

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (4): 697.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190661
• Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Congyuan,LIU Jia,DU Peiyao,ZHANG Zhen,LU Xiaoquan( )
)
Received:2019-12-12
Online:2020-04-10
Published:2020-02-07
Contact:
Xiaoquan LU
E-mail:luxq@tju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Congyuan, LIU Jia, DU Peiyao, ZHANG Zhen, LU Xiaoquan. Preparation of Hydrophilic FePt Nanoparticles and co-Catalyze Degrade Organic Pollutants †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 697.
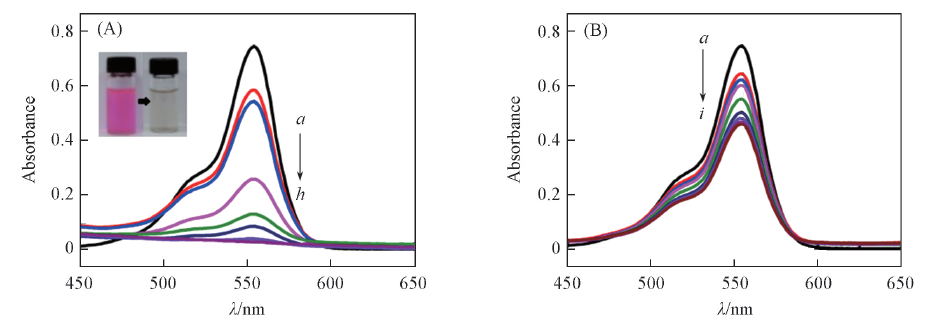
Fig.5 Degradation of RhB with(A) and without(B) FePt catalyst(A) a. RhB; b.—h. RhB+FePt+NaBH4. Reaction time/min, b.—h.: 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20. (B) a. RhB; b.—i. RhB+NaBH4. Reaction time/min, b.—i.: 0, 1, 3, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30. Inset of (A) show the color change of RhB solution before and after degradation.
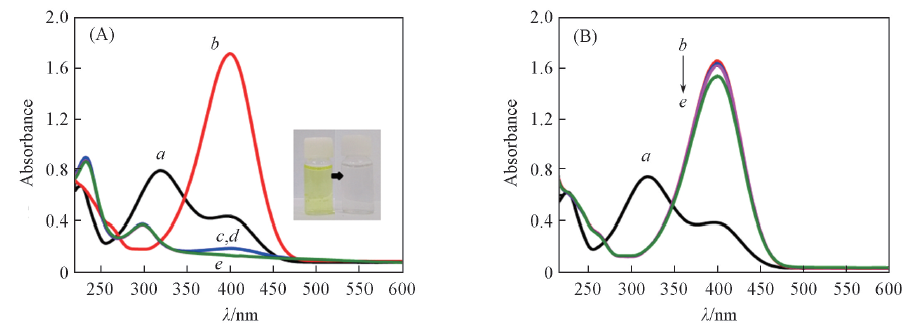
Fig.6 Degradation of 4-NP with(A) and without(B) PePt catalyst(A) a. 4-NP; b. 4-NP+NaBH4; c.—e. 4-NP+NaBH4+FePt. Reaction time/min, c.—e.: 1, 3, 5.^ (B) 4-NP+NaBH4. Reaction time/min, a.—e.: 0, 1, 3, 5, 7.
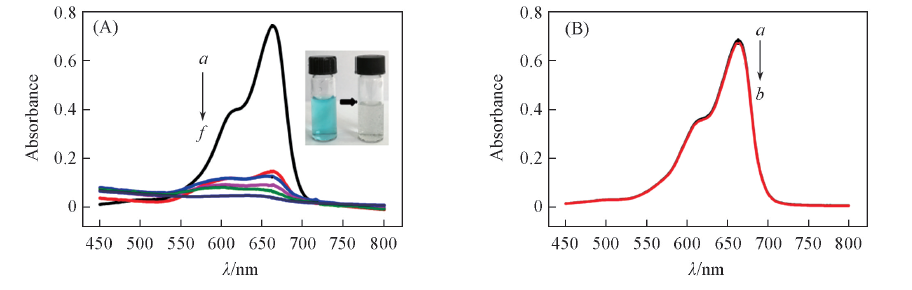
Fig.7 Degradation of MB P with(A) and without(B) PePt catalyst(A) a. MB; b. MB+FePt; c.—f. MB+FePt+H2O2. Reaction time/min, c.—f.: 1, 3, 8, 15. (B) a. MB; b. MB+H2O2, 20 min.
