

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (3): 521.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170405
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHENG Xueli1,*( ), LI Yanfei1, ZHAO Yanyun1, LIU Yongjun2,*(
), LI Yanfei1, ZHAO Yanyun1, LIU Yongjun2,*( )
)
Received:2017-06-26
Online:2018-03-10
Published:2018-01-17
Contact:
CHENG Xueli,LIU Yongjun
E-mail:ching108@sohu.com;x_cheng@tsu.edu.cn;yongjunliu_1@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
CHENG Xueli, LI Yanfei, ZHAO Yanyun, LIU Yongjun. Reaction Mechanism of Rh(I)-catalyzed Olefin Carboacylation:Enantioselectivity in the Formation of Chiral Poly-fused Rings†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 521.
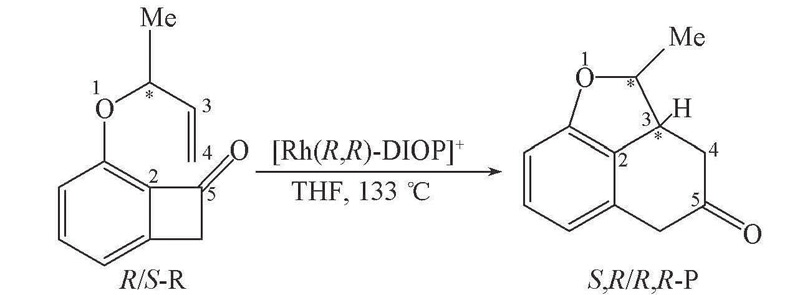
Scheme 1 Formation of poly-fused rings from benzocyclobutenone derivatives catalyzed by [Rh(R,R-DIOP)]+The Arabic numerals besides atoms are the selected atomic sequence numbers.
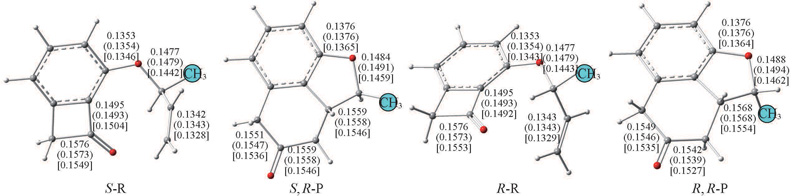
Fig.1 Optimized structures of S-R, R-R and their corresponding products obtained by BP86 functionals in gas phase and in THF(in brackets) as well as by M06-2X in THF(in square brackets)Bond lengths are in nm.
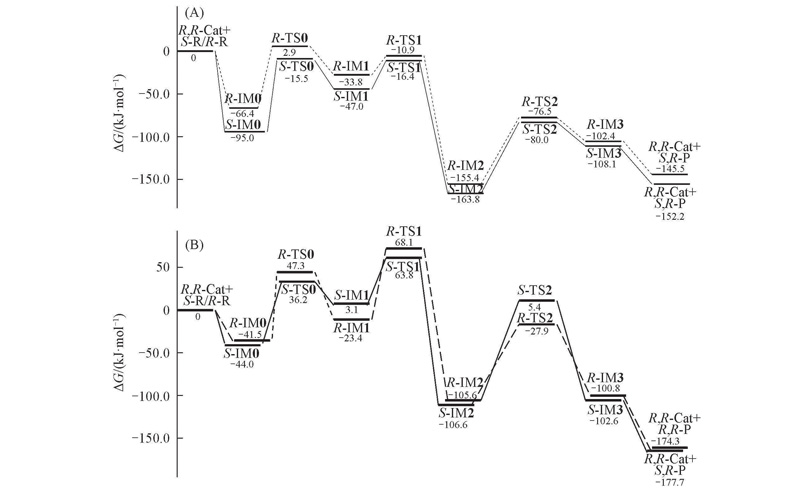
Fig.2 Gibbs free energy profiles obtained by BP86 functional in gas phase(A) and M06-2X functionals in THF(B)The S-R→S,R-P reaction channel are drawn in solid lines, and R-R→R,R-P channel are in dash lines.
