

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (2): 254.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150716
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Liang1,2,*( ), QU Xing1, LI Zhan1, GU Changhan1, HU Siqian1,2,*(
), QU Xing1, LI Zhan1, GU Changhan1, HU Siqian1,2,*( )
)
Received:2015-09-14
Online:2016-02-10
Published:2016-01-04
Contact:
WANG Liang,HU Siqian
E-mail:wangliang@jhun.edu.cn;husiqian@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Liang, QU Xing, LI Zhan, GU Changhan, HU Siqian. Metal-free C3—H Acetoxylation of Indoles Promoted by PhI(OAc)2†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 254.
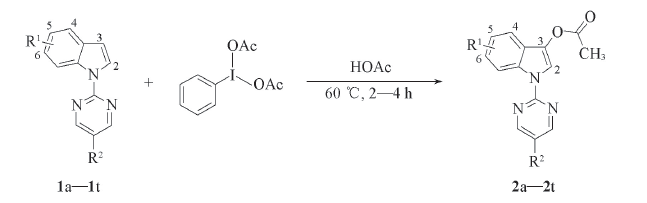
Scheme 1 Synthetic route for C3—H acetoxylation of indoles 2a: R1=H, R2=H; 2b: R1=4-Me, R2=H; 2c: R1=4-OBn, R2=H; 2d: R1=4-Cl, R2=H; 2e: R1=4-CO2Me, R2=H; 2f: R1=5-Me, R2=H; 2g: R1=5-OMe, R2=H; 2h: R1=5-OBn, R2=H; 2i: R1=5-OPh, R2=H; 2j: R1=5-Cl, R2=H; 2k: R1=5-Br, R2=H; 2l: R1=6-Me, R2=H; 2m: R1=6-CO2Me, R2=H; 2n: R1=6-F, R2=H; 2o: R1=6-Cl, R2=H; 2p: R1=6-Br, R2=H; 2q: R1=5,6-Ph, R2=H; 2r: R1=H, R2=Me; 2s: R1=H, R2=Ph; 2t: R1=H, R2=Br
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield*(%) | m. p./℃ | HRMS(calcd.), m/z [M+Na+] | IR(KBr), |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | White solid | 85 | 123—124 | 276.0747(276.0743) | 3195, 1743, 1573, 1458, 1428, 1369, 1316, 1208, 1158, 1124, 1073,1015 |
| 2b | Yellow solid | 76 | 143—144 | 290.0925(290.0900) | 3203, 2923, 2854, 1753, 1568, 1433, 1354, 1300, 1198, 1147 |
| 2c | White solid | 63 | 127—128 | 382.1155(382.1162) | 3210, 1738, 1573, 1499, 1448, 1362, 1271, 1232, 1160, 1096, 1064, 913 |
| 2d | White solid | 73 | 155—156 | 310.0352(310.0354) | 3192, 1756, 1563, 1452, 1360, 1309, 1212, 1001, 891, 770 |
| 2e | White solid | 75 | 134—135 | 334.0789(334.0798) | 2955, 1749, 1713, 1570, 1357, 1283, 1190, 1091, 1020, 954, 902, 740 |
| 2f | White solid | 78 | 165—166 | 290.0900(290.0900) | 3201, 1746, 1581, 1456, 1426, 1353, 1202, 1147, 1122, 864 |
| 2g | Yellow solid | 80 | 166—167 | 306.0849(306.0849) | 3209, 1744, 1536, 1436, 1366, 1210, 1075, 1020, 905, 801, 766, 747 |
| 2h | White solid | 65 | 166—167 | 382.1128(382.1162) | 3194, 1749, 1576, 1479, 1453, 1296, 1203, 1078, 1013, 919 |
| 2i | White solid | 86 | 139—140 | 368.1009(368.1006) | 3219, 1747, 1565, 1471, 1421, 1361, 1289, 1198, 1072, 965, 922 |
| 2j | Yellowish solid | 83 | 181—182 | 310.0335(310.0354) | 3206, 1756, 1573, 1459, 1373, 1346, 1292, 1203, 1065 |
| 2k | Yellowish solid | 85 | 182—183 | 353.9846(353.9846) | 3023, 1787, 1735, 1456, 1353, 1147, 1014, 919, 855, 784 |
| 2l | White solid | 83 | 153—154 | 290.0875(290.0900) | 3195, 2971, 2856, 1742, 1573, 1436, 1368, 1321, 1212, 1131, 789 |
| 2m | Yellow solid | 63 | 199—200 | 334.0896(334.0798) | 3197, 1752, 1717, 1571, 1441, 1373, 1280, 1210, 1140, 1064, 990 |
| 2n | Reddish solid | 77 | 167—168 | 294.0660(294.0649) | 3197, 1745, 1575, 1441, 1370, 1208, 1104, 976, 905, 855, 792 |
| 2o | White solid | 70 | 179—180 | 310.0339(310.0354) | 3199, 1793, 1744, 1440, 1367, 1209, 1129, 1066, 957, 792, 506 |
| 2p | White solid | 80 | 178—179 | 353.9838(353.9849) | 3202, 1746, 1577, 1441, 1367, 1209, 1128, 1080, 1001, 954, 786 |
| 2q | White solid | 45 | 155—157 | 326.0901(326.0900) | 3211, 1746, 1571, 1459, 1427, 1363, 1297, 1220, 1130, 1023, 883, 775 |
| 2r | Yellowish solid | 84 | 158—159 | 290.0900(290.0900) | 3207, 1745, 1598, 1556, 1444, 1366, 1317, 1207, 1008, 742 |
| 2s | White solid | 81 | 133—134 | 352.1062(352.1056) | 3195, 1752, 1589, 1548, 1444, 1366, 1197, 1123, 1009, 887, 746 |
