

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 733.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140905
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Xue, YANG Lili, WANG Chunzhong, CHEN Gang*( ), WEI Yingjin
), WEI Yingjin
Received:2014-10-11
Online:2015-04-10
Published:2015-03-27
Contact:
CHEN Gang
E-mail:gchen@jiu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Xue, YANG Lili, WANG Chunzhong, CHEN Gang, WEI Yingjin. Preparation and Characterizations of Zn-doped Li1.13Ni0.3-xMn0.57ZnxO2 Cathode Materials for Lithium Ion Batteries†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 733.
| x | a, b/nm | c/nm | c/a | I(003)/I(104) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.28782 | 1.42421 | 4.948 | 1.42 |
| 0.01 | 0.28786 | 1.43025 | 4.968 | 1.47 |
| 0.02 | 0.28852 | 1.43125 | 4.960 | 1.31 |
Table 1 Lattice parameters and intensity ratio of the (003) and (104) reflections of Zn-doped Li1.13Ni0.3-xMn0.57ZnxO2
| x | a, b/nm | c/nm | c/a | I(003)/I(104) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.28782 | 1.42421 | 4.948 | 1.42 |
| 0.01 | 0.28786 | 1.43025 | 4.968 | 1.47 |
| 0.02 | 0.28852 | 1.43125 | 4.960 | 1.31 |
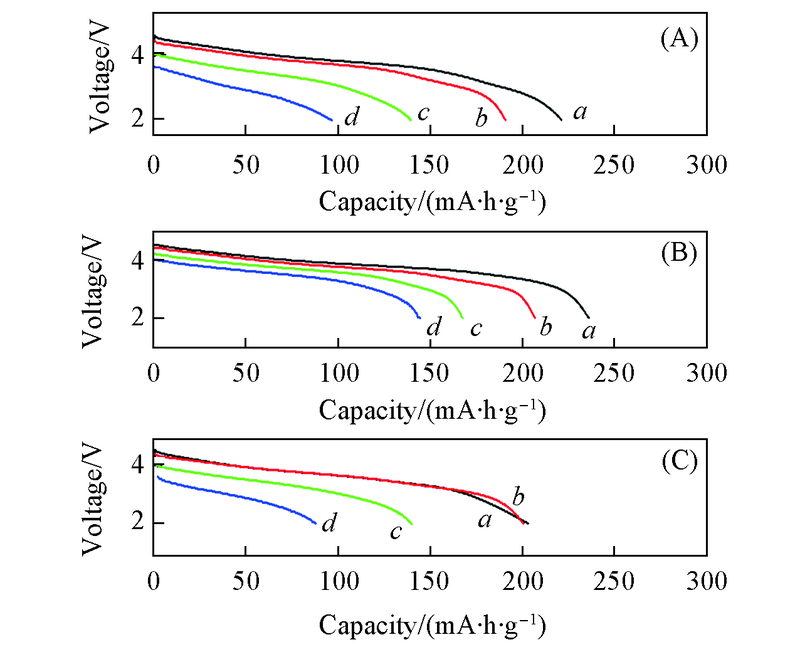
Fig.6 Discharge curves of Zn-doped Li1.13Ni0.3-xMn0.57·ZnxO2 at different current densities (A) x=0; (B) x=0.01; (C) x=0.02. Current density/(mA·g-1): a. 50; b. 100; c. 500; d. 1000.
| [1] | Lu Z. H., MacNeil D. D., Dahn J. R., Electrochemical and Solid-State Letters,2001, 4, A191—A194 |
| [2] | Zhao Y. J., Feng H. L., Zhao C. S., J. Inorg. Mater., 2011, 26, 673—679 |
| [3] | Thackeray M. M., Kang S. H., Johnson C. S., Vaughey J. T., Benedek R., Hackney S. A., J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17, 3112—3125 |
| [4] | Wang S. J., Zhao Y. J., Zhao C. S., Xia D. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2009, 30(12), 2358—2362 |
| (王绥军, 赵煜娟, 赵春松, 夏定国. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(12), 2358—2362) | |
| [5] | Lu J. B., Tang Z. L., Le B., Zhang Z. T., Shen W. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2005, 26(11), 2093—2096 |
| (卢俊彪, 唐子龙, 乐宾, 张中太, 沈万慈. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(11), 2093—2096) | |
| [6] | Wu F., Li N., Su Y. F., Lu H. Q., Zhang L. J., An R., Wang Z., Bao L. Y., Chen S., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 1489—1497 |
| [7] | Chen Y., Xu G. F., Li J. L., Zhang Y. K., Chen Z., Kang F. Y., Electrochimica Acta,2013, 88, 671—679 |
| [8] | Liu J., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 3961—3967 |
| [9] | Wang Q. Y., Liu J., Murugan A. V., J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, 4965—4972 |
| [10] | Wu Y., Manthiram A., Solid State Ionics,2009, 180, 50—56 |
| [11] | Zheng J. M., Li J., Zhang Z. R., Guo X. J., Yang Y., Solid State Ionics,2008, 179, 1794—1799 |
| [12] | Kang S. H., Thackeray M. M., Electrochem. Commun., 2009, 11, 748—751 |
| [13] | Wu Y., Murugan A. V., Manthiram A., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2008, 155, A635—A641 |
| [14] | Lee S. H., Koo B. K., Kim J. C., Kim K. M., J. Power Sources,2008, 184, 276—283 |
| [15] | Qiao Q. Q., Zhang H. Z., Li G. R., Ye S. H., Wang C. W., Gao X. P., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1, 5262—5268 |
| [16] | Li G. R., Feng X., Ding Y., Ye S. H., Gao X. P., Electrochimica Acta,2012, 78, 308—315 |
| [17] | Liu X. Y., Liu J. L., Huang T., Yu A. S., Electrochimica Acta,2013, 109, 52—58 |
| [18] | Sun Y.K., Lee M. J., Yoon C. S., Hassoun J., Amine K., Scrosati B.,Adv. Mater., 2012, 1192—1196 |
| [19] | Wu C. R., Fang X. P., Guo X. W., Mao Y., Ma J., Zhao C. C., Wang Z. X., Chen L. Q., J. Power Sources,2013, 231, 44—49 |
| [20] | Liu J., Wang Q. Y., Reeja J. B., Manthiram A., Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12, 750—753 |
| [21] | Song B. H., Lai. M. O., Liu Z. W., Lu L., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1, 9954—9965 |
| [22] | Kang S. H., Amine K., J. Power Sources,2005, 146, 654—657 |
| [23] | Ruth M. I., Park C. W., Yoon Y. K., Beom J. H., Kim J., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2007, 154(4), A359—A363 |