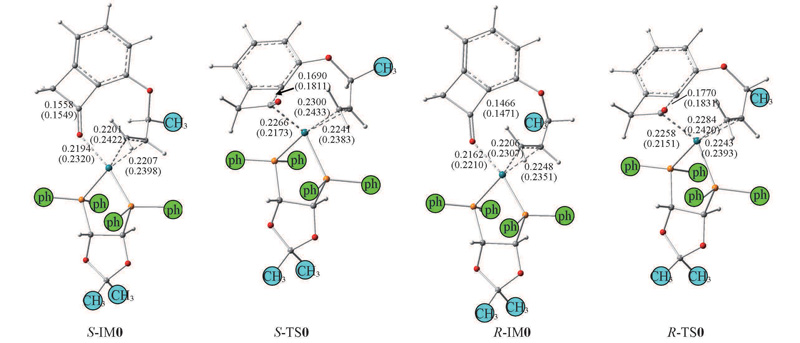
Fig.3 Intermediates and transition states of the C—C activation in the S- and R-channels optimized at BP86/6-31G(d,p) and M062X/6-31G(d,p)//PCM levelGeometrical structures are drawn on the basis of gas-phase skeletons, and the structural parameters obtained by M062X in THF are shown in brackets. Bond lengths are in nm.
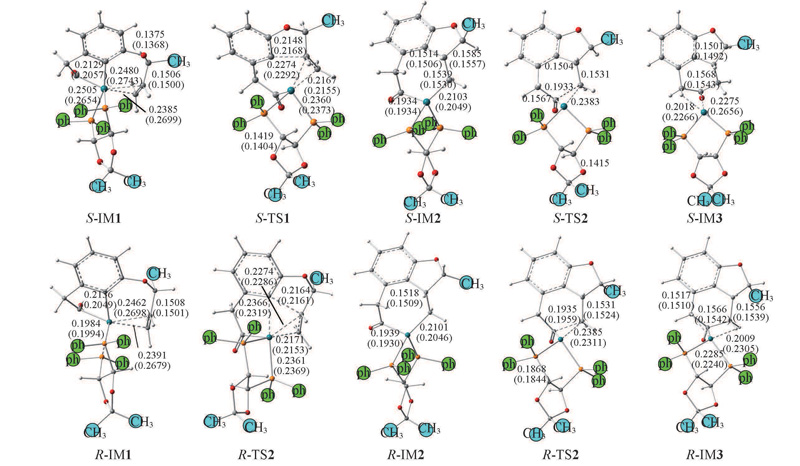
Fig.4 Intermediates and transition states in the S- and R-cyclization channels optimized at BP86/6-31G(d,p) and M062X/6-31G(d,p)//PCM level Structural parameters obtained by M062X in THF are shown in brackets. Bond lengths are in nm.
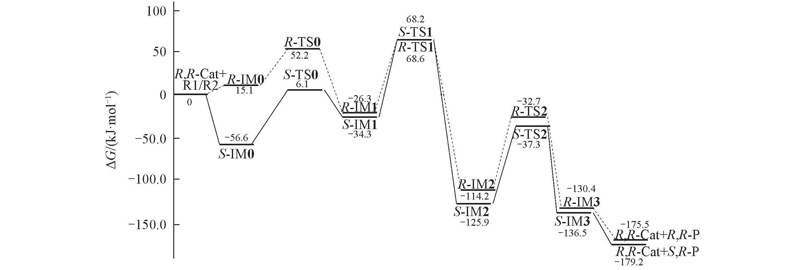
Fig.5 Gibbs free energy profiles in kJ/mol obtained by M06-2X functionals in waterThe S-R→S,R-P reaction channel are drawn in solid lines, and R-R→R,R-P channel are in dash lines.
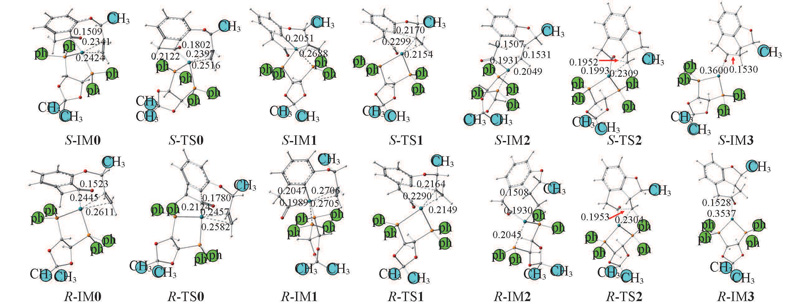
Fig.6 Optimized structural parameters of the intermediates and transition states in the S-R→S,R-P and R-R→R,R-P reaction channels at M062X/6-31G(d,p)//PCM level in waterBond lengths are in nm.
