

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 614.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170634
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HAO Yuanyuan, WU Qi, LI Ji, GE Chao, MA Chaoying, QIAN Yong, SU Zhi*( ), LIU Hongke*(
), LIU Hongke*( )
)
Received:2017-09-21
Online:2018-04-10
Published:2018-03-22
Contact:
SU Zhi,LIU Hongke
E-mail:zhisu@njnu.edu.cn;liuhongke@njnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HAO Yuanyuan, WU Qi, LI Ji, GE Chao, MA Chaoying, QIAN Yong, SU Zhi, LIU Hongke. Novel OsⅡ -arene Complexes Based on Bipyridyl Derivative Ligands: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Anticancer Activity and Interaction with DNA/BSA†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 614.
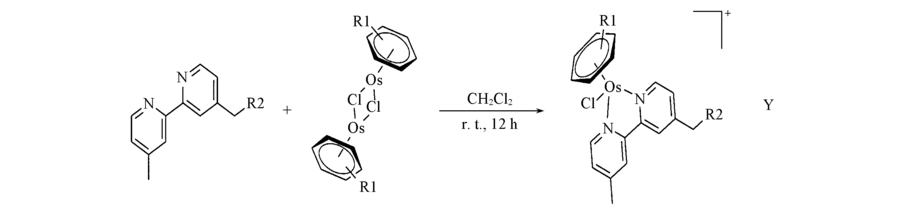
Scheme 1 Synthetic route and general structures of complexes 1-5 Complex 1: R1= p-cymene, R2=H, Y= Cl-; complex 2: R1=p-cymene, R2=NOH, Y=Cl-; complex 3: R1=biphenyl,R2=H, Y=Cl-; complex 4: R1=biphenyl, R2=NOH, Y=Cl-; complex 5: R1=biphenyl, R2=H, Y=PF6-

Fig.1 Molecular structure of complex 1(A), the π-π stacking interactions between two aryl rings of two adjacent units, with a “center-to-center” distance of 0.3584 nm(B), the π-π stacking interactions between two parallel bipyridyl rings of two adjacent units, with a “center-to-center” distance of 0.4003 nm(C) and the two-dimensional packing mode of complex 1(D)Counter anions, solvent molecules and hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity.
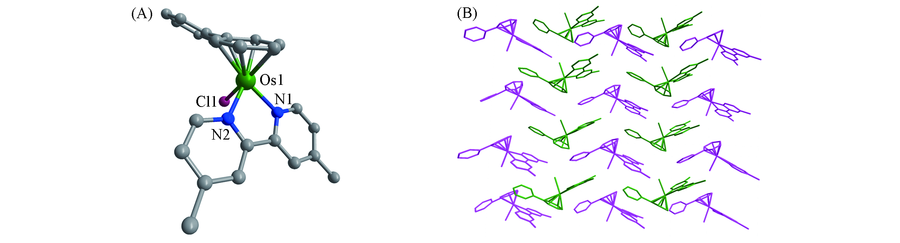
Fig.2 Molecular structure of complex 5(A) and the two-dimensional packing mode of complex 5(B)Counter anions, solvent molecules and hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity.