| 2t | White solid | 72 | 182—183 | 353.9681(353.9849) | 3199, 1746, 1598, 1557, 1440, 1317, 1207, 1116, 1010, 743 |
Table 1 Appearance, yields, melting points, HRMS and IR data of compounds 2a—2t
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield*(%) | m. p./℃ | HRMS(calcd.), m/z [M+Na+] | IR(KBr), |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2a | White solid | 85 | 123—124 | 276.0747(276.0743) | 3195, 1743, 1573, 1458, 1428, 1369, 1316, 1208, 1158, 1124, 1073,1015 |
| 2b | Yellow solid | 76 | 143—144 | 290.0925(290.0900) | 3203, 2923, 2854, 1753, 1568, 1433, 1354, 1300, 1198, 1147 |
| 2c | White solid | 63 | 127—128 | 382.1155(382.1162) | 3210, 1738, 1573, 1499, 1448, 1362, 1271, 1232, 1160, 1096, 1064, 913 |
| 2d | White solid | 73 | 155—156 | 310.0352(310.0354) | 3192, 1756, 1563, 1452, 1360, 1309, 1212, 1001, 891, 770 |
| 2e | White solid | 75 | 134—135 | 334.0789(334.0798) | 2955, 1749, 1713, 1570, 1357, 1283, 1190, 1091, 1020, 954, 902, 740 |
| 2f | White solid | 78 | 165—166 | 290.0900(290.0900) | 3201, 1746, 1581, 1456, 1426, 1353, 1202, 1147, 1122, 864 |
| 2g | Yellow solid | 80 | 166—167 | 306.0849(306.0849) | 3209, 1744, 1536, 1436, 1366, 1210, 1075, 1020, 905, 801, 766, 747 |
| 2h | White solid | 65 | 166—167 | 382.1128(382.1162) | 3194, 1749, 1576, 1479, 1453, 1296, 1203, 1078, 1013, 919 |
| 2i | White solid | 86 | 139—140 | 368.1009(368.1006) | 3219, 1747, 1565, 1471, 1421, 1361, 1289, 1198, 1072, 965, 922 |
| 2j | Yellowish solid | 83 | 181—182 | 310.0335(310.0354) | 3206, 1756, 1573, 1459, 1373, 1346, 1292, 1203, 1065 |
| 2k | Yellowish solid | 85 | 182—183 | 353.9846(353.9846) | 3023, 1787, 1735, 1456, 1353, 1147, 1014, 919, 855, 784 |
| 2l | White solid | 83 | 153—154 | 290.0875(290.0900) | 3195, 2971, 2856, 1742, 1573, 1436, 1368, 1321, 1212, 1131, 789 |
| 2m | Yellow solid | 63 | 199—200 | 334.0896(334.0798) | 3197, 1752, 1717, 1571, 1441, 1373, 1280, 1210, 1140, 1064, 990 |
| 2n | Reddish solid | 77 | 167—168 | 294.0660(294.0649) | 3197, 1745, 1575, 1441, 1370, 1208, 1104, 976, 905, 855, 792 |
| 2o | White solid | 70 | 179—180 | 310.0339(310.0354) | 3199, 1793, 1744, 1440, 1367, 1209, 1129, 1066, 957, 792, 506 |
| 2p | White solid | 80 | 178—179 | 353.9838(353.9849) | 3202, 1746, 1577, 1441, 1367, 1209, 1128, 1080, 1001, 954, 786 |
| 2q | White solid | 45 | 155—157 | 326.0901(326.0900) | 3211, 1746, 1571, 1459, 1427, 1363, 1297, 1220, 1130, 1023, 883, 775 |
| 2r | Yellowish solid | 84 | 158—159 | 290.0900(290.0900) | 3207, 1745, 1598, 1556, 1444, 1366, 1317, 1207, 1008, 742 |
| 2s | White solid | 81 | 133—134 | 352.1062(352.1056) | 3195, 1752, 1589, 1548, 1444, 1366, 1197, 1123, 1009, 887, 746 |
| 2t | White solid | 72 | 182—183 | 353.9681(353.9849) | 3199, 1746, 1598, 1557, 1440, 1317, 1207, 1116, 1010, 743 |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(100 MHz, CDCl3), δ |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | 8.81(d,J=8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.67(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 7.56(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.37(t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.29—7.25(m, 1H), 7.02(t, J=4.8 Hz, 1H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.1, 157.8, 133.5, 132.8, 124.6, 124.0, 122.2, 117.5, 116.4, 116.1, 114.6, 21.1 |
| 2b | 8.73—8.59(m, 3H), 8.36(s, 1H), 7.24(dd, J=10.3, 5.1 Hz, 1H), 7.02—6.92(m, 2H), 2.63(s, 3H), 2.37(s, 3H) | 168.7, 158.1, 157.7, 134.3, 133.2, 129.4, 124.5, 123.9, 122.7, 116.0, 114.8, 114.1, 29.7, 21.3, 18.8 |