| Species | BP86 in gas phase | M06-2X in THF | M06-2X in water | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | O1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | O1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |
| S-IM0 | -0.462 | -0.243 | -0.271 | -0.475 | 0.560 | -0.537 | -0.255 | -0.275 | -0.480 | 0.637 | -0.525 | -0.319 | -0.276 | -0.451 | 0.629 |
| S-TS0 | -0.517 | -0.232 | -0.264 | -0.453 | 0.515 | -0.571 | -0.254 | -0.249 | -0.438 | 0.627 | -0.556 | -0.271 | -0.266 | -0.430 | 0.620 |
| S-IM1 | -0.514 | -0.168 | -0.259 | -0.483 | 0.574 | -0.574 | -0.192 | -0.253 | -0.451 | 0.639 | -0.577 | -0.198 | -0.269 | -0.442 | 0.598 |
| S-TS1 | -0.505 | -0.147 | -0.220 | -0.526 | 0.600 | -0.561 | -0.178 | -0.185 | -0.526 | 0.688 | -0.563 | -0.177 | -0.183 | -0.524 | 0.684 |
| S-IM2 | -0.487 | -0.092 | -0.324 | -0.574 | 0.570 | -0.550 | -0.104 | -0.320 | -0.565 | 0.625 | -0.555 | -0.102 | -0.320 | -0.564 | 0.613 |
| S-TS2 | -0.492 | -0.092 | -0.316 | -0.586 | 0.500 | -0.555 | -0.096 | -0.314 | -0.599 | 0.577 | -0.559 | -0.095 | -0.310 | -0.615 | 0.570 |
| S-IM3 | -0.492 | -0.093 | -0.303 | -0.526 | 0.483 | -0.552 | -0.100 | -0.300 | -0.579 | 0.594 | -0.561 | -0.099 | -0.298 | -0.562 | 0.652 |
| R-IM0 | -0.476 | -0.231 | -0.271 | -0.483 | 0.561 | -0.540 | -0.259 | -0.263 | -0.459 | 0.645 | -0.529 | -0.307 | -0.278 | -0.445 | 0.627 |
| R-TS0 | -0.510 | -0.231 | -0.262 | -0.446 | 0.514 | -0.566 | -0.248 | -0.239 | -0.441 | 0.629 | -0.552 | -0.282 | -0.261 | -0.433 | 0.614 |
| R-IM1 | -0.509 | -0.173 | -0.262 | -0.484 | 0.564 | -0.575 | -0.197 | -0.261 | -0.447 | 0.595 | -0.577 | -0.195 | -0.267 | -0.441 | 0.598 |
| R-TS1 | -0.500 | -0.152 | -0.219 | -0.530 | 0.600 | -0.558 | -0.179 | -0.184 | -0.521 | 0.688 | -0.560 | -0.179 | -0.182 | -0.519 | 0.684 |
| R -IM2 | -0.492 | -0.090 | -0.325 | -0.578 | 0.567 | -0.554 | -0.100 | -0.318 | -0.568 | 0.624 | -0.558 | -0.098 | -0.318 | -0.566 | 0.617 |
| R-TS2 | -0.490 | -0.093 | -0.318 | -0.587 | 0.501 | -0.553 | -0.099 | -0.311 | -0.615 | 0.581 | -0.558 | -0.099 | -0.310 | -0.620 | 0.567 |
| R-IM3 | -0.489 | -0.096 | -0.305 | -0.524 | 0.482 | -0.551 | -0.103 | -0.303 | -0.560 | 0.590 | -0.559 | -0.102 | -0.300 | -0.565 | 0.652 |
Table 1 Selected NBO charges for O1, C2, C3, C4 and C5 acquired from 3 DFT functionals
| Species | BP86 in gas phase | M06-2X in THF | M06-2X in water | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | O1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | O1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |
| S-IM0 | -0.462 | -0.243 | -0.271 | -0.475 | 0.560 | -0.537 | -0.255 | -0.275 | -0.480 | 0.637 | -0.525 | -0.319 | -0.276 | -0.451 | 0.629 |
| S-TS0 | -0.517 | -0.232 | -0.264 | -0.453 | 0.515 | -0.571 | -0.254 | -0.249 | -0.438 | 0.627 | -0.556 | -0.271 | -0.266 | -0.430 | 0.620 |
| S-IM1 | -0.514 | -0.168 | -0.259 | -0.483 | 0.574 | -0.574 | -0.192 | -0.253 | -0.451 | 0.639 | -0.577 | -0.198 | -0.269 | -0.442 | 0.598 |
| S-TS1 | -0.505 | -0.147 | -0.220 | -0.526 | 0.600 | -0.561 | -0.178 | -0.185 | -0.526 | 0.688 | -0.563 | -0.177 | -0.183 | -0.524 | 0.684 |
| S-IM2 | -0.487 | -0.092 | -0.324 | -0.574 | 0.570 | -0.550 | -0.104 | -0.320 | -0.565 | 0.625 | -0.555 | -0.102 | -0.320 | -0.564 | 0.613 |
| S-TS2 | -0.492 | -0.092 | -0.316 | -0.586 | 0.500 | -0.555 | -0.096 | -0.314 | -0.599 | 0.577 | -0.559 | -0.095 | -0.310 | -0.615 | 0.570 |
