

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 132.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170229
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
KONG Yan, WANG Lizhang*( ), YANG Shengxiang, ZHAO Peng
), YANG Shengxiang, ZHAO Peng
Received:2017-04-13
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2017-12-13
Contact:
WANG Lizhang
E-mail:wlzh0731@126.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
KONG Yan, WANG Lizhang, YANG Shengxiang, ZHAO Peng. Preparation and Electro-catalytic Mechanisms for Nitrate Ion Reduction of Ti(100-δ)Cuδ(δ=0.02, 0.09, 0.28, 1.39, 5.65) Cathodes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 132.
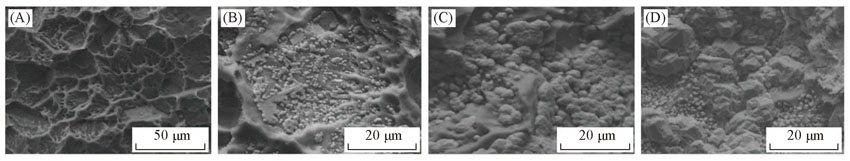
Fig.1 SEM images of the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes under different electro-deposition time(A) t=0 min(δ=0); (B) t=0.5 min(δ=0.02); (C) t=6 min(δ=0.28); (D) t=30 min(δ=1.39).
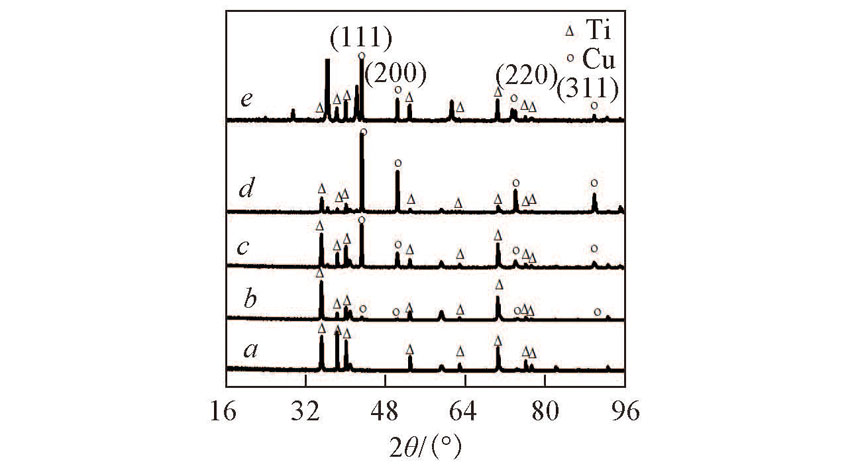
Fig.2 XRD patterns of the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes under different electro-deposition timea. t=0(δ=0); b. t=0.5 min(δ=0.02); c. t=6 min(δ=0.28); d. t=30 min(δ=1.39); e. t=120 min(δ=5.65).
| t/min | δ | Crystallinity(%) | D/nm | t/min | δ | Crystallinity(%) | D/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 30 | 1.39 | 74.71 | >100 | ||
| 0.5 | 0.02 | 3.03 | 35.7 | 120 | 5.65 | 15.93 | >100 |
| 6 | 0.28 | 41.69 | 73.1 |
Table 1 Effects of electro-deposition time(t) on the mass fraction(δ), crystallinity and grain size(D) of Cu on Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes
| t/min | δ | Crystallinity(%) | D/nm | t/min | δ | Crystallinity(%) | D/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 30 | 1.39 | 74.71 | >100 | ||
| 0.5 | 0.02 | 3.03 | 35.7 | 120 | 5.65 | 15.93 | >100 |
| 6 | 0.28 | 41.69 | 73.1 |
| δ | TC(%) | δ | TC(%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (111) | (200) | (220) | (311) | (111) | (200) | (220) | (311) | ||
