

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 1761.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140037
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Bing1, DONG Yongchun1,2,*( )
)
Received:2014-01-13
Online:2014-08-10
Published:2019-08-01
Contact:
DONG Yongchun
E-mail:teamdong@sina.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Bing, DONG Yongchun. Coordination Kinetics of Different Carboxylic Fiber with Fe3+ and Catalytic Degradation Performance of Their Fe3+ Complexes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(8): 1761.
| Carboxylic fiber | ACOOH/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 2.23 | 0.286 | 48.3 |
| PAA-g-PP | 2.27 | 0.251 | 85.8 |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 2.35 | 0.178 | 91.1 |
Table 1 ACOOH values and surface properties of three carboxylic fibers
| Carboxylic fiber | ACOOH/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 2.23 | 0.286 | 48.3 |
| PAA-g-PP | 2.27 | 0.251 | 85.8 |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 2.35 | 0.178 | 91.1 |
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | kL/(L·mmol-1) | Qm/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.4389ce/(1+0.1389ce) | 0.1389 | 3.16 | 0.9877 |
| 35 | Qe=0.2708ce/(1+0.1231ce) | 0.1231 | 2.20 | 0.9856 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1158ce/(1+1.1007ce) | 0.1007 | 1.15 | 0.9898 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.1400ce/(1+0.0625ce) | 0.0625 | 2.24 | 0.9862 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0705ce/(1+0.0538ce) | 0.0538 | 1.31 | 0.9933 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0367ce/(1+0.00448ce) | 0.0448 | 0.82 | 0.9861 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.1195ce/(1+0.0561ce) | 0.0561 | 2.13 | 0.9930 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0489ce/(1+0.0457ce) | 0.0457 | 1.07 | 0.9962 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0212ce/(1+0.0365ce) | 0.0365 | 0.58 | 0.9876 |
Table 2 Parameters and equations for Langmuir adsorption isothermals of Fe3+ onto three carboxylic fibers
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | kL/(L·mmol-1) | Qm/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.4389ce/(1+0.1389ce) | 0.1389 | 3.16 | 0.9877 |
| 35 | Qe=0.2708ce/(1+0.1231ce) | 0.1231 | 2.20 | 0.9856 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1158ce/(1+1.1007ce) | 0.1007 | 1.15 | 0.9898 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.1400ce/(1+0.0625ce) | 0.0625 | 2.24 | 0.9862 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0705ce/(1+0.0538ce) | 0.0538 | 1.31 | 0.9933 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0367ce/(1+0.00448ce) | 0.0448 | 0.82 | 0.9861 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.1195ce/(1+0.0561ce) | 0.0561 | 2.13 | 0.9930 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0489ce/(1+0.0457ce) | 0.0457 | 1.07 | 0.9962 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0212ce/(1+0.0365ce) | 0.0365 | 0.58 | 0.9876 |
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | n | kF | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.8929 | 3.720 | 0.8929 | 0.9258 |
| 35 | Qe=0.6090 | 3.697 | 0.6090 | 0.9579 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.3050 | 3.671 | 0.3050 | 0.9733 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.3707 | 2.664 | 0.3707 | 0.9710 |
| 35 | Qe=0.1998 | 2.656 | 0.1998 | 0.9530 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1051 | 2.460 | 0.1051 | 0.9464 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.3103 | 2.565 | 0.3103 | 0.9682 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0137 | 2.452 | 0.1376 | 0.9750 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0640 | 2.356 | 0.0640 | 0.9465 |