| 2c | 8.66(d,J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.44(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.06(s, 1H), 7.54—7.48(m, 2H), 7.40(dd, J=9.7, 5.6, 1.4 Hz, 3H), 7.25(d, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 7.02(t, J=4.8 Hz, 1H), 6.74(d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 5.11(s, 2H), 1.91(s, 3H) | 169.8, 158.1, 157.7, 152.0, 136.9, 135.1, 133.2, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 125.4, 116.2, 114.5, 114.2, 110.0, 104.1, 70.4, 20.4 |
| 2d | 8.79—8.72(m, 1H), 8.66—8.61(m, 2H), 8.27(d, J=2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.20(t, J=7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.02(t, J=4.8, 3.4 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 169.5, 158.1, 157.2, 134.6, 132.2, 125.0, 124.2, 123.3, 121.4, 116.9, 116.6, 115.3, 21.1 |
| 2e | 9.12(d,J=8.5 Hz, 1H), 8.66(d, J=4.7 Hz, 2H), 8.31(s, 1H), 7.82(d, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.37(t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.05(t, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.91(d, J=13.3 Hz, 3H), 2.41(s, 3H) | 170.1, 167.2, 158.2, 157.3, 134.5, 132.8, 125.4, 123.5, 123.0, 122.5, 120.7, 118.7, 116.7, 52.2, 21.0 |
| 2f | 8.69—8.59(m, 3H), 8.36(s, 1H), 7.33(s, 1H), 7.18(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.97(t, J=4.2 Hz, 1H), 2.47(s, 3H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.1, 157.7, 133.3, 131.7, 131.2, 126.1, 124.2, 117.2, 116.2, 115.9, 114.6, 21.4, 21.1 |
| 2g | 8.66(dd,J=22.8, 6.8 Hz, 3H), 8.39(s, 1H), 6.98(d, J=8.2 Hz, 3H), 3.89(s, 3H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 168.1, 158.1, 157.6, 155.6, 133.4, 127.8, 124.7, 117.5, 115.8, 115.1, 114.0, 99.4, 55.7, 21.1 |
| 2h | 8.70(d,J=8.7 Hz, 1H), 8.63(d, J=4.7 Hz, 2H), 8.40(s, 1H), 7.49(d, J=7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.40(t, J=7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.36—7.30(m, 1H), 7.06(d, J=9.8 Hz, 2H), 6.98(t, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.13(s, 2H), 2.39(s, 3H), 5.13(s, 2H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.1, 158.1, 157.6, 154.8, 137.3, 133.4, 128.6, 127.9, 127.7, 124.7, 117.6, 115.9, 115.2, 114.5, 101.0, 70.6, 21.1 |
| 2i | 8.83—8.76(m, 1H), 8.67(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.46(s, 1H), 7.38—7.29(m, 2H), 7.20(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.14—6.99(m, 5H), 2.35(s, 3H) | 168.1, 158.6, 158.1, 157.6, 152.0, 133.3, 129.7, 129.5, 125.0, 122.5, 117.8, 117.6, 116.1, 115.7, 107.9, 21.0 |
| 2j | 8.84—8.61(m, 3H), 8.44(s, 1H), 7.52(s, 1H), 7.36—7.24(m, 1H), 7.05(s, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.2, 157.5, 132.6, 131.1, 127.9, 125.1, 124.8, 117.7, 117.1, 116.4, 115.9, 21.0 |
| 2k | 8.67(t,J=7.2 Hz, 3H), 8.42(s, 1H), 7.68(s, 1H), 7.43(d, J=8.9 Hz, 1H), 7.04(t, J=4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.2, 157.4, 132.4, 131.4, 127.4, 125.6, 120.2, 118.1, 116.4, 115.7, 115.5, 21.0 |
| 2l | 8.81—8.55(m, 3H), 8.34(s, 1H), 7.42(d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.09(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.98(t, J=4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.53(s, 3H), 2.38(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.1, 157.8, 134.7, 133.6, 133.2, 123.8, 121.9, 117.1, 116.5, 115.9, 113.9, 22.2, 21.1 |
| 2m | 9.50(s, 1H), 8.72(d,J=4.6 Hz, 2H), 8.58(s, 1H), 7.95(d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.59(d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.08(t, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.98(s, 3H), 2.41(s, 3H) | 168.1, 168.0, 167.9, 158.3, 157.4, 133.1, 132.1, 127.3, 126.3, 123.2, 118.6, 117.7, 117.2, 116.6, 52.2, 29.7, 21.0 |
