

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (4): 745.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140728
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
YUE Hongyun1,2, WANG Qiuxian1,2, ZHANG Xue1, HUA Shuang1, MA Hua1, YUE Dongyuan1, YANG Shuting1,2,*( )
)
Received:2014-08-04
Online:2015-04-10
Published:2015-03-27
Contact:
YANG Shuting
E-mail:shutingyang@foxmail.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
YUE Hongyun, WANG Qiuxian, ZHANG Xue, HUA Shuang, MA Hua, YUE Dongyuan, YANG Shuting. Controllable Synthesis and Performance of Micro-nano Structure MFe2O4(M=Zn, Co) in Lithium-ion Batteries†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 745.
| Sample | (hkl) | 2θ/(°) | FWHM | Grain size/nm | Crystalline interplanar spacing of (311)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | (311) | 35.328 | 0.379 | 20.77 | 0.2538 |
| SZ | (311) | 35.403 | 0.498 | 16.56 | 0.2533 |
| JCPDS No.22-1012 | (311) | 35.264 | 0.2543 | ||
| HC | (311) | 35.562 | 0.580 | 14.22 | 0.2522 |
| SC | (311) | 35.250 | 0.655 | 12.58 | 0.2543 |
| JCPDS No.03-0864 | (311) | 35.451 | 0.2530 |
Table 1 XRD parameters and grain sizes of the samples
| Sample | (hkl) | 2θ/(°) | FWHM | Grain size/nm | Crystalline interplanar spacing of (311)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HZ | (311) | 35.328 | 0.379 | 20.77 | 0.2538 |
| SZ | (311) | 35.403 | 0.498 | 16.56 | 0.2533 |
| JCPDS No.22-1012 | (311) | 35.264 | 0.2543 | ||
| HC | (311) | 35.562 | 0.580 | 14.22 | 0.2522 |
| SC | (311) | 35.250 | 0.655 | 12.58 | 0.2543 |
| JCPDS No.03-0864 | (311) | 35.451 | 0.2530 |
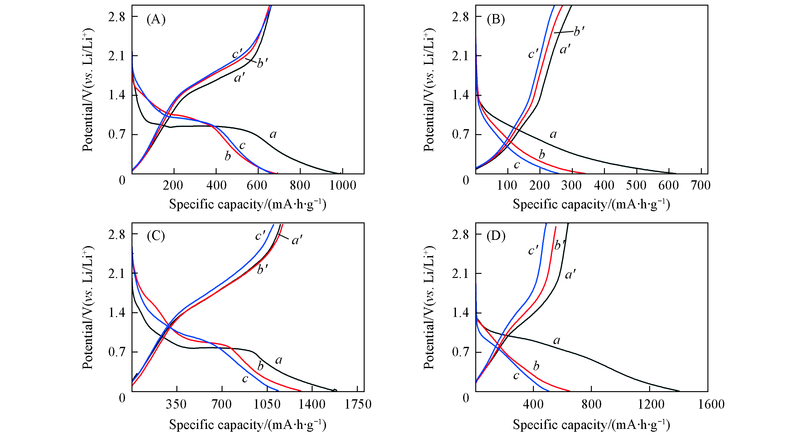
Fig.5 Discharge(a—c)-charge(a'—c') profiles of HZ(A), SZ(B), HC(C) and SC(D) in the voltage range between 0.005—3.0 V at a current density of 60 mA/g a, a': The 1st cycle; b, b': the 2nd cycle; c, c': the 10th cycle.
| [1] | Armand M., Tarascon J. M., Nature,2008, 451(7179), 652—657 |
| [2] | Goodenough J. B., Kim Y., Chem. Mater., 2010, 22(3), 587—603 |
| [3] | Goodenough J. B., Park K. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(4), 1167—1176 |
| [4] | Zhao H., Zhou L. N., Wei D. S., Zhou J. X., Shi H. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(8), 1731—1738 |
| (赵晗, 周丽娜, 魏东山, 周建新, 史浩飞. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8), 1731—1738) | |
| [5] | Ji L. W., Lin Z., Alcoutlabi M., Zhang X. W., Energy & Environmental Science,2011, 4(8), 2682—2699 |
| [6] | Etacheri V., Marom R., Elazari R., Salitra G., Aurbach D., Energy & Environmental Science,2011, 4(9), 3243—3262 |
| [7] | Goodenough J. B., Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 46(5), 1053—1061 |
| [8] | Hua C., Fang X., Wang Z., Chen L., Chem. Eur. J., 2014, 20(18), 5487—5491 |
| [9] | Alcantara R., Ortiz G., Lavela P., Tirado J., Electrochem. Commun., 2006, 8(5), 731—736 |
| [10] | Wang G., Gao X. P., Shen P. W., J. Power Sources,2009, 192(2), 719—723 |
| [11] | Yuvaraj S., Amaresh S., Lee Y. S., Selvan R. K., RSC Adv., 2014, 4(13), 6407—6416 |
| [12] | Wang N., Xu H., Chen L., Gu X., Yang J., Qian Y., J. Power Sources,2014, 247, 163—169 |
| [13] | Zhang Z., Wang Y., Tan Q., Zhong Z., Su F., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2013, 398, 185—192 |
| [14] | Ding Y., Yang Y., Shao H., Electrochimica Acta,2011, 56(25), 9433—9438 |
| [15] | Lavela P., Tirado J. L., J. Power Sources,2007, 172(1), 379—387 |
| [16] | Sharma Y., Sharma N., Rao G. V. S., Chowdari B. V. R., Electrochimica Acta,2008, 53(5), 2380—2385 |
| [17] | Xing Z., Ju Z., Yang J., Xu H., Qian Y., Nano Research,2012, 5(7), 477—485 |
| [18] | Cherian C. T., Sundaramurthy J., Reddy M. V., Suresh Kumar P., Mani K., Pliszka D., Sow C. H., Ramakrishna S., Chowdari B. V., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013, 5(20), 9957—9963 |
| [19] | Teh P. F., Sharma Y., Pramana S. S., Srinivasan M., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(38), 14999—15008 |
| [20] | Reddy M. V., Subba Rao G. V., Chowdari B. V., Chem. Rev., 2013, 113(7), 5364—5457 |
| [21] | Arico A. S., Bruce P., Scrosati B., Tarascon J. M., van Schalkwijk W., Nature Materials,2005, 4(5), 366—377 |
| [22] | Bai J., Li X. G., Liu G. Z., Qian Y. T., Xiong S. L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(20), 3012—3020 |
| [23] | Peng P., Wen Z. Y., Liu Y., Yang J. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(5), 1051—1056 |
