

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (11): 2477.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180530
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HOU Hua1, YU Xiaojuan1, ZHOU Wenjun2, LUO Yunbai1, WANG Baoshan1,*( )
)
Received:2018-07-27
Online:2018-11-10
Published:2018-09-29
Contact:
WANG Baoshan
E-mail:baoshan@whu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HOU Hua, YU Xiaojuan, ZHOU Wenjun, LUO Yunbai, WANG Baoshan. Theoretical Investigations on the Structure-activity Relationship to the Dielectric Strength of the Insulation Gases†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2477.
| Species | CAS registry | As/nm2 | ν | Π/eV | ρ/(g·cm-3) | Er,cal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | 1333-74-0 | 0.336 | 6.635 | 0.131 | 0.180 | 0.208 | 0.16 | 0.22 |
| O2 | 7782-44-7 | 0.506 | 1.400 | 0.091 | 1.624 | 0.296 | 0.34 | 0.33 |
| N2 | 7727-37-9 | 0.542 | 44.973 | 0.173 | 1.265 | 0.350 | 0.35 | 0.38 |
| N2O | 10024-97-2 | 0.666 | 182.831 | 0.430 | 1.541 | 0.342 | 0.40 | 0.46 |
| CO | 630-08-0 | 0.545 | 94.462 | 0.261 | 1.254 | 0.317 | 0.34 | 0.40 |
| CO2 | 124-38-9 | 0.647 | 207.724 | 0.532 | 1.591 | 0.301 | 0.27 | 0.35 |
| OCS | 463-58-1 | 0.819 | 215.830 | 0.277 | 1.546 | 0.518 | 0.93 | 0.90 |
| SF6 | 2551-62-4 | 1.034 | 0.140 | 0.087 | 2.777 | 0.733 | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| CH4 | 74-82-8 | 0.602 | 9.208 | 0.126 | 0.624 | 0.346 | 0.37 | 0.43 |
| CH3Cl | 74-87-3 | 0.816 | 192.564 | 0.558 | 1.299 | 0.410 | 0.33 | 0.32 |
| CH3Br | 74-83-9 | 0.882 | 196.293 | 0.525 | 2.181 | 0.429 | 0.49 | 0.45 |
| CH2F2 | 75-10-5 | 0.712 | 313.110 | 0.701 | 1.676 | 0.320 | 0.33 | 0.27 |
| CH2Cl2 | 75-09-2 | 1.014 | 194.823 | 0.481 | 1.634 | 0.402 | 0.69 | 0.68 |
| CHF2Cl | 75-45-6 | 0.914 | 152.353 | 0.450 | 1.945 | 0.345 | 0.51 | 0.42 |
| CHFCl2 | 75-43-4 | 1.057 | 146.752 | 0.382 | 1.881 | 0.424 | 0.78 | 0.92 |
| CF4 | 75-73-0 | 0.811 | 4.219 | 0.175 | 2.388 | 0.382 | 0.49 | 0.42 |