Table 3 Parameters and equations for Freundlich adsorption isothermals of Fe3+ onto three carboxylic fibers
| Fiber | Temperature/℃ | Linear regression equation | n | kF | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 50 | Qe=0.8929 | 3.720 | 0.8929 | 0.9258 |
| 35 | Qe=0.6090 | 3.697 | 0.6090 | 0.9579 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.3050 | 3.671 | 0.3050 | 0.9733 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 50 | Qe=0.3707 | 2.664 | 0.3707 | 0.9710 |
| 35 | Qe=0.1998 | 2.656 | 0.1998 | 0.9530 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.1051 | 2.460 | 0.1051 | 0.9464 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 50 | Qe=0.3103 | 2.565 | 0.3103 | 0.9682 |
| 35 | Qe=0.0137 | 2.452 | 0.1376 | 0.9750 | |
| 20 | Qe=0.0640 | 2.356 | 0.0640 | 0.9465 |
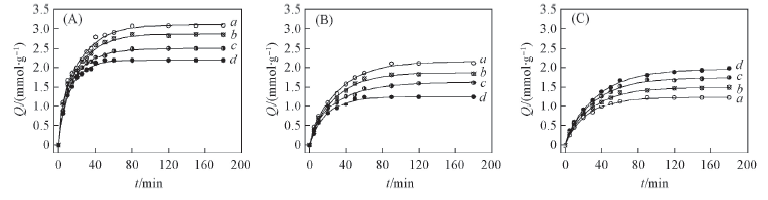
Fig.3 Coordination kinetics curves at different initial concentrations of Fe3+ on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE fibers(C) Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
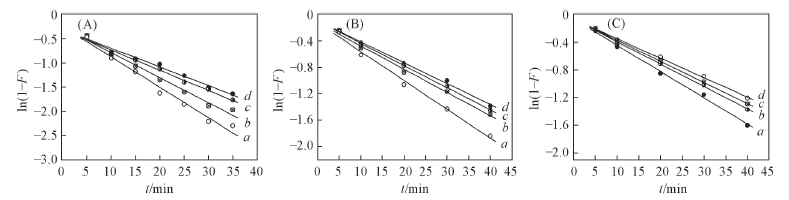
Fig.4 Simulation curves of Lagergren pseudo first-order equation plots on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE fibers(C) Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
| Fiber | c0/(mmol ·L-1) | Rate equation | k1 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0628t | 0.0628 | 0.9807 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0517t | 0.0517 | 0.9833 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0417t | 0.0417 | 0.9907 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0387t | 0.0387 | 0.9852 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0437t | 0.0437 | 0.9916 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0353t | 0.0353 | 0.9940 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0336t | 0.0336 | 0.9975 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0316t | 0.0316 | 0.9962 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0380t | 0.0380 | 0.9967 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0223t | 0.0323 | 0.9989 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0305t | 0.0305 | 0.9989 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0281t | 0.0281 | 0.9984 |
Table 4 Results from linear regression of Lagergren pseudo first-order equation plots
| Fiber | c0/(mmol ·L-1) | Rate equation | k1 | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0628t | 0.0628 | 0.9807 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0517t | 0.0517 | 0.9833 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0417t | 0.0417 | 0.9907 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0387t | 0.0387 | 0.9852 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0437t | 0.0437 | 0.9916 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0353t | 0.0353 | 0.9940 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0336t | 0.0336 | 0.9975 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0316t | 0.0316 | 0.9962 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | ln(1-F)=-0.0380t | 0.0380 | 0.9967 |
| 60 | ln(1-F)=-0.0223t | 0.0323 | 0.9989 | |
| 90 | ln(1-F)=-0.0305t | 0.0305 | 0.9989 | |
| 120 | ln(1-F)=-0.0281t | 0.0281 | 0.9984 |
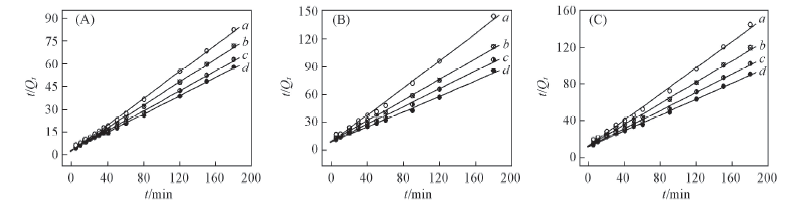
Fig.5 Simulation curves of Lagergren pseudo second-order equation plots on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE fibers(C) Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | k2 | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginatefiber | 30 | t/Qt=2.470+t/2.28 | 0.0781 | 2.28 | 0.9985 |
| 60 | t/Qt=2.943+t/2.64 | 0.0487 | 2.64 | 0.9991 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=2.979+t/3.04 | 0.0364 | 3.04 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=3.096+t/3.32 | 0.0293 | 3.32 | 0.9985 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | t/Qt=8.941+t/1.37 | 0.0598 | 1.37 | 0.9947 |
