

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 608.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20141079
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
XIE Xian1, YU Meihua2, ZHANG Huiping1, WANG Yilin1,*( )
)
Received:2014-12-05
Online:2015-04-10
Published:2015-03-27
Contact:
WANG Yilin
E-mail:theanalyst@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XIE Xian, YU Meihua, ZHANG Huiping, WANG Yilin. Aqueous Synthesis of CdTe Quantum Dots via Ascorbic Acid Reducing Sodium Tellurite†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 608.
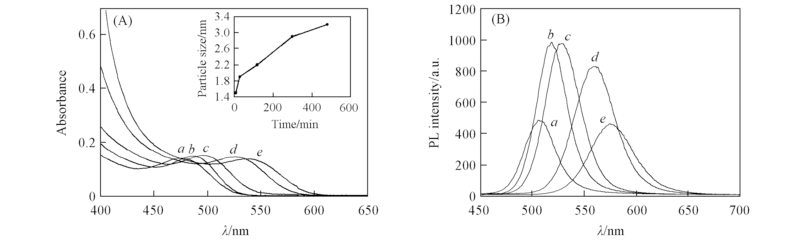
Fig.1 Absorption(A) and photoluminescence(B) spectra for a series of CdTe QDs prepared at pH=10.5, n(Cd):n(Te):n(TGA)=2:0.10:4.2 for different refluxing time Reflux time/min: a. 10; b. 30; c. 120; d. 300; e. 480. Inset of (A) shows the relationship between particle size and reflux time.
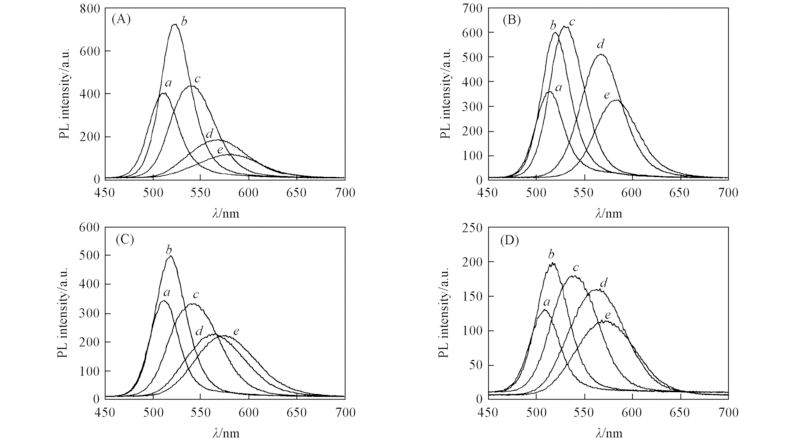
Fig.5 Influences of various TGA/Cd molar ratios on photoluminescence spectra of CdTeQDs prepared at pH=10.5n(Te):n(Cd)=0.1:2. n(TGA)/n(Cd): (A) 3.5/2; (B) 4.9/2; (C) 5.6/2; (D) 6.3/2. Reflux time/min: a. 10; b. 30; c. 120; d. 300; e. 480.
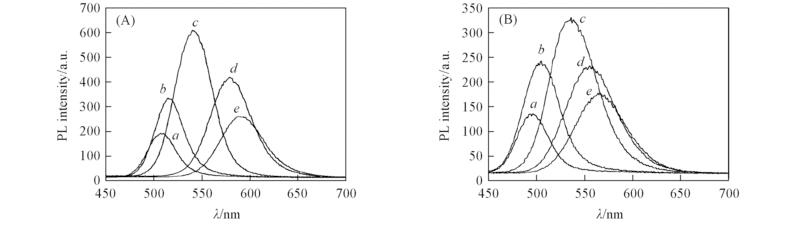
Fig.6 Influences of various Te/Cd molar ratios on photoluminescence spectra of CdTe QDs prepared at pH= 10.5 n(TGA):n(Cd)=4.2:2. n(Te)/n(Cd): (A) 0.05/2; (B) 0.15/2. Reflux time/min: a. 10; b. 30; c. 120; d. 300; e. 480.