| CF3Cl | 75-72-9 | 0.957 | 10.906 | 0.172 | 2.208 | 0.550 | 0.68 | 0.58 |
| CF2Cl2 | 75-71-8 | 1.095 | 38.548 | 0.176 | 2.108 | 0.576 | 0.91 | 0.99 |
| CF3Br | 75-63-8 | 1.023 | 20.324 | 0.187 | 2.864 | 0.517 | 0.78 | 0.75 |
| CH3CF3 | 420-46-2 | 0.977 | 170.332 | 0.564 | 1.745 | 0.425 | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| CH3CHCl2 | 75-34-3 | 1.204 | 214.009 | 0.461 | 1.497 | 0.544 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| C2F6 | 76-16-4 | 1.118 | 3.519 | 0.144 | 2.427 | 0.638 | 0.92 | 0.80 |
| CF3CF2Cl | 76-15-3 | 1.241 | 9.646 | 0.158 | 2.314 | 0.633 | 1.05 | 1.04 |
| F2C=CFCl | 79-38-9 | 1.103 | 76.028 | 0.251 | 2.089 | 0.557 | 0.89 | 0.72 |
| CF3CH=CH2 | 677-21-4 | 1.114 | 223.217 | 0.494 | 1.674 | 0.501 | 0.87 | 0.80 |
| CF3CF=CF2 | 116-15-4 | 1.261 | 55.424 | 0.296 | 2.291 | 0.609 | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| CF2=CF—CF=CF2 | 685-63-2 | 1.401 | 89.157 | 0.315 | 2.184 | 0.586 | 1.18 | 1.20 |
| c-C6F10 | 355-75-9 | 1.786 | 14.075 | 0.220 | 2.428 | 0.892 | 1.80 | 1.90 |
| c-C4F8 | 115-25-3 | 1.472 | 5.602 | 0.241 | 2.437 | 0.605 | 1.18 | 1.25 |
| c-C6F12 | 355-68-0 | 1.856 | 0.910 | 0.107 | 2.553 | 1.304 | 2.33 | 2.35 |
| c-CF3(C4F6)CF3 | 1583-97-7 | 1.935 | 7.545 | 0.176 | 2.512 | 1.063 | 2.19 | 2.30 |
| CF3OCF3 | 1479-49-8 | 1.214 | 8.963 | 0.163 | 2.442 | 0.601 | 1.01 | 1.00 |
| c-CF3(C2F2O)CF3 | 117642-58-7 | 1.590 | 33.769 | 0.221 | 2.406 | 0.793 | 1.53 | 1.60 |
| HC≡CH | 74-86-2 | 0.672 | 304.742 | 0.534 | 0.858 | 0.306 | 0.57 | 0.60 |
| SO2F2 | 2699-79-8 | 0.922 | 186.140 | 0.383 | 2.303 | 0.543 | 0.79 | 0.73 |
| CF3SO2F | 335-05-7 | 1.230 | 216.863 | 0.346 | 2.349 | 0.782 | 1.36 | 1.45 |
| CH3CN | 75-05-8 | 0.851 | 532.756 | 0.892 | 1.021 | 0.470 | 0.77 | 0.80 |
| CF3CN | 353-85-5 | 1.013 | 366.065 | 0.334 | 1.931 | 0.706 | 1.53 | 1.50 |
| C2F5CN | 422-04-8 | 1.304 | 297.109 | 0.257 | 2.110 | 0.940 | 1.88 | 2.00 |
| C3F7CN | 375-00-8 | 1.565 | 280.934 | 0.230 | 2.219 | 1.142 | 2.32 | 2.40 |