| Complex | A549 | A2780 | L02 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 110.8±8.0 | >200 | >200 |
| 2 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 3 | 88.0±1.7 | 166.1±0.3 | >200 |
| 4 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| CDDP | 14.1±0.8 | 46.1±4.2 |
Table 1 IC50 values(μmol/L) of complexes 1-4 and CDDP towards different cell lines in vitro
| Complex | A549 | A2780 | L02 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 110.8±8.0 | >200 | >200 |
| 2 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| 3 | 88.0±1.7 | 166.1±0.3 | >200 |
| 4 | >200 | >200 | >200 |
| CDDP | 14.1±0.8 | 46.1±4.2 |
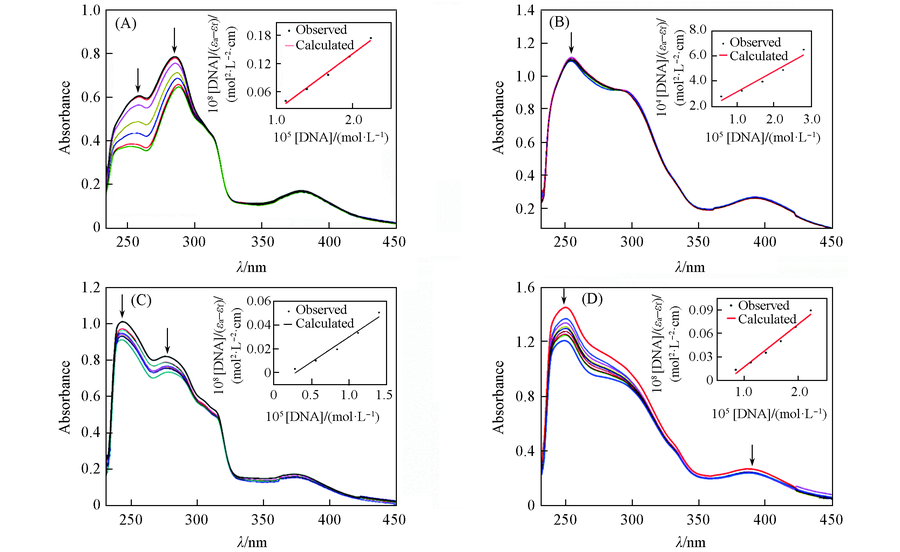
Fig.3 Absorption spectra of complexes 1(A), 2(B), 3(C) and 4(D)(50 μmol/L) in the absence and presence of increasing amount of CT-DNA at 298 K and pH=7.0Inset: plot of [DNA]/(εa-εf) vs. [DNA]. For complex 1, the cDNA was 0-22.38 μmol/L; for complex 2, the cDNA was 0-39.17 μmol/L; for complex 3, the cDNA was 0-16.79 μmol/L; for complex 4, the cDNA was 0-22.38 μmol/L; the arrows show the decrease of the absorbance intensities with the increasing DNA concentration.
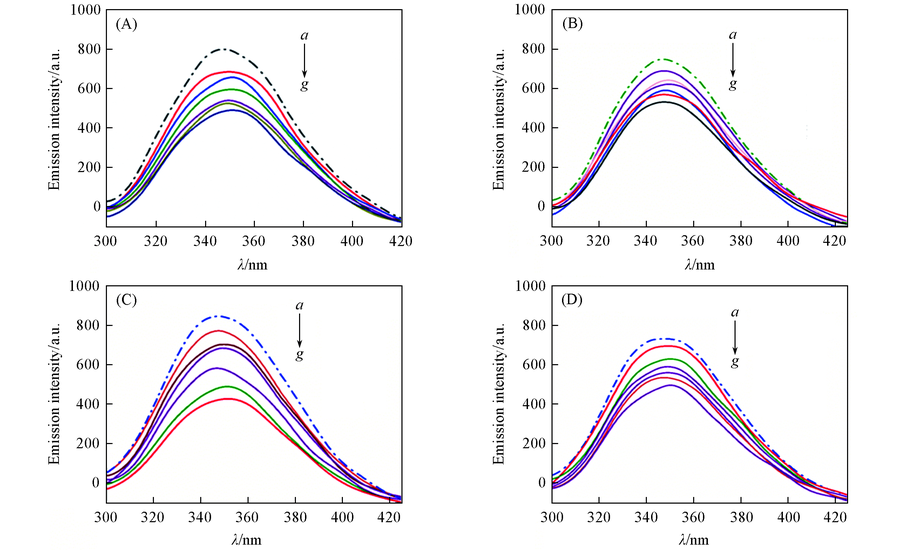
Fig.4 Fluorescence spectra of BSA(3 μmol/L) in the absence(dashed line) and presence(solid line) of increasing amount of complexes 1(A), 2(B), 3(C) and 4(D) at 298 K and pH=7.0From a to g, the ratios of cComplex/cBSA are 0, 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, respectively.