| [1] | Zhao A. T., Xiong Y. L., Zeng H. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2011, 32(5), 1094—1099 |
| (赵爱婷, 熊艳玲, 曾和平. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(5), 1094—1099) | |
| [2] | Wu Y., Xu F., Guo D. F., Gao Z. Y., Wu D. P., Jiang K., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 274(6), 39—44 |
| [3] | Yang M., Yu T., Zhang Z. P., Wang S. H., Jiang H., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2014, 42(3), 436—440 |
| (杨敏, 余涛, 张忠平, 王素华, 蒋辉. 分析化学, 2014, 42(3), 436—440) | |
| [4] | Zhang Y. N., Jiang D., He Z., Yu Y. W., Zhang H. B., Jiang Z. H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2014, 30(1), 176—180 |
| [5] | Cui X. T., Lü Y. Y., Liu Y., Wu B. Y., Acta Chim. Sinica,2014, 72(1), 75—82 |
| (崔晓腾, 吕玉洋, 刘颖, 吴伯岳. 化学学报, 2014, 72(1), 75—82) | |
| [6] | Dukes A. D., McBride J. R., Rosenthal S. J., Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(23), 6402—6408 |
| [7] | Shen Q. H., Liu Y., Zou M. Q., Li J. F., Zhou J. G., Meng C. G., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2010, 26(6), 880—883 |
| [8] | Shi J. J., Wang S., He T. T., Jiang L. P., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2013, 29(10), 2071—2078 |
| (石建军, 王圣, 何婷婷, 姜立萍. 无机化学学报, 2013, 29(10), 2071—2078) | |
| [9] | Yuwen L. H., Xue B., Wang L. H., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30(5), 994—1000 |
| (宇文力辉, 薛冰, 汪联辉. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30(5), 994—1000) | |
| [10] | Bian Q. Q., Liu Y. F.,Yu J. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(6), 1118—1125 |
| (卞倩茜, 刘应凡, 于俊生. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(6), 1118—1125) | |
| [11] | Wang Y. L., Tong Z. F., Lu J. P., Li J. H., J. Chemical Industry and Engineering,2011, 62(3), 875—879 |
| (王益林, 童张法, 陆建平, 黎建辉. 化工学报, 2011, 62(3), 875—879) | |
| [12] | Wang Y. L., Huang W., Wang R. F., Zhou L. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2011, 32(12), 2727—2732 |
| (王益林, 黄武, 王荣芳, 周立亚. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(12), 2727—2732) | |
| [13] | Wang Y. L., Ma H. D., Liu S. Y, Li H. M., Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2013, 44(5), 1781—1786 |
| (王益林, 马浩德, 刘声燕, 李怀美. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 44(5), 1781—1786) | |
| [14] | Wang Y. L., Liu S. Y., Mo F. P., Pan H. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(1), 45—49 |
| (王益林, 刘声燕, 莫凤萍, 潘华桥. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(1), 45—49) | |
| [15] | Nawaz F., Wang L., Zhu L. F., Meng X. J., Xiao F. S., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2013, 29(3), 401—403 |
| [16] | Crosby G. A., Demas J. N., J. Phys. Chem., 1971, 75(8), 991—1024 |
| [17] | Yu W. W., Qu L. H., Guo W. Z, Peng X. G., Chem. Mater., 2003, 15(14), 2854—2860 |
| [18] | Kalasad M. N., Rabinal M. K., Mulimani B. G., Langmuir,2009, 25(21), 12729—12735 |
| [19] | Hodlur R. M., Rabinal M. K., Chem. Eng. J., 2014, 244, 82—88 |
| [20] | He Y., Sai L. M., Lu H. T., Hu M., Lai W. Y., Fan Q. L., Wang L. H., Huang W., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(3), 359—365 |
| [21] | Guo J., Yang W. L., Wang C. C., J. Phys. Chem. B,2005, 109(37), 17467—17473 |
| [22] | Wang Y. L., Wan X., Liu S. Y., Zhou L. Y., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2012, 28(1), 97—102 |
| (王益林, 万鑫, 刘声燕, 周立亚. 无机化学学报, 2012, 28(1), 97—102) | |