| i-C3F7CN | 42532-60-5 | 1.548 | 245.345 | 0.218 | 2.227 | 1.138 | 2.22 | 2.20 |
| i-C3F7COCF3 | 756-12-7 | 1.812 | 165.640 | 0.210 | 2.428 | 1.045 | 2.38 | 2.10 |
| i-C3F7COC2F5 | 756-13-8 | 2.090 | 125.727 | 0.184 | 2.449 | 1.201 | 2.85 | 2.80 |
Table 1 GIPF parameters and dielectric strengths for a total of 43 insulation gaseous molecules
| Species | CAS registry | As/nm2 | ν | Π/eV | ρ/(g·cm-3) | Er,cal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | 1333-74-0 | 0.336 | 6.635 | 0.131 | 0.180 | 0.208 | 0.16 | 0.22 |
| O2 | 7782-44-7 | 0.506 | 1.400 | 0.091 | 1.624 | 0.296 | 0.34 | 0.33 |
| N2 | 7727-37-9 | 0.542 | 44.973 | 0.173 | 1.265 | 0.350 | 0.35 | 0.38 |
| N2O | 10024-97-2 | 0.666 | 182.831 | 0.430 | 1.541 | 0.342 | 0.40 | 0.46 |
| CO | 630-08-0 | 0.545 | 94.462 | 0.261 | 1.254 | 0.317 | 0.34 | 0.40 |
| CO2 | 124-38-9 | 0.647 | 207.724 | 0.532 | 1.591 | 0.301 | 0.27 | 0.35 |
| OCS | 463-58-1 | 0.819 | 215.830 | 0.277 | 1.546 | 0.518 | 0.93 | 0.90 |
| SF6 | 2551-62-4 | 1.034 | 0.140 | 0.087 | 2.777 | 0.733 | 0.99 | 1.00 |
| CH4 | 74-82-8 | 0.602 | 9.208 | 0.126 | 0.624 | 0.346 | 0.37 | 0.43 |
| CH3Cl | 74-87-3 | 0.816 | 192.564 | 0.558 | 1.299 | 0.410 | 0.33 | 0.32 |
| CH3Br | 74-83-9 | 0.882 | 196.293 | 0.525 | 2.181 | 0.429 | 0.49 | 0.45 |
| CH2F2 | 75-10-5 | 0.712 | 313.110 | 0.701 | 1.676 | 0.320 | 0.33 | 0.27 |
| CH2Cl2 | 75-09-2 | 1.014 | 194.823 | 0.481 | 1.634 | 0.402 | 0.69 | 0.68 |
| CHF2Cl | 75-45-6 | 0.914 | 152.353 | 0.450 | 1.945 | 0.345 | 0.51 | 0.42 |
| CHFCl2 | 75-43-4 | 1.057 | 146.752 | 0.382 | 1.881 | 0.424 | 0.78 | 0.92 |
| CF4 | 75-73-0 | 0.811 | 4.219 | 0.175 | 2.388 | 0.382 | 0.49 | 0.42 |
| CF3Cl | 75-72-9 | 0.957 | 10.906 | 0.172 | 2.208 | 0.550 | 0.68 | 0.58 |
| CF2Cl2 | 75-71-8 | 1.095 | 38.548 | 0.176 | 2.108 | 0.576 | 0.91 | 0.99 |
| CF3Br | 75-63-8 | 1.023 | 20.324 | 0.187 | 2.864 | 0.517 | 0.78 | 0.75 |
| CH3CF3 | 420-46-2 | 0.977 | 170.332 | 0.564 | 1.745 | 0.425 | 0.43 | 0.41 |
