

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 764.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170413
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yehua, JIANG Tao, LIU Shufeng, YU Yaqian, CHEN Yong*( )
)
Received:2017-06-28
Online:2018-04-10
Published:2018-02-12
Contact:
CHEN Yong
E-mail:yongchen@sit.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Yehua, JIANG Tao, LIU Shufeng, YU Yaqian, CHEN Yong. Ion Transfer of Leucovorin Ion Across the Membrane-modified Liquid/Liquid Interface†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 764.
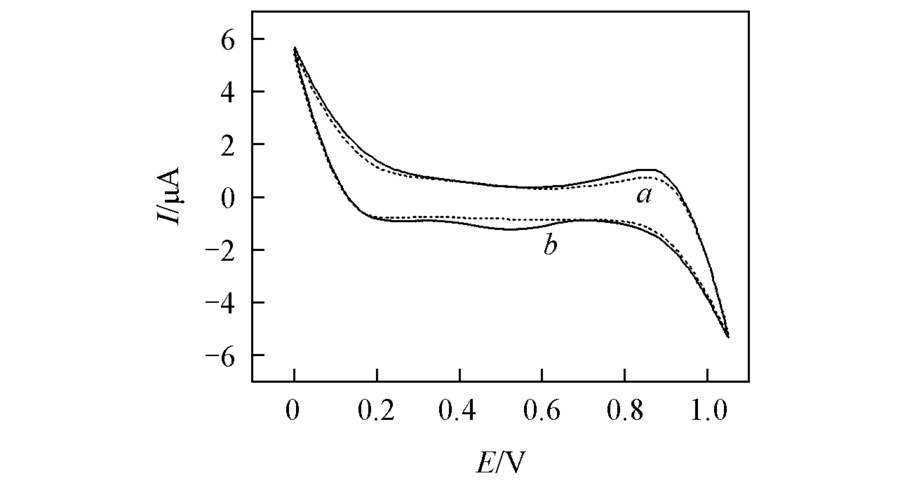
Fig.1 CVs obtained at the W/DCH interface modified by HMSM-CTAB in the absence of calcium leucovorin(a) and in the presence of 0.8 mmol/L calcium leucovorin(b) at a scan rate of 20 mV/s
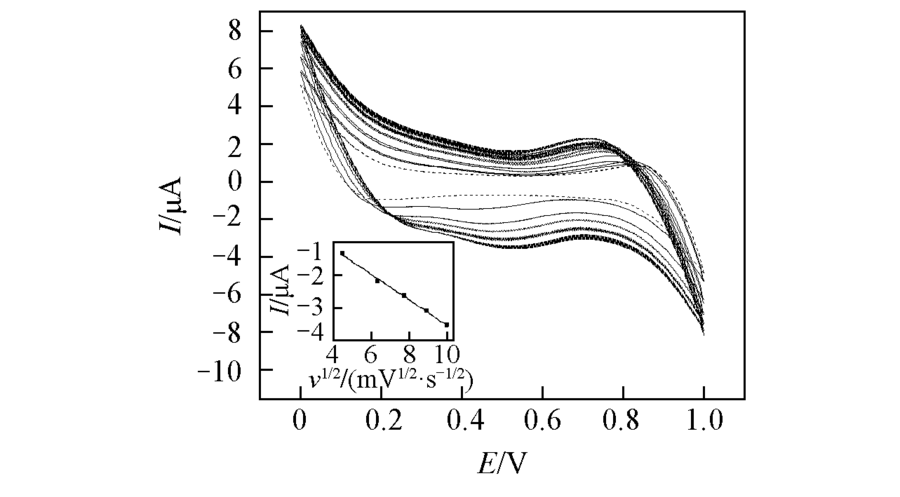
Fig.2 CVs obtained at the W/DCH interface modified by HMSM-CTAB in the absence of calcium leucovorin(dash line) and in the presence of 2 mmol/L calcium leucovorin(solid line) at different scan ratesFrom inner CVs to outer CVs, the scan rates are 20, 40, 60, 80 and 100 mV/s, respectively. Inset: the corresponding plot of peak current for calcium leucovorin from W to DCH against the square root of scan rate.
