

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (5): 814.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160875
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SUN Xiangli2, HE Hong1,2,3,*( ), SU Yaochao2, YAN Jingfang2, SONG Liyun1,2, QIU Wenge1,2
), SU Yaochao2, YAN Jingfang2, SONG Liyun1,2, QIU Wenge1,2
Received:2016-12-05
Online:2017-05-10
Published:2017-04-13
Contact:
HE Hong
E-mail:hehong@bjut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SUN Xiangli, HE Hong, SU Yaochao, YAN Jingfang, SONG Liyun, QIU Wenge. CeO2-TiO2 Mixed Oxides Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx with NH3: Structure-properties Relationships†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 814.
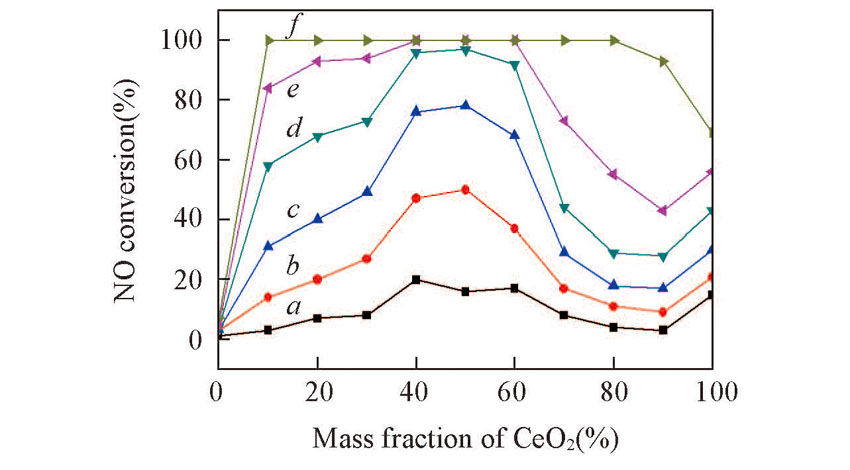
Fig.1 NH3-SCR activity of CeO2-TiO2 catalystsReaction condition: 1340 mg/m3 NO, 760 mg/m3 NH3, 6% O2, He balance, GHSV: 3×104 h-1. Temperature/℃: a. 140; b. 160; c. 180; d. 200; e. 220; f. 260.
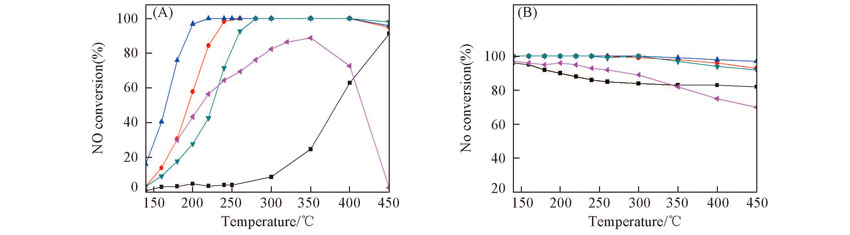
Fig.2 NH3-SCR activity(A) and N2 selectivity(B) over the catalystsReaction conditions: 1340 mg/m3 NO, 760 mg/m3 NH3, 6% O2, He balance, GHSV: 3×104 h-1.■ TiO2; ● 10CeTi; ▲ 50CeTi; ▼ 90CeTi; ? CeO2.
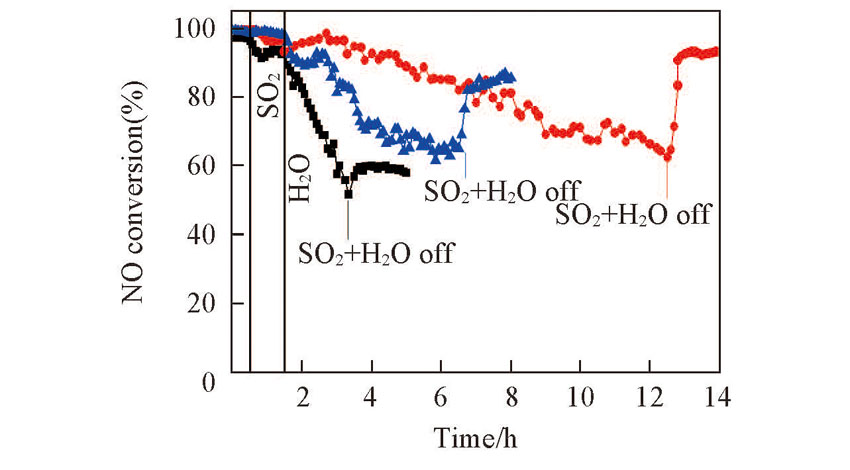
Fig.3 NH3-SCR activity over the catalysts in the presence of H2O/SO2 at 270 ℃Reaction condition: 1340 mg/m3 NO, 760 mg/m3 NH3, 6% O2, 5% H2O, 860 mg/m3 SO2, N2 balance, GHSV: 3×104 h-1. ■ 10CeTi; ● 50CeTi; ▲ 90CeTi.
