

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 20210739.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210739
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
BI Gening, XIAO Xiaohua( ), LI Gongke(
), LI Gongke( )
)
Received:2021-10-22
Online:2022-03-10
Published:2021-12-21
Contact:
XIAO Xiaohua,LI Gongke
E-mail:xiaoxhua@mail.sysu.edu.cn;cesgkl@mail.sysu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
BI Gening, XIAO Xiaohua, LI Gongke. Development and Validation of Multiple Physical Fields Coupling Model for Microwave-assisted Extraction[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210739.
| Variable symbol | Variable name | Values and units |
|---|---|---|
| wo | The width of microwave cavity | 348 mm |
| do | The depth of microwave cavity | 366 mm |
| ho | The height of microwave cavity | 248 mm |
| wg | The width of waveguide | 50 mm |
| dg | The depth of waveguide | 78 mm |
| hg | The height of waveguide | 18 mm |
| R_bottom_tube | The bottom diameter of sample bottle | 17.5 mm |
| H_bottom_tube | The height of sample holder bottom | 10 mm |
| R_bottom_hold | The radius of sample location | 35 mm |
| R_tube | The radius of flask circular cavity | 38.5 mm |
| tube2hold | Distance from bottom of beaker to top of support frame | 22 mm |
| R_tube_neck | The radius of the bottleneck | 14 mm |
| t_glass | The thickness of Glass wall | 1.3 mm |