| CH3CHCl2 | 75-34-3 | 1.204 | 214.009 | 0.461 | 1.497 | 0.544 | 1.01 | 1.01 |
| C2F6 | 76-16-4 | 1.118 | 3.519 | 0.144 | 2.427 | 0.638 | 0.92 | 0.80 |
| CF3CF2Cl | 76-15-3 | 1.241 | 9.646 | 0.158 | 2.314 | 0.633 | 1.05 | 1.04 |
| F2C=CFCl | 79-38-9 | 1.103 | 76.028 | 0.251 | 2.089 | 0.557 | 0.89 | 0.72 |
| CF3CH=CH2 | 677-21-4 | 1.114 | 223.217 | 0.494 | 1.674 | 0.501 | 0.87 | 0.80 |
| CF3CF=CF2 | 116-15-4 | 1.261 | 55.424 | 0.296 | 2.291 | 0.609 | 0.95 | 0.94 |
| CF2=CF—CF=CF2 | 685-63-2 | 1.401 | 89.157 | 0.315 | 2.184 | 0.586 | 1.18 | 1.20 |
| c-C6F10 | 355-75-9 | 1.786 | 14.075 | 0.220 | 2.428 | 0.892 | 1.80 | 1.90 |
| c-C4F8 | 115-25-3 | 1.472 | 5.602 | 0.241 | 2.437 | 0.605 | 1.18 | 1.25 |
| c-C6F12 | 355-68-0 | 1.856 | 0.910 | 0.107 | 2.553 | 1.304 | 2.33 | 2.35 |
| c-CF3(C4F6)CF3 | 1583-97-7 | 1.935 | 7.545 | 0.176 | 2.512 | 1.063 | 2.19 | 2.30 |
| CF3OCF3 | 1479-49-8 | 1.214 | 8.963 | 0.163 | 2.442 | 0.601 | 1.01 | 1.00 |
| c-CF3(C2F2O)CF3 | 117642-58-7 | 1.590 | 33.769 | 0.221 | 2.406 | 0.793 | 1.53 | 1.60 |
| HC≡CH | 74-86-2 | 0.672 | 304.742 | 0.534 | 0.858 | 0.306 | 0.57 | 0.60 |
| SO2F2 | 2699-79-8 | 0.922 | 186.140 | 0.383 | 2.303 | 0.543 | 0.79 | 0.73 |
| CF3SO2F | 335-05-7 | 1.230 | 216.863 | 0.346 | 2.349 | 0.782 | 1.36 | 1.45 |
| CH3CN | 75-05-8 | 0.851 | 532.756 | 0.892 | 1.021 | 0.470 | 0.77 | 0.80 |
| CF3CN | 353-85-5 | 1.013 | 366.065 | 0.334 | 1.931 | 0.706 | 1.53 | 1.50 |
| C2F5CN | 422-04-8 | 1.304 | 297.109 | 0.257 | 2.110 | 0.940 | 1.88 | 2.00 |
| C3F7CN | 375-00-8 | 1.565 | 280.934 | 0.230 | 2.219 | 1.142 | 2.32 | 2.40 |
| i-C3F7CN | 42532-60-5 | 1.548 | 245.345 | 0.218 | 2.227 | 1.138 | 2.22 | 2.20 |
| i-C3F7COCF3 | 756-12-7 | 1.812 | 165.640 | 0.210 | 2.428 | 1.045 | 2.38 | 2.10 |
| i-C3F7COC2F5 | 756-13-8 | 2.090 | 125.727 | 0.184 | 2.449 | 1.201 | 2.85 | 2.80 |
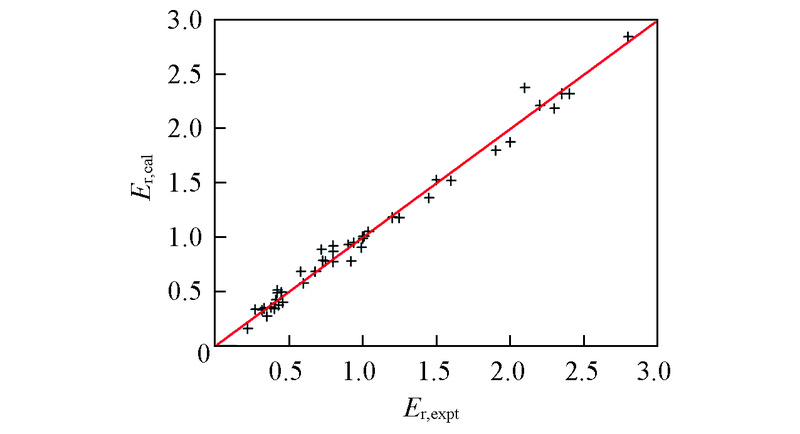
Fig.4 Theoretical dielectric strength predicted by the structure-activity relationship model S4 versus the experimental dataLine: diagonal line with y=x.