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Crystallite size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 57.1 | 0.11 | 21 |
| 10CeTi | 91.6 | 0.18 | 15 |
| 50CeTi | 129.0 | 0.21 | |
| 90CeTi | 85.3 | 0.15 | 10 |
| CeO2 | 70.1 | 0.17 | 13 |
Table 1 Specific surface area, pore volume and average crystallite sizes of the catalysts
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3·g-1) | Crystallite size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2 | 57.1 | 0.11 | 21 |
| 10CeTi | 91.6 | 0.18 | 15 |
| 50CeTi | 129.0 | 0.21 | |
| 90CeTi | 85.3 | 0.15 | 10 |
| CeO2 | 70.1 | 0.17 | 13 |
| Sample | Molar fraction(%) | Molar ratio(%) | H2 consumption/(mmol· | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | Ti | O | Ce3+/(Ce3++Ce4+) | Oα/(Oα+Oβ) | ||
| TiO2 | 36.1 | 63.9 | 12.2 | 0.13 | ||
| 10CeTi | 1.7 | 34.7 | 63.6 | 32.1 | 13.3 | 0.35 |
| 50CeTi | 7.3 | 24.2 | 68.5 | 18.5 | 25.5 | 2.30 |
| 90CeTi | 18.1 | 4.1 | 77.8 | 18.7 | 35.7 | 4.04 |
| CeO2 | 25.6 | 74.4 | 14.8 | 15.1 | 0.73 | |
Table 2 XPS data and H2 consumption of the catalysts
| Sample | Molar fraction(%) | Molar ratio(%) | H2 consumption/(mmol· | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce | Ti | O | Ce3+/(Ce3++Ce4+) | Oα/(Oα+Oβ) | ||
| TiO2 | 36.1 | 63.9 | 12.2 | 0.13 | ||
| 10CeTi | 1.7 | 34.7 | 63.6 | 32.1 | 13.3 | 0.35 |
| 50CeTi | 7.3 | 24.2 | 68.5 | 18.5 | 25.5 | 2.30 |
| 90CeTi | 18.1 | 4.1 | 77.8 | 18.7 | 35.7 | 4.04 |
| CeO2 | 25.6 | 74.4 | 14.8 | 15.1 | 0.73 | |
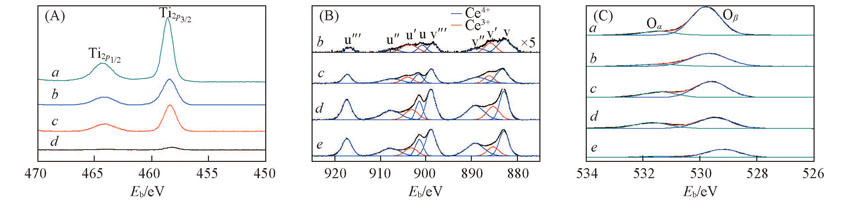
Fig.7 XPS spectra of Ti2p(A), Ce3d(B) and O1s(C) of the catalystsa.TiO2; b.10CeTi; c.50CeTi; d.90CeTi; e.CeO2.(C) Molar fraction of Oα: a. 12.2%; b. 13.3;c. 25.5%; d. 35.7%; e. 15.1%.
