[50]; (C) cycling performance of micro?Sn[51]; (D) nano?Sn at C/20 in Mg half?cell using 0.5 mol/L PhMgCl/THF and 0.5 mol/L EtMgCl/THF as electrolyte respectively[51].(A, B) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (C, D) Copyright 2018, MDPI AG.
Alloy element | Theoretical capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Cost/ (USD·kg-1) | Abundance | Reversibility/toxicity/ volume expansion | Conventional electrolyte | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Mg3Bi2 385 | 28.3 | 4.8×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Mg(BH4)2?LiBH4/diglyme | [ | |||||
| Sn | Mg2Sn 900 | 18.0 | 2.2 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic/120% | Mg(TFSI)2/DME | [ |
| Ga | Mg5Ga2 1920 | 2200.0 | 18.0 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Ge | Mg2Ge 1475 | 1200.0 | 1.8 ppm | Almost irreversible/Non?toxic/178% | ― | [ |
| Sb | Mg3Sb2 660 | 4.4 | 0.2 ppm | Almost irreversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/diglyme | [ |
| Si | Mg2Si 3817 | 1.4 | 27.7% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic/216% | ― | [ |
| Pb | Mg2Pb 517 | 0.2 | 14.0 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| In | Mg3In 1400 | 540.0 | 4.9×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| P | Mg2P 3461 | 300.0 | 1000.0 ppm | Maybe reversible/Non?toxic for black P | ― | [ |
| Al | Mg17Al12 2582 | 2.0 | 8.1% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic | ― | [ |
Table 2 Specific properties of representative alloy anodes
Alloy element | Theoretical capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Cost/ (USD·kg-1) | Abundance | Reversibility/toxicity/ volume expansion | Conventional electrolyte | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Mg3Bi2 385 | 28.3 | 4.8×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Mg(BH4)2?LiBH4/diglyme | [ | |||||
| Sn | Mg2Sn 900 | 18.0 | 2.2 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic/120% | Mg(TFSI)2/DME | [ |
| Ga | Mg5Ga2 1920 | 2200.0 | 18.0 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Ge | Mg2Ge 1475 | 1200.0 | 1.8 ppm | Almost irreversible/Non?toxic/178% | ― | [ |
| Sb | Mg3Sb2 660 | 4.4 | 0.2 ppm | Almost irreversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/diglyme | [ |
| Si | Mg2Si 3817 | 1.4 | 27.7% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic/216% | ― | [ |
| Pb | Mg2Pb 517 | 0.2 | 14.0 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| In | Mg3In 1400 | 540.0 | 4.9×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| P | Mg2P 3461 | 300.0 | 1000.0 ppm | Maybe reversible/Non?toxic for black P | ― | [ |
| Al | Mg17Al12 2582 | 2.0 | 8.1% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic | ― | [ |
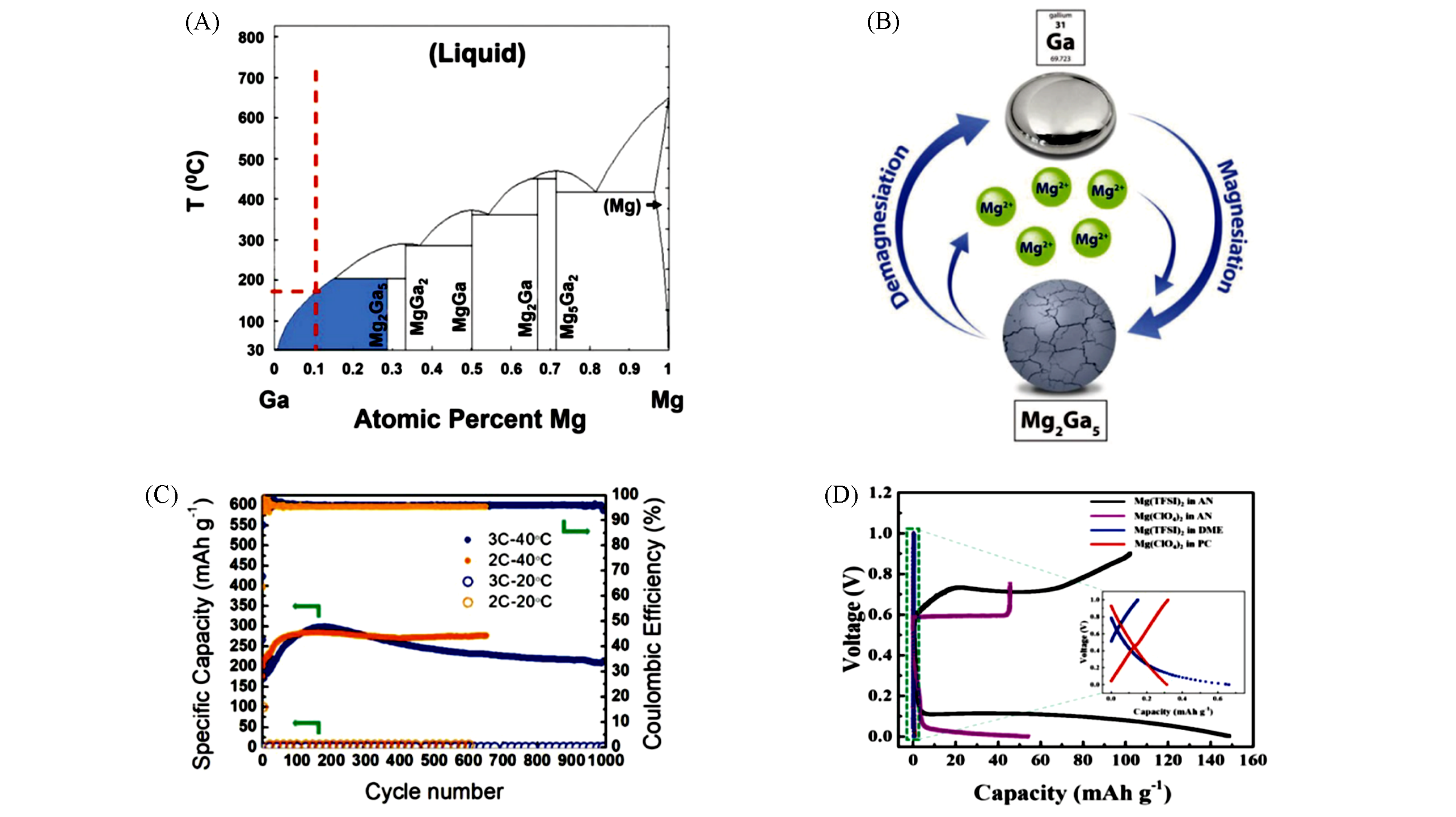
Fig.6 Mechanism and electrochemical performance of Ga?Mg alloy electrodes[61](A) Equilibrium phase diagram of the Mg?Ga system; (B) schematic of the magnesiation and demagnesiation process during which liquid Ga is reversibly converted into solid Mg2Ga5 at constant temperature and pressure; (C) long cycle?life of Mg2Ga5 alloy?type anode operating at 40 ℃ and 3C, 40 ℃ and 2C, 20 ℃ and 3C, 20 ℃ and 2C; (D) investigation of the compatibility of Mg2Ga5 with conventional electrolytes.Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH.
