

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 1542.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170193
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Huiqiang1, PENG Chao1,*( ), CHEN Ning2, LIU Yangping1,*(
), CHEN Ning2, LIU Yangping1,*( )
)
Received:2017-03-31
Online:2017-09-10
Published:2017-07-04
Contact:
PENG Chao,LIU Yangping
E-mail:pengchao@tmu.edu.cn;liuyangping@tmu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Huiqiang, PENG Chao, CHEN Ning, LIU Yangping. Novel Fluorescent/EPR Difunctional Probe for Detecting Hypochlorite†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1542.
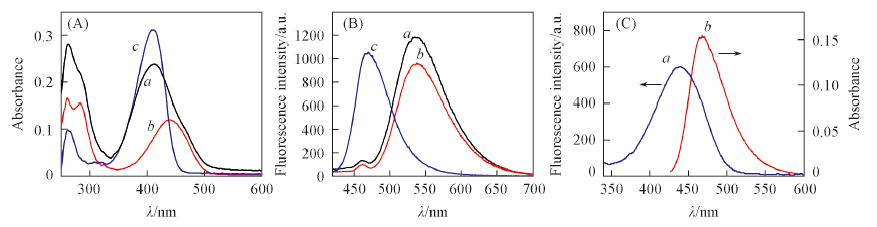
Fig.1 Absorption spectra of 10 μmol/L of CNNOH(a), compound 4(b) or compound 5(c) in PBS buffer(A), fluorescence spectra of 1 μmol/L of CNNOH(a), compound 4(b) or compound 5(c)(B) and overlap of fluorescence spectra(a) of compound 5(donor, 10 μmol/L) and absorption spectra(b) of compound 4(acceptor, 1 μmol/L)(C)
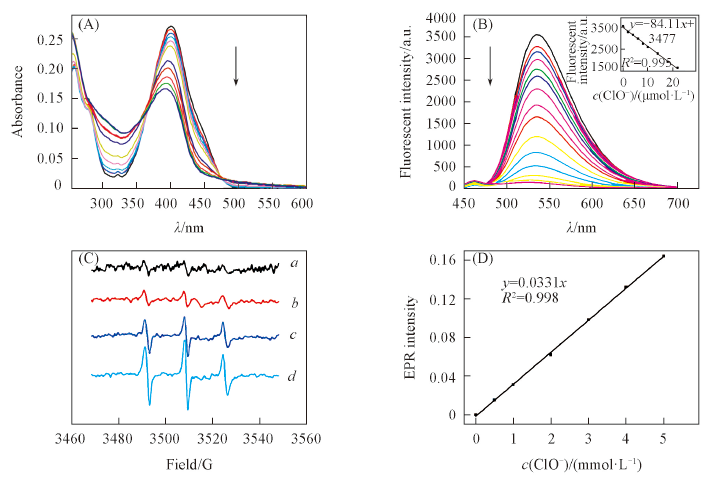
Fig.3 Spectra changes of CNNOH upon addition of ClO-(A) Absorption spectra of CNNOH(10 μmol/L) with the reaction of ClO-(0—1 mmol/L); (B) fluorescence spectra of CNNOH(1 μmol/L) with the reaction of ClO-(0—100 μmol/L); (C) EPR spectra of CNNOH(50 μmol/L) with the reaction of ClO-(0, 0.5, 2.5, 5 mmol/L); (D) fitting curve of EPR intensity with different concentrations of ClO-(0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 mmol/L).