| Sample | Desorption area in NO+O2-TPD | Desorption area in NH3-TPD, total N | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO* | N | ||
| TiO2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 10CeTi | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| 50CeTi | 3.4 | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| 90CeTi | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| CeO2 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
Table 3 Amounts of desorption species from the samples during NO+O2-TPD and NH3-TPD experiments
| Sample | Desorption area in NO+O2-TPD | Desorption area in NH3-TPD, total N | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NO* | N | ||
| TiO2 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| 10CeTi | 1.8 | 1.3 | 1.2 |
| 50CeTi | 3.4 | 2.2 | 1.9 |
| 90CeTi | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| CeO2 | 4.4 | 2.8 | 0.5 |
| [1] | Liu N., Wang J. Q., Chen B. H., Li Y. X., Zhang R. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10), 1817—1825 |
| (刘宁, 王继琼, 陈标华, 李英霞, 张润铎.高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(10), 1817—1825) | |
| [2] | Shan W. P., Liu F. D., Yu Y. B., He H., Chin. J. Catal., 2014, 35(8), 1251—1259 |
| (单文坡, 刘福东, 余运波, 贺泓.催化学报, 2014,35(8), 1251—1259) | |
| [3] | Liu J. D., Huang Z. G., Li Z., Guo Q. Q., Li Q. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3), 589—595 |
| (刘建东, 黄张根, 李哲, 郭倩倩, 李巧艳.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(3), 589—595) | |
| [4] | Tang C. J., Zhang H. L., Dong L., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2016, 6, 1248—1264 |
| [5] | Li Q., Gu H. C., Li P., Zhou Y. H., Liu Y., Qi Z. N., Xin Y., Zhang Z. L., Chin. J. Catal., 2014, 35(8), 1289—1298 |
| (李倩, 谷华春, 李萍, 周钰浩, 刘莹, 齐中囡, 辛颖, 张昭良.催化学报, 2014,35(8), 1289—1298) | |
| [6] | Li Z. G., Li J. H., Liu S. X., Ren X. N., Ma J., Su W. K., Peng Y., Catalysis Today, 2015, 258, 11—16 |
| [7] | Yu M., Li C. T., Zeng G. M., Zhou Y., Zhang X. N., Xie Y., Applied Surface Science, 2015, 342, 174—182 |
| [8] | Zhou A. Y., Yu D. Q., Yang L., Sheng Z. Y., Applied Surface Science, 2016, 378, 167—173 |
| [9] | Chen L., Si Z. C., Wu X. D., Weng D., Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 8134—8145 |
| [10] | Liu J., Li X. Y., Zhao Q. D., Ke J., Xiao H. N., Lv X. J., Liu S. M., Tadé M., Wang S. B., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2017, 200, 297—308 |
| [11] | Luo M. F., Chen J., Chen L. S., Lu J. Q., Feng Z. C., Li C., Chem. Mater., 2001, 13, 197—202 |
| [12] | Gao X., Jiang Y., Zhong Yi., Luo Z. Y., Cen K. F. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 174, 734—739 |
| [13] | Li P., Xin Y., Li Q., Wang Z. P., Zhang Z. L., Zheng L. R., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, 46, 9600—9605 |
| [14] | Wang H. Q., Cao S., Fang Z., Yu F. X., Liu Y., Weng X. L., Wu Z. B., Applied Surface Science, 2015, 330, 245—252 |
| [15] | Xiao X., Xiong S.C., Shi Y. J., Shan W. P., Yang S. J.,J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120, 1066—1076 |
| [16] | Song L. Y., Zhan Z. C., Liu X. J., He H., Qiu W. G., Zi X. H., Chin. J. Catal., 2014, 35(7), 1030—1035 |
| (宋丽云, 展宗城, 刘晓军, 何洪, 邱文革, 訾学红.催化学报, 2014,35(7), 1030—1035) | |
| [17] | Chao J. D., He H., Song L. Y., Fang Y. J., Liang Q. M., Zhang G. G., Qiu W. G., Zhang R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(3), 523—530 |
| (晁晶迪, 何洪, 宋丽云, 房玉娇, 梁全明, 张桂臻, 邱文革, 张然.高等学校化学学报, 2015,36(3), 523—530) | |
| [18] | Zhang T., Qu R. Y., Su W. K., Li J. H., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2015, 176/177, 338—346 |
| [19] | Yan D. J., Yu Y., Huang X. M., Liu S. J., Liu Y. H., J. Fuel. Chem. Technol., 2016, 44(2), 232—238 |
| [20] | Shi Z. N., Yang P., Tao F., Zhou R. X., Chem. Eng. J., 2016, 295, 99—108 |
| [21] | Song Z. X., Zhang Q. L., Ning P., Liu X., Fan J., Huang Z. Z., J. Rare Earths, 2016, 34(7), 667—674 |
| (宋忠贤, 张秋林, 宁平, 刘昕, 樊洁, 黄真真.稀土学报, 2016,34(7), 667—674) | |
| [22] | Chen L., Li J. H., Ge M. F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 21177—21184 |
| [23] | Su Y. F., Tang Z. C., Han W. L., Zhang P., Song Y., Lu G. X., Cryst. Eng. Comm., 2014, 16, 5189—5197 |
| [24] | Ferrizz R. M., Gorte R. J., Vohs J. M., Catal. Lett., 2002, 82(1/2), 123—129 |
| [25] | Bêche E., Charvin P., Perarnau D., Abanades S., Flamant G., Surface & Interface Analysis, 2008, 40(3/4), 264—267 |
| [26] | Peng Y., Wang C. Z., Li J. H., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2014, 144, 538—546 |