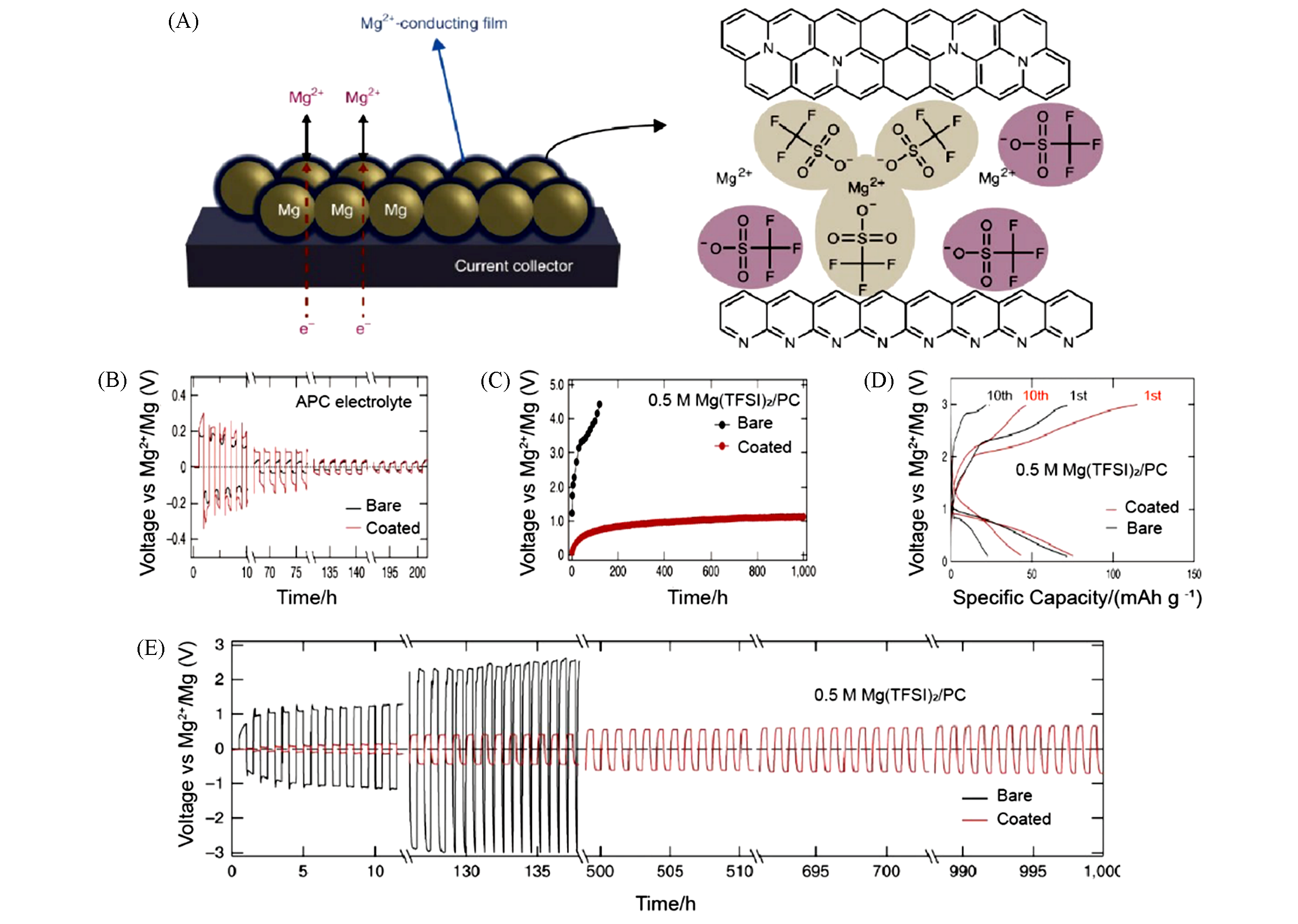
Fig.7 Structure of the interphase and electrochemical performance of coated or bare Mg anodes[64](A) Schematic of a Mg powder electrode coated with the artificial Mg2+?conducting interphase, and the proposed structure for the interphase; (B) reversible Mg deposition/stripping in APC electrolyte; (C) voltage hysteresis versus cycle numbers for symmetric Mg electrodes with 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/PC electrolyte; (D) voltage profiles of full cells using V2O5 as cathode in 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/PC electrolyte; (E) reversible Mg deposition/stripping in 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/PC electrolyte.Copyright 2018, Springer Nature.
