

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 1235.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160895
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2016-12-14
Online:2017-07-10
Published:2017-06-12
Contact:
WANG Rui
E-mail:wangrui@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Xinpeng, WANG Rui. Desulfurization Performance of Polyethylene Polyamine Supported on Modified Clay†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1235.
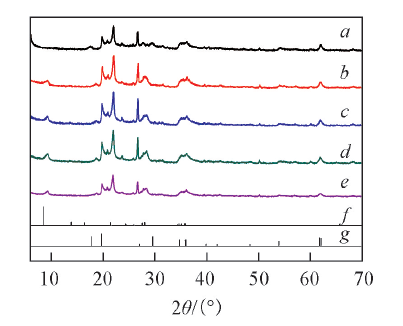
Fig.1 XRD patterns of the clay before(a) and after calcination(b—e)Temperature/℃: b. 300; c. 400; d. 500; e. 600. f. palygorskite-(Mg,Al)5(Si,Al)8O20(OH)2∙8H2O(PDF No.21-0958); g. montmorillonite-Ca0.2(Al,Mg)2Si4O10(OH)2∙4H2O(PDF No.13-0135).
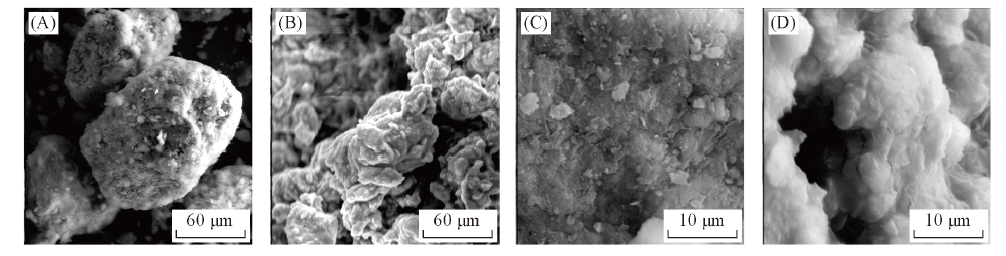
Fig.3 SEM images of sorbent before(A, C) and after(B, D) loading polyethylene polyamine Images (C) and (D) are the enlarged images of (A) and (B), respectively.
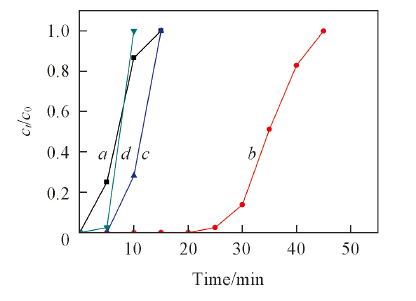
Fig.5 Effect of adsorption condition on the desulfurization performance of sorbenta. Without steam, 20 ℃; b. with steam, 20 ℃; c. with steam, 35 ℃; d. with steam, 50 ℃.
| [1] | Chen Q. J., Wang Z., Long D. H., Liu X. J., Zhan L., Liang X. Y., Qiao W. M., Ling L. C., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, 49(7), 3152—3159 |
| [2] | Wang X., Ma X., Xu X., Sun L., Song C., Top. Catal., 2008, 49(1/2), 108—117 |
| [3] | Wang R., Sep. Purif. Technol., 2003, 31(1), 111—121 |
| [4] | Tian S., Mo H., Zhang R., Ning P., Zhou T., Adsorption,2009, 15(5/6), 477—488 |
| [5] | Seredych M., Bandosz T. J., Energ. Fuel., 2008, 22(2), 850—859 |
| [6] | Shi Y., Ning P., Wang X., Jiang M., Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2009, 28(5), 890—893 |
| (师雁,宁平,王学谦,蒋明.化工进展, 2009, 28(5), 890—893) | |
| [7] | Belmabkhout Y., de Weireld G., Sayari A., Langmuir,2009, 25(23), 13275—13278 |
| [8] | Mohamadalizadeh A., Towfighi J., Rashidi A., Mohajeri A., Golkar M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2011, 50(13), 8050—8057 |
| [9] | Polychronopoulou K., Galisteo F. C., Granados M. L., Fierro J. L. G., Bakas T., Efstathiou A. M., J. Catal., 2005, 236(2), 205—220 |
| [10] | Yang H., Sothen R., Cahela D. R., Tatarchuk B. J., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2008, 47(24), 10064—10070 |
| [11] | Fan H. L., Sun T., Zhao Y. P., Shangguan J., Lin J. Y., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2013, 47(9), 4859—4865 |
| [12] | Jung K. D., Joo O. S., Cho S. H., Han S. H., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2003, 240(1), 235—241 |
| [13] | Ma Y. Q., Wang R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(7), 1515—1522 |
| (马云倩, 王睿. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(7), 1515—1522) | |
| [14] | Hamon L., Serre C., Devic T., Loiseau T., Millange F., Férey G., Weireld G. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(25), 8775—8777 |
| [15] | Huang Z. H., Liu G., Kang F., ACS Appl. Mater.Interfaces,2012, 4(9), 4942—4947 |
| [16] | Wang R., J. Chem. Eng. Jpn., 2002, 35(1), 15—21 |
| [17] | Wang R., Korean J. Chem. Eng., 2003, 20(4), 659—663 |
| [18] | Zou C., Zhao P., Ge J., Qin Y., Luo P., Fuel,2013, 104, 635—640 |
| [19] | Kim K., Song D., Han J. I., Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 241, 60—65 |
| [20] | Jalili A. H., Shokouhi M., Maurer G., Hosseini-Jenab M., J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2013, 67, 55—62 |
| [21] | Guo Z., Zhang T., Liu T., Du J., Jia B., Gao S., Yu J., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(9), 5697—5703 |
| [22] | Ma Y. Q., Wang R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(4), 760—765 |
| (马云倩, 王睿. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(4), 760—765) | |
| [23] | Ma X., Wang X., Song C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009, 131(16), 5777—5783 |
| [24] | Wang X., Ma X., Sun L., Song C., Green Chem., 2007, 9(6), 695—702 |