| H_liquid | The height of liquid level | 30 mm |
| H_sample | The sample height | 1 mm |
| Mole_Mass | The molar mass of the target molecule | 270.2 g/mol |
| Mass | The sample quality | 1 g |
Table 1 Geometric parameters of the multiple physical fields coupling model for MAE
| Variable symbol | Variable name | Values and units |
|---|---|---|
| wo | The width of microwave cavity | 348 mm |
| do | The depth of microwave cavity | 366 mm |
| ho | The height of microwave cavity | 248 mm |
| wg | The width of waveguide | 50 mm |
| dg | The depth of waveguide | 78 mm |
| hg | The height of waveguide | 18 mm |
| R_bottom_tube | The bottom diameter of sample bottle | 17.5 mm |
| H_bottom_tube | The height of sample holder bottom | 10 mm |
| R_bottom_hold | The radius of sample location | 35 mm |
| R_tube | The radius of flask circular cavity | 38.5 mm |
| tube2hold | Distance from bottom of beaker to top of support frame | 22 mm |
| R_tube_neck | The radius of the bottleneck | 14 mm |
| t_glass | The thickness of Glass wall | 1.3 mm |
| H_liquid | The height of liquid level | 30 mm |
| H_sample | The sample height | 1 mm |
| Mole_Mass | The molar mass of the target molecule | 270.2 g/mol |
| Mass | The sample quality | 1 g |
| Physical field | Initial condition | Boundary condition and equation |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave field | t=0, E=0, H=0 | (1) The boundary between the microwave cavity and the waveguide wall: |