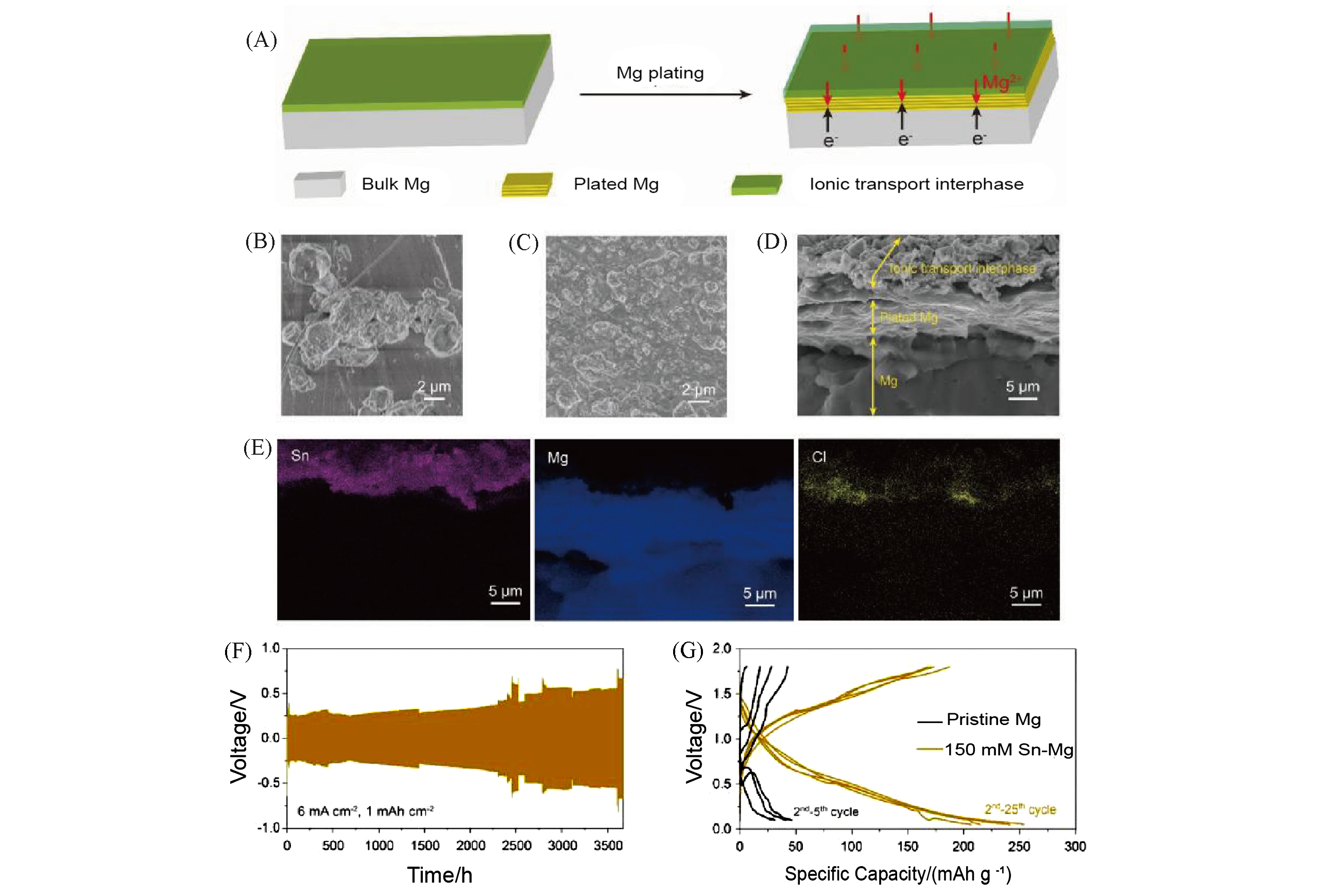
Fig.8 Morphology characterization and electrochemical performance of pristine and Sn based Mg anodes[65](A) Schematic showing the Mg deposition behavior in Mg(TFSI)2/DME electrolyte with ionic transport interphase on Mg metal anodes; (B, C) surface views of the pristine Mg anode(0.05 mA/cm2)(B) and modified Mg anode(2 mA/cm2) plated with 2 mA·h/cm2 of Mg(C); (D, E) cross?sectional image for modified Mg anode plated with 2 mA·h/cm2(D) and the corresponding EDS mappings of Sn, Mg and Cl, respectively(E); (F) voltage profiles in symmetric cells with modified Mg anodes at a current density of 6 mA/cm2; (G) galvanos?tatic voltage profiles of the pristine and modified Mg anodes paired with TiS2 cathode at a current density of 10 mA/g.Copyright 2019, Oxford University Press.
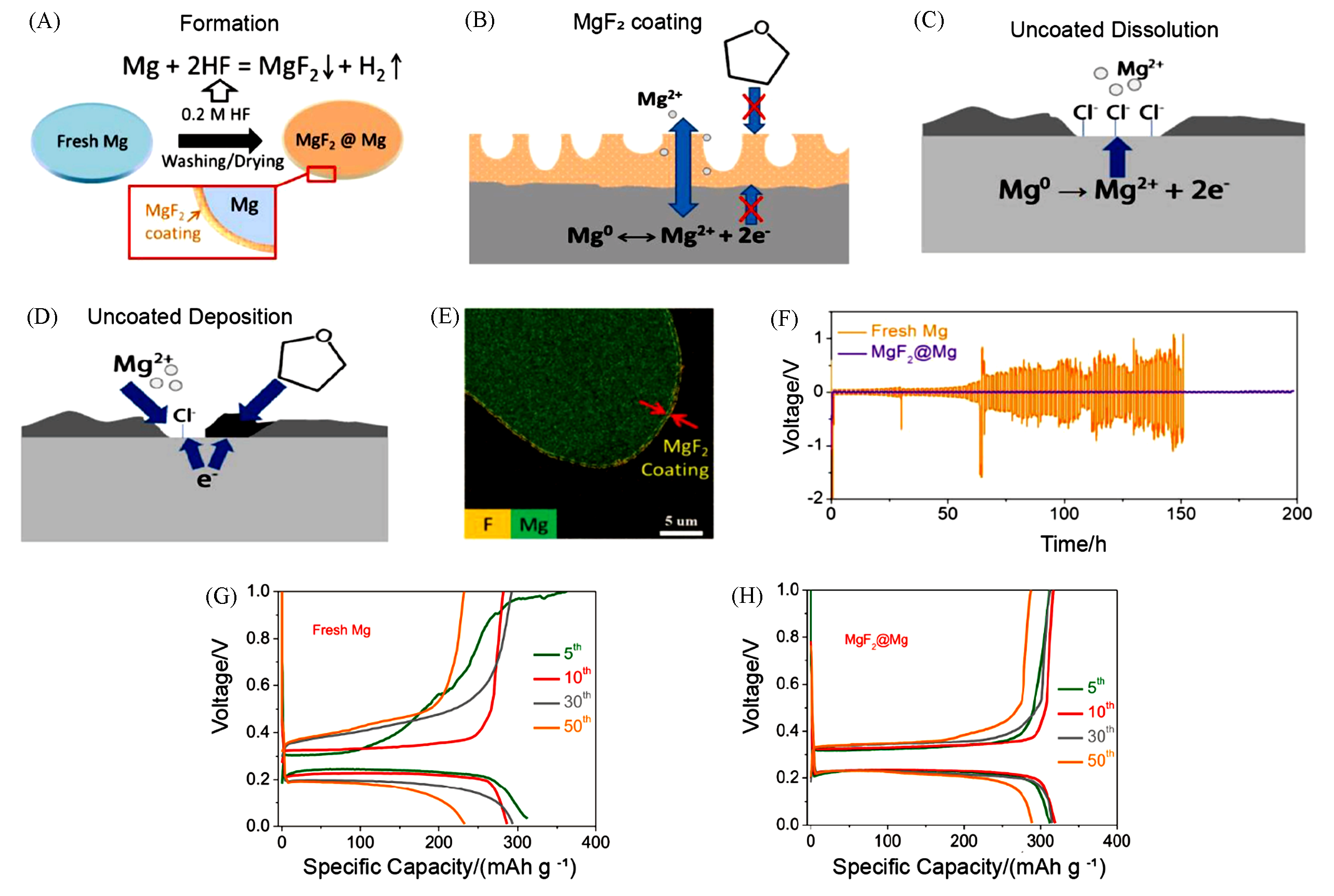
Fig.9 Formation and operating mechanism of MgF2 interphase and electrochemical performance of fresh or coated Mg anodes[66](A) Schematic illustration of the formation process of the MgF2 surface coating; (B) schematic of the operating mechanism of the MgF2 for stripping and deposition of Mg metal; (C, D) schematics of failure mechanism for the Mg metal