

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (2): 368.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140482
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Cunguo1,*( ), PAN Xuan1, ZHANG Lei1, ZHU Mengkang1, LI Dekai1, DIAO Lingbo1, LI Weiyan2
), PAN Xuan1, ZHANG Lei1, ZHU Mengkang1, LI Dekai1, DIAO Lingbo1, LI Weiyan2
Received:2014-05-23
Online:2015-02-10
Published:2015-01-22
Contact:
WANG Cunguo
E-mail:cunguow@yahoo.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Cunguo, PAN Xuan, ZHANG Lei, ZHU Mengkang, LI Dekai, DIAO Lingbo, LI Weiyan. Preparation and Properties of the High Capacity Si@PVP-GCB Core-shell Composite Anode Material Used in Li-ion Batteries†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(2): 368.
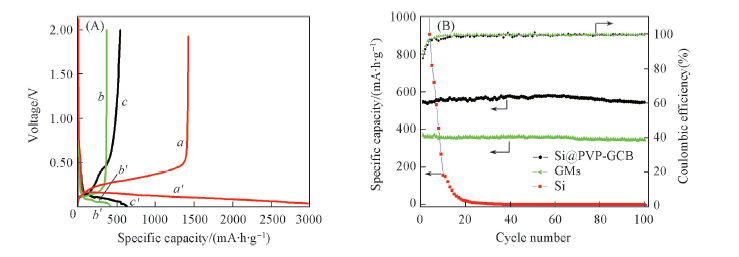
Fig.4 First discharge(a'—c')-charge(a—c) curves(A) and cycling property(B) for SiNPs, GMs and Si@PVP-GCB between 2.0 and 0.005 V at the current density of 50 mA/g (A) a, a'. SiNPs; b, b'. GMs; c, c'. Si@PVP-GCB.
| [1] | Kovalenko I., Zdyrko B., Magasinski A., Hertzberg B., Milicev Z., Burtovyy R., Luzinov I., Yushin G., Science, 2011, 334, 75—79 |
| [2] | Armand M., Tarascon J. M., Nature, 2008, 451, 652—657 |
| [3] | Chockla A. M., Harris J. T., Akhavan V. A., Bogart T. D., Holmberg V. C., Steinhagen C., Mullins C. B., Stevenson K. J., Korgel B. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 20914—20921 |
| [4] | Wang C. G., He L. X., Dong X. G., Wang Y. Z., Zhao S. G., Sun L., Lin L., Xiao H. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(12), 2373—2376 |
| (王存国, 何丽霞, 董献国, 王怡臻, 赵树高, 孙琳, 林琳, 肖红杰. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(12), 2373—2376) | |
| [5] | Yuan W. N., Wang C. G., Chemistry Bullitin, 2010, 66(3), 15—18 |
| (袁维娜, 王存国. 化学通报, 2010, 66(3), 15—18) | |
| [6] | Wang C.G., Lin L., Lu N.Q., Zhao Q., Sun L., Zhao S. G., Wang R. S., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2008, 16, 1909—1914 |
| (王存国, 林琳, 路乃群, 赵强, 孙琳, 赵树高, 王荣顺. 化学学报, 2008, 16, 1909—1914) | |
| [7] | Zhang L., Zhang M. J., Wang Y. H., Zhang Z. L., Kan G. W., Wang C. G., Zhong Z. Y., Su F. B., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 10161—10168 |
| [8] | Yu H. Y., Xie H. M., Zhang L. Y., Yan X. D., Yang G. L., Wang R. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(7), 1315—1318 |
| (于海英, 谢海明, 张凌云, 颜雪冬, 杨桂玲, 王荣顺. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(7), 1315—1318) | |
| [9] | Zhang L., Wang Y. H., Kan G. W., Zhang Z. L., Wang C. G., Zhong Z. Y., Su F. B., RCS Advances, 2014, 4, 43114—43120 |
| [10] | Yu J., Zhan H. H., Wang Y. H., Zhang Z. L., Chen H., Li H., Zhong Z. Y., Su F. B., J. Power Sources, 2013, 228, 112—119 |
| [11] | Wang W., Kumta P. N., ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 2233—2241 |
| [12] | Liu X. H., Zhong L., Huang S., Mao S. X., Zhu T., Huang J. Y., Acs Nano, 2012, 6, 1522—1531 |
| [13] | Kohandehghan A., Kalisvaart P., Cui K., Kupsta M., Memarzadeh E., Mitlin D., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1, 12850—12861 |
| [14] | Ge M., Rong J., Fang X., Zhou C., Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 2318—2323 |
| [15] | Song T., Xia J., Lee J. H., Lee D. H., Kwon M. S., Choi J. M., Wu J., Doo S. K., Chang H., Park W. I., Zang D. S., Kim H., Huang Y., Hwang K. C., Rogers J. A., Paik U., Nano Lett., 2010, 10, 1710—1716 |
| [16] | Kalnaus S., Rhodes K., Daniel C., J. Power Sources, 2011, 196, 8116—8124 |
| [17] | Ge M. Y., Rong J. P., Fang X., Zhang A. Y., Lu Y. H., Zhou C. W., Nano Res., 2013, 6, 174—181 |
| [18] | Liu B., Soares P., Checkles C., Zhao Y., Yu G., Nano Lett., 2013, 13, 3414—3419 |
