

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 2062.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180042
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Qi1, GUO Guibao1,*( ), AN Shengli2, LIU Jinyan1
), AN Shengli2, LIU Jinyan1
Received:2018-01-12
Online:2018-09-07
Published:2018-08-03
Contact:
GUO Guibao
E-mail:guogb@imust.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Qi,GUO Guibao,AN Shengli,LIU Jinyan. Preparation and Properties of Tetramethyl Ammonium Hydroxide Modified Polyvinylidene Fluoride with Styrene Sulfonated Membranes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2062.
| Sample | δ/MPa | ε(%) | SD(%) | WU(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion117 | 10.40 | 38.8 | 19.2 | 24.3 |
| TMAH-10 | 13.42 | 43.8 | 6.4 | 9.3 |
| TMAH-15 | 16.85 | 40.4 | 13.2 | 16.2 |
| TMAH-20 | 18.67 | 37.4 | 15.3 | 25.4 |
| TMAH-25 | 21.29 | 34.6 | 18.3 | 32.1 |
| TMAH-30 | 14.12 | 36.4 | 21.2 | 37.8 |
Table 1 Measurent results of the yield strength(δ), elongation at break(ε), swelling degree and water uptake of samples
| Sample | δ/MPa | ε(%) | SD(%) | WU(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nafion117 | 10.40 | 38.8 | 19.2 | 24.3 |
| TMAH-10 | 13.42 | 43.8 | 6.4 | 9.3 |
| TMAH-15 | 16.85 | 40.4 | 13.2 | 16.2 |
| TMAH-20 | 18.67 | 37.4 | 15.3 | 25.4 |
| TMAH-25 | 21.29 | 34.6 | 18.3 | 32.1 |
| TMAH-30 | 14.12 | 36.4 | 21.2 | 37.8 |
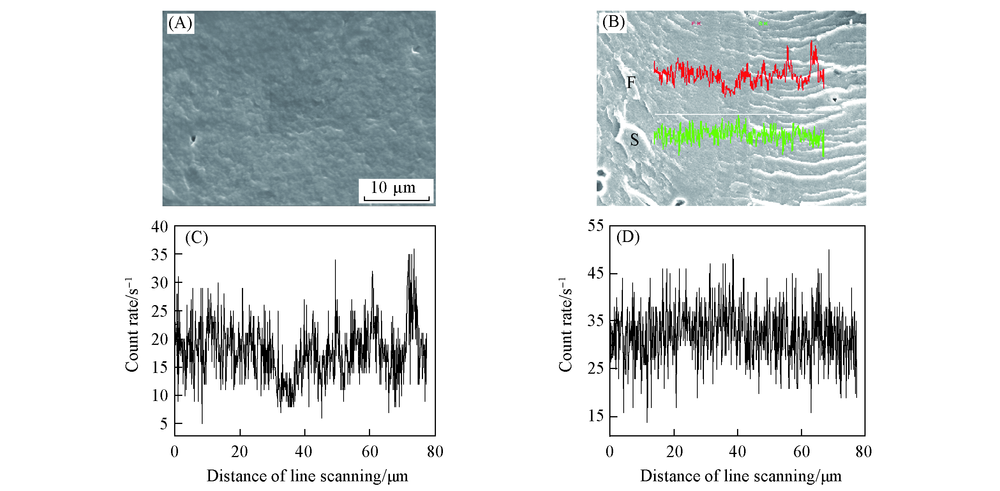
Fig.10 SEM images of PVDF-g-PSSA membrane(A, B)and distribution of fluorine(C) and sulfur(D) on the surface of the cross-section of the membrane measured by EDX (A) Surface of PVDF-g-PSSA membrane; (B) cross-section of PVDF-g-PSSA membrane.