| 0.02 | 20.8 | 19.9 | 41.7 | 17.5 | 1.39 | 34.9 | 23.5 | 23.5 | 18.1 |
| 0.28 | 32.0 | 24.8 | 24.5 | 18.7 | 5.65 | 38.0 | 27.3 | 22.4 | 12.3 |
Table 2 Calculated results of the texture coefficient(TC) of Cu coating on Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes from XRD patterns
| δ | TC(%) | δ | TC(%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (111) | (200) | (220) | (311) | (111) | (200) | (220) | (311) | ||
| 0.02 | 20.8 | 19.9 | 41.7 | 17.5 | 1.39 | 34.9 | 23.5 | 23.5 | 18.1 |
| 0.28 | 32.0 | 24.8 | 24.5 | 18.7 | 5.65 | 38.0 | 27.3 | 22.4 | 12.3 |
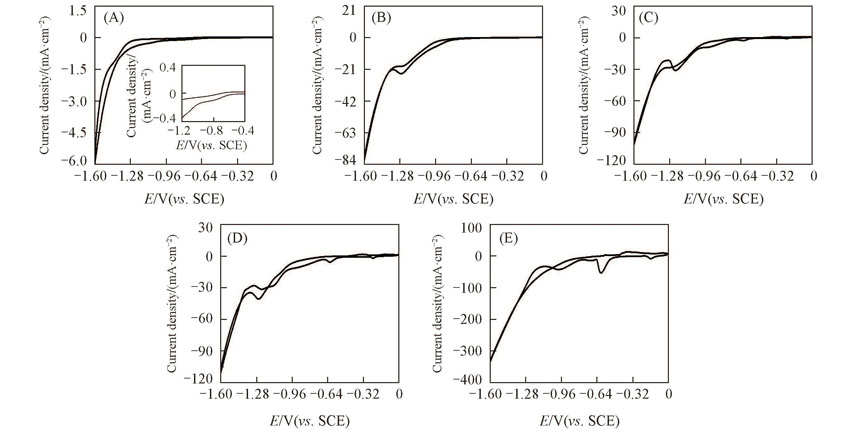
Fig.3 CV curves of the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes in hybrid of NaNO3(0.01 mol/L) and Na2SO4(3%, mass fraction) at a scanning rate of 10 mV/sδ: (A) 0; (B) 0.02; (C) 0.28; (D) 1.39; (E) 5.65.
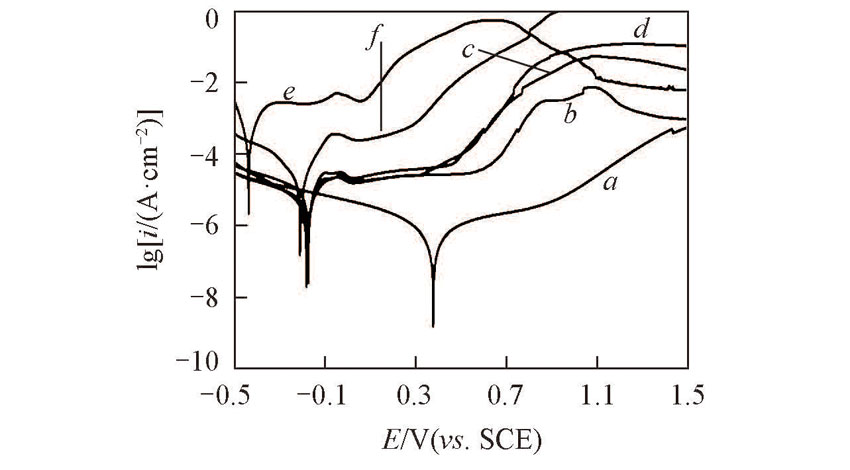
Fig.4 Tafel plots of the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes and copper in hybrid of NaNO3(0.01 mol/L) and Na2SO4(3%) at a scanning rate of 5 mV/sδ: a. 0; b. 0.02; c. 0.28; d. 1.39; e. 5.65; f. 100.
| δ | a/mV | b/mV | δ | a/mV | b/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 81.82 | 75.99 | 1.39 | 61.93 | 108.29 |
| 0.02 | 66.29 | 97.14 | 5.65 | 91.54 | 69.17 |
| 0.28 | 60.15 | 114.20 | 100 | 105.66 | 62.83 |
Table 3 Tafel constants(a,b) of Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes in NaNO3(0.01 mol/L) solution
| δ | a/mV | b/mV | δ | a/mV | b/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 81.82 | 75.99 | 1.39 | 61.93 | 108.29 |
| 0.02 | 66.29 | 97.14 | 5.65 | 91.54 | 69.17 |
| 0.28 | 60.15 | 114.20 | 100 | 105.66 | 62.83 |
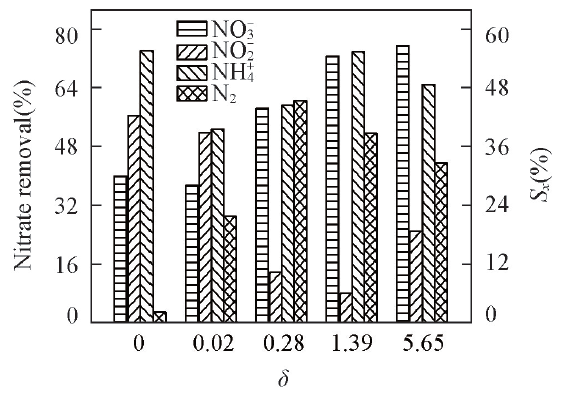
Fig.5 NO3- removal efficiency and product selectivity during electro-catalytic reduction on the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodesCurrent density: 20 mA/cm2; electrolysis time: 6 h.