| [1] | Nussbaum C., Klinke A., Adam M., Baldus S., Sperandio M., Antioxid. Redox. Sign., 2013, 18(6), 692—713 |
| [2] | Winter J., Ilbert M., Graf P. C. F., Özcelik D., Jakob U., Cell,2008, 135(4), 691—701 |
| [3] | Winterbourn C. C., BBA-Gen. Subjects, 2014, 1840(2), 730—738 |
| [4] | Kettle A. J., Albrett A. M., Chapman A. L., Dickerhof N., Forbes L. V., Khalilova I., Turner R., BBA-Gen. Subjects, 2014, 1840(2), 781—793 |
| [5] | Hawkins C. L., Davies M. J., Biochem. J., 1998, 332(3), 617—625 |
| [6] | Sugiyama S., Kugiyama K., Aikawa M., Nakamura S., Ogawa H., Libby P., Arterioscl. Throm. Vas., 2004, 24(7), 1309—1314 |
| [7] | Zavodnik L. B., Zavodnik I. B., Lapshyna E. A., Buko V. U., Bryszewska M. J., Bioelectrochem., 2002, 58(2), 157—161 |
| [8] | Liu B. Y., Hou X. R., Zhou Q. G., Tian J. W., Zhu P., Xu J., Hou F. F., Fu N., Free Radical Res., 2011, 45(6), 662—671 |
| [9] | Yap Y. W., Whiteman M., Cheung N. S., Cell Signal, 2007, 19(2), 219—228 |
| [10] | Podrez E. A., Abu-Soud H. M., Hazen S. L., Free Radical Bio. Med., 2000, 28(12), 1717—1725 |
| [11] | Wang Y. B., Zhao B. X., Chinese J. Org. Chem., 2016, 36(7), 1539—1554 |
| (王延宝, 赵宝祥.有机化学,2016, 36(7), 1539—1554) | |
| [12] | Gong H. L., Jiang Y., Hou R. C., Ding X. Q., J. Fluoresc., 2016, 26(2), 403—406 |
| [13] | Xing P., Gao K., Wang B., Gao J., Yan H., Wen J., Li W. S., Xu Y. Q., Li H. Q., Chen J. X., Wang W., Sun S. Q., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(28), 5064—5066 |
| [14] | Chen W. C., Venkatesan P., Wu S. P., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2015, 882, 68—75 |
| [15] | Lee H. J., Cho M. J., Chang S. K., Inorg. Chem., 2015, 54(17), 8644—8649 |
| [16] | Cheng G., Fan J., Sun W., Cao J., Hu C., Peng X., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(8), 1018—1020 |
| [17] | Wang C. P., Ye L., Xie A. J., Li G., Li A. X., Zhang Z. Y., Zhang H., Res. Explor. Lab., 2013, 32(5), 5—7 |
| (王翠平, 叶柳, 谢安建, 李广, 李爱侠, 张子云, 张惠.实验室研究与探索,2013, 32(5), 5—7) | |
| [18] | Wang B., Du L. B., Liu Y. P., Zhou J. W., Liu Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11), 2366—2369 |
| (王兵, 杜立波, 刘阳平, 周建威, 刘扬.高等学校化学学报,2014, 35(11), 2366—2369) | |
| [19] | Jia X., Chen Q., Yang Y., Tang Y., Wang R., Xu Y., Zhu W., Qian X., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(34), 10778—10781 |
| [20] | Liu Y., Song Y., De P. F., Liu X., Villamena F. A., Zweier J. L., Free Radical Bio. Med., 2012, 53(11), 2081—2091 |
| [21] | Xing P. P., Zhang H. Y., Li N., Tong L. L., Xu K. H., Tang B., J. Anal. Sci., 2009, 25(6), 721—725 |
| (邢佩佩, 张海燕, 李娜, 佟丽丽, 徐克花, 唐波.分析科学学报,2009, 25(6), 721—725) | |
| [22] | Zhou X., Su F., Lu H., Senechal-Willis P., Tian Y., Johnson R. H., Meldrum D. R., Biomaterials,2012, 33(1), 171—180 |
| [23] | Matsuoka Y., Yamato M., Yamada K., J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 2016, 58(1), 16—22 |
| [24] | Liang F., Wang D., Ma P., Wang X., Song D., Yu Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(5), 724—729 |
| [25] | Ganiev I. M., Timerghazin Q. K., Khalizov A. F., Shereshovets V. V., Grigor’ev A. I., Tolstikov G. A., J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2001, 14(1), 38—42 |
| [26] | Wang J., Ni Y., Shao S., Talanta,2016, 147, 468—472 |
| [27] | Zhang Y. R., Chen X. P., Jing S., Zhang J. Y., Yuan Q., Miao J. Y., Zhao B. X., Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(91), 14241—14244 |
| [28] | Wu Y., Wang J., Zeng F., Huang S., Huang J., Xie H., Yu C., Wu S., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2016, 8(2), 1511—1519 |