| 2n | 8.66(d,J=4.6 Hz, 2H), 8.57(d, J=11.0 Hz, 1H), 8.39(s, 1H), 7.52—7.38(m, 1H), 7.02(dd, J=11.8, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 162.3, 158.1, 157.5, 133.2, 132.8, 132.7, 120.5, 118.2, 118.1, 116.3, 114.7, 114.7, 110.7, 110.5, 103.9, 103.6 |
| 2o | 8.86(s, 1H), 8.66(d,J=4.5 Hz, 2H), 8.40(s, 1H), 7.45(d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.24(t, J=8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.04(t, J=4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.38(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.1, 157.4, 133.2, 132.9, 130.5, 122.7, 122.5, 118.3, 116.6, 116.4, 115.0, 21.0 |
| 2p | 9.03(s, 1H), 8.68(t,J=3.6 Hz, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 7.39(q, J=8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.14—6.96(m, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.1, 168.0, 158.2, 157.4, 133.2, 125.4, 122.9, 119.5, 118.6, 118.4, 116.5, 115.0, 21.0 |
| 2q | 9.00(dd,J=9.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 8.70—8.73(m, 2H), 8.59(d, J=8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.94(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.75(d, J=9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.62—7.56(m, 1H), 7.52—7.46(m, 1H), 7.06(s, 1H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.2, 157.8, 135.4, 130.3, 129.9, 128.4, 127.0, 126.1, 125.1, 124.3, 123.7, 117.1, 116.7, 116.6, 113.8, 21.6 |
| 2r | 8.77(d,J=8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.47(s, 2H), 8.39(s, 1H), 7.55(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.36(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.24(t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H), 2.27(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.0, 156.1, 133.1, 132.7, 125.1, 124.4, 123.8, 121.9, 117.4, 116.2, 114.7, 21.0, 15.0 |
| 2s | 8.89—8.81(m, 3H), 8.47(s, 1H), 7.57(d, J=6.3 Hz, 3H), 7.50(t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.46—7.36(m, 2H), 7.27(t, J=8.1 Hz, 1H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 168.1, 156.8, 156.0, 134.4, 133.6, 132.8, 129.4, 129.0, 128.4, 126.5, 124.7, 124.0, 122.3, 117.5, 116.4, 114.6, 21.0 |
| 2t | 8.73—8.60(m, 3H), 8.34(s, 1H), 7.55(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.36(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.26(t, J=6.3 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.5, 155.9, 133.9, 132.7, 124.9, 124.1, 122.5, 117.6, 116.4, 114.4, 113.0, 21.1 |
Table 2 1H NMR and 13C NMR data of compounds 2a—2t
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz, CDCl3), δ | 13C NMR(100 MHz, CDCl3), δ |
|---|---|---|
| 2a | 8.81(d,J=8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.67(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.43(s, 1H), 7.56(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.37(t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.29—7.25(m, 1H), 7.02(t, J=4.8 Hz, 1H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.1, 157.8, 133.5, 132.8, 124.6, 124.0, 122.2, 117.5, 116.4, 116.1, 114.6, 21.1 |
| 2b | 8.73—8.59(m, 3H), 8.36(s, 1H), 7.24(dd, J=10.3, 5.1 Hz, 1H), 7.02—6.92(m, 2H), 2.63(s, 3H), 2.37(s, 3H) | 168.7, 158.1, 157.7, 134.3, 133.2, 129.4, 124.5, 123.9, 122.7, 116.0, 114.8, 114.1, 29.7, 21.3, 18.8 |
| 2c | 8.66(d,J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.44(d, J=8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.06(s, 1H), 7.54—7.48(m, 2H), 7.40(dd, J=9.7, 5.6, 1.4 Hz, 3H), 7.25(d, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 7.02(t, J=4.8 Hz, 1H), 6.74(d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 5.11(s, 2H), 1.91(s, 3H) | 169.8, 158.1, 157.7, 152.0, 136.9, 135.1, 133.2, 128.5, 128.4, 128.2, 125.4, 116.2, 114.5, 114.2, 110.0, 104.1, 70.4, 20.4 |
