

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 187.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180342
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Yi1,2, XU Xiaozhou1,2, MO Song1, ZHAI Lei1, HE Minhui1, FAN Lin1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-05-03
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2018-09-22
Contact:
FAN Lin
E-mail:fanlin@iccas.ac.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Yi, XU Xiaozhou, MO Song, ZHAI Lei, HE Minhui, FAN Lin. Thermal Stability of Polyimide Resins Containing Siloxane Structure and Their High Temperature Structural Evolution[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 187.
| Sample | n(TFDB):n(APDS) | Mass fraction of siloxane(%) | n | Mn(Theoretical) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEPA-PIS-0 | 10:0 | 0 | 1.23 | 1500 |
| PEPA-PIS-1 | 9:1 | 1.29 | 1.25 | 1500 |
| PEPA-PIS-2 | 8:2 | 2.59 | 1.26 | 1500 |
| PEPA-PIS-3 | 7:3 | 3.92 | 1.28 | 1500 |
| PA-PIS-1 | 9:1 | 1.47 | 1.60 | 1500 |
| PA-PIS-10 | 0:10 | 15.81 | 1.76 | 1500 |
Table 1 Chemical composition of PEPA-terminated and PA-terminated oligoimides
| Sample | n(TFDB):n(APDS) | Mass fraction of siloxane(%) | n | Mn(Theoretical) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEPA-PIS-0 | 10:0 | 0 | 1.23 | 1500 |
| PEPA-PIS-1 | 9:1 | 1.29 | 1.25 | 1500 |
| PEPA-PIS-2 | 8:2 | 2.59 | 1.26 | 1500 |
| PEPA-PIS-3 | 7:3 | 3.92 | 1.28 | 1500 |
| PA-PIS-1 | 9:1 | 1.47 | 1.60 | 1500 |
| PA-PIS-10 | 0:10 | 15.81 | 1.76 | 1500 |
| Structure | 370 ℃ | 420 ℃ | 450 ℃ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eb/eV | Molar fraction of Si(%) | Eb/eV | Molar fraction of Si(%) | Eb/eV | Molar fraction of Si(%) | |||||
| D[(CH3)2SiO2/2] | | 102.01 | 90.19 | 102.06 | 14.76 | 101.96 | 6.90 | |||
| T[CH3SiO3/2] | | 102.97 | 9.81 | 102.90 | 48.34 | 102.93 | 23.61 | |||
| Q[SiO4/2] | | —— | —— | 103.53 | 36.90 | 103.51 | 69.49 | |||
Table 2 Curve fitting results of Si2p XPS spectra for cured and postcured PEPA-PIS-1
| Structure | 370 ℃ | 420 ℃ | 450 ℃ | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eb/eV | Molar fraction of Si(%) | Eb/eV | Molar fraction of Si(%) | Eb/eV | Molar fraction of Si(%) | |||||
| D[(CH3)2SiO2/2] | | 102.01 | 90.19 | 102.06 | 14.76 | 101.96 | 6.90 | |||
| T[CH3SiO3/2] | | 102.97 | 9.81 | 102.90 | 48.34 | 102.93 | 23.61 | |||
| Q[SiO4/2] | | —— | —— | 103.53 | 36.90 | 103.51 | 69.49 | |||
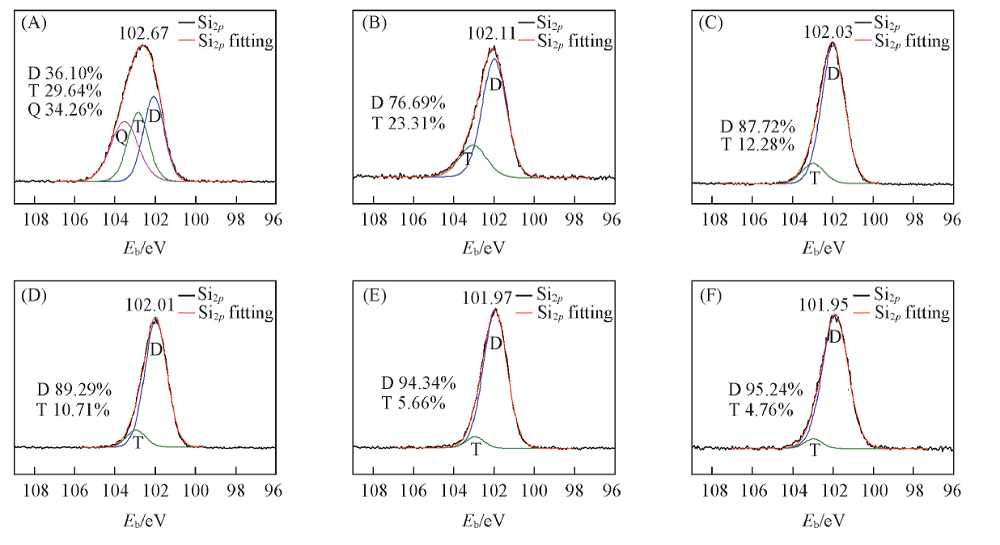
Fig.7 Si2p XPS spectra measured for different depths of PEPA-PIS-1 after post-curing at 450 ℃Depth/mm: (A) 0.02; (B) 0.10; (C) 0.15; (D) 0.20; (E) 0.40; (F) 0.80.