| (彭鹏, 温兆银, 刘宇, 杨建华. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(5), 1051—1056) | |
| [24] | Zhu L. P., Xiao H. M., Zhang W. D., Yang G., Fu S. Y., Crystal Growth & Design,2008, 8(3), 957—963 |
| [25] | Hu L., Qu B., Li C., Chen Y., Mei L., Lei D., Chen L., Li Q., Wang T., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1(18), 5596—5602 |
| [26] | Hu H., Xu J. Y., Yang H., Liang J., Yang S. P., Wu H. X., Mater. Res. Bull., 2011, 46(11), 1908—1915 |
| [27] | Yao L. M., Hou X. H., Hu S. J., Wang J., Li M., Su C., Tade M. O., Shao Z. P., Liu X., J. Power Sources,2014, 258, 305—313 |
| [28] | Guo F. L., Zheng J. W., Xu R., J. Phys. Chem. C,2008, 112(19), 7363—7370 |
| [29] | Bhaskar A., Deepa M., Ramakrishna M., Rao T. N., J. Phys. Chem. C,2014, 118(14), 7296—7306 |
| [30] | Liang Z. Q., Huo R. J., Yin S. H., Zhang F. Z., Xu S. L., J. Mater. Chem. A,2014, 2(4), 921—925 |
| [31] | Guo X., Lu X., Fang X., Mao Y., Wang Z., Chen L., Xu X., Yang H., Liu Y., Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12(6), 847—850 |
| [32] | Chen D. Z., Quan H. Y., Luo X. B., Luo S. L., Scripta Materialia,2014, 76, 1—4 |
| [33] | Hassan M. F., Rahman M. M., Guo Z., Chen Z., Liu H., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20(43), 9707—9712 |
| [1] | JIA Yanggang, SHAO Xia, CHENG Jie, WANG Pengpeng, MAO Aiqin. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of Pseudocapacitance-controlled Perovskite High-entropy Oxide La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| [2] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [3] | BAO Junquan, ZHENG Shibing, YUAN Xuming, SHI Jinqiang, SUN Tianjiang, LIANG Jing. An Organic Salt PTO(KPD)2 with Enhanced Performance as a Cathode Material in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2911. |
| [4] | WU Zhuoyan, LI Zhi, ZHAO Xudong, WANG Qian, CHEN Shunpeng, CHANG Xinghua, LIU Zhiliang. A Highly Efficient One-step Preparation Method of Nano-silicon and Carbon Composite for High-performance Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2500. |
| [5] | TIAN Runsai, LU Qian, ZHANG Hongbin, ZHANG Bo, FENG Yuanyuan, WEI Jinxiang, FENG Jijun. Design and Construction of N-Doping Carbon in⁃situ Coated Cu2O/Co3O4@C Heterostructured Composite Material for Highly Efficient Lithium-ion Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2592. |
| [6] | YI Conghua, SU Huajian, QIAN Yong, LI Qiong, YANG Dongjie. Preparation of Lignin Nanocarbon and Its Performance as a Negative Electrode for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1807. |
| [7] | MAO Eryang, WANG Li, SUN Yongming. Advances in Alloy-based High-capacity Li-containing Anodes for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1552. |
| [8] | WANG Yimeng, LIU Kai, WANG Baoguo. Coating Strategies of Ni-rich Layered Cathode in LIBs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1514. |
| [9] | ZHANG Huishuang, GAO Yanxiao, WANG Qiuxian, LI Xiangnan, LIU Wenfeng, YANG Shuting. High-low Temperature Properties of Ni-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material by Hydrothermal Synthesis with CTAB Assisted [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 819. |
| [10] | WANG Ye, ZHANG Xiaosi, SUN Lijing, LI Bing, LIU Lin, YANG Miao, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Morphology Control of SAPO Molecular Sieves under the Assistance of Organosilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 683. |
| [11] | SUN Quanhu, LU Tiantian, HE Jianjiang, HUANG Changshui. Advances in the Study of Heteratomic Graphdiyne Electrode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 366. |
| [12] | ZHOU Zhan, MA Lufang, TAN Chaoliang. Preparation of Layered (NH4)2V6O16·H2O Nanosheets as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 662. |
| [13] | HAN Muyao, ZHAO Lina, SUN Jie. Advances in Silicon and Silicon-based Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3547. |
| [14] | YE Yihua, BA Deliang, LIU Shuailei, CHEN Yinglin, LI Yuanyuan, LIU Jinping. Recent Progress on High⁃rate Niobium-based Oxides Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3005. |
| [15] | GONG Shanshan, WU Tong, WANG Guange, HUANG Qing, SU Yuefeng, WU Feng. Screening of Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Efficient Recovery of Spent Lithium⁃ion Battery Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3151. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||