| Species | As/nm2 | ν | Π/eV | ρ/(g·cm-3) | Er,cal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF5CF3 | 1.308 | 17.628 | 0.167 | 2.716 | 0.746 | 1.19 | 1.2—1.6 |
| NSF3 | 0.942 | 350.030 | 0.378 | 2.252 | 0.704 | 1.34 | 1.4 |
| SO2 | 0.754 | 462.050 | 0.762 | 1.849 | 0.361 | 0.71 | 0.52—1.0 |
| SeF6 | 1.101 | 0.858 | 0.131 | 3.413 | 0.687 | 1.00 | 1.03—1.14 |
| C6F6 | 1.551 | 35.222 | 0.380 | 2.150 | 0.738 | 1.11 | 1.05—1.15 |
| C4F10 | 1.639 | 2.661 | 0.129 | 2.502 | 1.125 | 1.76 | 1.0—1.58 |
Table 2 M06-2X/6-31++G(d,p) calculated GIPF parameters and dielectric strengths for the prototypical insulation gaseous molecules
| Species | As/nm2 | ν | Π/eV | ρ/(g·cm-3) | Er,cal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SF5CF3 | 1.308 | 17.628 | 0.167 | 2.716 | 0.746 | 1.19 | 1.2—1.6 |
| NSF3 | 0.942 | 350.030 | 0.378 | 2.252 | 0.704 | 1.34 | 1.4 |
| SO2 | 0.754 | 462.050 | 0.762 | 1.849 | 0.361 | 0.71 | 0.52—1.0 |
| SeF6 | 1.101 | 0.858 | 0.131 | 3.413 | 0.687 | 1.00 | 1.03—1.14 |
| C6F6 | 1.551 | 35.222 | 0.380 | 2.150 | 0.738 | 1.11 | 1.05—1.15 |
| C4F10 | 1.639 | 2.661 | 0.129 | 2.502 | 1.125 | 1.76 | 1.0—1.58 |
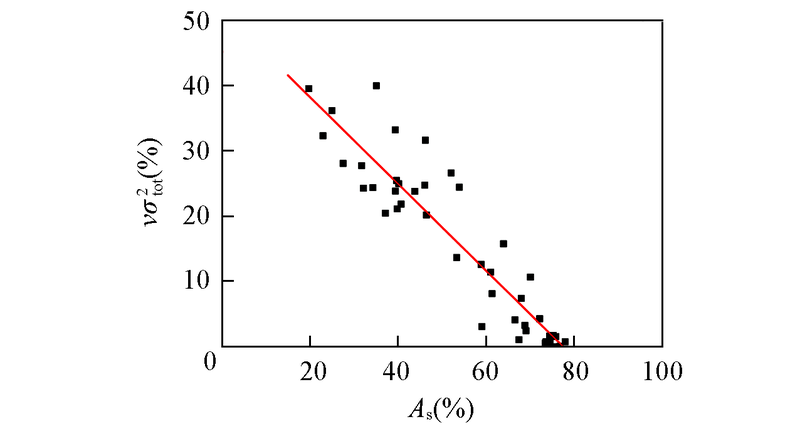
Fig.5 Dependence of the contribution percentages of νσtot2 to the dielectric strength on those of As predicted by the structure-activity relationship model S5
| [1] | Okubo H., Beroual A., IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag., 2011, 27(2), 34—42 |
| [2] | Du J. J., Xu H. C., Electr. Power Environ. Protect, 2009, 25(5), 58—60 |
| (杜建军, 徐慧超. 电力环境保护, 2009, 25(5), 58—60) | |
| [3] | Ko M., Sze N., Wang W. C., Shia G., Goldman A., Murcray F., Murcray D., Rinsland C., J. Geophys. Res., 1993, 98(D6), 10499—10507 |
| [4] | Fang X., Hu X., Greet J. M., Wu J., Han J., Su S., Zhang J., Hu J., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47(8), 3848—3855 |
| [5] | Franck C. M., Dahl D. A., Rabie M., Haefliger P., Koch M., Contrib. Plasma Phys., 2014, 54(1), 3—13 |
| [6] | Kieffel Y., Irwin T., Ponchon P., Owens J., IEEE Power Energy Mag., 2016, 14(2), 32—39 |
| [7] | Beroual A., Haddad A., Energies, 2017, 10(8), 1216 |
| [8] | Li Z. Y., Sci. China Ser. A, 1992, 35(4), 442—448 |
| (李正瀛. 中国科学A辑, 1992, 35(4), 442—448) | |
| [9] | Paschen F., Ann. Phys., 1889, 273(5), 69—75 |
| [10] | Boggs S. A., IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag., 1989, 5(6), 16—21 |
| [11] | Rothhardt L., Mastovsky J., Blaha J., J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys., 1985, 18(10), 155—157 |
| [12] | Zhang L. C., Xiao D. M., Zhang D., Wu B. T., Trans. China Electrotech. Soc., 2008, 23(6), 14—18 |
| (张刘春, 肖登明, 张栋, 吴变桃. 电工技术学报, 2008, 23(6), 14—18) | |
| [13] | Xing W. J., Zhang G. Q., Li K., Niu W. H., Wang X., Wang Y. Y., Proc. CSEE, 2011, 31(7), 119—124 |
| (邢卫军, 张国强, 李康, 牛文豪, 王新, 王迎迎. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31(7), 119—124) | |
| [14] | Pinheiro M. J., Loureiro J., J. Phys. D, Appl. Phys., 2002, 35(23), 3077—3084 |
| [15] | Wu B. T., Xiao D. M., Liu Z. S., Liu X. L., J. Phys. D., Appl. Phys., 2006, 39(19), 4204—4207 |
| [16] | Zhao H., Li X. W., Jia S. L., J. Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2013, 47(2), 109—115 |
| (赵虎, 李兴文, 贾申利. 西安交通大学学报, 2013, 47(2), 109—115) | |
| [17] | Hamilton J. R., Tennyson J., Huang S., Kushner M. J., Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 2017, 26(6), 065010 |