| 60 | t/Qt=9.936+t/1.80 | 0.0311 | 1.80 | 0.9983 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=9.020+t/2.09 | 0.0255 | 2.09 | 0.9970 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=9.898+t/2.42 | 0.0173 | 2.42 | 0.9976 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | t/Qt=12.665+t/1.40 | 0.0404 | 1.40 | 0.9962 |
| 60 | t/Qt=12.726+t/1.71 | 0.0268 | 1.71 | 0.9968 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=11.838+t/2.01 | 0.0209 | 2.01 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=11.628+t/2.29 | 0.0164 | 2.29 | 0.9984 |
Table 5 Results from linear regression of Lagergren pseudo second-order equation plots
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | k2 | Qe/(mmol·g-1) | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginatefiber | 30 | t/Qt=2.470+t/2.28 | 0.0781 | 2.28 | 0.9985 |
| 60 | t/Qt=2.943+t/2.64 | 0.0487 | 2.64 | 0.9991 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=2.979+t/3.04 | 0.0364 | 3.04 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=3.096+t/3.32 | 0.0293 | 3.32 | 0.9985 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | t/Qt=8.941+t/1.37 | 0.0598 | 1.37 | 0.9947 |
| 60 | t/Qt=9.936+t/1.80 | 0.0311 | 1.80 | 0.9983 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=9.020+t/2.09 | 0.0255 | 2.09 | 0.9970 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=9.898+t/2.42 | 0.0173 | 2.42 | 0.9976 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | t/Qt=12.665+t/1.40 | 0.0404 | 1.40 | 0.9962 |
| 60 | t/Qt=12.726+t/1.71 | 0.0268 | 1.71 | 0.9968 | |
| 90 | t/Qt=11.838+t/2.01 | 0.0209 | 2.01 | 0.9986 | |
| 120 | t/Qt=11.628+t/2.29 | 0.0164 | 2.29 | 0.9984 |
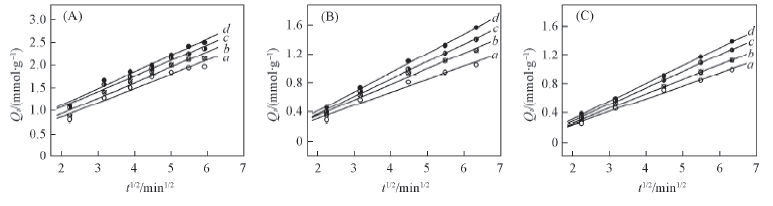
Fig.6 Simulation curves of intra-particle diffusion equation plots on alginate(A), PAA-g-PP(B) and PAA-g-PTFE(C) fibers Initial concentration of Fe3+/(mmol·L-1): a. 30; b. 60; c. 90; d. 120.
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | kp | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | Qt=0.3121t1/2 | 0.3121 | 0.9486 |
| 60 | Qt=0.3414t1/2 | 0.3415 | 0.9597 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.3428t1/2 | 0.3428 | 0.9787 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.3637t1/2 | 0.3637 | 0.9771 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | Qt=0.1816t1/2 | 0.1816 | 0.9692 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2176t1/2 | 0.2176 | 0.9861 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2436t1/2 | 0.2436 | 0.9957 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2693t1/2 | 0.2693 | 0.9983 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | Qt=0.1767t1/2 | 0.1767 | 0.9943 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2008t1/2 | 0.2008 | 0.9952 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2287t1/2 | 0.2287 | 0.9991 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2466t1/2 | 0.2466 | 0.9995 |
Table 6 Results from linear regression of intra-particle diffusion equation plots
| Fiber | c0/(mmol·L-1) | Rate equation | kp | r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alginate fiber | 30 | Qt=0.3121t1/2 | 0.3121 | 0.9486 |
| 60 | Qt=0.3414t1/2 | 0.3415 | 0.9597 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.3428t1/2 | 0.3428 | 0.9787 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.3637t1/2 | 0.3637 | 0.9771 | |
| PAA-g-PP | 30 | Qt=0.1816t1/2 | 0.1816 | 0.9692 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2176t1/2 | 0.2176 | 0.9861 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2436t1/2 | 0.2436 | 0.9957 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2693t1/2 | 0.2693 | 0.9983 | |