(2) The boundary of glass, solvent and air: | ||
| Temperature field | t=0, | |
| Concentration field | t=0, | Interface between solvent and glass: |
Table 2 Initial conditions, boundary conditions and equations
| Physical field | Initial condition | Boundary condition and equation |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave field | t=0, E=0, H=0 | (1) The boundary between the microwave cavity and the waveguide wall: |
(2) The boundary of glass, solvent and air: | ||
| Temperature field | t=0, | |
| Concentration field | t=0, | Interface between solvent and glass: |
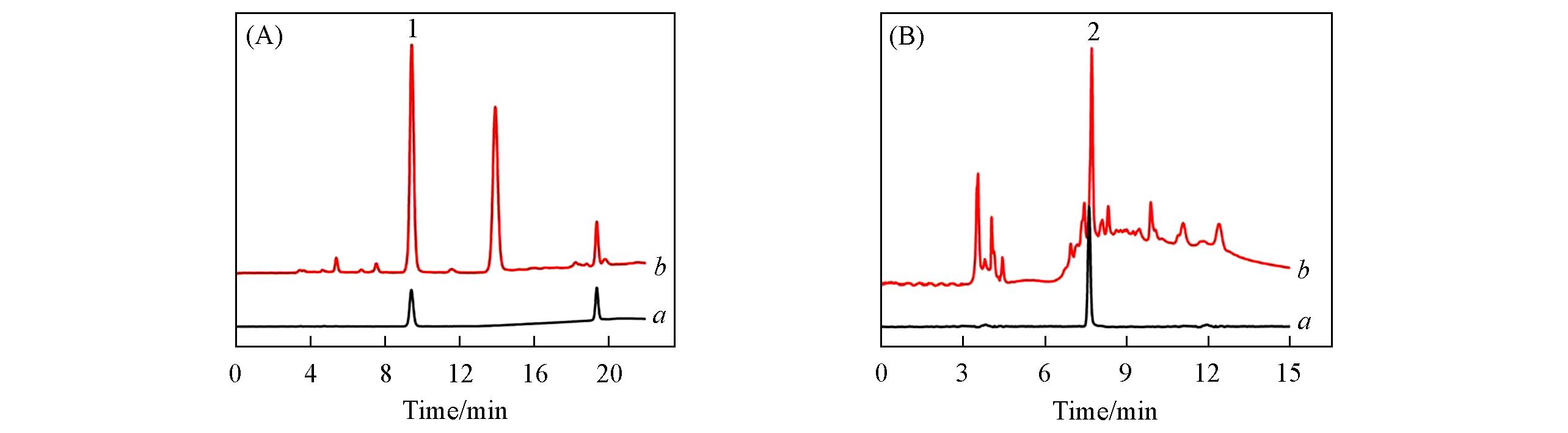
Fig.4 Typical chromatograms obtained by HPLC of 95.4 mg/L alpinetin standard solution(a) and extract of Alpinia katsumadai Hayata by MAE(b)(A) and 103.6 mg/L isoquercitrin standard solution(a) and extract of Amomum villosum by MAE(b)(B)Peak 1: alpinetin; peak 2: isoquercitrin.
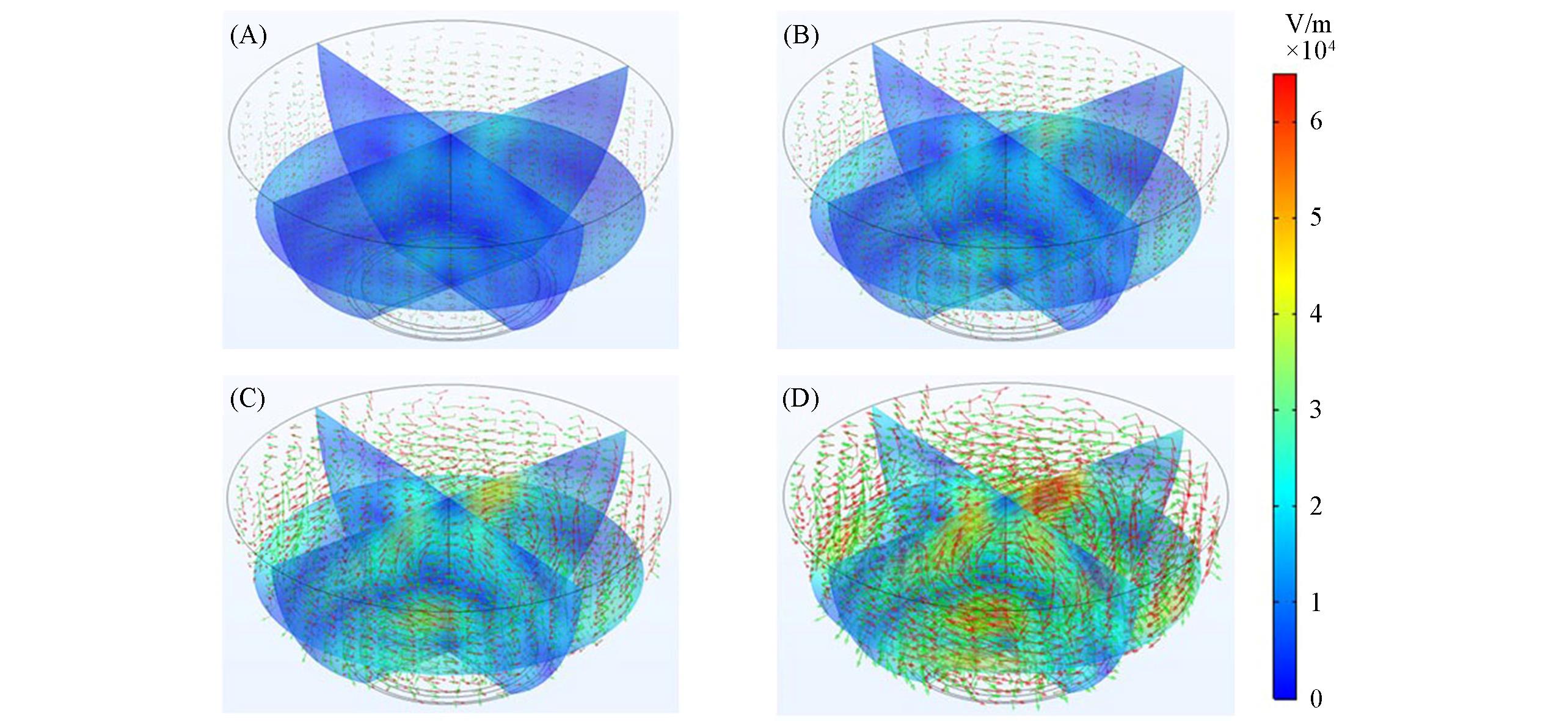
Fig.8 Simulation nephogram of electromagnetic field distribution of MAE under 100 s with microwave powers of 100 W(A), 200 W(B), 400 W(C) and 800 W(D)
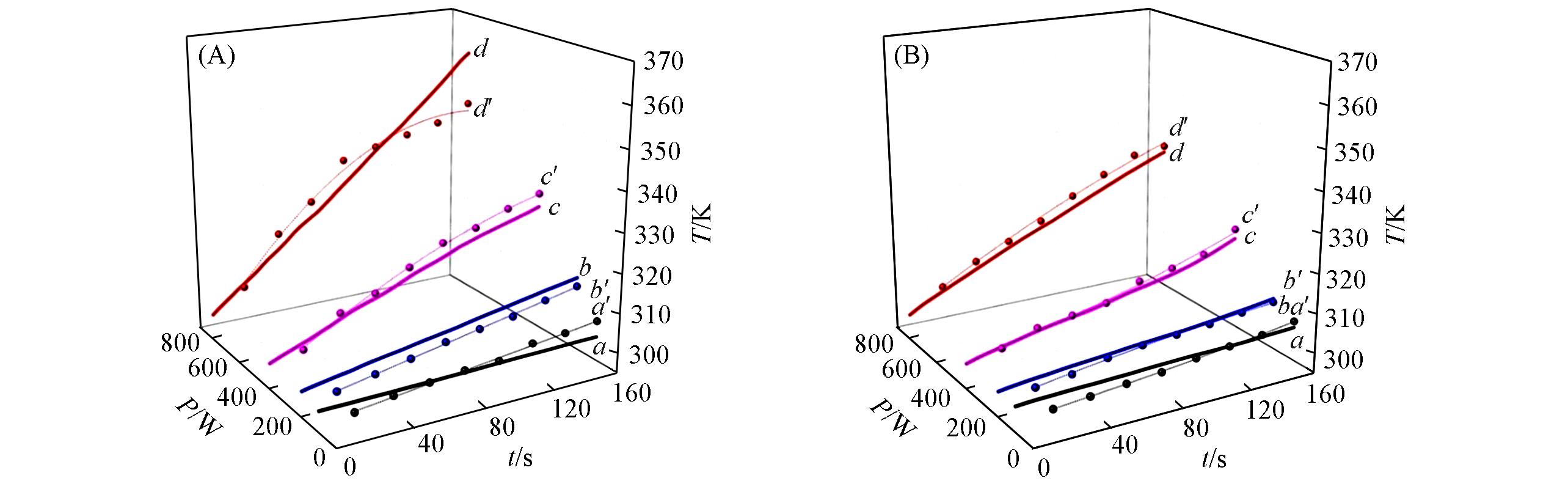
Fig.11 Comparison between simulated and experimental temperature evolutions for MAE alpinetin(A) and isoquercitrin(B)Simulation values: 100 W(a), 200 W(b), 400 W(c), 800 W(d); experimental values: 100 W(a′), 200 W(b′), 400 W(c′), 800 W(d′).