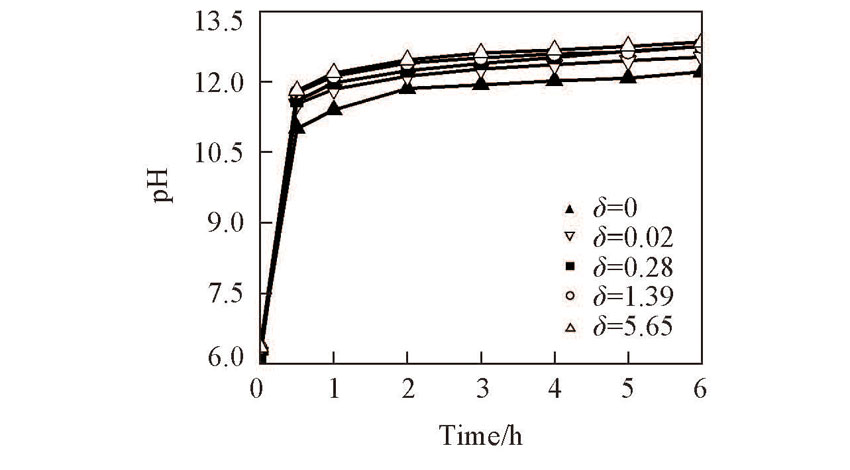
Fig.6 pH values during electro-catalytic reduction of N O 3 - on the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodesCurrent density: 20 mA/cm2; electrolysis time: 6 h.
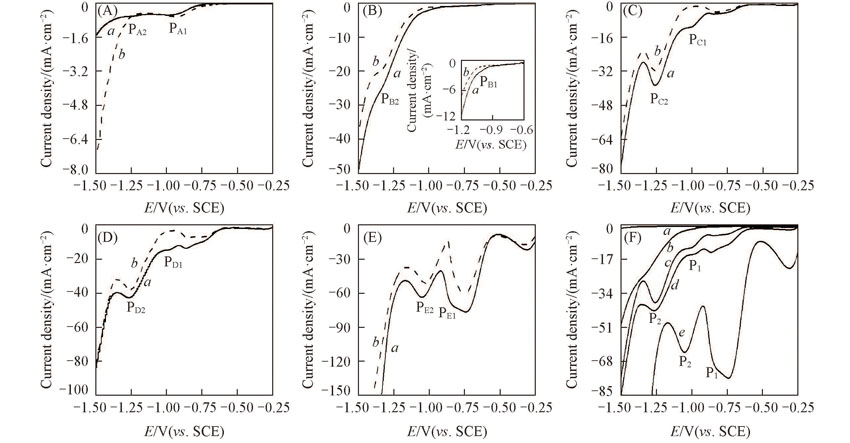
Fig.7 LSV curves of the prepared Ti(100-δ)Cuδ cathodes in 0.01 mol/L NaNO3(a) and 0.01 mol/L NaNO2(b) solutionsScanning rate: 10 mV/s. δ: (A) 0; (B) 0.02; (C) 0.28; (D) 1.39; (E) 5.65; (F) the enlarged panel in NaNO3 solution. P1 and P2 represent the reduction peaks of the nitrate and nitrite ions, respectively; the subscripts of A, B, C, D and E denote the peaks at δ values of 0, 0.02, 0.28, 1.39, 5.65, respectively.