| [24] | Dianat A., Seriani N., Bobeth M., Cuniberti G., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1, 9273—9280 |
| [25] | Lu Z. H., Beaulieu L. Y., Donaberger R. A., Thomas C. L., Dahn J. R., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2002, 149, A778—A791 |
| [26] | Armstrong A. R., Holzapfel M., Novák P., Johnson C. S., Kang S. H., Thackeray M. M., Bruce P. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128, 8694—8698 |
| [27] | Xu B., Fell C. R., Chi M. F., Meng Y. S., Energy & Environmental Science,2011, 4, 2223—2233 |
| [28] | Gu M., Belharouak I., Zheng J. M., Wu H. M., Xiao J., Genc A., Amine K., Thevuthasan S., Bear D. R., Zhang J. G., ACS Nano,2013, 7, 760—767 |
| [1] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [2] | ZHANG Jun, WANG Bin, PAN Li, MA Zhe, LI Yuesheng. Synthesis and Properties of Imidazolium-based Polyethylene Ionomer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2070. |
| [3] | BAI Yanqun,WANG Cunguo,LI Xue,FAN Wenqi,SONG Penghao,GU Yuanchun,LIU Faqian,LIU Guangye. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of S@C Composite Material with High Capacity and Ordered Alignment of Channels † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1306. |
| [4] | DENG Anqiang,LUO Yongchun,XIA Yuanhua,PENG Sihui,MA Weiqin,ZHAO Xudong,YANG Yang,HOU Xiaodong. Effect of Annealing Treatment on Structure and Electrochemical Properties of New Mg-free Y0.7La0.3Ni3.25Al0.1Mn0.15 Hydrogen Storage Alloys † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 145. |
| [5] | YANG Jinge, LI Yujie, LU Di, CHEN Yufang, SUN Weiwei, ZHENG Chunman. Morphology Control and Lithium Storage Performance of Micro/nano Li-rich Cathode Material† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1495. |
| [6] | RAN Shiya,SHEN Haifeng,LI Xiaonan,WANG Zilu,GUO Zhenghong,FANG Zhengping. Effect and Mechanism of Rare Earth Trifluoromethanesulfonate on the Thermal Stability of Polypropylene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1333. |
| [7] | CHEN Yaoyan,ZHAO Xin,WANG Zhe,DONG Jie,ZHANG Qinghua. Effects of Preparation Conditions on the Morphologies, Structures and Electrochemical Properties of MXene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1249. |
| [8] | FANG Xijie,LIU Ruiyun,LIN Sen,SHI Lei,WANG Runwei,LI Yi,LI Junying. Synthesis of STW-zeotype Germanosilicate via Steam-assisted Crystallization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 867. |
| [9] | YIN Mengxin,LIU Dongsheng,ZHAO Dongyue,DING Tong,TIAN Ye,LI Xingang. Effect of Copper Doping on Lean NOx Trap Performance of Pt/Ba/CuxMg1-xAl2O4 Catalysts at High Temperatures † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2170. |
| [10] | LIU Yi, XU Xiaozhou, MO Song, ZHAI Lei, HE Minhui, FAN Lin. Thermal Stability of Polyimide Resins Containing Siloxane Structure and Their High Temperature Structural Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 187. |
| [11] | ZHAO Lei,LUO Yongchun,DENG Anqiang,JIANG Wanting. Hydrogen Storage and Electrochemical Properties of the Mg-free A2B7-type La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 Alloys with Superlattice Structure† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1993. |
| [12] | MENG Jiafeng, NI Xufeng, ZHENG Hao, SHEN Zhiquan. Copolymerization of Norbornene and 1-Octene Catalyzed by Bis(phenoxy-imine) Titanium Complex† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1853. |
| [13] | DU Shanshan, LI Yang, GUO Lei, LI Pengyu, CHAI Zhilong, WANG Tao, QUAN Dongqin, HE Junlin. Modification of Aptamer TBA with Extra Functional Groups and the Biological Activities† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2445. |
| [14] | LI Yang, LI Zhiwen, ZHU Junfei, LIU Shihui, HE Junlin. Construction of Pyrenyl Pairs in dsDNA: Fluorescent Properties of Multiple Pyrenyl-attached dsDNAs Through 7-Substituted 8-Aza-7-deaza-2'-deoxyadenosine Analogues† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2206. |
| [15] | LI Caixin, LIANG Xiaorong, GU Ju. Preparation and Characterization of Bagasse Nanocellulose† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1286. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||