| [1] | Meador M. A., Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 1998, 28, 599—630 |
| [2] | Liaw D. J., Wang K. L., Huang Y. C., Lee K. R., Lai J. Y., Ha C. S., Prog. Polym. Sci.,2012, 37, 907—974 |
| [3] | Hergenrother P. M., High. Perform. Polym., 2003, 15, 3—45 |
| [4] | Miyauchi M., Ishida Y., Ogasawara T., Yokota R., Polym. J.s,2012, 44, 959—965 |
| [5] | Yu X. H., Zhao X. G., Liu C. W., Dang G. D., Wang Y. L., Zhou H. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2009, 30(11), 2297—2300 |
| (于晓慧, 赵晓刚, 刘长威, 党国栋, 王运良, 周宏伟. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(11), 2297—2300) | |
| [6] | Rao X. H., Dang G. D., Zhou H. W., Deng Y. Q., Lu Y. B., Chen C. H., Wu Z. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2006, 27(9), 1775—1778 |
| (饶先化, 党国栋, 周宏伟, 邓勇强, 路迎宾, 陈春海, 吴忠文. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(9), 1775—1778) | |
| [7] | Hergenrother P. M., Connell J. W., Smith J. G., Polymer,2000, 41, 5073—5081 |
| [8] | Su C. N., Ji M., Fan L., Yang S. Y., High Perform. Polym.,2011, 23, 352—361 |
| [9] | Vij V., Haddad T. S., Yandek G. R., Ramirez S. M., Mabry J. M., Silicon,2012, 4, 267—280 |
| [10] | Seurer B., Vij V., Haddad T., Marby J. M., Lee A., Macromolecules,2010, 43, 9337—9347 |
| [11] | Yue J., Li Y. T., Li H., Zhao Y., Zhao C. X., Wang X. Y., RSC. Adv.,2015, 5, 98010—98019 |
| [12] | Yue J., Li Y. T., Zhao Y., Xiang D., Dai Y. X., Polym. Degrad. Stab.,2016, 129, 286—295 |
| [13] | Lincoln J. E., Hout S., Flaherty K., Curliss D. B., Morgan R. J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci.,2008, 107, 3557—3567 |
| [14] | Lincoln J. E., Morgan R. J., Curliss D. B., Polym. Compos.,2008, 29, 585—596 |
| [15] | Liu Y., Mo S., He M.H., Zhai L., Xu C. H., Fan L.,High Perform. Polym., 2018, DOI: 10.1177/0954008 318780211 |
| [16] | Tiptipakorn S., Damrongsakkul S., Ando S., Hemvichian K., Rimdusit S., Polym. Degrad.Stab.,2007, 92, 1265—1278 |
| [17] | Lee Y. B., Park H. B., Shim J. K., Lee Y. M., J. Appl. Polym. Sci.,1999, 74, 965—973 |
| [18] | Coburn J. C., Soper P. D., Auman B. C., Macromolecules,1995, 28, 3253—3260 |
| [19] | Hergenrother P. M., Smith J. G., Polymer,1994, 35, 4857—4864 |
| [20] | Fang X. M., Xie X. Q., Simone C. D., Stevens M. P., Scola D. A., Macromolecules,2000, 33, 1671—1681 |
| [21] | Camino G., Lomakin S. M., Lazzari M., Polymer,2001, 42, 2395—2404 |
| [22] | Chang T. C., Wu K. H., Polym. Degrad. Stab.,1998, 60, 161—168 |
| [23] | Ahmad Z., Sagheer F. A., Arbash A. A., Ali A. A. M., J. Non-Cryst. Solids,2009, 355, 507—517 |
| [24] | O’Hare L. A., Parbhoo B., Leadley S. R., Surf. Interface. Anal.,2004, 36, 1427—1434 |
| [25] | Brookes P. N., Fraser S., Short R. D., Hanley L., Fuoco E., Roberts A., Hutton S., J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom.,2001, 121, 281—297 |
| [1] | CHANG Sihui, CHEN Tao, ZHAO Liming, QIU Yongjun. Thermal Degradation Mechanism of Bio-based Polybutylactam Plasticized by Ionic Liquids [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [2] | ZHANG Tao, SHAO Liang, ZHANG Menghui, MA Zhonglei, LI Xiaoqiang, MA Jianzhong. Preparation and Properties of Bifunctional Polydimethysiloxane/Copper Nanowire Composite Films [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220359. |