| S-IM3 | -0.492 | -0.093 | -0.303 | -0.526 | 0.483 | -0.552 | -0.100 | -0.300 | -0.579 | 0.594 | -0.561 | -0.099 | -0.298 | -0.562 | 0.652 |
| R-IM0 | -0.476 | -0.231 | -0.271 | -0.483 | 0.561 | -0.540 | -0.259 | -0.263 | -0.459 | 0.645 | -0.529 | -0.307 | -0.278 | -0.445 | 0.627 |
| R-TS0 | -0.510 | -0.231 | -0.262 | -0.446 | 0.514 | -0.566 | -0.248 | -0.239 | -0.441 | 0.629 | -0.552 | -0.282 | -0.261 | -0.433 | 0.614 |
| R-IM1 | -0.509 | -0.173 | -0.262 | -0.484 | 0.564 | -0.575 | -0.197 | -0.261 | -0.447 | 0.595 | -0.577 | -0.195 | -0.267 | -0.441 | 0.598 |
| R-TS1 | -0.500 | -0.152 | -0.219 | -0.530 | 0.600 | -0.558 | -0.179 | -0.184 | -0.521 | 0.688 | -0.560 | -0.179 | -0.182 | -0.519 | 0.684 |
| R -IM2 | -0.492 | -0.090 | -0.325 | -0.578 | 0.567 | -0.554 | -0.100 | -0.318 | -0.568 | 0.624 | -0.558 | -0.098 | -0.318 | -0.566 | 0.617 |
| R-TS2 | -0.490 | -0.093 | -0.318 | -0.587 | 0.501 | -0.553 | -0.099 | -0.311 | -0.615 | 0.581 | -0.558 | -0.099 | -0.310 | -0.620 | 0.567 |
| R-IM3 | -0.489 | -0.096 | -0.305 | -0.524 | 0.482 | -0.551 | -0.103 | -0.303 | -0.560 | 0.590 | -0.559 | -0.102 | -0.300 | -0.565 | 0.652 |
| [1] | Jones W. D., Nature, 1993, 364(6439), 676—677 |
| [2] | Li Y., Shi Z. J., Sci. Sin. Chem., 2016, 46(6), 579—587 |
| (李洋, 施章杰.中国科学:化学,2016, 46(6), 579—587) | |
| [3] | Huang G., Liu P., ACS Catal., 2016, 6(2), 809—820 |
| [4] | Jiang Y. Y., Xu Z. Y., Yu H. Z., Fu Y., Sci. China Chem., 2016, 59(6), 724—729 |
| [5] | Jiang Y. Y., Man X., Bi S., Sci. China Chem., 2016, 59(11), 1448—1466 |
| [6] | Misal Castro L. C., Chatani N., Chem. Lett., 2015, 44(4), 410—421 |
| [7] | Hirano K., Miura M., Chem. Lett., 2015, 44(7), 868—873 |
| [8] | Kim D. S., Park W. J., Jun C. H., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(13), 8977—9015 |
| [9] | Lutz J. P., Rathbun C. M., Stevenson S. M., Powell B. M., Boman T. S., Baxter C. E., Zona J. M., Johnson J. B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(1), 715—722 |
| [10] | Huang G., Org. Lett., 2015, 17(8), 1994—1997 |
| [11] | Huang G., J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80(15), 7564—7571 |
| [12] | Kawaguchi Y., Yasuda S., Mukai C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(35), 10473—10477 |
| [13] | Kong W. J., Liu Y. J., Xu H., Chen Y. Q., Dai H. X., Yu J. Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(7), 2146—2149 |
| [14] | Jia T., Zhao C., He R., Chen H., Wang C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(17), 5268—5271 |
| [15] | Chen F., Wang T., Jiao N., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(17), 8613—8661 |
| [16] | Namyslo J. C., Kaufmann D. E., Chem. Rev., 2003, 103(4), 1485—1538 |
| [17] | Rubin M., Rubina M., Gevorgyan V., Chem. Rev., 2007, 107(7), 3117—3179 |
| [18] | Shi M., Shao L. X., Lu J. M., Wei Y., Mizuno K., Maeda H., Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(10), 5883—5913 |
| [19] | Seiser T., Saget T., Tran D. N., Cramer N., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(34), 7740—7752 |
| [20] | XuT., Dong G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(30), 7567—7571 |
| [21] | Mack D. J., Njardarson J. T., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(2), 272—286 |
| [22] | Zeng R., Chen P., Dong G., ACS Catal., 2016, 6(2), 969—973 |