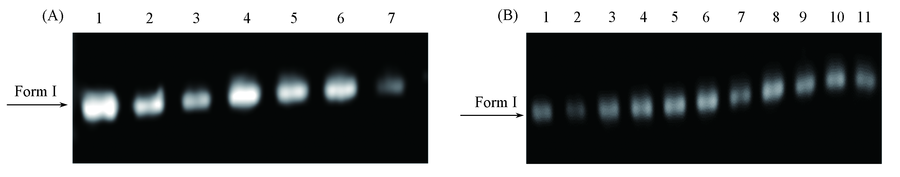
Fig.6 Gel electrophoresis assay of pBR322 DNA treated with complexes 1(A) and 3(B)(A) Lane 1: DNA control(10 μmol/L); lanes 2-7: DNA and 10-60 μmol/L complex 1;(B) lane 1: DNA control(10 μmol/L); lanes 2-11: DNA and 10-100 μmol/L complex 3.
| [1] | Garcia M., Jemal A., Ward E. M., Global Cancer Facts & Figures, American Cancer Society, Atalnta, 2007 |
| [2] | Zhang P. Y., Sadler P. J., J. Organomet. Chem., 2017, 839, 5-14 |
| [3] | Omae I., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2014, 280, 84-95 |
| [4] | Hanif M., Babak M. V., Hartinger C. G., Drug Discovery Today, 2014, 19(10), 1640-1648 |
| [5] | Clavel C. M., Paunescu E., Nowak-Sliwinska P., Griffioen A. W., Scopelliti R., Dyson P. J., J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57(8), 3546-3558 |
| [6] | Wheate N. J., Walker S., Craig G. E., Oun R., Dalton Trans., 2010, 39(35), 8113-8127 |
| [7] | Krishnamoorthy P., Sathyadevi P., Butorac R. R., Cowley A. H., Bhuvanesh N. S., Dharmaraj N., Dalton Trans., 2012, 41(15), 4423-4436 |
| [8] | Cui F. L., Wang J. L., Cui Y. R., Li J. P., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, 571(2), 175-183 |
| [9] | Timerbaev A. R., Hartinger C. G., Aleksenko S. S., Keppler B. K., Chem. Rev., 2006, 106(6), 2224-2248 |
| [10] | Kamal A., Ramu R., Tekumalla V., Khanna G. B., Barkume M. S., Juvekar A. S., Zingde S. M., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2007, 15(22), 6868-6875 |
| [11] | Rauf S., Gooding J. J., Akhtar K., Ghauri M. A., Rahman M., Anwar M. A., Khalid A. M., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2005, 37, 205-217 |
| [12] | Esposito B. P., Najjar R., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2002, 232(1/2), 137-149 |
| [13] | Liu Y. N., Yang F., Mei W. J., Liu J., Zheng W. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(3), 435-441 |
| (刘亚楠, 杨芳, 梅文杰, 刘杰, 郑文杰. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(3), 435-441) | |
| [14] | Weiss A., Berndsen R. H., Dubois M., Müller C., Schibli R., Griffioen A. W., Dyson P. J., Nowak-Sliwinska P., Chem. Sci., 2014, 5(12), 4742-4748 |
| [15] | Kong Y. Q., Li J., Hu X. Y., Wang F. X., Qian Y., Li L., Mao Z. W., Liu H. K., Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2017, 47(2), 277-283 |
| (孔亚琼, 李季, 胡晓莹, 王芳馨, 钱勇, 李利, 毛宗万, 刘红科. 中国科学: 化学, 2017, 47(2), 277-283) | |
| [16] | Gasser G., Ott I., Metzler-Nolte N., J. Med. Chem., 2011, 54(1), 3-25 |
| [17] | Yan Y.K., Melchart M., Habtemariam A., Sadler P. J.,Chem. Commun., 2005, (38), 4764-4776 |
| [18] | Wang H. Y., Qian Y., Wang F. X., Habtemariam A., Mao Z. W., Sadler P. J., Liu H. K., Eur. J. Inorg. Chem., 2017, 12, 1792-1799 |
| [19] | Peacock A. F. A., Sadler P. J., Chem. Asian J., 2008, 3(11), 1890-1899 |
| [20] | Peacock A. F. A., Melchart M., Deeth R. J., Habtemariam A., Parsons S., Sadler P. J., Chem. Eur. J., 2007, 13(9), 2601-2613 |
| [21] | Peacock A. F. A., Parsons S., Sadler P. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 128, 3348-3357 |
| [22] | Peacock A. F. A., Habtemariam A., Moggach S. A., Prescimone A., Parsons S., Sadler P. J., Inorg. Chem., 2007, 46(10), 4049-4059 |