| 2d | 8.79—8.72(m, 1H), 8.66—8.61(m, 2H), 8.27(d, J=2.0 Hz, 1H), 7.20(t, J=7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.02(t, J=4.8, 3.4 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 169.5, 158.1, 157.2, 134.6, 132.2, 125.0, 124.2, 123.3, 121.4, 116.9, 116.6, 115.3, 21.1 |
| 2e | 9.12(d,J=8.5 Hz, 1H), 8.66(d, J=4.7 Hz, 2H), 8.31(s, 1H), 7.82(d, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 7.37(t, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.05(t, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.91(d, J=13.3 Hz, 3H), 2.41(s, 3H) | 170.1, 167.2, 158.2, 157.3, 134.5, 132.8, 125.4, 123.5, 123.0, 122.5, 120.7, 118.7, 116.7, 52.2, 21.0 |
| 2f | 8.69—8.59(m, 3H), 8.36(s, 1H), 7.33(s, 1H), 7.18(d, J=8.5 Hz, 1H), 6.97(t, J=4.2 Hz, 1H), 2.47(s, 3H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.1, 157.7, 133.3, 131.7, 131.2, 126.1, 124.2, 117.2, 116.2, 115.9, 114.6, 21.4, 21.1 |
| 2g | 8.66(dd,J=22.8, 6.8 Hz, 3H), 8.39(s, 1H), 6.98(d, J=8.2 Hz, 3H), 3.89(s, 3H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 168.1, 158.1, 157.6, 155.6, 133.4, 127.8, 124.7, 117.5, 115.8, 115.1, 114.0, 99.4, 55.7, 21.1 |
| 2h | 8.70(d,J=8.7 Hz, 1H), 8.63(d, J=4.7 Hz, 2H), 8.40(s, 1H), 7.49(d, J=7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.40(t, J=7.3 Hz, 2H), 7.36—7.30(m, 1H), 7.06(d, J=9.8 Hz, 2H), 6.98(t, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 5.13(s, 2H), 2.39(s, 3H), 5.13(s, 2H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.1, 158.1, 157.6, 154.8, 137.3, 133.4, 128.6, 127.9, 127.7, 124.7, 117.6, 115.9, 115.2, 114.5, 101.0, 70.6, 21.1 |
| 2i | 8.83—8.76(m, 1H), 8.67(d, J=4.8 Hz, 2H), 8.46(s, 1H), 7.38—7.29(m, 2H), 7.20(d, J=2.4 Hz, 1H), 7.14—6.99(m, 5H), 2.35(s, 3H) | 168.1, 158.6, 158.1, 157.6, 152.0, 133.3, 129.7, 129.5, 125.0, 122.5, 117.8, 117.6, 116.1, 115.7, 107.9, 21.0 |
| 2j | 8.84—8.61(m, 3H), 8.44(s, 1H), 7.52(s, 1H), 7.36—7.24(m, 1H), 7.05(s, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.2, 157.5, 132.6, 131.1, 127.9, 125.1, 124.8, 117.7, 117.1, 116.4, 115.9, 21.0 |
| 2k | 8.67(t,J=7.2 Hz, 3H), 8.42(s, 1H), 7.68(s, 1H), 7.43(d, J=8.9 Hz, 1H), 7.04(t, J=4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.2, 157.4, 132.4, 131.4, 127.4, 125.6, 120.2, 118.1, 116.4, 115.7, 115.5, 21.0 |
| 2l | 8.81—8.55(m, 3H), 8.34(s, 1H), 7.42(d, J=7.9 Hz, 1H), 7.09(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 6.98(t, J=4.7 Hz, 1H), 2.53(s, 3H), 2.38(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.1, 157.8, 134.7, 133.6, 133.2, 123.8, 121.9, 117.1, 116.5, 115.9, 113.9, 22.2, 21.1 |
| 2m | 9.50(s, 1H), 8.72(d,J=4.6 Hz, 2H), 8.58(s, 1H), 7.95(d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.59(d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.08(t, J=4.6 Hz, 1H), 3.98(s, 3H), 2.41(s, 3H) | 168.1, 168.0, 167.9, 158.3, 157.4, 133.1, 132.1, 127.3, 126.3, 123.2, 118.6, 117.7, 117.2, 116.6, 52.2, 29.7, 21.0 |
| 2n | 8.66(d,J=4.6 Hz, 2H), 8.57(d, J=11.0 Hz, 1H), 8.39(s, 1H), 7.52—7.38(m, 1H), 7.02(dd, J=11.8, 6.6 Hz, 2H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 162.3, 158.1, 157.5, 133.2, 132.8, 132.7, 120.5, 118.2, 118.1, 116.3, 114.7, 114.7, 110.7, 110.5, 103.9, 103.6 |
| 2o | 8.86(s, 1H), 8.66(d,J=4.5 Hz, 2H), 8.40(s, 1H), 7.45(d, J=8.3 Hz, 1H), 7.24(t, J=8.2 Hz, 1H), 7.04(t, J=4.4 Hz, 1H), 2.38(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.1, 157.4, 133.2, 132.9, 130.5, 122.7, 122.5, 118.3, 116.6, 116.4, 115.0, 21.0 |
| 2p | 9.03(s, 1H), 8.68(t,J=3.6 Hz, 2H), 8.41(s, 1H), 7.39(q, J=8.4 Hz, 2H), 7.14—6.96(m, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.1, 168.0, 158.2, 157.4, 133.2, 125.4, 122.9, 119.5, 118.6, 118.4, 116.5, 115.0, 21.0 |