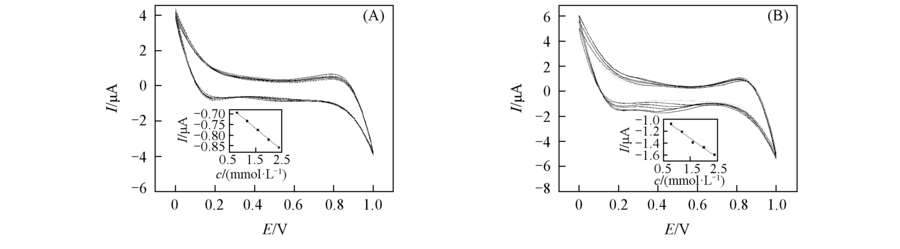
Fig.3 CVs obtained at the W/DCH interface modified by HMSM(A) and HMSM-CTAB(B) at a scan rate of 20 mV/sFrom inner CVs to outer CVs, the concentrations of calcium leucovorin are 0, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0 and 2.4 mmol/L, respectively. Insets: the corresponding plots of peak current for the transfer of leucovorin ion from W to DCH vs. the concentration of calcium leucovorin in aqueous solution.
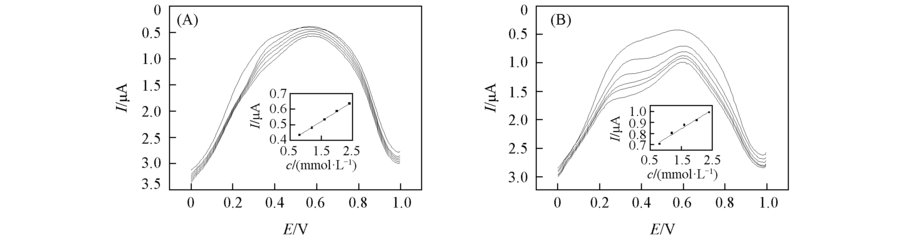
Fig.4 DPVs collected at the W/DCH interface modified by HMSM(A) and HMSM-CTAB(B) for different concentrations of calcium leucovorinFrom top to bottom, the concentrations of calcium leucovorin are 0, 0.8, 1.2, 1.6, 2.0, and 2.4 mmol/L, respectively.Insets: the corresponding plots of peak current for calcium leucovorin from W to DCH vs. the concentration of calcium leucovorin in aqueous solution.
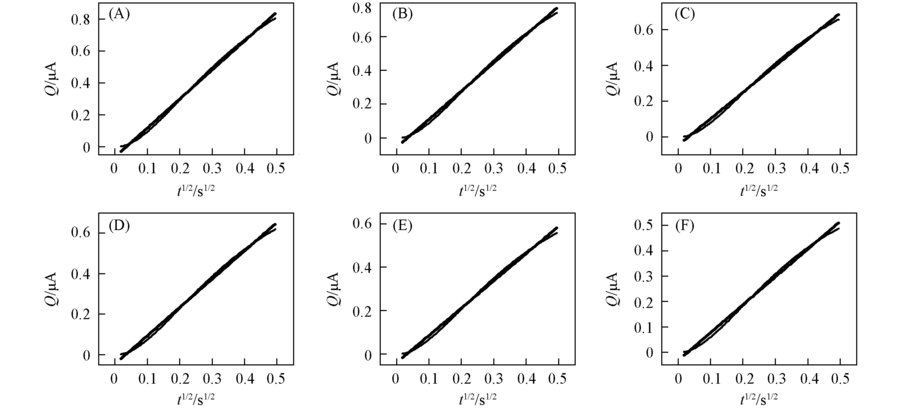
Fig.5 Plots of Q vs. t1/2 and their asymptotesStep potential: (A) 0.70-0.46 V; (B) 0.70-0.47 V; (C) 0.70-0.48 V; (D) 0.70-0.49 V;(E) 0.70-0.50 V; (F) 0.70-0.51 V.