| [23] | Needham R. J., Sanchez-Cano C., Zhang X., Romero-Canelon I., Habtemariam A., Cooper M. S., Meszaros L., Clarkson G. J., Blower P. J., Sadler P. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(4), 1017-1020 |
| [24] | Wang F., Chen H., Parsons S., Oswald I. D., Davidson J. E., Sadler P. J., Chem. Eur. J., 2003, 9(23), 5810-5820 |
| [25] | Liu H. K., Berners-Price S. J., Wang F., Parkinson J. A., Xu J., Bella J., Sadler P. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2006, 45(48), 8153-8156 |
| [26] | Kostrhunova H., Florian J., Novakova O., Peacock A. F. A., Sadler P. J., Brabec V., J. Med. Chem., 2008, 51, 3635-3643 |
| [27] | Liu H. K., Sadler P. J., Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44(5), 349-359 |
| [28] | Liu H. K., Parkinson J. A., Bella J., Wang F., Sadler P. J., Chem. Sci., 2010, 1(2), 258-270 |
| [29] | Liu H. K., Wang F., Parkinson J. A., Bella J., Sadler P. J., Chem. Eur. J., 2006, 12(23), 6151-6165 |
| [30] | Xun Z., Yu T., Zeng Y., Chen J., Zhang X., Yang G., Li Y., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(24), 12965-12971 |
| [31] | Xi P. X., Xu Z. H., Chen F. J., Zeng Z. Z., Zhang X. W., J. Inorg. Biochem., 2009, 103(2), 210-218 |
| [32] | Barton J. K., Danishefsky A. T., Goldberg J. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1984, 106, 2172-2176 |
| [33] | Bischof C., Joshi T., Dimri A., Spiccia L., Schatzschneider U., Inorg. Chem., 2013, 52(16), 9297-9308 |
| [34] | Wang T., Wang A., Zhou L., Lu S., Jiang W., Lin Y., Zhou J., Wei S., Spectrochim. Acta A, 2013, 115, 445-451 |
| [35] | Guo Q., Li L. Z., Dong J. F., Liu H. Y., Xue Z. C., Xu T., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2012, 70(15), 1617-1624 |
| (郭琼, 李连之, 董建芳, 刘鸿雁, 薛泽春, 许涛. 化学学报, 2012, 70(15), 1617-1624) | |
| [36] | Liu P., Wu B. Y., Liu J., Dai Y. C., Wang Y. J., Wang K. Z., Inorg. Chem., 2016, 55(4), 1412-1422 |
| [37] | Su W., Tang Z., Xiao Q., Li P., Qian Q., Lei X., Huang S., Peng B., Cui J., Huang C., J. Organomet. Chem., 2015, 783, 10-16 |
| [38] | An P. J., Yu N. N., Sun R. S., Sui X. F., Song Y. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8), 1354-1361 |
| (安鹏姣, 于楠楠, 孙睿声, 隋小芳, 宋玉光. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(8), 1354-1361) | |
| [39] | Mohanraj M., Ayyannan G., Raja G., Jayabalakrishnan C., Mat. Sci. Eng. C, 2016, 69, 1297-1306 |
| [40] | Kypr J., Kejnovska I., Renciuk D., Vorlickova M., Nucleic Acids Res., 2009, 37(6), 1713-1725 |
| [41] | Wu S. D., Wang X. Y., Zhu C. C., Song Y. J., Wang J., Li Y. Z., Guo Z. J., Dalton Trans., 2011, 40, 10376-10382 |
| [42] | Betanzos-Lara S., Salassa L., Habtemariam A., Novakova O., Pizarro A. M., Clarkson G. J., Liskova B., Brabec V., Sadler P. J., Organometallics,2012, 31(9), 3466-3479 |
| [43] | Michael Ushay H., source T. D., Lippard S. J., Biochemistry,1981, 20, 3744-3748 |
| [1] | LIU Suyu, DING Fei, LI Qian, FAN Chunhai, FENG Jing. Azobenzene-integrated DNA Nanomachine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220122. |