| [1] | Chen C., Zhou L., Yu J., Wang Y., Nie S., Zhu S., Zhu J., Nano. Energy, 2018, 51, 451— 456 |
| [2] | Zhang Y., Park S. J., Appl. Catal. B, 2019, 240, 92— 101 |
| [3] | Wang J. T., China High-Tech Enterprises, 2014, 30, 71— 71 |
| ( 王静涛 . 中国高新技术企业, 2014, 30, 71— 71) | |
| [4] | Liang N., Hu K., Yang X. L ., Guide to Getting Rich in Fishing, 2016, 10, 17— 19 |
| ( 梁楠, 胡鲲, 杨先乐 . 渔业致富指南, 2016, 10, 17— 19) | |
| [5] | Chen Y. M., Yu M., Friend of Science Amateurs, 2011, 27, 153— 157 |
| ( 陈艳美, 于淼 . 科学之友, 2011, 27, 153— 157) | |
| [6] | Qin L., Yi H., Zeng G., Lai C., Huang D., Xu P., Fu Y., He J., Li B., Zhang C., Cheng M., Wang H., Liu X., J. Hazard Mater., 2019, 380, 120864 |
| [7] | Yamamoto T., Kim S. I., Chaichanawong J., Apiluck E. U., Ohmori T., Appl. Catal. B, 2009, 88, 455— 461 |
| [8] | Bai X., Du Y., Hu X., He Y., He C., Liu E., Fan J., Appl. Catal. B, 2018, 239, 204— 213 |
| [9] | Xia H., Zhang Z., Liu J., Deng Y., Zhang D., Du P., Zhang S., Lu X., Appl. Catal. B, 2019, 259, 118058 |
| [10] | Wei M., Shi X., Xiao L., Zhang H., J. Hazard Mater., 2020, 382, 120993 |
| [11] | Dai C., Tian X., Nie Y., Lin H. M., Yang C., Han B., Wang Y., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52, 6518— 6525 |
| [12] | Samanta P., Desai A. V., Let S., Ghosh S. K., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2019, 7, 7456— 7478 |
| [13] | Mahmoodi N. M., Abdi J., J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2019, 80, 606— 613 |
| [14] | Li Q., Chen B., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 48, 4774— 4781 |
| [15] | An K., Xu X., Liu X., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017, 6, 1446— 1455 |
| [16] | Shao L., Gao J., Xia X., Dong W., Cheng S., Zhu Y., Liu Y ., J. Photochem. Photobiol. A: Chem., 2019, 382, 111972 |
| [17] | Trotochaud L., Young S. L., Ranney J. K., Boettcher S. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 6744— 6753 |
| [18] | Lee J., Yoo J. M., Ye Y., Mun Y., Lee S., Kim O. H., Rhee H. W., Lee H. I., Sung Y. E., Lee J., Adv. Energy Mater., 2015, 5, 1402093 |
| [19] | Li Q., Wu L., Wu G., Su D., Lv H., Zhang S., Zhu W., Casimir A., Zhu H., Mendoza-Garcia A., Sun S., Nano. Lett., 2015, 15, 2468— 2473 |
| [20] | Chen M., Yang B., Zhu J., Liu H., Zhang X., Zheng X., Liu Q., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2018, 90, 610— 620 |
| [21] | Moghimi N., Leung K. T., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 5974— 5980 |
| [22] | Chou S. W., Shau Y. H., Wu P. C., Yang Y. S., Shieh D. B., Chen C. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 13270— 13278 |
| [23] | Yue L., Wang J., Dai Z., Hu Z., Chen X., Qi Y., Zheng X., Yu D., Bioconjuge Chem., 2017, 28, 400— 409 |
| [24] | Kim J., Rong C., Liu J. P., Sun S., Adv. Mater., 2009, 21, 906— 909 |
| [25] | Liu Y., Purich D. L., Wu C., Wu Y., Chen T., Cui C., Zhang L., Cansiz S., Hou W., Wang Y., Yang S., Tan W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 14952— 14958 |
| [26] | Wang C., Yu X., Zhang X., Lu Z., Wang X., Han X., Zhao J., Li L., Yang X., J. Alloys Compd., 2020, 815, 152431 |
| [27] | Shou S., Murray C., Weller D ., Science, 2000, 287, 1989— 1992 |
| [28] | Sun Y., Miao H., Ma S., Zhang L., You C., Tang F., Yang C., Tian X., Wang F., Luo Y., Lin X., Wang H., Li C., Li Z., Yu H., Liu X., Xiao Y., Gong Y., Zhang J., Quan H., Xie C., Cancer Lett., 2018, 418, 27— 40 |