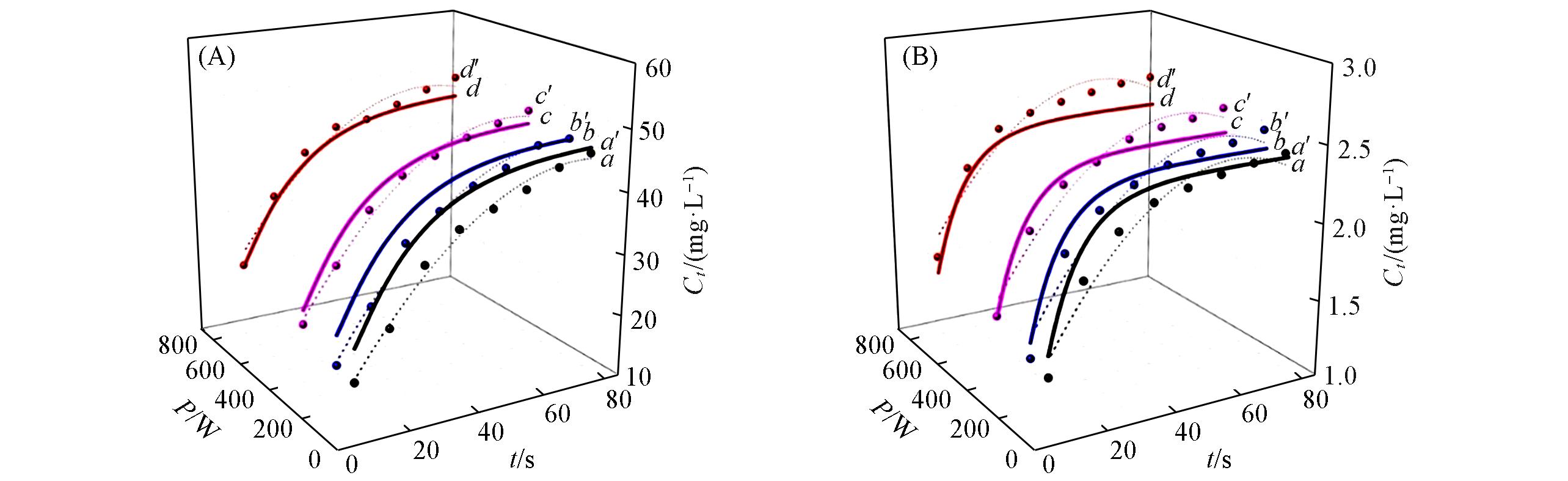
Fig.12 Comparison between simulated and experimental concentration evolutions for MAE alpinetin(A) and isoquercitrin(B)Simulation values: 100 W(a), 200 W(b), 400 W(c), 800 W(d); experimental values: 100 W(a′), 200 W(b′), 400 W(c′), 800 W(d′).
| 1 | Jiang H., Liu Z. G., Wang S. J., Criti. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr., 2018, 58(14), 2476―2489 |
| 2 | Kostas E. T., Beneroso D., Robinson J. P., Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2017, 77, 12―27 |
| 3 | Li Y., Huang K. M., Yang C., Gu M. J., J. Microwaves, 1999, 15(4), 345―353 |
| 4 | Pound R. V., Rev. Sci. Instrum., 1946, 17(11), 490―505 |
| 5 | Zhang F. S., Zhao Q., Yan X., Li H. L., Zhang P., Wang L., Zhou T. Y., Li Y., Ding L., Food Chem., 2016, 197, 943―949 |
| 6 | Li G. J., Zhang X., Liu T. T., Fan H. X., Liu H. C., Li S. Y., Wang D. W., Ding L., Food Sci. Hum. Well., 2021, 10, 375―382 |
| 7 | Llompart M., Celeiro M., Dagnac., TrAC. Trends Anal. Chem., 2019, 116, 136―150 |
| 8 | Liu Z. Y., Hu X. L., Bu F. Q., Ding L., Zhang H. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(3), 431―435(刘忠英, 胡秀丽, 卜凤泉, 丁兰, 张寒琦. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(3), 431―435) |
| 9 | Song W. T., Cai H. R., Du L. P., Zhao Q., Chen H. Y., Li G. J., Wang H., Xu Y., Ding L., Ren N. Q., Chromatographia, 2012, 75, 747―753 |
| 10 | Mirzadeh M., Arianejad M. R., Khedmat L., Carbohydr. Polym., 2020, 229, 115421 |
| 11 | Zhang H. F., Yang X. H., Wang Y., Trends Food Sci. Technol., 2011, 22(12), 672―688 |
| 12 | Franco⁃Vega A., Ramírez⁃Corona N., López⁃Malo A., Palou E., J. Food Eng., 2019, 247, 1―8 |
| 13 | Albarri R., Toprakçı İ., Kurtulbaş E., Şahin S., Biomass Convers. Biorefin., 2021, doi: 10.1007/s13399⁃021⁃014438 |
| 14 | Fan H. J., Xiao X. H., Li G. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6), 1049―1054(范华均, 肖小华, 李攻科. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(6), 1049―1054) |
| 15 | Fan H. J., Lin G. X., Xiao X. H., Li G. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(12), 2271―2276(范华均, 林广欣, 肖小华, 李攻科. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(12), 2271―2276) |
| 16 | Zin M. M., Anucha C. B., Bánvölgyi S., Foods, 2020, 9(7), 918 |
| 17 | Bagade S. B., Patil M., Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2021, 51(2), 138―149 |
| 18 | Zhao J. H., Yan X., Li H. Y., Zhang P., Zhou T. Y., Li Y., Cheng Y. H., Ding L., Anal. Methods, 2016, 8(45), 8015―8021 |
| 19 | Wang N. N., Zheng T., Jiang J. P., Wang P., Energy Conserv., 2020, 8, 98―102 |
| 20 | Pitchai K., Chen J., Birla S., Gonzalez R., Jones D., Subbiah J., J. Food Eng., 2014, 128, 60―71 |