| [29] | Wen J., Zhang X., Chen X., Guo Y., Chang P., J. Food Sci., 2004, 25(10), 351—357 |
| (文镜, 张西, 陈曦, 郭豫, 常平.食品科学,2004, 25(10), 351—357) |
| [1] | CHU Yuyi, LAN Chang, LUO Ergui, LIU Changpeng, GE Junjie, XING Wei. Single-atom Cerium Sites Designed for Durable Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalyst with Weak Fenton Effect [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [2] | ZHAO Yongmei, MU Yeshu, HONG Chen, LUO Wen, TIAN Zhiyong. Bis-naphthalimide Derivatives for Picronitric Acid Detection in Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210765. |
| [3] | TANG Qian, DAN Feijun, GUO Tao, LAN Haichuang. Synthesis and Application of Quinolinone-coumarin-based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Recognition of Hg2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210660. |
| [4] | LI Lun, ZHANG Jingyan, LUO Jing, LIU Ren, ZHU Yi. Synthesis and Properties of UV/Vis-LED Excitable Photoinitiators Based on Coumarin Pyridinium Salt [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220178. |
| [5] | ZHANG Xiaofei, LIU Jiaxin. Visible Light Induced Cyclization of O-Alkenylcarboxanilide to 2-Quinolinone [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220274. |
| [6] | WANG Di, ZHONG Keli, TANG Lijun, HOU Shuhua, LYU Chunxin. Synthesis of Schiff-based Covalent Organic Framework and Its Recognition of I ‒ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220115. |
| [7] | LI Anran, ZHAO Bing, KAN Wei, SONG Tianshu, KONG Xiangdong, BU Fanqiang, SUN Li, YIN Guangming, WANG Liyan. ON-OFF-ON Double Colorimetric and Fluorescent Probes Based on Phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole Derivatives and Their Living Cells Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2403. |
| [8] | LIU Simei, LIU Weihua, LU Manli, ZHANG Wenli, SHEN Rongfang, WANG Mouhua. Evolution of the Radicals in γ-Rays Irradiated Medical Grade Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2602. |
| [9] | HUANG Shan, YAO Jiandong, NING Gan, XIAO Qi, LIU Yi. Efficient Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2412. |
| [10] | YANG Xinjie, LAI Yanqiong, LI Qiuyang, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, PANG Pengfei, YANG Wenrong. An Enzyme-free and Label-free Fluorescent Probe for Detection of Microcystin-LR Based on Circular DNA-Silver Nanoclusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3600. |
| [11] | CHEN Weiju, CHEN Shiya, XUE Caoye, LIU Bo, ZHENG Jing. Fluorescent Probe for Hypoxia-triggered Imaging and Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3433. |
| [12] | HUANG Jialing,LIU Fengjiao,WANG Tingting,LIU Cuie,ZHENG Fengying,WANG Zhenhong,LI Shunxing. Nitrogen and Sulfur co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Accurate Detection of pH in Gastric Juice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [13] | XU Wenyi,FENG Yisi. Oxidative Trifluoromethylation of CF3SO2Na with Olefins Mediated by Diacetyl† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1567. |
| [14] | WANG Qianying, CUI Shuxun. Investigation of Formation Mechanism of Polydopamine by Adding Free Radical Quencher † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1378. |
| [15] | HU Zhiyuan, WAN Qiuxiang, ZHOU Hang, SONG Chuanjun, CHANG Junbiao. Synthesis of 6β-Hydroxy-5,5,8aβ-trimethyloctahydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one Toward the Establishment of the Scaffold of Phenylspirodrimane Meroterpenoid Natural Products † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 955. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||