| [29] | Rather M. A., Bhat S. A., Pandit S. A., Bhat F. A., Rather G. M., Bhat M. A., Catal. Lett., 2019, 149, 2195— 2203 |
| [30] | Shahzeydi A., Ghiaci M., Jameie L., Panjepour M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 485, 194— 203 |
| [31] | Nagajyoyhi P. C., Devarayapalli K. C., Sreekanth T. V. M., Vattikuti S. V. P., Shim J., Mater. Res. Express., 2019, 6, 105069 |
| [32] | Zhang T., Li X., Kang S. Z., Qin L., Li G., Mu J., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 2952— 2959 |
| [33] | Abay A. K., Chen X., Kuo D. H., New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 5628— 5638 |
| [34] | Zhou Y., Zhang L., Liu J., Fan X., Wang B., Wang M., Ren W., Wang J., Li M., Shi J., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 3862— 3867 |
| [35] | Nasrollahzadeh M., Sajadi S. M., Hatamifard A., Appl. Catal. B, 2016, 191, 209— 227 |
| [36] | Zhang C., Zhang R., He S., Li L ., ChemCatChem, 2017, 9, 980— 986 |
| [37] | Zhu X. Y., Lv Z. S., Feng J. J., Yuan P. X., Zhang L., Chen J. R., Wang A. J., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2018, 516, 355— 363 |
| [38] | Ma Y., Wu X., Zhang G., Appl. Catal. B, 2017, 205, 262— 270 |
| [39] | Jiang L., Zhu W., Wang C., Dong W., Zhang L., Wang G., Chen B., Li C., Zhang X., Appl. Catal. B, 2016, 180, 344— 350 |
| [40] | Yan Z., X., Xu Z., H., Yang Z., H., Yue L., Huang L., Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 467, 277— 285 |
| [41] | Li B., Ma J. G., Cheng P., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 6834— 6837 |
| [42] | Qin L., Huang D., Xu P., Zeng G., Lai C., Fu Y., Yi H., Li B., Zhang C., Cheng M., Zhou C., Wen X., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 534, 357— 369 |
| [43] | Zou F., Ding Q., Tran V. T., Wang G., Zhang Y., Kang S., Lee J., Zhou H., RSC Adv., 2015, 5, 56653— 56657 |
| [44] | Xia H., Zhang Z., Liu J., Ning X., Zhang S., Lu X., Appl. Catal. B, 2019, 250, 189— 199 |
| [45] | Ma C., Feng S., Zhou J., Chen R., Wei Y., Liu H., Appl. Catal. B, 2019, 259, 118015 |
| [46] | Xiao Y., Huo W., Yin S., Jiang D., Zhang Y., Zhang Z., Liu X., Dong F., Wang J., Li G., Hu X., Yuan X., Yao H. C., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 556, 466— 475 |
| [47] | Hou X., Huang X., Jia F., Ai Z., Zhao J., Zhang L., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2017, 51, 5118— 5126 |
| [48] | Liu Y., Jin W., Zhao Y., Zhang G., Zhang W., Appl. Catal. B, 2017, 206, 642— 652 |
| [49] | Li Y., Qu J., Gao F., Lv S., Shi L., He C., Sun J., Appl. Catal. B, 2015, 162, 268— 274 |
| [50] | Kim J., Zhang T., Liu W., Du P., Dobson J. T., Huang C. H., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, 53, 13312— 13322 |
| [51] | Yang B., Zhou P., Cheng X., Li H., Huo X., Zhang Y., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2019, 555, 383— 393 |
| [52] | Mao X., Kwon J., Koh E. K., Hwang D. Y., Lee J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2015, 7, 15522— 15530 |
| [1] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [2] | PENG Xiaoming, WU Jianqun, DAI Hongling, YANG Zhanhong, XU Li, XU Gaoping, HU Fengping. Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Single Atom Catalysts Ni⁃N⁃C for High Efficiency Degradation of Phenol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2581. |