| PAA-g-PTFE | 30 | Qt=0.1767t1/2 | 0.1767 | 0.9943 |
| 60 | Qt=0.2008t1/2 | 0.2008 | 0.9952 | |
| 90 | Qt=0.2287t1/2 | 0.2287 | 0.9991 | |
| 120 | Qt=0.2466t1/2 | 0.2466 | 0.9995 |
| Complex | Q/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-ALG | 2.32 | 0.248 | 82.1 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PP | 2.37 | 0.263 | 100.3 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PTFE | 2.29 | 0.151 | 104.6 |
Table 7 Q values and surface properties of three carboxylic fiber-Fe(Ⅲ) complexes
| Complex | Q/(mmol·g-1) | Specific surface area/(m2·g-1) | Water contact angle/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe-ALG | 2.32 | 0.248 | 82.1 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PP | 2.37 | 0.263 | 100.3 |
| Fe-PAA-g-PTFE | 2.29 | 0.151 | 104.6 |
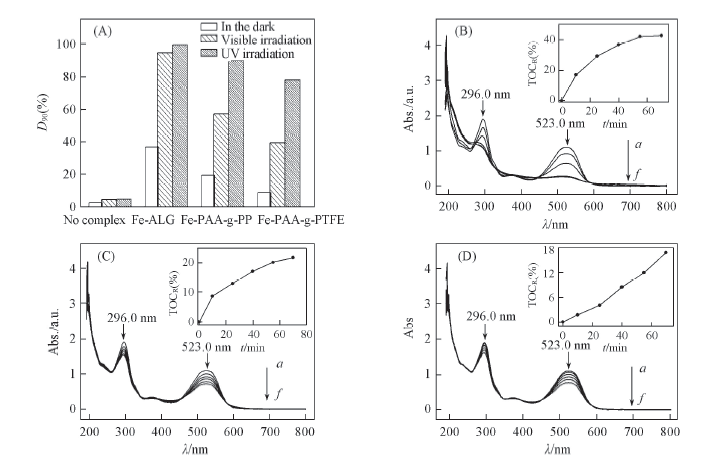
Fig.7 Decoloration rate and mineralization of RR 195 in the presence of different complexes (A) D90 values under different irradiation; (B—D) UV-Vis spectra and TOCR(%) of dye degradation with Fe-ALG(B), Fe-PAA-g-PP(C) and Fe-PAA-g-PTFE(D), respectively. (B—D) t/min: a. 0; b. 10; c. 25; d. 40; e. 55; f. 70.
| [1] | Espenson J.H., Chemical Kinetics and Reaction Mechanisms, 2nd Ed., McGraw-Hill Inc., New York, 1995 |
| [2] | Xu Y., Chemical Reaction Kinetics, Press of Chemical Industry, Beijing, 2005 |
| (许越. 化学反应动力学. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005) | |
| [3] | Song X. P., Huang M. Y., Jiang Y. Y., Journal of Functional Polymers, 1994, 7(2), 136—141 |
| (宋啸平, 黄美玉, 江英彦. 功能高分子学报, 1994, 7(2), 136—141) | |
| [4] | Ishtchenko V. V., Huddsman K. D., Vitkovskaya R. F., Appl. Catal. A., 2003, 242, 123—137 |
| [5] | Tao T. X., Wu Z. C., Wang X. Q., Li M. S., Zhang J. H., Acta Polymerica Sinica, 2006, 3, 387—390 |
| (陶庭先, 吴之传, 汪学骞, 李梅生, 张俊华. 高分子学报, 2006, 3, 387—390) | |
| [6] | Dong Y. C., Du F., Han Z. B., Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2008, 24(11), 2114—2121 |
| (董永春, 杜芳, 韩振邦. 物理化学学报, 2008, 24(11), 2114—2121) | |
| [7] | Dong Y. C., Zhao J. Z., Hou C. Y., Wu D. Z., Journal of Sichuan University(Natural Science Edition), 2009, 41(4), 125—131 |
| (董永春, 赵娟芝, 侯春燕, 吴多智, 四川大学学报(工程科学版), 2009, 41(4), 125—131) | |
| [8] | Zhang Y., Wu Z. C., Tao T. X., Tong W., Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 25(7), 1299—1303 |
| (张勇, 吴之传, 陶庭先, 童伟, 无机化学学报, 2009, 25(7), 1299—1303) | |
| [9] | Liu X., Tang R., He Q., Liao X., Shi B., J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 174, 687—693 |
| [10] | Dong Y., Han Z., Liu C., Du F., Sci. Total Environ., 2010, 408, 2245—2253 |
| [11] | Dong Y., Han Z., Dong S., Wu J., Ding Z., Catal. Today, 2011, 175, 299—309 |
| [12] | Li B., Dong Y., Ding Z., Color. Technol., 2013, 129, 403—411 |
| [13] | Ding Z. Z., Dong Y. C., Li B., Li M., Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin., 2013, 29(1), 157—166 |
| (丁志忠, 董永春, 李冰, 李淼.物理化学学报, 2013, 29(1), 157—166) | |
| [14] | Han Z. B., Dong Y. C., Liu C. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 5(11), 986—993 |
| (韩振邦, 董永春, 刘春燕. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 5(11), 986—993) | |
| [15] | Ding Y. Y., Wang C. Z., Wen X. F., Zhang X. P., Ye L., Zhang A. Y., Feng Z. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(7), 1758—1764 |
| (丁耀莹, 王成志, 问县芳, 张鑫鹏, 叶霖, 张爱英, 冯增国. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(7), 1758—1764) | |
| [16] | Yang X.W., Luo Y. Y., Textbook of Chemical Products: Dyestuffs, Press of Chemical Industry, Beijing, 2005 |
| (杨新玮, 罗钰言. 化工产品手册: 染料. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005) | |
| [17] | Dong Y. C., Zhang B. H., Water Cooled Temperature Controlling Photoreaction System, CN03275610.0, 2003-07-11) |
| (董永春, 张宝华. 水冷式控温光反应器, CN03275610.0, 2003-07-11) | |