| [2] | WU Yushuai, SHANG Yingxu, JIANG Qiao, DING Baoquan. Research Progress of Controllable Self-assembled DNA Origami Structure as Drug Carrier [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220179. |
| [3] | WANG Junyang, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Qian, SUN Chunyan, LI Hongxia. Application of DNA Silver Nanoclusters in the Fluorescence Biosensors based on Functional Nucleic Acids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [4] | WU Yangyi, CHEN Jianping, Ai Yijing, WANG Qingxiang, GAO Fei, GAO Feng. Synthesis of 2-(2-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-C60 and Its Application for Sensing of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S Promotor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1754. |
| [5] | YANG Xinjie, LAI Yanqiong, LI Qiuyang, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, PANG Pengfei, YANG Wenrong. An Enzyme-free and Label-free Fluorescent Probe for Detection of Microcystin-LR Based on Circular DNA-Silver Nanoclusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3600. |
| [6] | LIU Xuejiao, YANG Fan, LIU Shuang, ZHANG Chunjuan, LIU Qiaoling. Progress in Aptamer-targeted Membrane Protein Recognition and Functional Regulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3277. |
| [7] | HU Ling, YIN Yao, KE Guoliang, ZHANG Xiaobing. Regulation of Cell-cell Interactions Based on DNA Nanostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3284. |
| [8] | MAO Yu, QU Hao, ZHENG Lei. Research Progress on RNA⁃cleaving DNAzyme for the Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3445. |
| [9] | PENG Huo, GAO Zehang, LIAO Chengyue, WANG Xiaodong, ZHOU Hongbo, ZHAO Jianlong. Robust Droplet Digital PCR Chip for Absolute Quantitative Detection of Nucleic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1760. |
| [10] | REN Yushuang, GUO Yuanyuan, LIU Xueyi, SONG Jie, ZHANG Chuan. Platinum(Ⅳ) Prodrug-grafted Phosphorothioate DNA and Its Self-assembled Nanostructure for Targeted Drug Delivery [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1721. |
| [11] | YAN Lei, MAO Xiuhai, ZUO Xiaolei. Biomimicry of Cellular Membrane with Framework Nucleic Acids† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1415. |
| [12] | ZHANG Kaixiang, LIU Junjie, SONG Qiaoli, WANG Danyu, SHI Jinjin, ZHANG Haiyue, LI Jinghong. Multifunctional DNA Nanoflowers for Autophagy Inhibition and Enhanced Antitumor Chemotherapy† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1461. |
| [13] | ZHANG Luhao, CAO Shuting, LIU Jiangbo, ZUO Xiaolei, WANG Lihua, FAN Chunhai, LI Jiang. Construction of Controllable Lipid-DNA Complex for Study in Membrane Biology † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1151. |
| [14] | LI Xianming, ZHENG Ting, GAO Lu, LI Feng, HOU Xiandeng, WU Peng. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification: from Principle to Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2587. |
| [15] | TONG Zongxuan, HU Qinqin, GU Hongzhou. Deoxyribozymes: Selection, Biosensing and Outlook [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2345. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||