| [18] | Vijh A. K., IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 1982, 17(4), 84—87 |
| [19] | Brand K. P., IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 1982, 17(5), 451—456 |
| [20] | Meurice N., Sandre E., Aslanides A., Vercauteren D. P., IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2004, 11(6), 946—948 |
| [21] | Rabie M., Dahl D. A., Donald S. M. A., Reiher M., Franck C. M., IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2013, 20(3), 856—863 |
| [22] | Jiao J., Xiao D., Zhao X., Deng Y., Plasma Sci. Technol., 2016, 18(5), 554—559 |
| [23] | Zhang C., Shi H., Cheng L., Zhao K., Xie X., Ma H., IEEE Trans. Dielect. Electr. Insul., 2016, 23(5), 2572—2578 |
| [24] | Yu X., Hou H., Wang B., J. Comput. Chem., 2017, 38(10), 721—729 |
| [25] | Murray J. S., Brinck T., Politzer P., Chem. Phys., 1996, 204(2/3), 289—299 |
| [26] | Murray J. S., Brinck T., Lane P., Paulsen K., Politzer P., J. Mol. Struct.(Theochem.), 1994, 307(1), 55—64 |
| [27] | Politzer P., Murray J. S., Theor. Chem. Acc., 2002, 108(3), 134—142 |
| [28] | Pearson R. G., Inorg. Chem., 1988, 27(4), 734—740 |
| [29] | Nie X. Q., Xu W. G., Lu S. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2008, 29(8), 1629—1634 |
| (聂小琴, 徐文国, 卢士香. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(8), 1629—1634) | |
| [30] | Yu X., Hou H., Wang B., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2018, 122(13), 3462—3469 |
| [31] | Jonathan C. R., Gregory S. T., Henry F. S., Sreela N., Ellison G. B., Chem. Rev., 2002, 102(1), 231—282 |
| [32] | Anderson L. N., Oviedo M. B., Wong B. M., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2017, 13(4), 1656—1666 |
| [33] | Bozkaya U., Ünal A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2018, 122(17), 4375—4380 |
| [34] | Bozkaya U., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2014, 10(5), 2041—2048 |
| [35] | Soydas E., Bozkaya U., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2015, 11(4), 1564—1573 |
| [36] | Curtiss L. A., Redfern P. C., J. Chem. Phys., 1998, 109(1), 42—55 |
| [37] | Eisfeld W., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 134(5), 054303 |
| [38] | Troe J., Miller T. M., Viggiano A. A., J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 136(12), 121102 |
| [39] | Menk S., Das S., Blaum K., Froese M. W., Lange M., Mukherjee M., Repnow R., Schwalm D., Hahn R., Wolf A., Phys. Rev. A, 2014, 89(2), 022502 |
| [40] | Olivet A., Duque D., Vega L. F., J. Appl. Phys., 2007, 101(2), 023308 |
| [41] | Christophorou L. G., Olthoff J. K., Green D. S., NIST Technical Note 1425, US Government Printing Office, Washington, 1997, 1—35 |
| [42] | Devins J. C., IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 1980, 15(2), 81—86 |
| [43] | Christophorou L. G., Sauers I., James D. R., Rodrigo H., Pace M. O., Carter J. G., Hunter S. R., IEEE Trans. Electr. Insul., 1984, 19(6), 550—566 |
| [44] | Wooton R. E., Kegelman M. R., Electric Power Research Institute EL-2620, Westinghouse Research and Development Center, Pennsylvania, 1982, 1—85 |
| [45] | Zhao Y., Truhlar D. G., Theor. Chem. Acc., 2008, 120(1—3), 215—241 |
| [46] | Frisch M. J., Pople J. A., Binkley J. S., J. Chem. Phys., 1984, 80(7), 3265—3269 |
| [47] | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S., Tomasi S. J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., et al., Gaussian 09, Revision E.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [48] | Geballe R., Linn F. S., J. Appl. Phys., 1950, 21(6), 592—594 |
