

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (5): 932.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150973
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Changmin, LIU Tingyu*( ), CHANG Qiuxiang, LUO Guoyin
), CHANG Qiuxiang, LUO Guoyin
Received:2015-12-23
Online:2016-05-10
Published:2016-04-20
Contact:
LIU Tingyu
E-mail:liutyyxj@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MA Changmin, LIU Tingyu, CHANG Qiuxiang, LUO Guoyin. Theoretical Studies on the Intrinsic Defects in ZnO and ZnS Crystal†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 932.
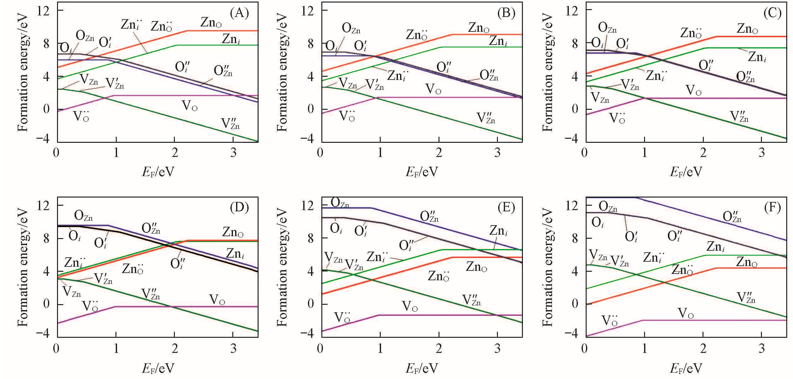
Fig.4 Formation energies of point defects in ZnO as a function of the Fermi level(A)—(C) T=300 K, pO2=103, 10-5, 10-10 Pa; (D)—(F) T=1300 K, pO2=103, 10-5, 10-10 Pa.
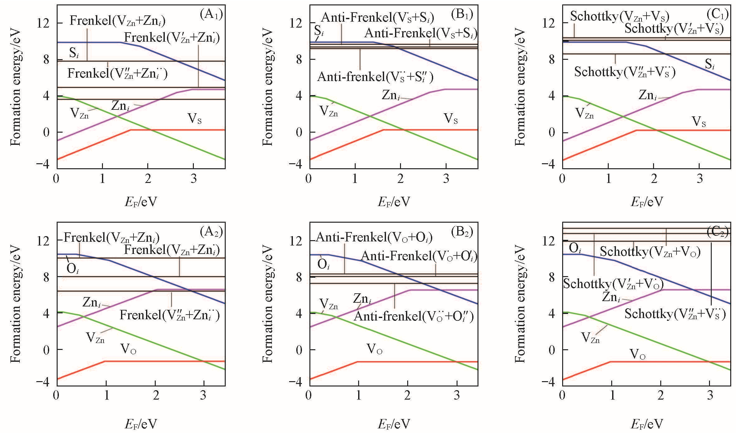
Fig.5 Calculated formation energies of intrinsic point defect complexes(A1, A2) Frenkel; (B1, B2) anti-Frenkel; (C1, C2) schottky pairs. (A1—C1) ZnS; (A2—C2) ZnO.