| 2q | 9.00(dd,J=9.2, 2.5 Hz, 1H), 8.70—8.73(m, 2H), 8.59(d, J=8.8 Hz, 2H), 7.94(d, J=8.0 Hz, 1H), 7.75(d, J=9.2 Hz, 1H), 7.62—7.56(m, 1H), 7.52—7.46(m, 1H), 7.06(s, 1H), 2.53(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.2, 157.8, 135.4, 130.3, 129.9, 128.4, 127.0, 126.1, 125.1, 124.3, 123.7, 117.1, 116.7, 116.6, 113.8, 21.6 |
| 2r | 8.77(d,J=8.4 Hz, 1H), 8.47(s, 2H), 8.39(s, 1H), 7.55(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.36(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.24(t, J=7.5 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H), 2.27(s, 3H) | 168.2, 158.0, 156.1, 133.1, 132.7, 125.1, 124.4, 123.8, 121.9, 117.4, 116.2, 114.7, 21.0, 15.0 |
| 2s | 8.89—8.81(m, 3H), 8.47(s, 1H), 7.57(d, J=6.3 Hz, 3H), 7.50(t, J=7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.46—7.36(m, 2H), 7.27(t, J=8.1 Hz, 1H), 2.40(s, 3H) | 168.1, 156.8, 156.0, 134.4, 133.6, 132.8, 129.4, 129.0, 128.4, 126.5, 124.7, 124.0, 122.3, 117.5, 116.4, 114.6, 21.0 |
| 2t | 8.73—8.60(m, 3H), 8.34(s, 1H), 7.55(d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.36(t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 7.26(t, J=6.3 Hz, 1H), 2.39(s, 3H) | 168.0, 158.5, 155.9, 133.9, 132.7, 124.9, 124.1, 122.5, 117.6, 116.4, 114.4, 113.0, 21.1 |
| Entry | R | T/℃ | Molar fraction(%) | Yieldb(%) | Entry | R | T/℃ | Molar fraction(%) | Yieldb(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | 50 | 150 | 0 | 10 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 25 | 150 | 0 |
| 2 | Me | 50 | 150 | 0 | 11 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 40 | 150 | 45 |
| 3 | Bn | 50 | 150 | 0 | 12 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 150 | 85 |
| 4 | Ph | 50 | 150 | 40 | 13 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 70 | 150 | 83 |
| 5 | 2-Py | 50 | 150 | 65 | 14 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 80 | 150 | 80 |
| 6 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 50 | 150 | 78 | 15 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 110 | 83 |
| 7 | Ac | 50 | 150 | 0 | 16 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 120 | 85 |
| 8 | Boc | 50 | 150 | 0 | 17 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 200 | 80 |
| 9 | PhSO2 | 50 | 150 | 0 | 18 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 250 | 76 |
Table 3 Optimization of the reaction conditionsa
| Entry | R | T/℃ | Molar fraction(%) | Yieldb(%) | Entry | R | T/℃ | Molar fraction(%) | Yieldb(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | 50 | 150 | 0 | 10 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 25 | 150 | 0 |
| 2 | Me | 50 | 150 | 0 | 11 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 40 | 150 | 45 |
| 3 | Bn | 50 | 150 | 0 | 12 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 150 | 85 |
| 4 | Ph | 50 | 150 | 40 | 13 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 70 | 150 | 83 |
| 5 | 2-Py | 50 | 150 | 65 | 14 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 80 | 150 | 80 |
| 6 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 50 | 150 | 78 | 15 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 110 | 83 |
| 7 | Ac | 50 | 150 | 0 | 16 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 120 | 85 |
| 8 | Boc | 50 | 150 | 0 | 17 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 200 | 80 |
| 9 | PhSO2 | 50 | 150 | 0 | 18 | 2-Pyrimidyl | 60 | 250 | 76 |
| Entry | Product | R1 | R2 | Yield*(%) | Entry | Product | R1 | R2 | Yield*(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | H | H | 85 | 11 | 2k | 5-Br | H | 85 |