| [49] | Eibeck R. E., Dielectric Gaseous Mixture of Thiazyltrifluoride and SF6, US3390091, 1968-06-25 |
| [50] | Vijh A. K., IEEE. Trans. Electr. Insul., 1977, 12(4), 313—315 |
| [51] | Banks A. A., Rudge A. J., Nature, 1953, 171(4348), 390—391 |
| [1] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yingzhe, ZHANG Jianling. Applications of Metal-organic Framework-based Material in Carbon Dioxide Photocatalytic Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [3] | HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Group Additivity Theoretical Model for the Prediction of Dielectric Strengths of the Alternative Gases to SF6 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3709. |
| [4] | YE Xiaodong, QI Guodong, XU Jun, DENG Feng. Glucose Oxidation on Au-supported SBA-15 Molecular Sieve † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 960. |
| [5] | CHANG Junpeng,ZHAO Jiarui,CHEN Sijia,MENG Kai,SHI Weini,LI Ruifang. Structure-activity Relationship of Antimicrobial Peptide SAMP1 and Its Analog Peptides† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 705. |
| [6] | YU Min, HUANG Jingjing, MA Min, FU Ruiyan, YAN Yan, ZHANG Fusheng, YIN Junfeng, XIE Ningning. Zinc Chelating Activity and Quantitative Structure-activity Relationship of Tripeptides† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 234. |
| [7] | WANG Lei, ZHENG Guojun, JI Qi, CHEN Bo, GONG Longlong, GAO Congmin, DU Zhenjian, ZHANG Xingmin. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel PI3K/mTOR Inhibitors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1590. |
| [8] | LIU Yuming, TIAN Lijun, HU Dong, NIE Jianbing. yntheses and Anti-cholinesterase Activity of 4-N-Phenylaminoquinoline Derivatives † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 392. |
| [9] | LIU Benguo, LIU Jiangwei, LI Jiaqi, GENG Sheng, MO Haizhen, LIANG Guizhao. 3D-QSAR and Interaction Mechanism of Flavonoids s P-glycoprotein Inhibitors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 41. |
| [10] | GUO Liang, CAO Rihui, FAN Wenxi, GAN Ziyun, MA Qin. Design, Synthesis and in vitro Antitumor Activities of Novel Bivalent β-Carbolines† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1093. |
| [11] | ZHANG Jie, ZHOU Changjian, XIE Jianwei, DAI Bin. Synthesis and Antitumor Activities of Rhein-Valine Adducts† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12): 2159. |
| [12] | ZHANG Jing, MU Boshuai, WU Meng, BIAN Yanqing, LI Yuan. Synthesis, Antifungal Activity and Structure-activity Relationship of -Fluorophenyl-2,3-dihydro-1,5-benzothiazepines Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 687. |
| [13] | WANG Gang, HAN Leiqiang, FANG Hao. Syntheses and Antitumor Activities of Phenylpiperazine Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(12): 2435. |
| [14] | KANG Wang, BU Huijuan, LI Wenhong, LI Yuan. Preliminary Structure-activity Relationship of 2-Ethoxycarbonyl-4-aryl-1,5-benzothiazepines with Antifungal Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 766. |
| [15] | GUO Liang, CAO Rihui, FAN Wenxi, MA Qin. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of 1,2,7,9-Tetrasubstituted Harmine Derivatives as Potential Antitumor Agents† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 518. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||