| [3] | JIANG Liqi, WEI Ke, WANG Lang, XIAO Houdi, YANG Jiuxiang, HU Zhiyi, LIU Jing, LI Yu, LYU Mingyun, SU Baolian. Electrochromic Property of the WO3/PANI Core-Shell Inverse Opal Structure Film [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2996. |
| [4] | WANG Xianwei, KE Hongjun, YUAN Hang, LU Gewu, LI Liying, MENG Xiangsheng, SONG Shulin, WANG Zhen. High Temperature Resistant and Soluble Polyimide Resins and Their Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2041. |
| [5] | WU Tao, FANG Yuting, DONG Jie, ZHAO Xin, ZHANG Qinghua. Synthesis and Properties of Polyimide Resin Containing Acetylene and Benzoxazine Double Crosslinking Moieties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1978. |
| [6] | HAN Yandong, HAN Mingyong, YANG Wensheng. Sol-gel Construction of Mesoporous Silica Nanomicrostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 965. |
| [7] | CHEN Binggang, LIU Sanrong, YU Xifei, JIANG Zijiang. Preparation and Properties Characterization of Polysiloxane Skin Tissue Adhesive [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3746. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiayi, DING Zhenyao, WANG Dandan, CHEN Liping, FENG Xinjian. Fabrication of Triphase Enzyme Electrode Based on Porous Gold Substrate for High-performance Electrochemical Biosensor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3167. |
| [9] | ZHANG Jun, WANG Bin, PAN Li, MA Zhe, LI Yuesheng. Synthesis and Properties of Imidazolium-based Polyethylene Ionomer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2070. |
| [10] | JIANG Huayi,LIU Mei,QI Hongyuan,LIANG Aiguo,WANG Yulong,SUN Nana,WU Zhe. Fractal Characteristics of the Microstructures of Three Hydrophobic Surfaces with Steel Substrate and Their Effects on Wettability † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1313. |
| [11] | RAN Shiya,SHEN Haifeng,LI Xiaonan,WANG Zilu,GUO Zhenghong,FANG Zhengping. Effect and Mechanism of Rare Earth Trifluoromethanesulfonate on the Thermal Stability of Polypropylene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1333. |
| [12] | FANG Xijie,LIU Ruiyun,LIN Sen,SHI Lei,WANG Runwei,LI Yi,LI Junying. Synthesis of STW-zeotype Germanosilicate via Steam-assisted Crystallization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 867. |
| [13] | REN Xiaorui,LIU Chao,LI Huanhuan,YANG Jingshuai,HE Ronghuan. Siloxane Crosslinked Imidazolium PPO/PTFE Membranes for High Temperature Proton Exchange Membranes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1089. |
| [14] | YIN Mengxin,LIU Dongsheng,ZHAO Dongyue,DING Tong,TIAN Ye,LI Xingang. Effect of Copper Doping on Lean NOx Trap Performance of Pt/Ba/CuxMg1-xAl2O4 Catalysts at High Temperatures † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2170. |
| [15] | ZHAO Lei,LUO Yongchun,DENG Anqiang,JIANG Wanting. Hydrogen Storage and Electrochemical Properties of the Mg-free A2B7-type La1-xYxNi3.25Mn0.15Al0.1 Alloys with Superlattice Structure† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1993. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||