| [19] | Kong J. H., Yee W. A., Wei Y. F., Yang L. P., Ang J. M., Phua S. L., Wong S. Y., Zhou R., Dong Y. L., Li X., Lu X. H., Nanoscale, 2013, 5, 2967—2973 |
| [20] | De Guzman R. C., Yang J. H., Cheng M. M. C., Salley S. O., Ng K. Y. S., J. Mater. Sci., 2013, 48, 4823—4833 |
| [21] | Wu H., Yu G.H., Pan L. J., Liu N., McDowell M. T., Bao Z., Cui Y., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1943—1948 |
| [22] | Li W., Zhang Q., Zheng G., Seh Z. W., Yao H., Cui Y., Nano Lett., 2013, 13, 5534—5540 |
| [23] | Yang S., Feng X., Zhi L., Cao Q., Maier J., Müllen K., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 838—842 |
| [24] | Shi L., Li H., Wang Z., Huang X., Chen L., J. Mater. Chem., 2001, 11, 1502—1505 |
| [25] | Erk C., Brezesinski T., Sommer H., Schneider R., Janek J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 7299—7307 |
| [26] | Lin L., Studies on Prepation and Properties of the Novel Modified Pyrolysis Carbon Materials from Phenol-formaldehyde Resin for Lithium Ion Batteries, Qingdao University of Science and Technology, Qingdao, 2008 |
| (林琳. 用于锂离子电池的新型酚醛树脂热解碳改性材料的制备与性能研究, 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2008) | |
| [27] | Lin L., Wang C. G., Yang L., Sun L., Xiao H. J., Yuan T., Chemical and Physics Power Sources, 2008, 1(4), 8—13 |
| [28] | Gu P., Cai R., Zhou Y., Shao Z., Electrochim. Acta, 2010, 55, 3876—3883 |
| [29] | Lee J. I., Lee K. T., Cho J., Kim J., Choi N. S., Park S., Angew. Chem., 2012, 124, 2821—2825 |
| [30] | Ray S., Pao C., Tsai H., Bose B., Chiou J., Pong W., Dasgupta D., Carbon, 2006, 44, 1982—1985 |
| [31] | Ji L., Zhang X., Carbon, 2009, 47, 3219—3226 |
| [32] | Su F., Zhao X., Wang Y., Zeng J., Zhou Z., Lee J. Y., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2005, 109, 20200—20206 |
| [33] | Cuesta A., Dhamelincourt P., Laureyns J., Martinez-Alonso A., Tascón J. M., J. Mater. Chem., 1998, 8, 2875—2879 |
| [34] | Yang Q., Xu W., Tomita A., Kyotani T., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127, 8956—8957 |
| [35] | Bokobza L., Bruneel J. L., Couzi M., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2013, 590, 153—159 |
| [36] | Bakandritsos A., Simopoulos A., Petridis D., Chem. Mater., 2005, 17, 3468—3474 |
| [37] | Magasinski A., Dixon P., Hertzberg B., Kvit A., Ayala J., Yushin G., Nat. Mater., 2010, 9, 353—358 |
| [38] | Guo Y. G., Hu J. S., Wan L. J., Adv. Mater., 2008, 20, 2878—2887 |
| [39] | Mabuchi A., Tokumitsu K., Fujimoto H., Kasuh T., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1995, 142, 1041—1046 |
| [40] | Liu Y., Xue J., Zheng T., Dahn J., Carbon, 1996, 34, 193—200 |
| [41] | Buiel E., Dahn J., Electrochim. Acta, 1999, 45, 121—130 |
| [42] | Fujimoto H., Mabuchi A., Tokumitsu K., Kasuh T., J. Power Sources, 1995, 54, 440—443 |
| [43] | Feng X., Yang J., Gao P., Wang J., Nuli Y., RSC Advances, 2012, 2, 5701—5706 |
| [44] | Vu A., Qian Y., Stein A., Adv. Energy Mater., 2012, 2, 1056—1085 |
| [45] | Liu N., Wu H., McDowell M. T., Yao Y., Wang C., Cui Y., Nano Lett., 2012, 12, 3315—3321 |
| [46] | Cetinkaya T., Uysal M., Guler M. O., Akbulut H., Alp A., Powder Technol., 2014, 253, 63—69 |
| [47] | Hu J., Li H., Huang X., Solid State Ionics, 2007, 178, 265—271 |
| [48] | Hu J., Li H., Huang X., Solid State Ionics, 2005, 176, 1151—1159 |
| [49] | Wang Q., Li H., Chen L., Huang X., Carbon, 2001, 39, 2211—2214 |
| [50] | Wang Q., Li H., Chen L., Huang X., Solid State Ionics, 2002, 152, 43—50 |
| [51] | Ebner M., Chung D. W., García R. E., Wood V., Adv. Energy Mater., 2014, 4, 1301278—1301283 |
| [52] | Chen L., Xie X., Wang B., Wang K., Xie J., Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2006, 131, 186—190 |