| [1] | Cercos F. T., Casabo V. G., Nacher A., Cejudo F. E., Polache A., Merino M., Int. J. Pharm., 1997, 155(1), 109-119 |
| [2] | Klaassen U., Borquez D., Lang S., Oberhoff C., Harstrick A., Seeber S., Benner S., Oncology(Williston Park, N.Y.), 1999, 13(7 Suppl. 3), 71-73 |
| [3] | Dickson N. R., Nicholson B. P., Hande K., Blanke C., Johnson D., Cohen A., Oncology(Williston Park, N.Y.), 1999, 13(7 Suppl. 3), 69-70 |
| [4] | Ma N., Wang C. J., Zhou Y., China Pharmacy, 2015, 26(35), 4995-4997 |
| (马宁, 王朝杰, 周云. 中国药房, 2015, 26(35), 4995-4997) | |
| [5] | Köllermann M. W., Sprenk P., Mühlfait V., Kahla H., Köllermann J., Eur. Urol., 1992, 24(3), 337-341 |
| [6] | Kim Y. H., Kim B. S., Seo J. H., Choi C. W., Kim J. S., Chun H. J., Hyun J. H., Oncology(Williston Park, N.Y.), 1999, 13(7 Suppl. 3), 64-68 |
| [7] | Han J. Q., Chen Y. L., Qin K., Niu Y. C., Chin. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 2014, 30(8), 674-678 |
| (韩江琼, 陈云兰, 秦锴, 牛义淳. 中国临床药理学杂志, 2014, 30(8), 674-678) | |
| [8] | National Pharmacopoeia Commission.Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010(2), People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, 2010, 252.(App.)61 |
| (国家药典委员会. 中国药典2010版(二部). 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2010, 252.附录61) | |
| [9] | Gu J., Qiao Y. H., Zhu X. Y., Yin X. H., Zhang X., Chen Y., Zhu Z. W., Shao Y. H., J. Electrochem., 2014, 20(3), 234-242 |
| (顾菁, 乔永辉, 朱新宇, 阴笑弘, 张欣, 陈烨, 朱志伟, 邵元华. 电化学, 2014, 20(3), 234-242) | |
| [10] | Liu S. J., Li Q., Shao Y. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(5), 2236-2253 |
| [11] | Li Q., Xie S., Liang Z., Meng X., Liu S., Girault H. H., Shao Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(43), 8010-8013 |
| [12] | Yuan Y., Su B., Shao Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2001, 22(11), 1819-1823 |
| (袁艺, 苏彬, 邵元华. 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22(11), 1819-1823) | |
| [13] | Chen Y., Su B., Shao Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(10), 1834-1837 |
| (陈勇, 苏彬, 邵元华. 高等学校化学学报, 2003, 24(10), 1834-1837) | |
| [14] | Qian Q. S., Wilson G. S., Bowman J. K., Girault H. H., Anal. Chem., 2001, 73(3), 497-503 |
| [15] | Huang X., Xie L. S. Q., Lin X. Y., Su B., Anal. Chem., 2017, 89(1), 945-951 |
| [16] | Liu Y., Strutwolf J., Arrigan D. W. M., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(8), 4487-4494 |
| [17] | Sairi M., Arrigan D. W. M., Procedia Chemistry, 2016, 20, 76-80 |
| [18] | De Eulate E. A., Serls L., Lauren S., Arrigan D. W. M., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2013, 405(11), 3801-3806 |
| [19] | Austen B. J. J., Arrigan D. W. M., Electrochimica Acta, 2016, 221, 62-69 |
| [20] | Amemiya S., Kim Y., Ishimatsu R., Kabagambe B., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2011, 399(2), 571-579 |
| [21] | Jiang X. H., Gao K., Hu D. P., Wang H. H., Bian S. J., Chen Y., Analyst,2015, 140(8), 2823-2833 |
| [22] | Chen Y., Bian S. J., Gao K., Cao Y. Y., Wu H. Q., Liu C. X., Jiang X. H., Sun X. L., J. Membrane Sci., 2014, 457, 9-18 |
| [23] | Gao K., Jiang X. H., Hu D. P., Bian S. J., Wang M., Chen Y., Chem. Lett., 2015, 26(3), 285-288 |
| [24] | Lee H. J., Beattie P. D., Seddon B. J., Osborne M. D., Girault H. H., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1997, 440(1/2), 73-82 |
| [25] | Kasahara T., Nishi N., Yamamoto M., Kakiuchi T., Langmuir,2004, 20(3), 875-881 |
| [26] | Li F., Chen Y., Zhang M., Jing P., Gao Z., Shao Y., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2005, 579(1), 89-102 |
