

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (4): 678.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160711
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Pinghui1,2, ZHU Jiafeng1,2, SUN Wei1,2,*( ), ZHOU Wanrong1,2
), ZHOU Wanrong1,2
Received:2016-10-11
Online:2017-04-10
Published:2017-03-22
Contact:
SUN Wei
E-mail:sunwei@nbu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YANG Pinghui, ZHU Jiafeng, SUN Wei, ZHOU Wanrong. Self-assembly Behavior of Amphiphilic Janus Particles in the Acting Process of Breath Figure Method†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 678.
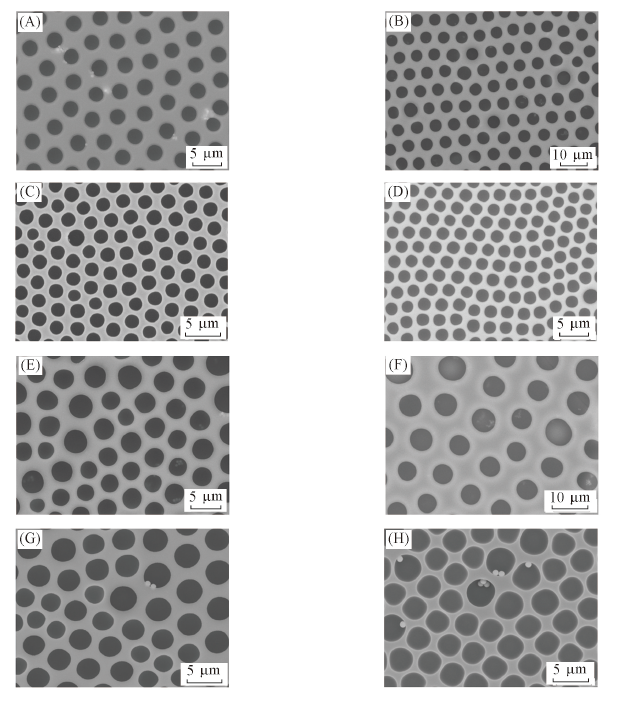
Fig.3 SEM images of porous films fabricated from solutions prepared by adding Janus particles(A—D) and hydrophilic particles suspension(E—H) with concentration of 10 mg/mL into 1 mL PS chloroform solution with concentration of 15 g/LThe amounts of Janus particles(or hydrophilic SiO2 particles) suspension are 10 μL(A, E), 15 μL(B, F), 20 μL(C, G), 25 μL(D, H), respectively.
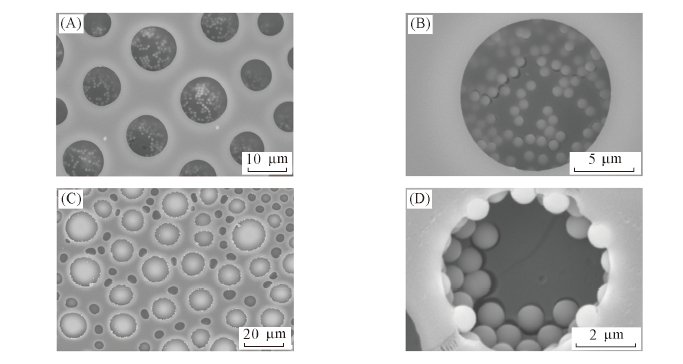
Fig.4 SEM images of porous films fabricated from solutions prepared by adding Janus particles(A, B) and hydrophilic particles alcoholic suspension(C, D) with the concentration of 10 mg/mL into 1 mL PS chloroform solution with concentration of 15 mg/mLThe amount of particles alcoholic suspension was 45 μL.
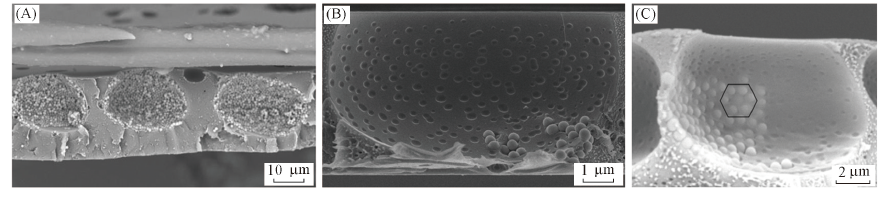
Fig.5 Cross-sectional SEM images of porous films fabricated from solutions prepared by adding Janus particles with the concentration of 10 mg/mL into 1 mL PS chloroform solution with concentration of 15 mg/mLThe amount of particles suspension is 60 μL.