| [1] | Kumar P., Dutta K., Kundu P.P., International Journal of Energy Research, 2014, 38, 41—50 |
| [2] | Zhang H. W., Shen P. K., Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(5), 2780—2832 |
| [3] | Peighambardoust S. J., Rowshanzamir S., Amjadi M., International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010, 35, 9349—9384 |
| [4] | Casciola M., Alberti G., Sganappa M., Narducci R., Journal of Power Sources, 2006, 162, 141—145 |
| [5] | Mauritz K. A., Moore R. B., Chemical Reviews, 2004, 104, 4535—4585 |
| [6] | Sun P., Li Z., Wang S., Yin X., Journal of Membrane Science, 2017, 549, 660—669 |
| [7] | Ran J., Ding L., Yu D., Zhang X., Hu M., Wu L., Xu T., Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 549, 631—637 |
| [8] | Song M., Lu W., Li Z., Liu G., Yin X., Wang Y., International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(28), 12069—12081 |
| [9] | Nasef M. M., Saidi H., Dahlan K. Z. M., Journal of Membrane Science, 2009, 339, 115—119 |
| [10] | Sinirlioglu D., Muftuoglu A. E., Golcuk K., Bozkurt A., Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemisity, 2014, 52(13), 1885—1897 |
| [11] | Sezgin S., Sinilioglu D., Muftuoglu A. E., Bozkurt A., Journal of Chemistry, 2014, 2014(7), 1—11 |
| [12] | Hong J., Yang S. Y., Zhang X. Q., Lu W., Zhang J. Y., Acta Chimica Sinica, 1997, (8), 817—823 |
| (洪洁, 杨士勇, 张旭庆, 陆伟, 张景云. 化学学报, 1997, (8), 817—823) | |
| [13] | Sermili S., Eisen M.S., Israel Journal of Chemistry, 2012, 52(3/4), 347—358 |
| [14] | Wang G. H., Zhang X. S., Chemical Production and Technology, 2006, 13(5), 37—39 |
| (王宏葛, 张新胜. 化工生产与技术, 2006, 13(5), 37—39) | |
| [15] | Xing Q.Y., Pei W. W., Xu R. Q., Pei J., Basic Organic Chemistry, Higher Education Press, Beijing, 2005, 290—291 |
| (刑其毅, 裴伟伟, 徐瑞秋, 裴坚. 基础有机化学(上册), 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005, 290—291) | |
| [16] | Ross G. J., Watts J. F., Hill M. P., Morrissey P., Polymer, 2000, 41(5), 1685—1696 |
| [17] | Brewis D. M., Mathieson I., Sutherland I., Cayless R. A., Dahm R. H., International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives, 1996, 16(2), 87—95 |
| [18] | Tricoli V., Carretta N., Bartolozzi M., Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2000, 147(4), 1286—1290 |
| [1] | LI Wei, LUO Piao, HUANG Lianzhan, CUI Zhiming. Lithium Polystyrene Sulfonate Based Interfacial Protective Layer for Lithium Metal Anodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220166. |
| [2] | LI Weihui, LI Haobo, ZENG Cheng, LIANG Haoyue, CHEN Jiajun, LI Junyong, LI Huiqiao. Hot-pressed PVDF-based Difunctional Protective Layer for Lithium Metal Anodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210629. |
| [3] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [4] | GAO Yifei, XIAO Changfa, JI Dawei, HUANG Yangzheng. Preparation of PVDF Hollow Fiber Membranes via Melt Spinning-stretching Method and Its Oil-water Separation Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2065. |
| [5] | CHENG Jifeng,JIANG Tuanhui,ZHAN Xiaomei,QI Yating,YANG Yuanyuan,KANG Xun,QIN Shuhao. Preparation and Properties of Superhydrophilic Polyvinylidene Fluoride Hollow Fiber Membrane † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 358. |
| [6] | WANG Lin, ZHANG Yanhui, Arzugul Muslim, LAN Haidie. Morphology and Size Regulation of Polyaniline Induced by PS-b-P2VP as Template and Its Electrochemical Characters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1748. |
| [7] | FENG Wei,WANG Bowei,JIANG Yang,LI Longyun. Design, Preparation and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering(SERS) Spectrum of Single Ag Nanodot† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1345. |
| [8] | ZOU Xiaochuan,WANG Yue,WANG Cun,HU Shiwen,SHI Kaiyun. Synthesis of Amine Functionalized ZPS-PVPA Supported Chiral MnⅢ(salen) and Asymmetric Catalytic Olefin Epoxidation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1488. |
| [9] | XIONG Zhengrong,DONG Li,LIU Xiangdong,YANG Yuming. Preparation and Properties Characterization of PDA/PVDF UV Shielding Composite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 849. |
| [10] | CAI Lei,ZHAO Yuanjin,ZHANG Xingping,HE Aihua,DING Tao,LI Xiaohong,ZHANG Zhijun. Structure and Properties of SSBR/BR/Surface-modified SiO2 Green Tire Tread Stock † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2388. |
| [11] | LIU Zihao,XIAO Han,YAO Yuan,WANG Ting,WU Liguang,ZHANG Xueyang. Fabrication of PVDF Hybrid Blending Membrane via Microemulsion Polymerization Coupling with Blending Method † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2248. |
| [12] | ZHU Xingye,QIAN Huidong,JIANG Jingjing,YUE Zhouying,XU Jianfeng,ZOU Zhiqing,YANG Hui. Cross-linking of Imidazole-grafted Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone) as Proton Exchange Membranes for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2046. |
| [13] | XU Dan,DING Yadan,WANG Xue,CONG Tie,LIU Junping,HONG Xia,PAN Ying. Microdroplet Detection of Protein Based on Superhydrophobic Polystyrene Film† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1913. |
| [14] | FENG Wei,WANG Bowei,ZHENG Yan,JIANG Yang. Preparation and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering(SERS) of Single Au Nanodot† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1875. |
| [15] | SHI Yue,MAO Qing,XIAO Cheng,JING Weiyun,ZHANG Xueyuan. Nonlinear Spectroscopy Analysis for Electrocatalytic Oxidation of Methanol on PtRu/C Surface† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2017. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||