

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 559.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150605
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Qiang1, XIAO Jijun1,*( ), ZHANG Jiang1, ZHAO Feng2, HE Zhenghua2, XIAO Heming1,*(
), ZHANG Jiang1, ZHAO Feng2, HE Zhenghua2, XIAO Heming1,*( )
)
Received:2015-07-31
Online:2016-03-10
Published:2016-01-24
Contact:
XIAO Jijun,XIAO Heming
E-mail:xiao_jijun@njust.edu.cn;xiao@mail.njust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Qiang, XIAO Jijun, ZHANG Jiang, ZHAO Feng, HE Zhenghua, XIAO Heming. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on CL-20/TNT Cocrystal Explosive†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 559.
| T/K | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95 | 0.935 | 1.958 | 2.470 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.94 | 4.521 |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.18) | (0.14) | (0.13) | (0.01) | (0.011) | |
| 195 | 0.872 | 2.216 | 2.452 | 90.02 | 90.02 | 89.99 | 1.86 | 4.739 |
| (0.014) | (0.011) | (0.007) | (0.36) | (0.25) | (0.22) | (0.01) | (0.016) | |
| 245 | 0.878 | 2.210 | 2.462 | 90.01 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.85 | 4.775 |
| (0.003) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.42) | (0.27) | (0.25) | (0.01) | (0.179) | |
| 295 | 0.882 | 2.208 | 2.473 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.84 | 4.815 |
| (0.007) | (0.020) | (0.010) | (0.44) | (0.31) | (0.31) | (0.01) | (0.023) | |
| 345 | 0.886 | 2.211 | 2.483 | 89.99 | 89.99 | 90.00 | 1.82 | 4.860 |
| (0.008) | (0.021) | (0.011) | (0.49) | (0.34) | (0.33) | (0.01) | (0.024) | |
| 395 | 0.892 | 2.212 | 2.491 | 90.02 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.80 | 4.912 |
| (0.009) | (0.024) | (0.012) | (0.53) | (0.37) | (0.36) | (0.01) | (0.027) | |
| Exp.[ | 0.967 | 1.937 | 2.469 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.91 | 4.626 |
Table 1 Primitive lattice parameters, cell densities and volumes of CL-20/TNT cocrystal at different temperatures*
| T/K | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95 | 0.935 | 1.958 | 2.470 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.94 | 4.521 |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.18) | (0.14) | (0.13) | (0.01) | (0.011) | |
| 195 | 0.872 | 2.216 | 2.452 | 90.02 | 90.02 | 89.99 | 1.86 | 4.739 |
| (0.014) | (0.011) | (0.007) | (0.36) | (0.25) | (0.22) | (0.01) | (0.016) | |
| 245 | 0.878 | 2.210 | 2.462 | 90.01 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.85 | 4.775 |
| (0.003) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.42) | (0.27) | (0.25) | (0.01) | (0.179) | |
| 295 | 0.882 | 2.208 | 2.473 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.84 | 4.815 |
| (0.007) | (0.020) | (0.010) | (0.44) | (0.31) | (0.31) | (0.01) | (0.023) | |
| 345 | 0.886 | 2.211 | 2.483 | 89.99 | 89.99 | 90.00 | 1.82 | 4.860 |
| (0.008) | (0.021) | (0.011) | (0.49) | (0.34) | (0.33) | (0.01) | (0.024) | |
| 395 | 0.892 | 2.212 | 2.491 | 90.02 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.80 | 4.912 |
| (0.009) | (0.024) | (0.012) | (0.53) | (0.37) | (0.36) | (0.01) | (0.027) | |
| Exp.[ | 0.967 | 1.937 | 2.469 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.91 | 4.626 |
| Sample | T/K | vdW energy/(kJ·cm-3) | Electrostatic energy/(kJ·cm-3) | CED/(kJ·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 0.37(0.01) | 0.54(0.01) | 0.91(0.01) |