| [53] | Fu L., Liu H., Li C., Wu Y., Rahm E., Holze R., Wu H., Solid State Sci., 2006, 8, 113—128 |
| (Ed.: S, Z, M) |
| [1] | ZHANG Zhicai, WANG Yuge, GU Qianqian, LYU Yongpeng, XIAO Jianshu, YIN Yuan, SUN Hongguo, ZHENG Yafang, SUN Zhaoyan. Flocculation of Fillers in Isoprene Rubber and Its Effects on Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220155. |
| [2] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [3] | LI Huiyang, ZHU Siying, LI Sha, ZHANG Qiaobao, ZHAO Jinbao, ZHANG Li. Influencing Factors and Promotion Strategies of the First-cycle Coulombic Efficiency of Silicon Suboxide Anodes in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2342. |
| [4] | LIU Tiefeng, ZHANG Ben, SHENG Ouwei, NAI Jianwei, WANG Yao, LIU Yujing, TAO Xinyong. Research Progress of the Binders for the Silicon Anode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1446. |
| [5] | WANG Renheng, XIAO Zhe, LI Yan, SUN Yiling, FAN Shuting, ZHENG Junchao, QIAN Zhengfang, HE Zhenjiang. Synthesis of Li2FeP2O7 Cathode Material at Different Temperatures and Its Electrochemical Performance for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1299. |
| [6] | HAN Muyao, ZHAO Lina, SUN Jie. Advances in Silicon and Silicon-based Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3547. |
| [7] | XIA Yun, Lü Wangyang, CHEN Wenxing, LI Nan. Fiber Supported Carbon Black Metal Phthalocyanine Axial Complex to Mimic Enzyme for Highly Efficient Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutant in Water† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1582. |
| [8] | ZHANG Chenyang,WEN Yuehua,ZHAO Pengcheng,CHENG Jie,QIU Jingyi,SUN Yanzhi. Effect of Organic Carbon Source on Performance of LiTi2(PO4)3/C Composite Electrodes in Aqueous Solutions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1352. |
| [9] | JI Tianyi, LIU Xiaoxu, ZHAO Jiupeng, LI Yao. Synthesis and Lithium-storage Characteristics of Three-dimensional Cross-linked Graphene Nanofibers † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 821. |
| [10] | FANG Liang,DING Xiaoli,SONG Yun,LIU Dongming,LI Yongtao,ZHANG Qingan. Effect of Morphological Tuning on Electrochemical Performance of Perovskite LaCoO3 Anodes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1456. |
| [11] | SUI Jiayang, LIU Xiaoyang, QIAN Miaomiao, ZHU Yanchao, XUE Beichen, FENG Yi, TIAN Yumei, WANG Xiaofeng. Surface Modification of Silica/carbon Black Derived from Rice Husks and Its Influence on Natural Rubber Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1561. |
| [12] | Yuzhen DUAN,Jinyu ZHU,Junming GUO,Mingwu XIANG,Xiaofang LIU,Hongli BAI,Changwei SU. Synthesis and Electrochemical Properties of Spinel Lithium Manganese Cathode Material LiNi0.01Co0.03Mn1.96O4 † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2574. |
| [13] | LI Xiangnan,YU Mingming,FAN Yong,WANG Qiuxian,ZHANG Huishuang,YANG Shuting. Study on Electrochemical Performances of N-doped P/C Composite as Anode Material of Lithium Ion Batteries † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2360. |
| [14] | WU Wei, LIU Yuchun, ZHU Guancun, AN Jiayu, DOU Guangpeng, WANG Yuyan, LIU Jing, SUN Donglan, GUO Yeping. Application of Polyethylene Separator Modified by Methyl Acrylic Polymer in Lithium Ion Battery † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2332. |
| [15] | QIN Yanli, XU Haiping, QIU Houtian, ZHAI Yue, DAI Xiujuan, YANG Dandan, WANG Jingrong. Preparation and PTC Properties of HIPS/HDPE/CB Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1305. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||