anode; (E) cross?section EDS mapping of as?prepared MgF2@Mg electrode; (F) voltage profiles of the symmetric cells cycling of fresh Mg and MgF2 coated Mg at current density of 0.25 mA/cm2; (G, H) voltage profiles(with Bi as cathode) of fresh Mg(G) and MgF2@Mg(H) at 120 mA/g.Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
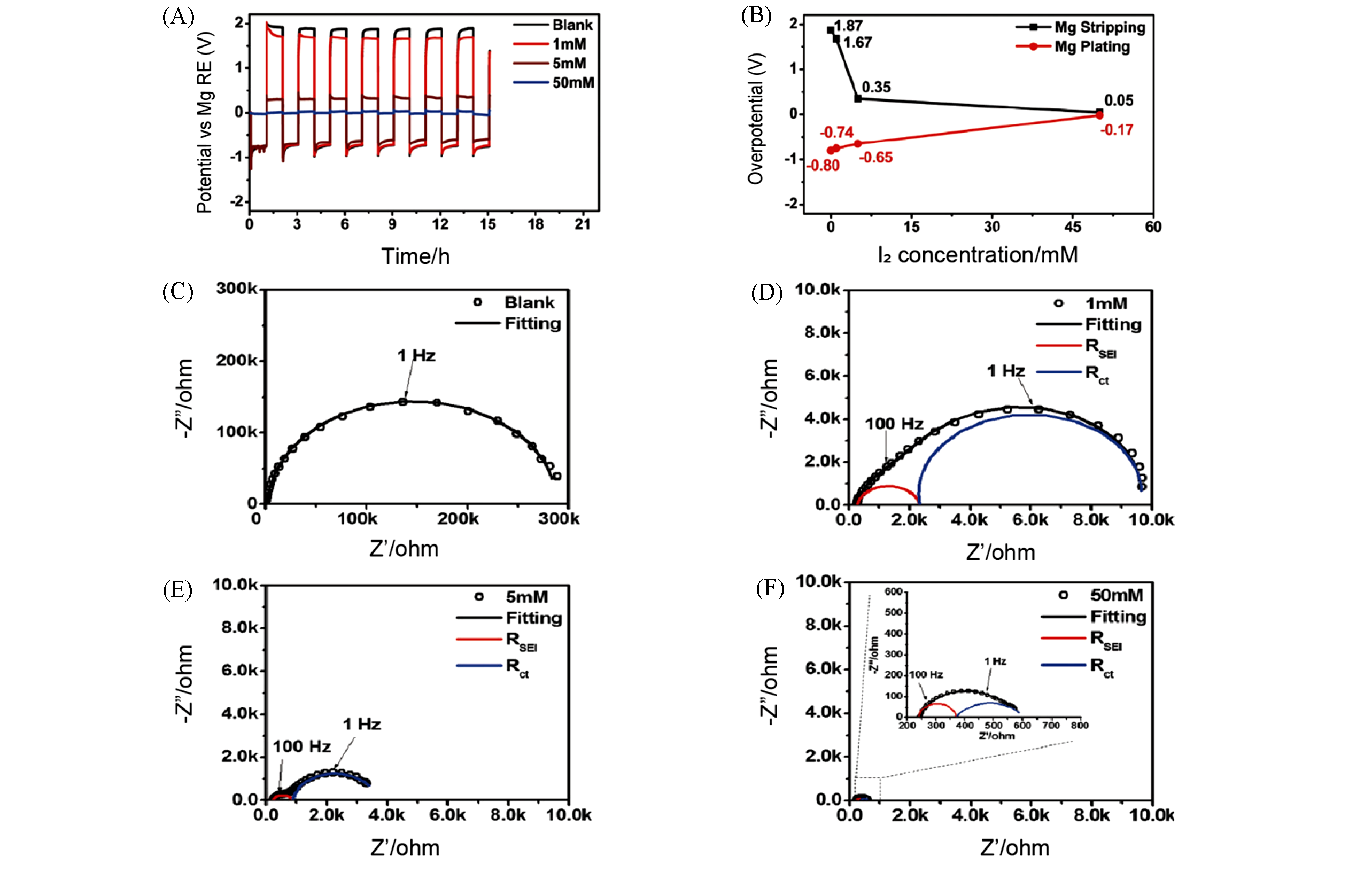
Fig.10 Electrochemical performance of Mg anodes in electrolytes with or without I2 additive[68](A) Potential of Mg electrode during cycling in 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/DME electrolytes with different amounts of I2 additive; (B) overpotentials for deposition and stripping; (C―F) EIS of Mg electrodes cycled in blank electrolyte and electrolytes with different concentrations of I2 additive.Copyright 2017, Wiley?VCH.
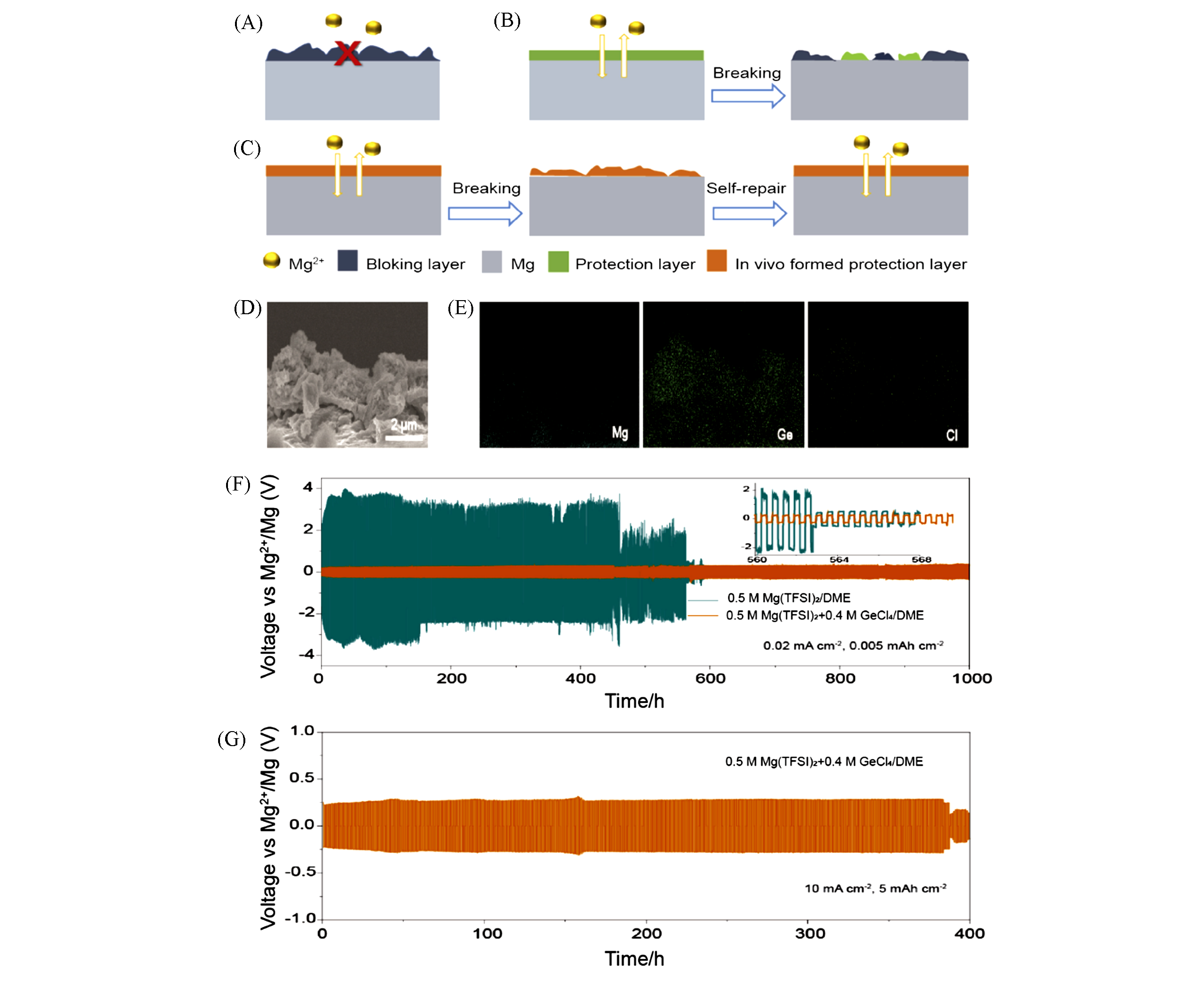
Fig.11 Operating mechanism of interphase and electrochemical performance of anodes in electrolytes with or without GeCl4 additive[69](A) Schematic diagrams showing the passivation layer in blank electrolyte; (B, C) breaking process for protection layer(B) and breaking and self?repair process for in situ?formed protection layer(C) during Mg deposition/stripping in conventional