| 21 | Laura A. C., Carlos A. P., Rodolfo H. M., Food Bioproc. Tech., 2012, 5(2), 738―749 |
| 22 | Chumnanpaisont N., Niamnuy C., Devahastin S., Chem. Eng. Sci., 2014, 116, 442―451 |
| 23 | Liu C. H., Xue H. K., Shen L. Y., Liu C., Zheng X. Z., Shi J., Xue S., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2019, 226, 286―298 |
| 24 | Pozar D., Microwave Engineering., 3rd Edition, Wiley, New York, 2005 |
| 25 | Jian Y., Yang X. Q., Huang K. M., Prog. Electromagn. Res. C, 2010, 17, 105―119 |
| 26 | Clark D. E., Folz D. C., West J. K., Mater. Sci. Eng., 2000, 287(2), 153―158 |
| 27 | Zhu H. C., He J. B., Hong T., Yang Q. Z., Wu Y., Yang Y., Huang K. M., Appl. Therm. Eng., 2018, 141, 648―658 |
| 28 | Wang J., Wang W., Guan Q., J. Beijing Jiaotong Univ., 2014, 38(5), 49―53 |
| 29 | Budd C. J., Hill A. D. C., Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer., 2011, 54(4), 807―817 |
| 30 | Thuto W., Banjong K., Processes, 2019, 7(8), 545 |
| 31 | Liu S. X., Ogiwara Y., Fukuoka M., Sakai N., J. Food Eng., 2014, 131, 142―153 |
| 32 | Yi Z. K., Gu W. J., Xu H. X., Cheng Y. D., Jin Y. Z., Sci. Technol. Food Ind., 2018, 39(24), 350―356 |
| 33 | Xiao X. H., Si X. X., Tong X., Li G. K., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2011, 81(3), 265―269 |
| 34 | Zhou Y. L., Lv H. T., Chinese Tradit. Pat. Med., 2011, 33(1), 145―148 |
| 35 | Li Z. Z., Pan R. L., Li Z., Zhao X. H., Si J. Y., Sci. Technol. Rev., 2009, 27(9), 30―33 |
| 36 | Lee C. S., Binner E., Winkworth-Smith C., John R., Gomes R., Robinson J., Chem. Eng. Sci., 2016, 149, 97―103 |
| 37 | Yeong S. P., Law M. C., Lee C. C. V., Chan Y. S., Int. Conf. Mater. Technol. Energy, 2017, 217, 012035 |
| 38 | González-Rivera J., Spepi A., Ferrari C., Duce C., Longo I., Falconieri D., Piras A., Tinè M. R., Green Chem., 2016, 18(24), 6482―6492 |
| 39 | Deng X., Huang H. H., Mod. Food Sci. Technol., 2011, 27(6), 626―629 |
| 40 | Jin Q. H., Chin. J. Anal. Chem., 1988, 16(7), 668―674 |
| [1] | SUN Zhetao, HE Yingjie, CHEN Shaojie, NIE Lu, HUANG Yuanqi, LIU Wei. Simulation of the Electrochemistry Process with the Coupling of Multiple Physical Fields for All-solid-state Lithium Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1598. |
| [2] | LI Jianwei,LI Xiang,ZHANG Jie,LEI Zhigang. Mechanism of the Interaction Between Ionic Liquid [Bmim][DBP] and Methanol for Seperation of Mixed C4/Methanol† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 983. |
| [3] | ZHU Xiao-Nan, WEI Shi-Gang, WANG Hao-Nan, SUN Ying, JIANG Chun-Zhu, ....... Analysis of Essential Oil from Cinnamomum cassia Presl by Microwave-assisted Extraction Coupled with Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(7): 1300. |
