

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 2156.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170221
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
GAO Ye1,3, WANG Wei2, PANG Liyun2, CAO Liyuan2, GUO Yupeng2,*( ), ZHAO Chun1,*(
), ZHAO Chun1,*( )
)
Received:2017-04-11
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-11-21
Contact:
GUO Yupeng,ZHAO Chun
E-mail:guoyupeng@jlu.edu.cn;zchun@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GAO Ye, WANG Wei, PANG Liyun, CAO Liyuan, GUO Yupeng, ZHAO Chun. One-step Synthesis of Activated Carbon from Molasses and Its Interfacial Adsorption Behavior†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2156.
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vt/(cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) | Vmes/(cm3·g-1) | Dave/nm | Smic/(m2·g-1) | Sext/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC/850/1/4∶1 | 1023 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 23.8 | 675 | 328 |
| CC | 544 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 10.3 | 345 | 199 |
Table 1 Textural characteristics and the specific capacity of AC/850/1/4∶1 and CC*
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Vt/(cm3·g-1) | Vmic/(cm3·g-1) | Vmes/(cm3·g-1) | Dave/nm | Smic/(m2·g-1) | Sext/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC/850/1/4∶1 | 1023 | 0.49 | 0.08 | 0.35 | 23.8 | 675 | 328 |
| CC | 544 | 0.26 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 10.3 | 345 | 199 |
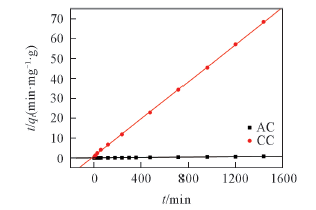
Fig.5 Linear kinetic plots of pseudo-second order model for Pb(Ⅱ) adsorptionPb(Ⅱ) concentration: 70 mg/L; volume of Pb(Ⅱ) solution: 50 mL; mass of AC and CC: 0.1 g; pH=5; contact time: 0~1440 min; temperature: 298 K.
| Adsorbent | qe,cal/(mg·g-1) | qe,exp/(mg·g-1) | 103 k2/g·(mg·min)-1 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 33.03 | 34.98 | 10.00 | 0.99999 |
| CC | 19.15 | 20.94 | 2.71 | 0.99981 |
Table 2 Pseudo-second order kinetic model constants for the adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ) onto adsorbents
| Adsorbent | qe,cal/(mg·g-1) | qe,exp/(mg·g-1) | 103 k2/g·(mg·min)-1 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 33.03 | 34.98 | 10.00 | 0.99999 |
| CC | 19.15 | 20.94 | 2.71 | 0.99981 |
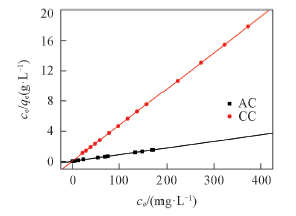
Fig.6 ce/qe-ce plots for Pb(Ⅱ) adsorptionPb(Ⅱ) concentration: 25—400 mg/L; volume of Pb(Ⅱ) solution: 50 mL; mass of AC and CC: 0.1 g; pH=5; contact time: 240 min; temperature: 298 K.
| Adsorbent | qm/(mg·g-1) | kL/(L·mg-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 880.0 | 0.74 | 0.9999 |
| CC | 480.2 | 0.43 | 0.9998 |
Table 3 Langmuir parameters for the adsorption of Pb(Ⅱ) onto adsorbents
| Adsorbent | qm/(mg·g-1) | kL/(L·mg-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AC | 880.0 | 0.74 | 0.9999 |
| CC | 480.2 | 0.43 | 0.9998 |
| [1] | Lee S. M., Laldawngliana C., Tiwari D., Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 195, 103—111 |
| [2] | Demiral H., Güngor C., J. Clean Prod., 2016, 124, 103—113 |
| [3] | Altun T., Pehlivan E., Food Chem., 2012, 132(2), 693—700 |
| [4] | Bouhamed F., Elouear Z., Bouzid J., Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng., 2012, 43, 741—749 |
| [5] | Silva T. L., Ronix A., Pezoti O., Souza L. S., Leandro P. K. T., Bedin K. C., Beltrame K. K., Cazetta A. L., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 3, 467—476 |
| [6] | Ma X., Liu X., Anderson D. P., Chang P. R., Food Chem., 2015, 181, 133—139 |
| [7] | Barczak M., Katarzyna M. Z., Gdula K., Katarzyna T. R., Dobrowolski R., Dabrowski A., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2015, 211, 162—173 |
| [8] | Liu X., Lee D. J., Bioresource Technol., 2014, 160, 24—31 |
| [9] | Gao Y., Yue Q., Gao B., Sun Y., Wang W., Li Q., Wang Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 217, 345—353 |
| [10] | Kyzas G. Z., Deliyanni E. A., Matis K. A., Colloid Surf. A, 2016, 490, 74—83 |
| [11] | Maneerung T., Liew J., Dai Y., Kawi S., Chong C., Wang C. H., Bioresource Technol., 2016, 200, 350—359 |
| [12] | Gao Y., Yue Q. Y., Wang W. Y., Li Q., Wang Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 232, 582—590 |
| [13] | Sun Y. Y., Yue Q. Y., Gao B. Y., Xu X., Li Q., Chem. Eng. J., 2012, 181, 790—797 |
| [14] | Ding L. L., Zou B., Gao W., Liu Q., Wang Z., Guo Y., Wang X., Liu Y., Colloid Surf. A, 2014, 446, 1—7 |