organic electrolyte; (D, E) cross?section SEM image(D) and the corresponding EDX mapping analysis(E) of the Ge?based protection layer; (F, G) voltage responses of symmetric Mg cells under repeated polarization from 1/4 h charge/discharge cycling at 0.02 mA/cm2(F) and 1/2 h charge/discharge cycling at 10 mA/cm2(G).Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
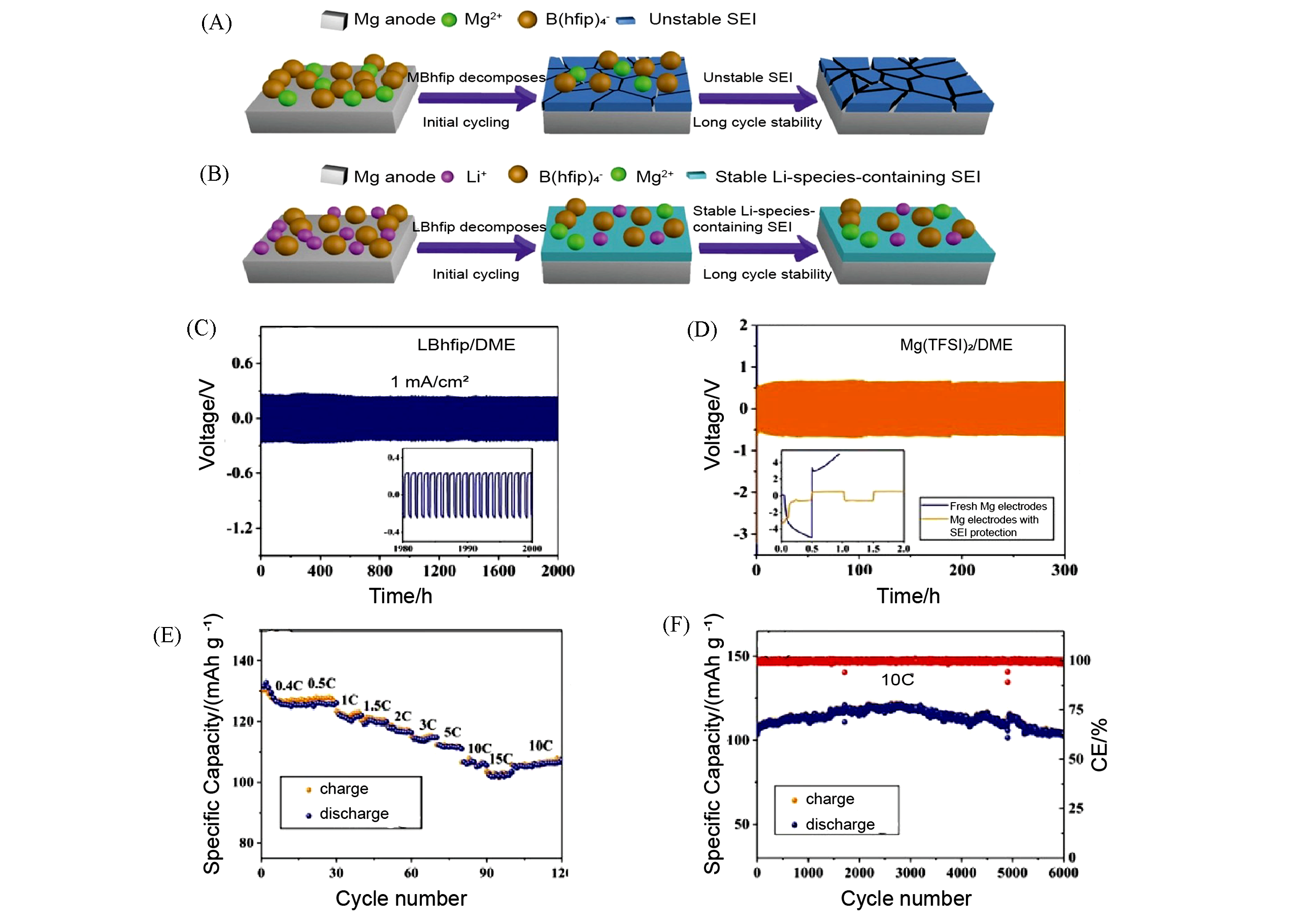
Fig.12 Mechanism of SEI formation and electrochemical performance of anodes in MBhfip/DME or LBhfip/DME electrolyte[70](A, B) The specific mechanism of SEI formation on the Mg anode surface in MBhfip/DME electrolyte(A) and LBhfip/DME electrolyte(B); (C) long?term cycling behavior of the Mg/Mg symmetrical cell(with LBhfip/DME) at the current density of 1.0 mA/cm2; (D) polarization behavior of the Mg/Mg symmetric cell with bare Mg electrodes and SEI protecting Mg electrodes at the current density of 0.1 mA/cm2 in Mg(TFSI)2/DME electrolyte; (E) charge?discharge profiles of Mo6S8/Mg battery(with LBhfip/DME electrolyte) at diffe?rent rates; (F) cycling stability and corresponding Coulombic efficiency of this Mo6S8/Mg battery for 6000 cycles at the rate of 10C.Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH.