| [23] | Xu T., Ko H. M., Savage N. A., Dong G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(49), 20005—20008 |
| [24] | Lu Q., Wang B., Yu H., Fu Y., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(8), 4881—4889 |
| [25] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision C.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2010 |
| [26] | Sarrafi Y., Hamzehloueian M., Alimohammadi K., Yeganegi S., J. Mol. Struct., 2012, 1030, 168—176 |
| [27] | González-Juárez D. E., García-Vázquez J. B., Zúñiga-García V., Trujillo-Serrato J. J., Súarez-Castillo O. R., Joseph-Nathan P., Morales-Ríos M. S., Tetrahedron, 2012, 68(35), 7187—7195 |
| [28] | Meng Q., Wang F., Li M., J. Mol. Model., 2012, 18(12), 4955—4963 |
| [29] | Jeletic M. S., Lowry R. J., Swails J. M., Ghiviriga I., Veige A. S., J. Organomet. Chem., 2011, 696(20), 3127—3134 |
| [30] | Wei D., Zhu Y., Zhang C., Sun D., Zhang W., Tang M., J. Mol. Catal. A, 2011, 334(1/2), 108—115 |
| [31] | Liao C., Li B., Wang J., Wang Y., Chin. J. Chem., 2012, 30(4), 951—958 |
| [32] | Zhang Y., Wang C., Zhang S., Li G. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(12), 2260—2267 |
| (张宇, 王翀, 张帅, 李根全.高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(12), 2260—2267) | |
| [33] | Tang Y. H., Wang Z. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10), 1849—1855 |
| (唐艳辉, 王志栋.高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(10), 1849—1855) | |
| [34] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [35] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94(14), 5523—5527 |
| [36] | Domingo L. R., Picher M. T., Sáez J. A., J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74(7), 2726—2735 |
| [37] | Ma Q., Wang W. N., Zhao Q. L., Liu F. Y., Wang W. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4), 613—621 |
| (马倩, 王渭娜, 赵强莉, 刘峰毅, 王文亮.高等学校化学学报,2017, 38(4), 613—621) | |
| [38] | Leven M., Schlörer N. E., Neudörfl J. M., Goldfuss B., Chem. Eur. J., 2010, 16(45), 13443—13449 |
| [39] | Karnahl M., Tschierlei S., Kuhnt C., Dietzek B., Schmitt M., Popp J., Schwalbe M., Krieck S., Görls H., Heinemann F. W., Rau S., Dalton Trans., 2010, 39(9), 2359—2370 |
| [40] | Liu N. N., Yu S., Ding Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11), 2006—2011 |
| (刘楠楠, 于爽, 丁益宏.高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(11), 2006—2011) | |
| [41] | Darmon J. M., Stieber S. C. E., Sylvester K. T., Fernández I., Lobkovsky E., Semproni S. P., Bill E., Wieghardt K., DeBeer S., Chirik P. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(41), 17125—17137 |
| [42] | Chang Y., Chen H. Y., Li Q. S., Sci. Sin. Chem., 2016, 46(1), 59—68 |
| (常玉, 陈红雨, 李前树.中国科学: 化学,2016, 46(1), 59—68) | |
| [43] | Jansen H. B., Ros P., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1969, 3(3), 140—143 |
| [44] | Boys S. F., Bernardi F., Mol. Phys., 1970, 19(4), 553—566 |
| [45] | Yan Y., Shi W., Feng G., Ren F., Wang Y., Comput. Theor. Chem., 2012, 996, 91—102 |
| [46] | Schenker S., Schneider C., Tsogoeva S. B., Clark T., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2011, 7(11), 3586—3595 |
| [47] | Vandavasi J. K., Hu W. P., Chen H. Y., Senadi G. C., Chen C. Y., Wang J. J., Org. Lett., 2012, 14(12), 3134—3137 |
| [48] | Sengupta A., Sunoj R. B., J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77(23), 10525—10536 |