| 245 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.52(0.01) | 0.88(0.01) | |
| 295 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.50(0.01) | 0.86(0.01) | |
| 345 | 0.35(0.00) | 0.48(0.01) | 0.83(0.01) | |
| 395 | 0.34(0.00) | 0.47(0.01) | 0.81(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 0.31(0.01) | 0.45(0.01) | 0.76(0.01) |
Table 2 Cohesive energy density(CED) and its components of CL-20/TNT cocrystal at different temperatures and CL-20/TNT composite at 295 K*
| Sample | T/K | vdW energy/(kJ·cm-3) | Electrostatic energy/(kJ·cm-3) | CED/(kJ·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 0.37(0.01) | 0.54(0.01) | 0.91(0.01) |
| 245 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.52(0.01) | 0.88(0.01) | |
| 295 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.50(0.01) | 0.86(0.01) | |
| 345 | 0.35(0.00) | 0.48(0.01) | 0.83(0.01) | |
| 395 | 0.34(0.00) | 0.47(0.01) | 0.81(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 0.31(0.01) | 0.45(0.01) | 0.76(0.01) |
| Sample | T/K | Ebind/ (kJ·mol-1) | Nonbond energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | vdW energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Repulsive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Dispersive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Electrostatic energy/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 178.90(0.37) | 178.90(0.37) | 65.73(0.21) | -181.76(0.77) | 247.48(0.65) | 113.17(0.39) |
| 245 | 176.77(0.26) | 176.77(0.26) | 65.94(0.24) | -178.47(0.60) | 244.41(0.63) | 110.83(0.31) | |
| 295 | 174.19(0.30) | 174.19(0.44) | 65.50(0.39) | -176.72(1.32) | 242.22(1.02) | 108.69(0.64) | |
| 345 | 169.43(0.42) | 169.43(0.42) | 64.78(0.26) | -170.80(0.99) | 235.58(0.82) | 104.65(0.34) | |
| 395 | 166.18(0.65) | 166.18(0.65) | 63.82(0.39) | -166.96(1.05) | 230.78(0.85) | 102.36(0.39) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 75.27(0.42) | 75.27(0.42) | 29.66(0.19) | -74.03(0.62) | 103.69(0.68) | 45.61(0.29) |
Table 3 Binding energy and its components of CL-20/TNT cocrystal at different temperatures and CL-20/TNT composite at 295 K*
| Sample | T/K | Ebind/ (kJ·mol-1) | Nonbond energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | vdW energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Repulsive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Dispersive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Electrostatic energy/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 178.90(0.37) | 178.90(0.37) | 65.73(0.21) | -181.76(0.77) | 247.48(0.65) | 113.17(0.39) |
| 245 | 176.77(0.26) | 176.77(0.26) | 65.94(0.24) | -178.47(0.60) | 244.41(0.63) | 110.83(0.31) | |
| 295 | 174.19(0.30) | 174.19(0.44) | 65.50(0.39) | -176.72(1.32) | 242.22(1.02) | 108.69(0.64) | |
| 345 | 169.43(0.42) | 169.43(0.42) | 64.78(0.26) | -170.80(0.99) | 235.58(0.82) | 104.65(0.34) | |
| 395 | 166.18(0.65) | 166.18(0.65) | 63.82(0.39) | -166.96(1.05) | 230.78(0.85) | 102.36(0.39) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 75.27(0.42) | 75.27(0.42) | 29.66(0.19) | -74.03(0.62) | 103.69(0.68) | 45.61(0.29) |
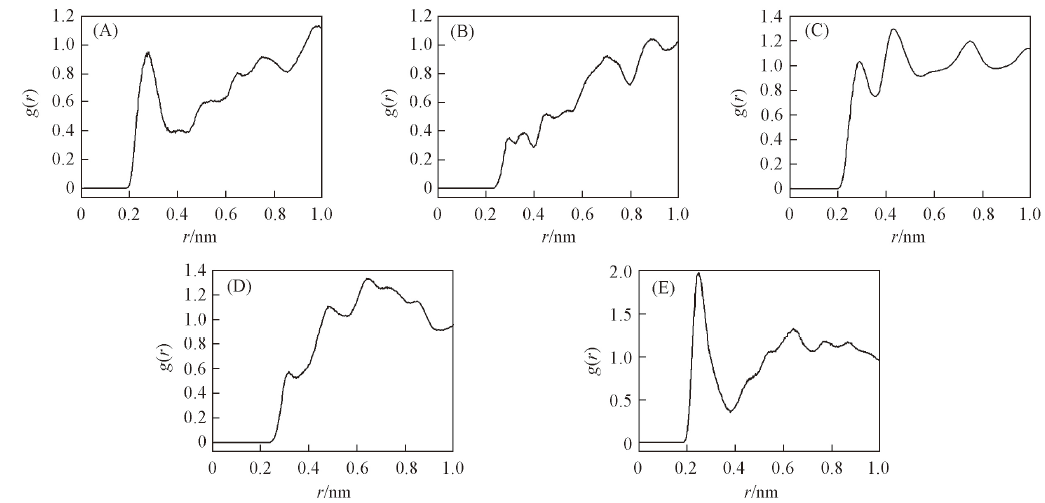
Fig.4 g(r)-r curves of H-O pairs and H-N pairs among CL-20 molecules and between CL-20 and TNT molecules in cocrystal (A) H(2)-O(2); (B) H(2)-N(2); (C) H(1)-O(2); (D) H(1)-N(2); (E) H(2)-O(1).