| 2 | 2b | 4-Me | H | 76 | 12 | 2l | 6-Me | H | 83 |
| 3 | 2c | 4-OBn | H | 63 | 13 | 2m | 6-CO2Me | H | 63 |
| 4 | 2d | 4-Cl | H | 73 | 14 | 2n | 6-F | H | 77 |
| 5 | 2e | 4-CO2Me | H | 75 | 15 | 2o | 6-Cl | H | 70 |
| 6 | 2f | 5-Me | H | 78 | 16 | 2p | 6-Br | H | 80 |
| 7 | 2g | 5-OMe | H | 80 | 17 | 2q | 5,6-Ph | H | 45 |
| 8 | 2h | 5-OBn | H | 65 | 18 | 2r | H | Me | 84 |
| 9 | 2i | 5-OPh | H | 86 | 19 | 2s | H | Ph | 81 |
| 10 | 2j | 5-Cl | H | 83 | 20 | 2t | H | Br | 72 |
Table 4 Substrate scope of the C3—H acetoxylation of indoles
| Entry | Product | R1 | R2 | Yield*(%) | Entry | Product | R1 | R2 | Yield*(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2a | H | H | 85 | 11 | 2k | 5-Br | H | 85 |
| 2 | 2b | 4-Me | H | 76 | 12 | 2l | 6-Me | H | 83 |
| 3 | 2c | 4-OBn | H | 63 | 13 | 2m | 6-CO2Me | H | 63 |
| 4 | 2d | 4-Cl | H | 73 | 14 | 2n | 6-F | H | 77 |
| 5 | 2e | 4-CO2Me | H | 75 | 15 | 2o | 6-Cl | H | 70 |
| 6 | 2f | 5-Me | H | 78 | 16 | 2p | 6-Br | H | 80 |
| 7 | 2g | 5-OMe | H | 80 | 17 | 2q | 5,6-Ph | H | 45 |
| 8 | 2h | 5-OBn | H | 65 | 18 | 2r | H | Me | 84 |
| 9 | 2i | 5-OPh | H | 86 | 19 | 2s | H | Ph | 81 |
| 10 | 2j | 5-Cl | H | 83 | 20 | 2t | H | Br | 72 |
| [1] | Cacchi S., Fabrizi G., Chem. Rev., 2005, 105(7), 2873—2920 |
| [2] | Kang C. M., Zhao X. H., Yu Y. Q., Lü Y. T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(3), 550—554 |
| (康从民, 赵绪浩, 于玉琪, 吕英涛. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(3), 550—554) | |
| [3] | Zhang J. H., Lü Y., Jia H. L., Song Y. Y., Sun X. X., Chai D. X., Wang L. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10), 1924—1932 |
| (张江华, 吕英, 贾红亮, 宋银银, 孙晓霞, 柴敦宵, 王兰英. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(10), 1924—1932) | |
| [4] | Cheng X., Li X. L., Wan W. L., Hao W. M., Hai L., Wu Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(1), 53—59 |
| [5] | Li X. L., Qiu R., Wan W. L., Cheng X., He Y., Hai L., Wu Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(4), 539—542 |
| [6] | Guyen B., Schultes C. M., Hazel P., Mann J., Neidle S., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2004, 2(7), 981—988 |
| [7] | Arnold R. D., Nutter W. M., Stepp W. L., J. Org. Chem., 1959, 24(1), 117—118 |
| [8] | Bandini M., Eichholzer A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48(51), 9608—9644 |
| [9] | Chen J. R., Li C. F., An X. L., Zhang J. J., Zhu X.Y., Xiao W. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008, 47(13), 2489—2492 |
| [10] | An X. L., Chen J. R., Li C. F., Zhang F. G., Zou Y. Q., Guo Y. C., Xiao W. J., Chem. Asian J., 2010, 5(10), 2258—2265 |
| [11] | Cho S. H., Kim J. Y., Kwak J., Chang S., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(10), 5068—5083 |
| [12] | Stuart D. R., Fagnou K., Science, 2007, 316(5), 1172—1175 |
| [13] | Liu H. H., Wang Y., Deng G., Yang L., Adv. Synth. Catal., 2013, 355(17), 3369—3374 |
| [14] | Li Y. X., Wang H. X., Ali S., Xia X. F., Liang Y. M., Chem. Commun., 2012, 48(17), 2343—2345 |
| [15] | Liu Q., Li G., Yi H., Wu P., Liu J., Lei A., Chem. Eur. J., 2011, 17(8), 2353—2357 |
| [16] | Sun C. L., Shi Z. J., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(18), 9219—9280 |
| [17] | Allais C., Grassot J. M., Rodriguez J., Constantieux T., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(21), 10829—10868 |
| [18] | Zhdankin V. V., Stang P. J., Chem. Rev., 2002, 102(7), 2523—2584 |
| [19] | Wirth T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44(24), 3656—3665 |
| [20] | Cho S. H., Yoon J., Chang S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(15), 5996—6005 |
| [21] | Liu K., Wen P., Liu J., Huang G., Synthesis, 2010, 21, 3623—3626 |