| [1] | Triboulet R., Proc.SPIE, 2001, 4412, 1—8 |
| [2] | Wang Z. L., J. Phys.: Condens.Matter., 2004, 16, 829—858 |
| [3] | Ling J., Cong R. M., Acta Chim.Sinica, 2008, 66(18)2070—2074, |
| (凌剑, 丛日敏. 化学学报, 2008, 66(18), 2070—2074) | |
| [4] | Song J. Z., He Y., Zhu D., Chen J., Pei C. L., Wang J. A., Acta Phys.-Chim.Sin., 2011, 27(5), 1207—1213 |
| (宋继中, 贺英, 朱棣, 陈杰, 裴昌龙, 王均安. 物理化学学报, 2011, 27(5), 1207—1213) | |
| [5] | Xin D. S., Shi J. X., Pang Q., Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2003, 42(6), 125—127 |
| (邢德松, 石建新, 庞起. 中山大学学报(自然科学版), 2003, 42(6), 125—127) | |
| [6] | Yan Y. F., Li J. B., Wei S. H., Al-Jassim M. M., Phys. Rev.Lett., 2007, 98, 1—4 |
| [7] | Deng B., Luo M., Dong H. N., ElectronicQuality, 2012, 1, 8—10 |
| (邓博, 罗敏, 董会宁. 电子质量, 2012, 1, 8—10) | |
| [8] | Chen L. J., Li W. X., Dai J. F., Wang Q., Acta Phys.Sin., 2014, 63(19), 196101 |
| (陈立晶, 李维学, 戴剑锋, 王青. 物理学报, 2014, 63(19), 196101) | |
| [9] | Yang T. Y., Kong C. Y., Ruan H. B., Qin G. P., Li W. J., Liang W. W., Meng X. D., Zhao Y. H., Fang L., Cui Y. T., Acta Phys.Sin., 2012, 61, 168101 |
| (杨天勇, 孔春阳, 阮海波, 秦国平, 李万俊, 梁薇薇, 孟祥丹, 赵永红, 方亮, 崔玉婷. 物理学报, 2012, 61, 168101) | |
| [10] | Wang H. B., Zhang J. W., Yang X. D., Liu Z. L., Xu Q. A., Hou X., Acta Phys.Sin., 2005, 54(6), 2893—2898 |
| (王洪波, 张景文, 杨晓东, 刘振玲, 徐庆安, 侯洵. 物理学报, 2005, 54(6), 2893—2898) | |
| [11] | Xu P. S., Shun Y. M., Shi C. S., Xu F. Q., Pang H. B., Science ChinaA, 2001, 31(4), 358—365 |
| (徐彭寿, 孙玉明, 施朝淑, 徐法强, 潘海斌. 中国科学, A辑, 2001, 31(4), 358—365) | |
| [12] | Kohan A. F., Ceder G., Morgan D., Phys. Rev.B, 1995, 61, 15019—15027 |
| [13] | Oba F., Choi M., Togo A., Tanaka I., Sci. Technol. Adv.Mater., 2011, 12, 034302 |
| [14] | Li P., Deng S. H., Zhang L., Liu G. H., Yu J. Y., Chem. Phys.Lett., 2012, 531, 75—79 |
| [15] | Morozova N. K., Karetnikov I. A., Golub K. V., Gavrishchuk E. M., Yashina E. V., Plotnichenko V. G., Galstyan V. G., Inorg.Mater., 2004, 40(11), 1138—1145 |
| [16] | Lott K., Shinkarenko S., Turn L., Nirk T., Opik A., Kallavus U., Gorokhova E., Grebennik A., Vishnjakov A., Phys.B, 2009, 404, 5006—5008 |
| [17] | Lott K., Turn L., Volobujeva O., Leskela M., Phys.B, 2001, 949, 308—310 |
| [18] | Anderson J., Van de Walle C. G., Phys. Rev.B, 2007, 76, 165202 |
| [19] | Li P., Deng S. H., Zhang L., Yu J., Chem. Phys.Lett., 2012, 531, 75—79 |
| [20] | Kohan A. F., Ceder G., Morgan D., Van de Walle C. G., Phys. Rev.B, 2000, 61, 15019 |
| [21] | Van de Walle C. G., Neugebauer J., J. Appl.Phys., 2004, 95, 3851—3879 |
| [22] | Zhang S. B., Northrup S. B., Phys. Rev.B, 1991, 67(17), 2339—2346 |
| [23] | Batyrev I. G., Alavi A., Finnis M. W., Phys. Rev.B, 2000, 62(7), 4698—4707 |
| [24] | Finnis M. W., Lozovoi A. Y., Alavi A., Ann. Rev. Mat.Res., 2005, 35, 167—179 |
| [25] | Gale J. D., Chem. J. Soc. Faraday Trans., 1997, 93, 629—637 |
| [26] | Oba F., Adachi H., J. Mater.Res., 2000, 15(10), 2168—2175 |
| [27] | Janotti A., Van de Walle C. G., J. Cryst.Growth, 2006, 287, 58—65 |
| [28] | Santana J. A., Krogel J. T., Kim J., Paul R. C. K., Reboredo F. A., Cond. Mat. Mtrl.Sci., 2014, 12, 23—30 |