| [23] | Gaponik N., Talapin D. V., Rogach A. L., Hoppe K., Shevchenko E.V., Kornowski A., Eychmuller A., Weller H., J. Phys. Chem. B,2002, 106(29), 7177—7185 |
| [1] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [2] | SUN Xuefeng, RENAGUL Abdurahman, YANG Tongsheng, YANG Qianting. Synthesis and Luminescence Properties of Cr,In Co-doped Small Size MgGa2O4 Near-infrared Persistent Luminescence Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210850. |
| [3] | ZHENG Xuelian, YANG Cuicui, TIAN Weiquan. The Second Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Azulene-defect Graphene Nanosheets with Full Armchair Edge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [4] | ZHOU Yonghui, LI Yao, WU Yuxuan, TIAN Jing, XU Longquan, FEI Xu. Synthesis of A Novel Photoluminescence Self-healing Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210606. |
| [5] | ZHANG Liling, LIU Liu, ZHENG Mingqiu, FANG Wenkai, LIU Da, TANG Hongwu. Dual Signal Detection of HPV16 DNA by CRISPR/Cas12a Biosensing System Based on Upconversion Luminescent Resonance Energy Transfer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220412. |
| [6] | DU Shunfu, WANG Wenjing, EL⁃SAYED El⁃Sayed M., SU Kongzhao, YUAN Daqiang, HONG Maochun. A Chemiluminescent Zirconocene Coordination Tetrahedron [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210628. |
| [7] | WEI Minmin, YUAN Ze, LU Min, MA Hui, XIE Xiaoji, HUANG Ling. Recent Advances in Lanthanide Doped Upconversion Nanoparticle-Metal Organic Framework Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2313. |
| [8] | MENG Yan, WANG Xiufeng, ZHANG Li, LIU Minghua. Helical Structure and Circularly Polarized Luminescence of Naphthalene Derived Amphiphilic Molecules Through Air/water Interface Assembly [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1253. |
| [9] | ZHANG Huidong, GU Panpan, ZHANG Fang, DU Mingxu, YE Kaiqi, LIU Yu. Design and Electroluminescence Properties of Narrow-spectrum Phosphorescent Complexes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3571. |
| [10] | XI Jing, CHEN Na, YANG Yanbing, YUAN Quan. Recent Progress in Controlled Synthesis of Persistent Luminescence Nanomaterials for Diagnosis Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3247. |
| [11] | WANG Bodong, PAN Meichen, ZHUO Ying. Construction of Electrochemiluminescence Sensing Interface Based on Silver Nanoclusters-Silica Nanoparticles and Biomolecular Recognition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3519. |
| [12] | WANG Bolun, ZONG Siyu, LI Jiyang. Recent Progress on Photoluminescent Zeolite-based Composite Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 299. |
| [13] | LIAO Ni, ZHANG Jieyuan, HUANG Ziyang, ZHAO Yanxi, CHAI Yaqin, YUAN Ruo, ZHUO Ying. Construction of High Efficiency Uric Acid Sensor Based on the co-Crystal Enhanced Electrochemiluminescence from 9,10-Diphenylanthracene-perylene Microcrystals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1989. |
| [14] | CAO Zhiyuan, SUN Hui, SU Bin. Electrochemiluminescence of Quantum Dots: Research Progress and Future Perspectives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 1945. |
| [15] | XIE Ziyi, LIU Dan, ZHANG Yihan, LIU Qingqing, DONG Huanli, HU Wenping. Recent Advances on High Mobility Emissive Anthracene-derived Organic Semiconductors † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1179. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||