| [49] | Qu Z., Chen X., Wei D., Ke D., Qu L., Yuan J., Bai Y., Wang F., Zhao Y., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2012, 112(5), 1449—1459 |
| [50] | Ruan J., Iggo J. A., Berry N. G., Xiao J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(46), 16689—16699 |
| [51] | Iannazzo D., Brunaccini E., Giofrè S. V., Piperno A., Romeo G., Ronsisvalle S., Chiacchio M. A., Lanza G., Chiacchio U., Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2010, 2010(30), 5897—5905 |
| [52] | Lu G., Fang C., Xu T., Dong G., Liu P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(25), 8274—8283 |
| [1] | CAO Shujie, LI Hongjun, GUAN Wenli, REN Mengtian, ZHOU Chuanzheng. Progress on the Stereocontrolled Synthesis of Phosphorothioate Oligonucleotides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220304. |
| [2] | TANG Quanjun, LIU Yingxin, MENG Rongwei, ZHANG Ruotian, LING Guowei, ZHANG Chen. Application of Single-atom Catalysis in Marine Energy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220324. |
| [3] | WEI Chunhong, JIANG Qian, WANG Panpan, JIANG Chengfa, LIU Yuefeng. Atomic Scale Investigation of Pt Atoms/clusters Promoted Co-catalyzed Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220074. |
| [4] | ZHANG Xinxin, XU Di, WANG Yanqiu, HONG Xinlin, LIU Guoliang, YANG Hengquan. Effect of Mn Promoter on CuFe-based Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Higher Alcohols [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [5] | WANG Zhengwen, GAO Fengxiang, CAO Han, LIU Shunjie, WANG Xianhong, WANG Fosong. Synthesis and Property of CO2 Copolymer⁃based UV-curable Polymer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220236. |
| [6] | LIU Xiaolei, LU Yongqiang, YOU Qi, LIU Guohui, YAO Wei, HU Riming, YAN Jixian, CUI Yu, YANG Xiaofeng, SUN Guoxin, JIANG Xuchuan. A 3-Hydroxythalidomide-based Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of H2O2 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220070. |
| [7] | MIN Jing, WANG Liyan. 1H NMR Study on the Conformation of Aromatic Amides Limited by Three-center Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220084. |
| [8] | WANG Junyang, LIU Zheng, ZHANG Qian, SUN Chunyan, LI Hongxia. Application of DNA Silver Nanoclusters in the Fluorescence Biosensors based on Functional Nucleic Acids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [9] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [10] | JIANG Xiaokang, ZHOU Qi, ZHOU Hengwei. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Gd2ZnTiO6∶Dy3+, Eu3+ Single Phase White Light-emitting Phosphors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220029. |
| [11] | XIA Tian, WAN Jiawei, YU Ranbo. Progress of the Structure-property Correlation of Heteroatomic Coordination Structured Carbon-based Single-atom Electrocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220162. |
| [12] | TAO Yu, OU Honghui, LEI Yongpeng, XIONG Yu. Research Progress of Single-atom Catalysts in Photocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220143. |
| [13] | XU Dandan, ZOU Xiucheng, LUO Jing, LIU Ren. Synthesis and Characterization of Phenothiazine-based Schiff Bases as Visible Light Photoinitiators [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210857. |
| [14] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [15] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||