| [22] | Ackermann L., Dell’Acqua M., Fenner S., Vicente R., Sandmann R., Org. Lett., 2011, 13(9), 2358—2360 |
| [23] | Wen J., Zhang R. Y., Chen S. Y., Zhang J., Yu X. Q., J. Org. Chem., 2012, 77(1), 766—771 |
| [24] | Wang L., Qu X., Li Z., Peng W. M., Tetrahedron Lett., 2015, 56(24), 3754—3757 |
| [25] | Wang L., Qu X., Li Z., Peng W. M., Chin. J. Org. Chem., 2015, 35(3), 688—697 |
| (王亮, 瞿星, 李站, 彭望明. 有机化学, 2015, 35(3), 688—697) |
| [1] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [2] | JIN Ruiming, MU Xiaoqing, XU Yan. Bio-chemical Synthesis of Melanin Precursor—— 5,6-Dihydroxyindole(DHI) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220134. |
| [3] | MU Hongwen, WU Hao, GAO Yingying, JIN Ying, WANG Liming. Organocatalyzed Asymmetric Friedel-Crafts Alkylation in the Carbocyclic Ring of Indole [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210571. |
| [4] | LIU Miao, LIU Ruibo, LIU Badi, QIAN Ying. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Lysosome-targeted Indole-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [5] | LI Pengjie, ZHOU Chunni, WANG Zetian, ZHENG Ziang, ZHANG Yumin, WANG Liang, XIAO Biao. Rhodium⁃catalyzed C—H Alkenylation of Indoles and Vinyltriethoxysilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2450. |
| [6] | NAN Jiang, CHEN Pu, MA Yangmin. Acid-promoted [5+1] Annulation of 2-Vinylanilines with Diazo Compounds to 2-Arylquinolines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2457. |
| [7] | SO Chauming, YUEN Onying, KWONG Fukyee, CHEN Chihchiang, PAI Chengchao, SUN Raymond Waiyin. Application of CM-Phos Ligand in Palladium-catalyzed Cross-coupling Reactions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(10): 2185. |
| [8] | LI Bing,WANG Xuemin,BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing. Synthesises, Structures and Antibacterial Activities of a Series of Rare Earth Nitrogen Heterocyclic Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 632. |
| [9] | LIU Tianwei, ZHANG Sutao, HE Jianghua, ZHANG Yuetao. Metal-free B(C6F5)3 Catalyzed Regioselective Addition of Indole to Phenylacetylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 719. |
| [10] | Yingying ZHANG,Yiwen HUANG,Bing ZHAO,Liyan WANG,Bo SONG. Synthesis of a Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe of Cr 3+ and Its Application in Cell Imaging † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2486. |
| [11] | . Co-immobilized Laccase-Mediator System with Ionic Liquids-regenerated Cellulose Microspheres for Indole Degradation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1846. |
| [12] | GUO Ming, ZHANG Xinge, ZENG Chuchu, YIN Xinxin. Preparation and Properties Characterization of Intelligent Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on Diles-Alder Reaction† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 566. |
| [13] | LIN Hai, LI Yawei, LIN Huakuan. Anion Recognition of Indole-3-Aldehyde-o-Nitrophenylsemicarbazone† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 480. |
| [14] | ZHANG Jianghua, LÜ Ying, JIA Hongliang, SONG Yinyin, SUN Xiaoxia, CHAI Dunxiao, WANG Lanying. Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Spectral Properties of Six Indole Dimethine Cyanines as Well as Their Biological Application† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1924. |
| [15] | WU Qiong, MEI Wen-Jie, WU Wei-Li, CHEN Yan-Hua, ZENG Ling-Li, ZHENG Wen-Jie. Microwave-assisted Synthesis of Arene Ru(Ⅱ) Complex [(η6-C6H6)Ru(H2iiP)Cl]Cl in SiC Vessel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(8): 1863. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||