| [27] | Wang H. H., Hu D. P., Jiang X. H., Zhang Y. H., Chen Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3), 546-551 |
| (王欢欢, 胡道盼, 江旭恒, 张烨桦, 陈勇. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3), 546-551) | |
| [28] | Senthilkumar S., Dryfe R. A. W., Saraswathi R., Langmuir,2007, 23(6), 3455-3461 |
| [29] | Bard A. J., Faulkner L. R., Translated by Shao Y. H., Dong X. D., Zhang B. L., Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd Edition, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2005, 145-202 |
| (邵元华, 董献堆, 张柏林[译]. 电化学方法: 原理和应用(第2版), 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005, 145-202) | |
| [30] | Shao Y. H., Girault H. H., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1990, 282(1/2), 59-72 |
| [31] | Li F., Chen Y., Sun P., Zhang M. Q., Gao Z., Zhan D. P., Shao Y. H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108(10), 3295-3302 |
| [1] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [2] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [3] | LI Yidi, TIAN Xiaochun, LI Junpeng, CHEN Lixiang, ZHAO Feng. Electron Transfer on the Semiconductor-microbe Interface and Its Environmental Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220089. |
| [4] | LUO Bian, ZHOU Fen, PAN Mu. Study on Preparation and Accessibility of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Supported Platinum Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [5] | LI Hua, YANG Ke, HUANG Junfeng, CHEN Fengjuan. Design and Construction of UiO-66-NH2/wood Composite for Efficient Removal of Trace Heavy Metal Ions from Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210701. |
| [6] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [7] | WANG Shoubai, WU Xiuming, SHU Chen, ZHONG Min, HUANG Wei, YAN Deyue. Gas Separation Performance of Polyimide Homogeneous MembranesContaining tert-Butyl Groups [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220357. |
| [8] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| [9] | TANG Yuanhui, LI Chunyu, LIN Yakai, ZHANG Chunhui, LIU Ze, YU Lixin, WANG Haihui, WANG Xiaolin. Dissipative Particle Dynamics Simulation of the Effect of Polymer Chain Rigidity on Membranes Formation by Nonsolvent Induced Phase Separation Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220169. |
| [10] | SHAO Wenhui, HU Xin, SHANG Jing, LIN Feng, JIN Liming, QUAN Chunshan, ZHANG Yanmei, LI Jun. Design, Synthesis and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Mechanism of Ag-AgVO3/BiVO4 Composite as a High-efficient and Broad-spectral Antibacterial Agent [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220132. |
| [11] | WEI Lina, PENG Li, ZHU Feng, GU Pengfei, GU Xuehong. Preparation of Au-CeZr/FAU Catalytic Membranes for Preferential Oxidation of CO in H2-rich Stream [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220175. |
| [12] | ZHANG Chi, SUN Fuxing, ZHU Guangshan. Synthesis, N2 Adsorption and Mixed-matrix Membrane Performance of Bimetal Isostructural CAU-21 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [13] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [14] | FU Zhinan, TAN Yunlong, XIAO Guyu, YAN Deyue. Synthesis and Properties of Sulfonated Poly(phthalazinone ether phosphine oxide)s with Perfluorobiphenyl Moieties for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2635. |
| [15] | YAN Tingting, ZHANG Na, LI Qiang, LI Zhenhua, LI Chunhui, LI Xue, YU Ru, WANG Rui, WANG Jihua, CAO Zanxia. Effects of Co-reagent for Improving the Performance of Polyamide Composite Reverse Osmosis Membrane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2008. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||