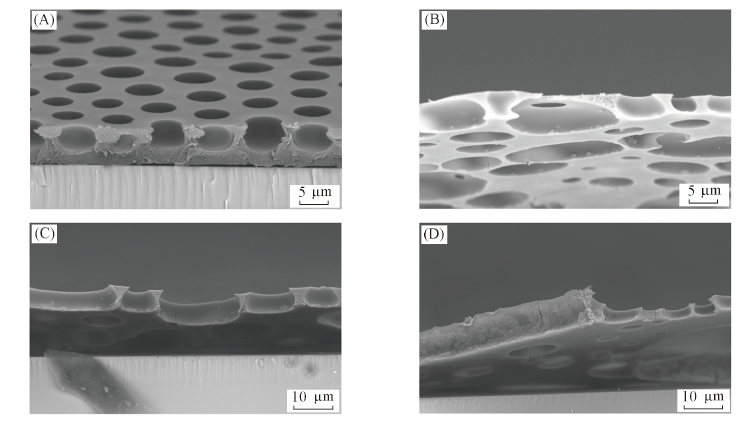
Fig.6 Cross-sectional SEM images of porous films fabricated from solutions prepared by pure PS chloroform(A) or adding Janus particles(B—D ) with the concentration of 10 mg/mL into 1 mL PS chloroform solution with concentration of 15 mg/mLThe amount of particles alcoholic suspension is 15 μL(B ), 30 μL(C ) and 45 μL(D).
| [1] | Widawski G., Rawiso M., Francois B., Nature,1994, 369, 387—389 |
| [2] | Böker A., Lin Y., Chiapperini K., Horowitz R., Thompson M., Carreon V., Xu T., Abetz C., Skaff H., Dinsmore A. D., Emrick T., Russell T. P., Nat. Mater., 2004, 3, 302—306 |
| [3] | Tu Z. K., Tang H. L., Shen X. T., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2014, 6, 12931—12938 |
| [4] | Yonezawa T., Onoue S., Kimizuka N., Adv. Mater., 2001, 13, 140—142 |
| [5] | Sun W., Tang Y. C., Ji J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(7), 1388—1392 |
| (孙巍, 唐越超, 计剑. 高等学校化学学报, 2007,28(7), 1388—1392) | |
| [6] | Sun W., Shao Z., Ji J., Polymer,2010, 51, 4169—4175 |
| [7] | Sun W., Ji J., Shen J., Langmuir,2008, 24, 11338—11341 |
| [8] | Julthogpiput D., Lin Y. H., Teng J., Zubarev E. R., Tsukruk V. V., Langmuir,2003, 19, 7832—7836 |
| [9] | Steyer A., Guenoun P., Beysens D., Konbler C. M., Phys. Rev. B: Condens Matter,1990, 42, 1086—1089 |
| [10] | Pickering S.U., J. Chem. Soc., 1907, 91, 2001—2021 |
| [11] | Ramsden W., Proc. R. Soc. London, 1903, 72, 156—164 |
| [12] | Binks B., Curr. Opin. Colloid. Interface. Sci., 2002, 7, 21—41 |
| [13] | De Genns P. G., Rev. Mod. Phys., 1992, 64, 645—648 |
| [14] | Vanakaras A. G., Langmuir, 2006, 22, 88—93 |
| [15] | Xu L., Pradhan S., Chen S., Langmuir,2007, 23, 8544—8548 |
| [16] | Takei H., Shimizu N., Langmuir,1997, 13, 1865—1868 |
| [17] | Tan Y., Yang K.J., Cao Y. X., Zhou R., Chen M., Qian W. P., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2004, 26,2089—2092) |
| (谈勇, 杨可靖, 曹跃霞, 周蓉, 陈明, 钱卫平. 化学学报, 2004, 26,2089—2092) | |
| [18] | Walther A., Matussek K., Müller A. H. E., ACS Nano, 2008, 2, 1167—1178 |
| [19] | Glaser N., Adams D. J., Böker A., Krausch G., Langmuir,2006, 22, 5227—5229 |
| [20] | Binks B. P., Fletcher P. D. I., Langmuir,2001, 17, 4708—4710 |
| [21] | Yang W. Y., Cui Y. L., Dai L. J., J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. : Nat. Sci. Ed., 2003, 31(2), 71—73 |
| (杨文玉, 崔亚丽, 代丽君. 陕西师范大学学报, 自然科学版, 2003,31(2), 71—73) | |
| [22] | Takahara Y. K., Ikeda S., Ishino S., Tachi K., Ikeue K., Sakata T., Hasegawa T., Mori H., Matsumura M., Ohtani B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 6271—6275 |
| [23] | Pastorizasantos I., Gomez D., Pérezjuste J., Lizmarzán L. M., Mulvaney P., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2004, 6, 5056—5060 |
| [24] | Aveyard R., Binks B. P., Clint J. H., Adv. Colloid. Interfaces. Sci., 2003, 100, 503—546 |
| [25] | Hong L., Jiang S., Granick S., Langmuir,2006, 22, 9495—9499 |
| [26] | Dinsmore A., Hsu M. F., Nikolaides M. G., Marquez M., Bausch A. R., Weitz D. A., Science,2002, 298, 1006—1009 |
| [27] | Jiang S., Schultz M. J., Chen Q., Moore J. S., Granick S., Langmuir,2008, 24, 10073—10077 |
| [28] | Luo Q., Hickey J., Park S., ACS Macro. Lett., 2013, 2, 107—111 |