| Sample | T/K | Mechanical modulus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12-C44/GPa | E/GPa | K/GPa | G/GPa | ν | K/G | ||
| ε-CL-20 | 195 | -6.30(0.14) | 19.50(0.08) | 11.44(0.06) | 8.02(0.03) | 0.22(0.00) | 1.43(0.03) |
| 245 | -5.64(0.21) | 18.47(0.09) | 11.30(0.08) | 7.52(0.05) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 295 | -5.08(0.11) | 17.11(0.02) | 10.46(0.08) | 6.96(0.01) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 345 | -5.23(0.10) | 15.93(0.24) | 9.78(0.06) | 6.49(0.11) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.04) | |
| 395 | -4.32(0.07) | 14.93(0.04) | 9.17(0.05) | 6.08(0.02) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT | 195 | 6.49(0.11) | 7.57(0.06) | 9.38(0.09) | 2.77(0.03) | 0.37(0.00) | 3.39(0.05) |
| 245 | 6.26(0.07) | 6.30(0.06) | 8.94(0.07) | 2.28(0.02) | 0.38(0.00) | 3.92(0.06) | |
| 295 | 5.50(0.04) | 5.65(0.07) | 8.20(0.05) | 2.04(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.02(0.06) | |
| 345 | 4.93(0.06) | 5.10(0.14) | 7.59(0.05) | 1.84(0.05) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.14(0.13) | |
| 395 | 4.32(0.06) | 4.58(0.08) | 6.84(0.04) | 1.65(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.15(0.08) | |
| TNT | 195 | -1.51(0.07) | 7.13(0.03) | 7.00(0.04) | 2.68(0.01) | 0.33(0.00) | 2.61(0.02) |
| 245 | -1.47(0.10) | 5.99(0.05) | 6.08(0.08) | 2.24(0.02) | 0.34(0.00) | 2.71(0.02) | |
| 295 | 0.37(0.06) | 5.50(0.04) | 5.99(0.02) | 2.04(0.02) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.93(0.03) | |
| 345 | 0.84(0.14) | 5.43(0.03) | 5.98(0.12) | 2.01(0.01) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.97(0.05) | |
| 395 | |||||||
Table 4 Mechanical properties for ε-CL-20 crystal, CL-20/TNT cocrystal and TNT crystal at different temperatures*
| Sample | T/K | Mechanical modulus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12-C44/GPa | E/GPa | K/GPa | G/GPa | ν | K/G | ||
| ε-CL-20 | 195 | -6.30(0.14) | 19.50(0.08) | 11.44(0.06) | 8.02(0.03) | 0.22(0.00) | 1.43(0.03) |
| 245 | -5.64(0.21) | 18.47(0.09) | 11.30(0.08) | 7.52(0.05) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 295 | -5.08(0.11) | 17.11(0.02) | 10.46(0.08) | 6.96(0.01) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 345 | -5.23(0.10) | 15.93(0.24) | 9.78(0.06) | 6.49(0.11) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.04) | |
| 395 | -4.32(0.07) | 14.93(0.04) | 9.17(0.05) | 6.08(0.02) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT | 195 | 6.49(0.11) | 7.57(0.06) | 9.38(0.09) | 2.77(0.03) | 0.37(0.00) | 3.39(0.05) |
| 245 | 6.26(0.07) | 6.30(0.06) | 8.94(0.07) | 2.28(0.02) | 0.38(0.00) | 3.92(0.06) | |
| 295 | 5.50(0.04) | 5.65(0.07) | 8.20(0.05) | 2.04(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.02(0.06) | |
| 345 | 4.93(0.06) | 5.10(0.14) | 7.59(0.05) | 1.84(0.05) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.14(0.13) | |
| 395 | 4.32(0.06) | 4.58(0.08) | 6.84(0.04) | 1.65(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.15(0.08) | |
| TNT | 195 | -1.51(0.07) | 7.13(0.03) | 7.00(0.04) | 2.68(0.01) | 0.33(0.00) | 2.61(0.02) |
| 245 | -1.47(0.10) | 5.99(0.05) | 6.08(0.08) | 2.24(0.02) | 0.34(0.00) | 2.71(0.02) | |
| 295 | 0.37(0.06) | 5.50(0.04) | 5.99(0.02) | 2.04(0.02) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.93(0.03) | |
| 345 | 0.84(0.14) | 5.43(0.03) | 5.98(0.12) | 2.01(0.01) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.97(0.05) | |
| 395 | |||||||
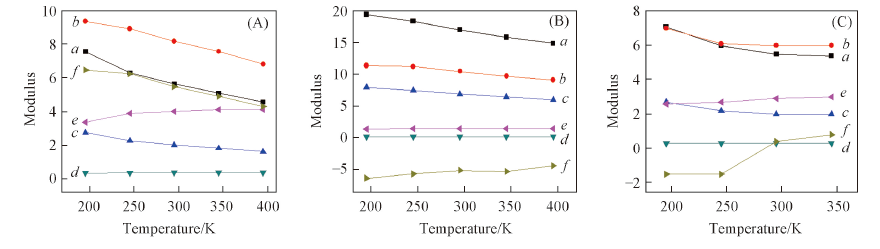
Fig.8 Mechanical properties of CL-20/TNT cocrystal(A), ε-CL-20(B) and TNT(C) crystals vs. temperatureModulus: a. E/GPa; b. K/GPa; c. G/GPa; d. ν; e. K/G; f. C12-C44/GPa.