| [15] | Preethi S., Sivasamy A., Sivanesan S., Ramamurthi V., Swaminathan G., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2006, 45, 7627—7632 |
| [16] | Han X., Zou B., Gu X. X., Pang L. Y., Cao L. Y., Liu Q., Guo Y. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6), 1135—1139 |
| ( 韩雪, 邹博, 顾晓雪, 庞丽云, 曹礼媛, 刘琦, 郭玉鹏. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6 ), 1135—1139) | |
| [17] | Tseng R. L., Hazard. Mater., 2007, 147, 1020—1027 |
| [18] | Pang L. Y., Zou B., Zou Y. C., Guo Y. P., Colloid Surf. A, 2016, 504, 26—33 |
| [19] | Hayeeye F., Sattar M., Chinpa W., Sirchote O., Colloid Surf. A, 2017, 513, 259—266 |
| [20] | Lin T., Fu Y., Xu Y. J., Zhang D. J., Zhu Z. F., Transactions of China Pulp and Paper,2016, 31(1), 7—12 |
| ( 林涛, 付玥, 徐永建, 张鼎军, 朱振峰. 中国造纸学报, 2016, 31(1 ), 7—12 |
| [1] | LI Xiangnan,YU Mingming,FAN Yong,WANG Qiuxian,ZHANG Huishuang,YANG Shuting. Study on Electrochemical Performances of N-doped P/C Composite as Anode Material of Lithium Ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2360. |
| [2] | LIU Yanhua, JIN Lu, XUE Beichen, GUO Yupeng. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of Rice Husk Based Activated Carbon Modified by Pitch† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1242. |
| [3] | GAO Jun, HU Hui, LIU Xueyan. Preparation and Evaluation of Modified Cyanobacteria-derived Activated Carbon for CO2 Adsorption† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 284. |
| [4] | WANG Danfeng, YANG Haiyan, NING Yuesheng, ZHAO Binyuan. Morphosynthesis of Porous Silver Cubes on the Surface of Hydrogen-pretreated Monolithic Activated Carbon [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1503. |
| [5] | LIU Zile, ZENG Zequan, YANG Jieyang, CUI Yan, WU Ailian, LI Zhe, HUANG Zhanggen. Degradation of Phenol with Persulfate Activated by Surface Modified Activated Carbon† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1241. |
| [6] | GAO Ye, PANG Liyun, CAO Liyuan, WANG Wei, GUO Yupeng, ZHAO Chun. Application in Electric Double Layer Capacitor of Porous Carbon Derived from Potassium Carbonate Activated Molasses† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 341. |
| [7] | ZHANG Rongbin, TONG Sai, YANG Jinmei, TANG Xiannong, HUANG Chuanqing, WANG Xuewen, FENG Gang, CAI Jianxin. Graphene Supported Nickel Catalyst for Methanation of Carbon Dioxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2255. |
| [8] | ZHANG Yuanyuan, LI Fenpei, LIU Xiangqing, CHEN Haiyan, LUO Ying, JING Lihong, LU Jiaxing, ZHANG Guirong. Methanol Electrocatalytic Oxidation on Pt/Poly(o-toluidine) Film/Activated Carbon Doped Graphite Carbon Paste Electrode† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2320. |
| [9] | LU Miao, LIU Jianyun, WANG Shiping, CHENG Jian. Preparation of Sulfonated Graphene/Activated Carbon Composite Electrode for Asymmetric Capacitive Deionization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1546. |
| [10] | GAO Jichao, QI Li, WANG Hongyu. EQCM Studies on the Effect of Anti-freezing Additives on the Storage Behavior of Ions at Activated Carbon Electrodes in NaClO4 Aqueous Solutions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3): 608. |
| [11] | GAO Ji-Chao, YIN Jiao, QI Li, WANG Hong-Yu. Electrochemical Quartz Crystal Microbalance Studies on the Storage Behavior of Ions at Activated Carbon Electrodes in NaClO4 Aqueous Solutions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7): 1743. |
| [12] | WEN Bin, WEI Shuang, SHI Zhan, LIN Hai-Bo, LU Hai-Yan. Capacitance Performance and Model Analysis of Activated Carbon Derived from Rice Husks [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(3): 674. |
| [13] | LI Na, ZHU Jian, ZHA Qing-Fang. Quantitative and Qualitative Analyses of Oxygen-containing Surface Functional Groups on Activated Carbon [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(03): 548. |
| [14] | NIU Yao-Lan, MA Cheng-Yu*, LI Deng-Xin, LI Xue-Wen. Preparation and Characterization of Activated Carbon from Potassium Hydroxide Activated Linen Fabric Waste [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(10): 1929. |
| [15] | ZHANG Yue, ZHANG Hong-Sheng, GUO Wei-Hong, WU Chi-Fei*. Effects of Annealing Condition on the Glass Transition Behavior of PET in R-PET/LLDPE-g-MA Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(5): 1024. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||