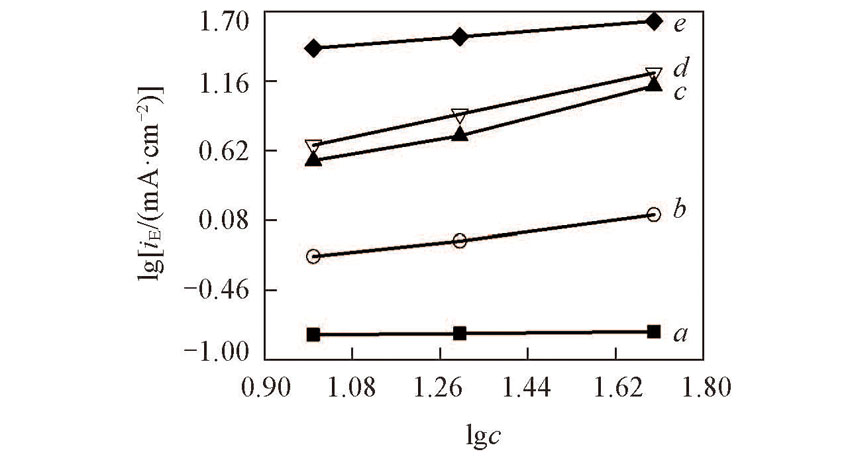
Fig.8 Linear relationship between concentration and peak currents obtained by recorded LSV data in NaNO3(0.01 mol/L) solutionScanning rate: 10 mV/s. δ: a. 0; b. 0.02; c. 0.28; d. 1.39; e. 5.65.
| [1] | Li R., Song C. Z., Zhao X., Mao R., Chin. J. Environ. Eng., 2016, 10(2), 648—654 |
| (李熔, 宋长忠, 赵旭, 冒冉.环境工程学报, 2016, 10(2), 648—654) | |
| [2] | Ding J., Li W., Zhao Q. L., Wang K., Zheng Z., Gao Y. Z., Chem. Eng. J., 2015, 271, 252—259 |
| [3] | Gao M. C., Wang S., Ren Y., Jin C. J., She Z. L., Zhao Y. G., Yang S. Y., Guo L., Zhang J., Li Z. W., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 284, 1008—1016 |
| [4] | Ye S. F., Hu X. M., Zhang Y., Dong J., Environ. Sci., 2010, 31(8), 1827—1833 |
| (叶舒帆, 胡筱敏, 张杨, 董俊.环境科学, 2010, 31(8), 1827—1833) | |
| [5] | Ye S. F., Hu X. M., Dong J., Zhang Y., He Y. D., China Environ. Sci., 2011, 31(1), 44—49 |
| (叶舒帆, 胡筱敏, 董俊, 张杨, 和英滇.中国环境科学, 2011, 31(1), 44—49) | |
| [6] | Hasnat M. A., Islam M. A., Aoun S.B., Safwan J. A., Rahman M. M., Asiri A. M., ChemPlusChem, 2015, 80(11), 1634—1641 |
| [7] | Molodkina E. B., Botryakova I. G., Danilov A. I., Souza-Garcia J., Feliu J. M., Russ. J. Electrochem., 2012, 48(3), 302—315 |
| [8] | Comisso N., Cattarin S., Stefania F., Luca M., Marco M., Lourdes V., Enrico V., Electrochem. Commun., 2012, 25, 91—93 |
| [9] | Zhou L., Deng H. P., Sang S. B., Environ. Chem., 2008, 27(2), 172—176 |
| (周丽, 邓慧萍, 桑松表.环境化学, 2008, 27(2), 172—176) | |
| [10] | González P. O., Bisang J. M., Electrochim. Acta, 2016, 194, 448—453 |
| [11] | David R., Daniel B., Lionel R., Electrochim. Acta, 2008, 53(20), 5977—5984 |
| [12] | Ma X. J., Li M., Feng C. P., Hu W. W., Wang L. L., Liu X. J., Electroanal. Chem., 2016, 782, 270—277 |
| [13] | Yang S. X., Wang L. Z., Jiao X. M., Li P., Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 2017, 12(5), 4370—4383 |
| [14] | Du N., Shu W. F., Zhao Q., Chen Q. L., Wang S. X., Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2013, 23(2), 426—433 |
| (杜楠, 舒伟发, 赵晴, 陈庆龙, 王帅星.中国有色金属学报, 2013, 23(2), 426—433) | |
| [15] | Guo X. H., Li S. P., Hou W. G., Han S. H., Hu J. F., Li D. Q., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2003, 19(2), 211—215 |
| [16] | Wong K. N., Khiew P. S., Isa D., Chiu W. S., Mater. Lett., 2014, 128, 97—100 |
| [17] | Editorial Committee of “Determination Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater” of State Environmental Protection Administration, Determination Methods for Examination of Water and Wastewater, China Environmental Science Press, Beijing, 2002, 258—281 |
| (国家环境保护总局《水和废水监测分析方法》编委会. 水和废水监测分析方法,北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002, 258—281) | |
| [18] | Jung J., Bae S., Lee W., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2012, 127, 148—158 |
| [19] | Fan N. W., Li Z. K., Zhao L., Wu N. M., Zhou T., Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 214, 83—90 |
| [20] | David R., Daniel B., Lionel R., J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 192(2), 507—513 |
| [21] | Fan G.N., Zheng H. B., Han P., Zhao J. L.,Chem. Eng., 2015, (8), 22—24, 30 |
| (范国宁, 郑红兵, 韩萍, 赵家琳. 化学工程师, 2015, (8), 22—24, 30) | |
| [22] | Gu M., Yang F. Z., Huang L., Yao S. B., Zhou S. M., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2002, 18(11), 973—978 |
| (辜敏, 杨防祖, 黄令, 姚士冰, 周绍民.物理化学学报, 2002, 18(11), 973—978) | |