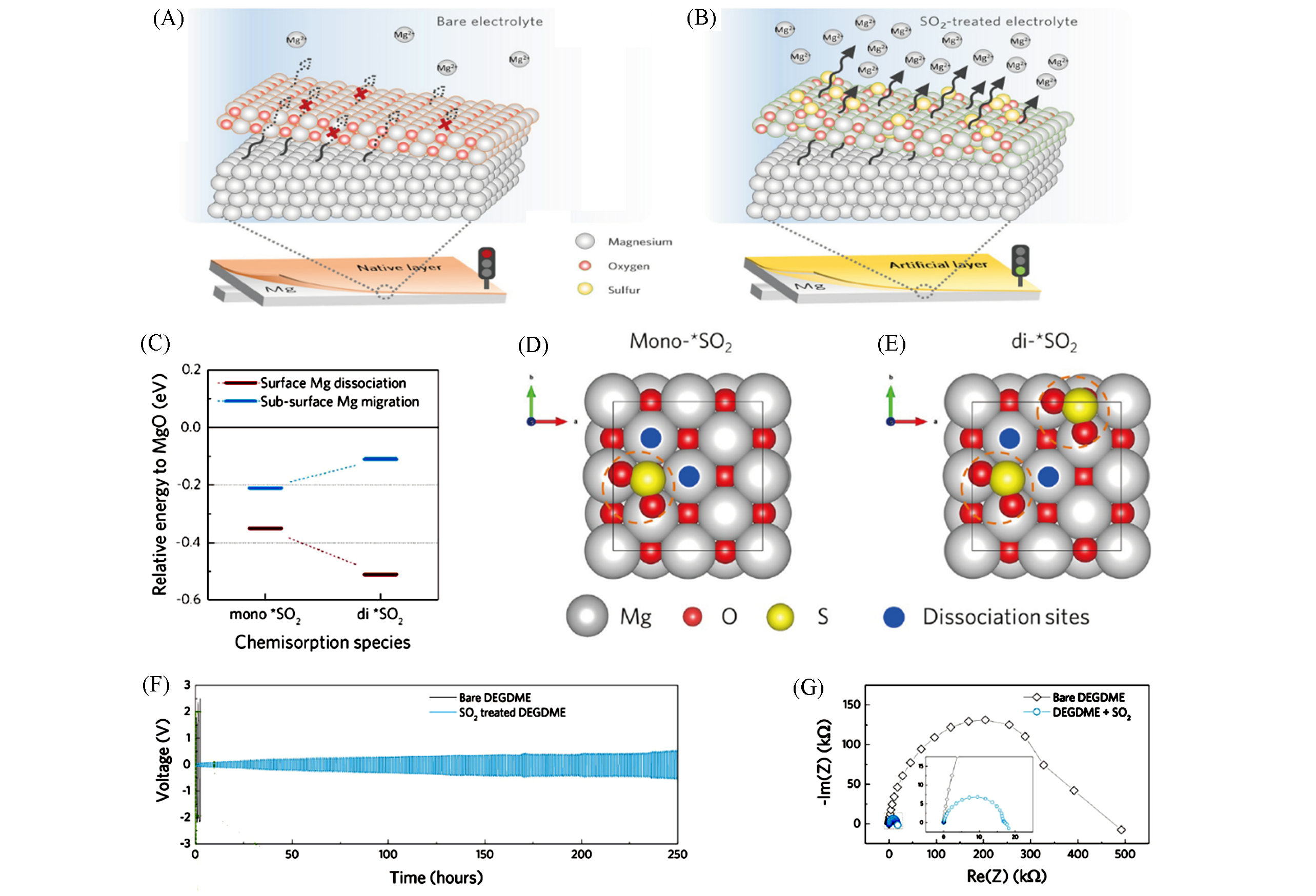
Fig.13 Operating mechanism of the tailored interphase on Mg anode and electrochemical performance in conventional electrolytes[71](A) Native passivation oxide layers on Mg anode; (B) artificial Mg2+?conducting layers tailored by SO2 chemisorption; (C) DFT calculation results for the energetics of Mg dissociation and migration with surface chemisorption structures; (D, E) top view of the calculated models of the mono?(D) and di?SO2 cases(E); (F) galvanostatic voltage profiles of Mg symmetric cells at 0.01 mA/cm2; (G) nyquist plots for Mg symmetric cells.Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Armand M., Tarascon J. M., Nature,2008, 451(7179), 652―657 |
| 2 | Noorden R. V., Nature,2014, 507(7490), 26―28 |
| 3 | Schmuch R., Wagner R., Hörpel G., Placke T., Winter M., Nat. Energy,2018, 3(4), 267―278 |
| 4 | Xu K., Chem. Rev.,2004, 104(10), 4303―4417 |
| 5 | Muldoon J., Bucur C. B., Gregory T., Chem. Rev.,2014, 114(23), 11683―11720 |
| 6 | Yang C., Feng J., Lv F., Zhou J., Lin C., Wang K., Zhang Y., Yang Y., Wang W., Li J., Guo S., Adv. Mater.,2018, 30(27), 1800036 |
| 7 | Pramudita J. C., Sehrawat D., Goonetilleke D., Sharma N., Adv. Energy Mater.,2017, 7(24), 1602911 |
| 8 | Liu Y., Gao C., Dai L., Deng Q., Wang L., Luo J., Liu S., Hu N., Small,2020, 16(44), 2004096 |
| 9 | Cui J., Wang A., Li G., Wang D., Shu D., Dong A., Zhu G., Luo J., Sun B., J. Mater. Chem. A,2020, 8(31), 15399―15416 |
| 10 | Leng K., Li G., Guo J., Zhang X., Wang A., Liu X., Luo J., Adv. Funct. Mater.,2020, 30(23), 2001317 |
| 11 | Long Y., Li H., Ye M., Chen Z., Wang Z., Tao Y., Weng Z., Qiao S. Z., Yang Q. H., Energy Storage Mater.,2021, 34, 194―202 |
| 12 | Song H., Su J., Wang C., Adv. Mater.,2021, 33(2), 2170015 |
| 13 | Tian H., Gao T., Li X., Wang X., Luo C., Fan X., Yang C., Suo L., Ma Z., Han W., Wang C., Nat. Commun.,2017, 8(1), 1―8 |
| 14 | Guan X., Wang A., Liu S., Li G., Liang F., Yang Y. W., Liu X., Luo J., Small,2018, 14(37), 1―21 |
| 15 | Attias R., Salama M., Hirsch B., Goffer Y., Aurbach D., Joule,2019, 3(1), 27―52 |
| 16 | Yoo H. D., Shterenberg I., Gofer Y., Gershinsky G., Pour N., Aurbach D., Energy Environ. Sci.,2013, 6(8), 2265―2279 |
| 17 | Kuvancheva A. M., Nauryzbayev M. K., Ishkenov A. R., Kurbatov A. P., Eurasian Chem. Technol. J.,2016, 3(1), 17―27 |
| 18 | Aurbach D., Gizbar H., Schechter A., Chusid O., Gottlieb H. E., Gofer Y., Goldberg I., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2002, 149(2), A115―A121 |
| 19 | Shterenberg I., Salama M., Gofer Y., Levi E., Aurbach D., MRS Bull.,2014, 39(5), 453―460 |
| 20 | Nelson J., Evans W., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2002, 39(1), 82―83 |
| 21 | Lu Z., Schechter A., Moshkovich M., Aurbach D., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1999, 466(2), 203―217 |
| 22 | Aurbach D., Lu Z., Schechter A., Gofer Y., Gizbar H., Turgeman R., Cohen Y., Moshkovich M., Levi E., Nature,2000, 407(6805), 724―727 |
| 23 | Gizbar H., Vestfrid Y., Chusid O., Gofer Y., Gottlieb H., Marks V., Aurbach D., Organometallics,2004, 23(16), 3826―3831 |
| 24 | Aurbach D., Suresh G. S., Levi E., Mitelman A., Mizrahi O., Chusid O., Brunelli M., Adv. Mater.,2007, 19(23), 4260―4267 |
| 25 | Salama M., Shterenberg I., Shimon L. J. W., Keinan⁃Adamsky K., Afri M., Gofer Y., Aurbach D., J. Phys. Chem. C,2017, 121(45), 24909―24918 |
| 26 | Mizrahi O., Amir N., Pollak E., Chusid O., Aurbach D., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2008, 155(2), A103―A109 |
| 27 | Kim H. S., Arthur T. S., Allred G. D., Zajicek J., Newman J. G., Rodnyansky A. E., Oliver A. G., Boggess W. C., Muldoon J., Nat. Commun.,2011, 2(1), 427 |
| 28 | Muldoon J., Bucur C. B., Oliver A. G., Sugimoto T., Matsui M., Kim H. S., Allred G. D., Zajicek J., Kotani Y., Energy Environ. Sci.,2012, 5(3), 5941―5950 |
| 29 | Guo Y. S., Zhang F., Yang J., Wang F. F., Hirano S. I., Energy Environ. Sci.,2012, 5(10), 9100―9106 |
| 30 | Mohtadi R., Matsui M., Arthur T. S., Hwang S. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2012, 124(39), 9918―9921 |
| 31 | Arthur T. S., Glans P. A., Singh N., Tutusaus O., Nie K., Liu Y. S., Mizuno F., Guo J., Alsem D. H., Salmon N. J., Mohtadi R., Chem. Mater.,2017, 29(17), 7183―7188 |
| 32 | Rajput N. N., Qu X., Sa N., Burrell A. K., Persson K. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2015, 137(9), 3411―3420 |