| [3] | CHANG Shuqing, XIN Xu, HUANG Yaqi, ZHANG Xincong, FU Yanghe, ZHU Weidong, ZHANG Fumin, LI Xiaona. Pyroelectrically-induced Catalytic Performance of Zr-based MOF Under Cold-hot Alternation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2558. |
| [4] | LI Dongping, LI Bin, LI Changheng, YU Xuegang, SHAN Yan, CHEN Kezheng. Synthesis and Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Ni5P4/g-C3N4 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1292. |
| [5] | YAO Mingcai, YANG Qiang, MENG Jian, LIU Xiaojuan. Effect of Zn2+ Substituting Ga3+ on Structure and Photocatalytic Properties of Wurtzite β-CuGa1-xZnxO2 with Unequal Doping [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3561. |
| [6] | LI Li, LI Pengfei, WANG Bo. Photocatalytic Application of Covalent Organic Frameworks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1917. |
| [7] | LI Xiaoqian, ZHANG Hua, LU Haijian, LIU Chang, LIU Qinglong, MA Xiayu, FANG Yuanping, LIANG Dapeng. Mechanism of Photocatalytic Degradation of Rhodamine B by TiO2 Nanowire Array with Internal Extraction Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2003. |
| [8] | GAO Xia,PAN Huibin,QIAO Chengfang,CHEN Fengying,ZHOU Yuan,YANG Wenhua. Construction of HRP Immobilized Enzyme Reactor Based on Hierarchically Porous Metal-organic Framework and Its Dye Degradation Application† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1591. |
| [9] | XIA Yun, Lü Wangyang, CHEN Wenxing, LI Nan. Fiber Supported Carbon Black Metal Phthalocyanine Axial Complex to Mimic Enzyme for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutant in Water† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1582. |
| [10] | WANG Rui,XU Mei,XIE Jiawen,YE Shengying,SONG Xianliang. Effects of Hydrothermal Reaction Conditions on the Structure and Properties of Porous Spherical Bi2WO6 Photocatalyst † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1320. |
| [11] | LIU Dongxu, CHEN Xuebing, YANG Xia, ZHANG Jing, CHEN Changdong. Controllable Fabrication of Photogenerated Charges Gradient Continuous Transfer Chain to Enhance Photocatalytic Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 742. |
| [12] | LIU Yigang,ZHAO Peng,HAN Yugui,SONG Xin,HAN Zhipeng,XIE Liangbo,LI Zhuang,JIA Xiaoqing,LI Yi. W Element Doped CeO2 as Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Catalyst for Efficient Treatment of Oily Wastewater † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 498. |
| [13] | HUA Tao, LI Shengnan, LI Fengxiang, WANG Haonan. Treatment of Naphthalene by Microbial Electrochemical System and the Analysis of Microbial Communities † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1964. |
| [14] | ZHANG Kejie,LI Yu,XIA Yuan,HAN Shuo,CAO Jing,WANG Hanyang,LUO Wentao,ZHOU Zhiping. Synthesis and Photocatalytic Performance of CdS/CuS Core-shell Nanocomposites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 489. |
| [15] | GAN Lu,DONG Yongchun. Photocatalytic Performance of Fe-complexes Prepared Using Cotton Fiber Modified with Different Dicarboxylic Acids † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2205. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||