| [1] | LI Lin, QI Fenglian, QIU Lili, MENG Zihui. Dynamic Amorphous Photonic Structure Patterns Assembled by Hexagonal Magnetic Nanosheets [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220123. |
| [2] | WU Yushuai, SHANG Yingxu, JIANG Qiao, DING Baoquan. Research Progress of Controllable Self-assembled DNA Origami Structure as Drug Carrier [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220179. |
| [3] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [4] | LI Bo, MENG Yuxi, WANG Wenwen, ZANG Hongying. Synthesis and Proton Conductivity of Polynuclear Polyoxothiomolybdate Compound [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210657. |
| [5] | DU Shunfu, WANG Wenjing, EL⁃SAYED El⁃Sayed M., SU Kongzhao, YUAN Daqiang, HONG Maochun. A Chemiluminescent Zirconocene Coordination Tetrahedron [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210628. |
| [6] | XUE Jin, CAO Xiaowei, LIU Yifan, WANG Min. Preparation of Paper Hollow Gold Nanocage SERS Sensor and Its Rapid and Highly Sensitive Detection for miRNAs in Sputum of Patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2393. |
| [7] | ZHANG Juan, HU Xinyue, WANG Hongbo, LIAN Ying, LE Jinyu, YANG Zihao. Crystal-like Hydrogels Consisting of Parallel Hexahedrons Obtained from the Self-assembly ofβ⁃Cyclodextrin/perfluorononanoic Acid Inclusion Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3187. |
| [8] | TANG Wentao, LI Shengkai, WANG Shen, CHEN Long, CHEN Zhuo. Laser-mediated Enrichment Based Surface Enhanced Raman Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3054. |
| [9] | HOU Chunxi, LI Yijia, WANG Tingting, LIU Shengda, YAN Tengfei, LIU Junqiu. Application of Elastin-like Polypeptides in Supramolecular Assembly † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1163. |
| [10] | LI Honghong,GENG Keying,TIAN Fuyue,GU Fang,WANG Haijun. Regulation of Phase State of Dipolar Janus Particles and Its Application † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 1042. |
| [11] | BAI Ruonan, LI Qing, QIAO Shanlin, ZHANG Chunhuan, ZHAO Yongsheng. Controlled Preparation and Optical Waveguide Property of 1,4-Dicarbazolidinylbenzene Microwires † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 967. |
| [12] | WANG Jun, WANG Tie. Recent Progress in Functional Nanomaterials Based on Self-assembly Technology † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 377. |
| [13] | LI Dong,SUN Yinghui,WANG Zhongshun,HUANG Jing,Lü Nan,JIANG Lin. Large-scale Multiplexed Surface Plasmonic Gold Nanostructures Based on Nanoimprint and Self-assembly † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 221. |
| [14] | GAO Miaomiao,WANG Chenglong,DOU Hongjing,XU Guoxiong. One-step Self-assembly/polymerization Fabrication and Biomedical Application of Carboplatin@Dextran Nanocarrier† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1301. |
| [15] | WANG Yanhui,ZOU Qingzhi,ZHU Youliang,FU Cuiliu,HUANG Yineng,LI Zhanwei,SUN Zhaoyan. Simulation Study on the Self-assembly of Softtriblock Janus Particles† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1037. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||