| 33 | Connell J. G., Genorio B., Lopes P. P., Strmcnik D., Stamenkovic V. R., Markovic N. M., Chem. Mater.,2016, 28(22), 8268―8277 |
| 34 | Terada S., Mandai T., Suzuki S., Tsuzuki S., Watanabe K., Kamei Y., Ueno K., Dokko K., Watanabe M., J. Phys. Chem. C,2016, 120(3), 1353―1365 |
| 35 | Shterenberg I., Salama M., Yoo H. D., Gofer Y., Park J. B., Sun Y. K., Aurbach D., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2015, 162(13), A7118―A7128 |
| 36 | Arthur T. S., Singh N., Matsui M., Electrochem. Commun.,2012, 16(1), 103―106 |
| 37 | Niu J., Zhang Z., Aurbach D., Adv. Energy Mater.,2020, 10(23), 2000697 |
| 38 | Kravchyk K. V., Piveteau L., Caputo R., He M., Stadie N. P., Bodnarchuk M. I., Lechner R. T., Kovalenko M. V., ACS Nano,2018, 12(8), 8297―8307 |
| 39 | Jung S. C., Han Y. K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2018, 122(31), 17643―17649 |
| 40 | Nayeb⁃Hashemi A. A., Clark J. B., Bull. Alloy Phase Dirgrams,1985, 6(6), 528―533 |
| 41 | Shao Y., Gu M., Li X., Nie Z., Zuo P., Li G., Liu T., Xiao J., Cheng Y., Wang C., Zhang J. G., Liu J., Nano Lett.,2014, 14(1), 255―260 |
| 42 | Yang B., Mo M., Hu H., Li C., Yang X., Li Q., Qian Y., ChemInform,2004, 35(28), 1785―1787 |
| 43 | Liu Z., Lee J., Xiang G., Glass H. F. J., Keyzer E. N., Dutton S. E., Grey C., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(4), 743―746 |
| 44 | He M., Protesescu L., Caputo R., Krumeich F., Kovalenko M. V., Chem. Mater.,2015, 27(2), 635―647 |
| 45 | Tan Y. H., Yao W. T., Zhang T., Ma T., Lu L. L., Zhou F., Yao H. B., Yu S. H., ACS Nano,2018, 12(6), 5856―5865 |
| 46 | Penki T. R., Valurouthu G., Shivakumara S., Sethuraman V. A., Munichandraiah N., New J. Chem.,2018, 42(8), 5996―6004 |
| 47 | Xu X., Chao D., Chen B., Liang P., Li H., Xie F., Davey K., Qiao S. Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2020, 59(48), 21728―21735 |
| 48 | Singh N., Arthur T. S., Ling C., Matsui M., Mizuno F., Chem. Commun.,2013, 49(2), 149―151 |
| 49 | Wang Z., Su Q., Shi J., Deng H., Yin G. Q., Guan J., Wu M. P., Zhou Y. L., Lou H. L., Fu Y. Q., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2014, 6(9), 6786―6789 |
| 50 | Yaghoobnejad Asl H., Fu J., Kumar H., Welborn S. S., Shenoy V. B., Detsi E., Chem. Mater.,2018, 30(5), 1815―1824 |
| 51 | Nacimiento F., Cabello M., Pérez⁃Vicente C., Alcántara R., Lavela P., Ortiz G. F., Tirado J. L., Nanomaterials,2018, 8(7), 501 |
| 52 | Wang L., Welborn S. S., Kumar H., Li M., Wang Z., Shenoy V. B., Detsi E., Adv. Energy Mater.,2019, 9(45), 1―7 |
| 53 | Legrain F., Manzhos S., J. Chem. Phys.,2016, 146(3), 034706 |
| 54 | Malyi O. I., Tan T. L., Manzhos S., J. Power Sources,2013, 233, 341―345 |
| 55 | Periyapperuma K., Tran T. T., Purcell M. I., Obrovac M. N., Electrochim. Acta,2015, 165, 162―165 |
| 56 | Murgia F., Weldekidan E. T., Stievano L., Monconduit L., Berthelot R., Electrochem. Commun.,2015, 60, 56―59 |
| 57 | Hembram K., Jung H., Yeo B. C., Pai S. J., Lee H. J., Lee K. R., Han S. S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2016, 18(31), 21391―21397 |
| 58 | Tran T., Obrovac M., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2011, 158(12), A1411―A1416 |
| 59 | Ho L. T., Appl. Phys. Lett.,1979, 35(5), 409―410 |
| 60 | Cheng Y., Shao Y., Parent L. R., Sushko M. L., Li G., Sushko P. V., Browning N. D., Wang C., Liu J., Adv. Mater.,2015, 27(42), 6598―6605 |
| 61 | Wang L., Welborn S. S., Kumar H., Li M., Wang Z., Shenoy V. B., Detsi E., Adv. Energy Mater.,2019, 9(45), 1902086 |
| 62 | Cheng Y., Shao Y., Parent L., Sushko M., Li G., Sushko P., Browning N., Wang C., Liu J., Adv. Mater.,2015, 27(42), 6598―6605 |
| 63 | Niu J., Gao H., Ma W., Luo F., Yin K., Peng Z., Zhang Z., Energy Storage Mater.,2018, 14, 351―360 |
| 64 | Son S. B., Gao T., Harvey S. P., Steirer K. X., Stokes A., Norman A., Wang C., Cresce A., Xu K., Ban C., Nat. Chem.,2018, 10(5), 532―539 |
| 65 | Lv R., Guan X., Zhang J., Xia Y., Luo J., Natl. Sci. Rev.,2020, 7, 333―341 |
| 66 | Li B., Masse R., Liu C., Hu Y., Li W., Zhang G., Cao G., Energy Storage Mater.,2019, 22, 96―104 |
| 67 | Nandiyanto A. B. D., Iskandar F., Ogi T., Okuyama K., Langmuir,2010, 26(14), 12260―12266 |
| 68 | Li X., Gao T., Han F., Ma Z., Fan X., Hou S., Eidson N., Li W., Wang C., Adv. Energy Mater.,2018, 8(7), 1―6 |