| [27] | Boningari T., Ettireddy P. R., Somogyvari A., Liu Y., Vorontsov A., McDonald C. A., Smirniotis P. G., J. Catal., 2015, 325, 145—155 |
| [28] | Shan W. P., Liu F. D., He H., Shi X. Y., Zhang C. B., Catal. B: Environ., 2012, 115/116, 100—106 |
| [29] | Chu X. L., Lu Z. S., Yang Z. X., Ma D. W., Zhang Y. X., Li S. S., Gao P. Y.,Phys. Lett. A, 2014, 378, 659—666 |
| [30] | Xu W. Q., He H., Yu Y. B., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2009, 113, 4426—4432 |
| [31] | Creaser D. A., Harrison P. G., Catal. Lett., 1994, 23, 13—24 |
| [32] | Maqbool M. S., Pullur A. K., Ha H. P., Catal. B: Environ., 2014, 152/153, 28—37 |
| [33] | Li X., Li J. H., Peng Y., Chang H. Z., Zhang T., Zhao S., Si W. Z., Hao J. M., Catal. B: Environ., 2016, 184, 246—257 |
| [34] | Zhou A. Y., Yu D. Q., Yang L., Sheng Z. Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 378, 167—173 |
| [35] | Yang N. Z., Guo R. T., Pan W. G., Chen Q. L., Wang Q. S., Lu C. Z., Wang S. X., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 378, 513—518 |
| [1] | LIU Qingqing, WANG Pu, WANG Yongshuai, ZHAO Man, DONG Huanli. Synthesis and Topochemical Polymerization Study of Naphthalene/perylene Imides Substituted Diacetylene Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220091. |
| [2] | SHI Naike, ZHANG Ya, SANSON Andrea, WANG Lei, CHEN Jun. Uniaxial Negative Thermal Expansion and Mechanism in Zn(NCN) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [3] | YUE Shengli, WU Guangbao, LI Xing, LI Kang, HUANG Gaosheng, TANG Yi, ZHOU Huiqiong. Research Progress of Quasi-two-dimensional Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1648. |
| [4] | TIAN Xia,YANG Fuqun,YUAN Wei,ZHAO Lei,YAO Lei,ZHEN Xiaoli,HAN Jianrong,LIU Shouxin. Synthesis, Structure and Recognition Properties of Macrocyclic Crown Ethers with Oxadiazole † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 490. |
| [5] | LIU Dongmei,SU Yajing,LI Shanshan,XU Qiwei,LI Xia. Transition Metal Coordination Polymers Constructed by 4-(4-Carboxyphenoxy)isophthalic Acid: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Fluorescence Sensing and Photocatalysis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 253. |
| [6] | QIN Liulei,LIU Yang,GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi. Synthesis and Switchable Dielectric Properties of an Inorganic-organic Hybrid Complex [H2(DABCO)CuCl4]·H2O † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 70. |
| [7] | ZHANG Ling,DUAN Hongchang,TAN Zhengguo,WU Qinming,MENG Xiangju,XIAO Fengshou. Recent Advances in the Preparation of 8MR Zeolites for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx(NH3-SCR) in Diesel Engines † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 19. |
| [8] | LI Chunxiao, LI Jian, LIANG Wenjun, LIANG Quanming. Low Temperature NH3-SCR Activity of Cr Doped V2O5-WO3/TiO2 Catalyst† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1447. |
| [9] | LI Bing,WANG Xuemin,BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing. Synthesises, Structures and Antibacterial Activities of a Series of Rare Earth Nitrogen Heterocyclic Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 632. |
| [10] | ZHU Hongtai,SONG Liyun,HE Hong,YIN Mengqi,CHENG Jie,SUN Yanming,LI Shining,QIU Wenge. Sulfur Tolerance of the CeTiOx Catalysts for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO with NH3† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 350. |
| [11] | WANG Dongmei,LIU Zihua,LI Guanghua,LIU Yunling,LI Chunxia. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescent Property of Indium-based Bimetallic Metal-organic Frameworks† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1886. |
| [12] |
TIAN Huan, ZHANG Menglong, WANG Lisha, TONG Bihai, ZHAO Zhuo.
Synthesis of 4,13-Dithio Benzene and-18-Crown-6 and Its Selective Extractability on A |
| [13] | ZHU Lei,HAN Junyan,CHANG Haizhen,QIU Yuyuan,ZHANG Yanan,PENG Danni,HU Wei,MIAO Shaobin. Different Pathways for the Cyclocondensation Reactions of 1,2-Diamine and 1,2-Diketone† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2686. |
| [14] | CHEN Qidan, TANG Junjie, FANG Qianrong. Highly Stable Fluorine Containing Hierarchical Porous Covalent Organic Framework† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2357. |
| [15] | LI Zheng, LI Rui, LI Xia. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Fluorescent Properties of Transition Metal Complexes Constructed with 2-(3'-Carboxyphenoxy)benzoic Acid and N-Donor Ligands† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2363. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||