| [25] | Chen Q., Fan F., Long D., Liu X., Liang X., Qiao W., Ling L., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2010, 49(22), 11408—11414 |
| [26] | Xue A., Zhou S., Zhao Y., Lu X., Han P., J. Hazard. Mater., 2011, 194, 7—14 |
| [27] | Liu X., Wang R., Petroleum Coal,2014, 56(5), 503—508 |
| [28] | Ma Y. H., Fang W. M., Ma X. J., Mater. Rev., 2006, 20(9), 43—46 |
| (马玉恒,方卫民,马小杰.材料导报, 2006, 20(9), 43—46) | |
| [29] | Wang J., Chen H., Zhou H., Liu X., Qiao W., Long D., Ling L., J. Environ. Sci., 2013, 25(1), 124—132 |
| [30] | Li L., Yu S. R., Chen X. F., Zhou Z. F., Wang Q. N., J. Mineral Petrol., 2011, 31(4), 19—24 |
| (李澜, 余树荣, 陈学福, 周智芳, 王青宁.矿物岩石, 2011, 31(4), 19—24) |
| [1] | HUAN Xinyu, LAI Ganqiang, HUANG Yue, YANG Caiguang. Research Progress on Chemical Intervention of N6-methyladenosine Modification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220340. |
| [2] | CHEN Jialu, HUANG Shuo. Application of Nanopore Sequencing Technology in the Detection of Nucleic Acid Modifications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220333. |
| [3] | ZHANG Qingyi, CAO Jie, SHU Xiao, LIU Jianzhao. Effects of Exogenous N6-methyladenosine (m6A) Incorporation on the Expression of Cellular mRNA Transcripts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220173. |
| [4] | YAN Zhixuan, MA Ji, QU Jinlei, LIU Li, SUN Chong, LIU Jiwen, LIU Guangye, SUN Lishui, HE Lixia. Synthesis and Application of Modified Low Molecular Weight Polyisoprene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220066. |
| [5] | JIANG Hongbin, DAI Wenchen, ZHANG Rao, XU Xiaochen, CHEN Jie, YANG Guang, YANG Fenglin. Research on Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3 Ceramic Membrane Separation and Catalytic Spraying Industry VOCs Waste Gas [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [6] | HAO Honglei, MENG Fanyu, LI Ruoyu, LI Yingqiu, JIA Mingjun, ZHANG Wenxiang, YUAN Xiaoling. Biomass Derived Nitrogen Doped Porous Carbon Materials as Adsorbents for Removal of Methylene Blue in Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [7] | ZHAO Sheng, HUO Zhipeng, ZHONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Hong, HU Liqun. Preparation of Modified Gadolinium/Boron/Polyethylene Nanocomposite and Its Radiation Shielding Performance for Neutron and Gamma-ray [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [8] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, JIANG Wei, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Activation of Biochar from Cattail and the VOCs Adsorption Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [9] | HU Huimin, CUI Jing, LIU Dandan, SONG Jiaxin, ZHANG Ning, FAN Xiaoqiang, ZHAO Zhen, KONG Lian, XIAO Xia, XIE Zean. Influence of Different Transition Metal Decoration on the Propane Dehydrogenation Performance over Pt/M-DMSN Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210815. |
| [10] | CHEN Xiaolu, YUAN Zhenyan, ZHONG Yingchun, REN Hao. Preparation of Triphenylamine Based PAF-106s via Mechanical Ball Milling and C2 Hydrocarbons Adsorption Property [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [11] | MENG Xianglong, YANG Ge, GUO Hailing, LIU Chenguang, CHAI Yongming, WANG Chunzheng, GUO Yongmei. Synthesis of Nano-zeolite and Its Adsorption Performance for Hydrogen Sulfide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [12] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| [13] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [14] | ZHENG Meiqi, MAO Fangqi, KONG Xianggui, DUAN Xue. Layered Double Hydroxides as Sorbent for Remediation of Radioactive Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [15] | TIAN Xiaokang, ZHANG Qingsong, YANG Shulin, BAI Jie, CHEN Bingjie, PAN Jie, CHEN Li, WEI Yen. Porous Materials Inspired by Microbial Fermentation: Preparation Method and Application [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