| 69 | Zhang J., Guan X., Lv R., Wang D., Liu P., Luo J., Energy Storage Mater.,2020, 26, 408―413 |
| 70 | Tang K., Du A., Dong S., Cui Z., Liu X., Lu C., Zhao J., Zhou X., Cui G., Adv. Mater.,2020, 32(6), 1―7 |
| 71 | Park H., Lim H. K., Oh S. H., Park J., Lim H. D., Kang K., ACS Energy Lett.,2020, 5(12), 3733―3740 |
| 72 | Aziz A., Tominaga Y., Ionics,2018(11), 24, 3475―3481 |
| 73 | Polu A. R., Kumar R., Bull. Mater. Sci.,2011, 34(5), 1063―1067 |
| 74 | Liang Y., Feng R., Yang S., Ma H., Liang J., Chen J., Adv. Mater.,2011, 23(5), 640―643 |
| 75 | Li W., Li C., Zhou C., Ma H., Chen J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2006, 45(36), 6009―6012 |
| 76 | Guo W., Liu S., Guan X., Zhang X., Liu X., Luo J., Adv. Energy Mater.,2019, 9(20), 1900193 |
| 77 | Park B., Schaefer J. L., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2020, 167(7), 070545 |
| 78 | Canepa P., Bo S. H., Sai Gautam G., Key B., Richards W. D., Shi T., Tian Y., Wang Y., Li J., Ceder G., Nat. Commun.,2017, 8(1), 1759 |
| [1] | SUN Zhumei, FU Jie, LI Xing, WANG Haifang, LU Jing, TONG Tianxing, ZHU Mingfei, WANG Yunyan. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy and Kinetics of Chloride Ion Removal by Electroadsorption [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220528. |
| [2] | CHEN Jiaqi, CHENG Wanting, WEN Qiuhui, HAN Jingru, MA Fuqiu, YAN Yongde, XUE Yun. Modification of activated carbon electrode for efficient electrosorption of Co2+, Mn2+ and Ni2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220598. |
| [3] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [4] | LIU Kun, YIN Yuan, GENG Wenqiang, XIA Haotian, LI Hua. Influence Mechanism of Filling Transition Metal Oxide Catalyst with Different Components on Nitrogen Fixation in Dielectric Barrier Discharge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220278. |
| [5] | DING Qin, ZHANG Zixuan, XU Peicheng, LI Xiaoyu, DUAN Limei, WANG Yin, LIU Jinghai. Effects of Cu, Ni and Co Hetroatoms on Constructions and Electrocatalytic Properties of Fe-based Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220421. |
| [6] | HE Yujing, LI Jiale, WANG Dongyang, WANG Fuling, XIAO Zuoxu, CHEN Yanli. Zinc-based Activated Fe/Co/N Doped Biomass Carbon Electrocatalysts with High Oxygen Reduction Activity [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [7] | HU Pingao, ZHANG Qi, ZHANG Huiru. Theoretical prediction on the Catalytic Effect of selenium-deficient WSe2 in lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220595. |
| [8] | WU Yujie, HUANG Wenzhi, PAN Junda, SHI Kaixiang, LIU Quanbing. Design, Regulation and Applications in Lithium-sulfur Battery Cathodes of Yolk-Shell Nanoreactors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220619. |
| [9] | . Progress of Hollow Carbon Materials as Anode for Sodium-Ion Battery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220620. |
| [10] | HOU Congcong, WANG Huiying, LI Tingting, ZHANG Zhiming, CHANG Chunrui, AN Libao. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH Composite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [11] | JIANG Baozheng, HUANG Wenting, LIU Wenbao, GUO Rongsheng, XU Chengjun, KANG Feiyu. Preparation of Nano-copper Modified Three-dimensional Zinc Mesh Electrode and Its Performance as Anode for Zinc-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220257. |
| [12] | LIU Kun, ZUO Jie, LI Hua, XIANG Hongfu, RAN Congfu, YANG Minghao, GENG Wenqiang. Effects of Electron Energy on the Chemical Products of Surface Dielectric Barrier Discharge Plasma [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220249. |
| [13] | WANG Pengfei, FU Wenhao, SUN Shaoni, CAO Xuefei, YUAN Tongqi. Preparation of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Materials Using Cellulose Nanocrystals as Templates and Their Electrochemical Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220497. |
| [14] | HU Shiying, SHEN Jiayan, HAN Junshan, HAO Tingting, LI Xing. Preparation of CoO Nanoparticles/Hollow Graphene Nanofiber composites and Its Electrochemical Performances [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220462. |
| [15] | REN Shijie, QIAO Sicong, LIU Chongjing, ZHANG Wenhua, SONG Li. Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Research Progress on Platinum Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220466. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||