| [1] | Lara O. F., Espinosa P. G., Supramolecular Chemistry, 2007, 19(8), 553—557 |
| [2] | Stahly G. P., Crystal Growth and Design, 2009, 9(10), 4212—4229 |
| [3] | Ji B. M., Deng D. S., Ma N., Miao S.B., Liu P., Li X. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9), 2114—2122 |
| (吉保明, 邓冬生, 马宁, 苗少斌, 刘鹏, 李贤飞. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(9), 2114—2122) | |
| [4] | Chen J. M., Wu C. B., Lu T. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9), 1996—2009 |
| (陈嘉媚, 吴传斌, 鲁统部. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(9), 1996—2009) | |
| [5] | Michael L., Propellant Made with Cocrystals of Cyclotetramethy Lenetetramine and AmmoniumPerchlorate,US 4086110, 1978-04-25 |
| [6] | Levakova I. V., Korobko A. P., Krasheninnikov S. V., Zavodnik V. E., Kristallografiya,1996, 41(6), 963—965 |
| [7] | Jin P. S., Xiao H. D., Qing P. L., Yong Z., Qiao L. B., Yong J. L., Chong H. P., Crystal Growth and Design,2011, 11, 1759—1765 |
| [8] | Wei C. X., Duan X. H., Liu C. J., Liu Y G., Li J. S., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2009, 67(24), 2822—2826 |
| (卫春雪, 段晓惠, 刘成建, 刘永刚, 李金山. 化学学报, 2009, 67(24), 2822—2826) | |
| [9] | Guo C. Y., Zhang H. B., Wang X. C., Sun J., Materials Review, 2012, 26(19), 49—53 |
| (郭长艳, 张浩斌, 王晓川, 孙杰. 材料导报, 2012, 26(19), 49—53) | |
| [10] | Bolton O., Matzger A. J., Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed., 2011, 50(38), 8960—8963 |
| [11] | Yang Z. W., Zhang Y. L., Li H. Z., Zhou X. Q., Nie F. D., Li J. S., Huang H., Chin. J. Energetic Materials, 2012, 20(6), 674—679 |
| (杨宗伟, 张艳丽, 李洪珍, 周小青, 聂福德, 李金山, 黄辉. 含能材料. 2012, 20(6), 674—679) | |
| [12] | Yang Z. W, Huang H., Li H. Z., Zhou X. Q., Li J. S., Nie F. D., Chin. J. Energetic Materials, 2012, 20(2), 256—257 |
| (杨宗伟, 黄辉, 李洪珍, 周小清, 李金山, 聂福德. 含能材料. 2012, 20(2), 256—257) | |
| [13] | Yang Z. W., Li H. Z., Huang H., Zhou X. Q., Li J. S., Nie F. D., Propellants, Explosives Pyrotechnics, 2013, 38(4), 495—501 |
| [14] | Aldoshin S. M., Aliev Z. G., Goncharov T. K., Kazakov A. I., Milekhin Yu. M., Plishkin N. A., Shishov N. I. Russ. Chem. Bull., Int.Ed..2013, 62(6), 1354—1360 |
| [15] | Liu H., Li Q. K., He Y. H., Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(20), 208202 |
| (刘海, 李启楷, 何远航. 物理学报, 2013, 62(20), 208202) | |
| [16] | Ou Y. X., Meng Z., Liu J. Q., Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2007, 26(12), 1690—1694 |
| (欧育湘, 孟征, 刘进全. 化工进展. 2007, 26(12), 1690—1694) | |
| [17] | Xiao H.M., Xu X, J., Qiu L., The Theoretical Design of High Energy Density Material, Science Press, Beijing, 2008, 19—32 |
| (肖鹤鸣, 许晓娟, 邱玲. 高能量密度材料的理论设计, 北京: 科学出版社, 2008, 19—32) | |
| [18] | Xu X. J., Xiao H. M., Ju X. H., Gong X. D., Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry,2005, 25(5), 536—539 |
| (许晓娟, 肖鹤鸣, 居学海, 贡雪东. 有机化学, 2005, 25(5), 536—539) | |
| [19] | Agrawal J. P., Propellants,Explosives,Pyrotechnics.2005, 30(5), 316—328 |
| [20] | Foltz M. F., Coon C. L., Garcia F., Nichols A. L., Propellants, Explosives Pyrotechnics, 1994, 19(1), 19—25 |
| [21] | Sun H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(38), 7338—7364 |
| [22] | Xu X. J., Xiao H. M., Xiao J. J., Zhu W., Huang H., Li J. S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(14), 7203—7207 |