| [29] | Zhang S. B., Wei S. H., Zunger A., Phys. Rev.B, 2001, 63, 075205 |
| [30] | Gai Y., Li J., Yao B., Xia J. B., J. Appl.Phys., 2009, 105, 113704 |
| [31] | He J., Behera R. K., Finnis M. W., ActaMat., 2007, 55, 4325—4337 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WANG Kun, ZOU Xingli, CAO Zhanmin, LI Chonghe, LU Xionggang. Modified Quasichemical Model for Manifold Short-range Orders in Binary Solutions: Unity of Opposites for the Ordered Pairs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220391. |
| [3] | DONG Yanhong, LU Xinhuan, YANG Lu, SUN Fanqi, DUAN Jingui, GUO Haotian, ZHANG Qinjun, ZHOU Dan, XIA Qinghua. Preparation of Bifunctional Metal-organic Framework Materials and Application in Catalytic Olefins Epoxidation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [4] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [5] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [6] | ZHAO Peng,ZHANG Jinteng,LIN Yanhong. Excellent Ultraviolet Photocatalytic Efficiency of Mg 2+ Doped ZnO and Analysis on Its Synergetic Effect † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 538. |
| [7] | CAO Hongyu,MA Zihui,ZHANG Wenqiong,TANG Qian,LI Ruyu,ZHENG Xuefang. Structures and Electronic Absorption Spectra of N/Neo-Confused, Doubly N-Confused and Neo-Confused N-Confused Porphyrin Isomers † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 341. |
| [8] | WEI Xin, DENG Yaoliang, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Ground Structure and Excited State Proton Transfer Reaction of 2-Aminobenzothiazole [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1679. |
| [9] | HE Zijun,XIAO Ming,MA Xiangying,QIU Jiangyuan,XIAO Biyuan,QIN Fanghong,HUANG Zaiyin. Facet and Temperature Effects on Dissolution Thermodynamic Functions of Ag3PO4 Microcrystals† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 959. |
| [10] | ZHI Shasha,BAN Ying,XU Zhiguang,XU Xuan. Electron Transport of Metal String Complexes of [MM'M″(dpa)4(Cl)2](M=Co, Ni; M',M″=Co, Rh)† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 980. |
| [11] | LIU Qiuna,XU Wenwen,LIU Maozhu,WANG Huigang,ZHENG Xuming. Study on Raman Spectroscopy Non-coincidence Effect of Propionic Anhydride C=O Vibration Mode† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 932. |
| [12] |
ZHOU Xiaofeng,ZHOU Yanbing,TANG Chunmei.
Hydrogen Storage Capacity of the Alkaline Earth Metal Mg Exohedral Doped Boron Cage B40M |
| [13] | ZHOU Hegen,JIN Hua,GUO Huirui,LIN Jing,ZHANG Yongfan. Electronic Structures and Optical Properties of Cu-based Semiconductors with Chalcopyrite-type Structure† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 518. |
| [14] | LU Simin, YU Rujia, LONG Yitao. Single Nanoparticle Sizing Based on the Confined Glass Nanopore † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2281. |
| [15] | XIAO Biyuan,QIU Jiangyuan,QIN Fanghong,WAN Ting,XU Yaqun,NONG Xiaohui,HUANG Zaiyin. Study on Particle Size Effect on Adsorption Thermodynamics and Kinetics of Cubic Nano-Cu2O † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2214. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||