| [4] | ZHANG Fan1, YANG Yi1*, GUO Zhen-Ku2. Microwave-assisted Extraction of Rutin and Quercetin from Euonymus alatus(Thunb.) Sieb [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(8): 1480. |
| [5] | FAN Hua-Jun1,2, XIAO Xiao-Hua1, LI Gong-Ke1*. Kinetic Model of Microwave-assisted Extraction of the Effective Constituents from Lycoris radiata and Rhizma Polygoni Cuspidati [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6): 1049. |
| [6] | LIU Zhong-Ying1,2, HU Xiu-Li1,2, BU Feng-Quan2, DING Lan1, ZHANG Han-Qi1. Studies on the Chemical Change in the Process of Microwave-assisted Extraction of Flavonoids from Acanthopanax Senticosus Harms [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(3): 431. |
| [7] | FAN Hua-Jun1,2, LIN Guang-Xin1, XIAO Xiao-Hua1, LI Gong-Ke1. Investigation of Thermodynamic Mechanism for Extraction of Active Constituents in Lycoris radiata and Rhizma Polygoni Cuspidati Using Microwave-assisted Extraction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(12): 2271. |
| [8] | WANG Yu-Tang, YU Yong, WANG Zi-Ming, ZHOU Xin, BAI Li-Fei, DING Lan, ZHANG Han-Qi. High-pressure Microwave-assisted Extraction of Baicalin from Niuhuang Shangqing Pills [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(10): 1862. |
| [9] | WANG Zi-Ming, ZHOU Xin, ZHENG Jian, ZHANG Han-Qi, LIU Li, LI Ying, LIU Zhi-Hong, WANG Hong-Ju, ZENG Hong, HE Hui. Determination of Aromatic Amine Compounds in Lipstick by Microwave-assisted Extraction High Performance Liquid Chromatography [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(9): 1618. |
| [10] | YANG Yi, HOU Xiang-Yan, GUO Zhen-Ku. Microwave-assisted Extraction of Aloin from Fresh Aloe Leaves [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2005, 26(9): 1623. |
| [11] | LI Min-Jing, YOU Jing-Yan, LIU Zhong-Ying, ZHANG Han-Qi. Microwave-assisted Dynamic Extraction of Flavonoids from Flos Sophaoae [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(5): 850. |
| [12] | CHEN Lei, YANG Yi, ZHANG Xin-Xiang, GUO Zhen-Ku . Studies on the Microwave-assisted Extraction of Efficacious Ingredients in Salvia Mltiorrhiza Bunge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(1): 35. |
| [13] | XIONG Guo-Hua, LIANG Jin-Ming, ZOU Shi-Chun, HE Xiao-Qing, ZHANG Zhan-Xia . Microwave-assisted Extraction of PAHs from Soils [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1998, 19(10): 1560. |
| [14] | ZENG Ping, HU Jing-Yu. Studies on the Extraction Mechanism of Molybdenum by Primary Amine N1923 in Kerosene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 1994, 15(11): 1588. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||