| [23] | Xu X. J., Xiao J. J., Huang H., Li J. S., Xiao H. M., Science in China B, Chemistry,2007, 50(6), 737—745 |
| [24] | Zhou Y., Long X. P., Wei X. W., Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2011, 17(11), 3015—3019 |
| [25] | Zhao X. Q., Shi N. C., Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(23), 2158—2160 |
| (赵信岐, 施倪承. 科学通报, 1995, 40(23), 2158—2160) | |
| [26] | Vrcelj R. M., Sherwood J. N., Kennedy A. R., Gallagher H. G., Gelbrich T., Crystal Growth and Design,2003, 3(6), 1027—1032 |
| [27] | Andersen H. C., J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72(4), 2384—2393 |
| [28] | Parrinello M., Rahman A., J. Appl. Phys., 1981, 52, 7182—7190 |
| [29] | Xiao J.J.,Zhu W. H., Zhu W., Xiao H. M., Molecular Dynamics Study on High Energy Materials, Science Press, Beijing, 2013, 54—65 |
| (肖继军, 朱卫华, 朱伟, 肖鹤鸣. 高能材料分子动力学, 北京: 科学出版社, 2013, 54—65) | |
| [30] | Pugh S. F., Philosophical Magazine, 1954, A45, 823—843 |
| [31] | Pettifor D. G., Materials Science and Technology, 1992, 8(4), 345—349 |
| [32] | Xiao J. J., Wang W. R., Chen J., Ji G. F., Zhu W., Xiao H. M., Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2012, 999, 21—27 |
| [1] | LUO Xinyan, JIA Ruonan, XIANG Yong, ZHANG Xiaokun. Progress on the Stretchable Composite Solid Polymer Electrolytes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220149. |
| [2] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [3] | ZENG Xianyang, ZHAO Xi, HUANG Xuri. Mechanism of Inhibition of Glucose and Proton Cotransport Protein GlcPSe by Cytochalasin B [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [4] | CHEN Hanxiang, BIAN Shaoju, HU Bin, LI Wu. Molecular Simulation of the Osmotic Pressures for LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O Solution System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [5] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [6] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [7] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [8] | XU Huan, KE Lyu, TANG Mengke, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, ZHANG Zilin, FU Yanan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, GAO Jiefeng, ZHANG Shenghui, HE Xinjian. In⁃situ Liquid Exfoliation of Montmorillonite Nanosheets in Poly(lactic acid) to Resist Oxygen Permeation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220316. |
| [9] | ZHANG Lingyu, ZHANG Jilong, QU Zexing. Dynamics Study of Intramolecular Vibrational Energy Redistribution in RDX Molecule [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [10] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [11] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [12] | LIU Shasha, ZHANG Heng, YUAN Shiling, LIU Chengbu. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Pulsed Electric Field O/W Emulsion Demulsification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| [13] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [14] | WANG Xianwei, KE Hongjun, YUAN Hang, LU Gewu, LI Liying, MENG Xiangsheng, SONG Shulin, WANG Zhen. High Temperature Resistant and Soluble Polyimide Resins and Their Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2041. |
| [15] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||