| [23] | Ding X. C., Zhang Z., Nonferr. Metal. Soc., 2015, 25(3), 815—823 |
| (丁辛城, 张震.中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(3), 815—823) | |
| [24] | Jafari Y., Ghoreishi S. M., Shabani-Nooshabadi M., Synthetic Met., 2016, 217, 220—230 |
| [25] | Huang J. Z., Xu Z., Li H. L., Kang G. H., Wang W. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(5), 909—913 |
| (黄金昭, 徐征, 李海玲, 亢国虎, 王文静.高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(5), 909—913) | |
| [26] | Shin H., Jung S., Bae S., Lee W., Kim H., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2014, 48(21), 12768—12774 |
| [27] | Szpyrkowicz L., Daniele S., Radaelli M., Specchia S., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2006, 66(1/2), 40—50 |
| [28] | Fernandes A., Santos D., Pacheco M. J., Ciríaco L., Lopes A., Santos D., Pacheco M. J., Ciríaco L., Lopes A., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2014, 148/149, 288—294 |
| [1] | PENG Kuilin, LI Guilin, JIANG Chongyang, ZENG Shaojuan, ZHANG Xiangping. Research Progress for the Role of Electrolytes in the CO2 Electrochemical Reduction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [2] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [3] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [4] | ZHOU Leilei, CHENG Haiyang, ZHAO Fengyu. Research Progress of CO2 Hydrogenation over Pd-based Heterogeneous Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [5] | REN Nana, XUE Jie, WANG Zhifan, YAO Xiaoxia, WANG Fan. Effects of Thermodynamic Data on Combustion Characters of 1,3-Butadiene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [6] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [7] | CHANG Yunfei, LIAO Mingyi, WEN Jiaming. Reduction Performance and Mechanism of Liquid Terminated-carboxyl Fluoroelastomers Using NaBH4/MCl x Reduction System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20210835. |
| [8] | ZHANG Shiyu, HE Runhe, LI Yongbing, WEI Shijun, ZHANG Xingxiang. Fabrication of Lithium-sulfur Battery Cathode with Radiation Crosslinked Low Molecular Weight of Polyacrylonitrile and the Mechanism of Sulfur Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210632. |
| [9] | BI Gening, XIAO Xiaohua, LI Gongke. Development and Validation of Multiple Physical Fields Coupling Model for Microwave-assisted Extraction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210739. |
| [10] | SUN Cuihong, LYU Liqiang, LIU Ying, WANG Yan, YANG Jing, ZHANG Shaowen. Mechanism and Kinetics on the Reaction of Isopropyl Nitrate with Cl, OH and NO3 Radicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [11] | WEN Zhiguo, QIAO Zaiyin, TIAN Chong, MAXIM Borzov, NIE Wanli. Catalytic Activity and Reaction Mechanism of FLPs for the Reduction of Enamine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220555. |
| [12] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [13] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [14] | MENG Fanwei, GAO Qi, YE Qing, LI Chenxi. Potassium Poisoning Mechanism of Cu-SAPO-18 Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Ammonia [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2832. |
| [15] | YANG Yiying, ZHU Rongxiu, ZHANG Dongju, LIU Chengbu. Theoretical Study on Gold-catalyzed Cyclization of Alkynyl Benzodioxin to 8-Hydroxy-isocoumarin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||