| [18] | Xiong C., Yao C., J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 170, 541—542 |
| [19] | Wei J. F., Wang Z. P., Zhang J., Wu Y. Y., Zhang Z. P., Xiong C. H., React. Funct. Polym., 2005, 65, 127—134 |
| [20] | Park H. J., Na C. K., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2006, 301, 46—54 |
| [21] | Park H. J., Na C. K., J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, 166, 1201—1209 |
| [22] | Ibrahim N. A., Abo-Shosha H., Elnagdy E. I., Gaffari M. A., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 84, 2243—2253 |
| [23] | Park B. H., Lee M., Kim S. B., Jo Y. M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011, 257, 3709—3716 |
| [24] | Dong Y., Dong W., Cao Y., Han Z., Ding Z., Catal. Today, 2011, 175, 346—355 |
| [25] | Qin Y., Text. Res. J., 2005, 75, 165—168 |
| [26] | Lv F., Zhu P., Wang C., Zheng L. J., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2012, 126, 383—388 |
| [27] | Naeem M., El-Sawy Z. I. A., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2007, 103, 4065—4071 |
| [28] | Kong Q., Wang B., Ji Q., Xia Y., Guo Z., Yu J., Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2009, 27, 807—812 |
| [29] | Cheng X. S., Guan H. M., Su Y. C., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2000, 58, 407—413 |
| [30] | Cheng M., Song W., Ma W., Chen C., Zhao J., Lin J., Zhu H., Appl. Catal. B., 2008, 77, 355—363 |
| [31] | Ma W., Huang Y., Li J., Chen M., Song W., Zhao J.,Chem. Commun., 2003, 1582—1583 |
| (Ed.: V, Z ) |
| [1] | YANG Jingyi, LI Qinghe, QIAO Botao. Synergistic Catalysis Between Ir Single Atoms and Nanoparticles for N2O Decomposition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220388. |
| [2] | LIN Gaoxin, WANG Jiacheng. Progress and Perspective on Molybdenum Disulfide with Single-atom Doping Toward Hydrogen Evolution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [3] | WANG Sicong, PANG Beibei, LIU Xiaokang, DING Tao, YAO Tao. Application of XAFS Technique in Single-atom Electrocatalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [4] | TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325. |
| [5] | YANG Jingyi, SHI Siqi, PENG Huaitao, YANG Qihao, CHEN Liang. Integration of Atomically Dispersed Ga Sites with C3N4 Nanosheets for Efficient Photo-driven CO2 Cycloaddition [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220349. |
| [6] | WANG Ruyue, WEI Hehe, HUANG Kai, WU Hui. Freezing Synthesis for Single Atom Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220428. |
| [7] | WANG Xintian, LI Pan, CAO Yue, HONG Wenhao, GENG Zhongxuan, AN Zhiyang, WANG Haoyu, WANG Hua, SUN Bin, ZHU Wenlei, ZHOU Yang. Techno-economic Analysis and Industrial Application Prospects of Single-atom Materials in CO2 Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [8] | TANG Quanjun, LIU Yingxin, MENG Rongwei, ZHANG Ruotian, LING Guowei, ZHANG Chen. Application of Single-atom Catalysis in Marine Energy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220324. |
| [9] | QIN Yongji, LUO Jun. Applications of Single-atom Catalysts in CO2 Conversion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [10] | YAO Qing, YU Zhiyong, HUANG Xiaoqing. Progress in Synthesis and Energy-related Electrocatalysis of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [11] | JIANG Bowen, CHEN Jingxuan, CHENG Yonghua, SANG Wei, KOU Zongkui. Recent Progress of Single-atom Materials in Electrochemical Biosensing [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220334. |
| [12] | LIN Zhi, PENG Zhiming, HE Weiqing, SHEN Shaohua. Single-atom and Cluster Photocatalysis: Competition and Cooperation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| [13] | HUANG Qiuhong, LI Wenjun, LI Xin. Organocatalytic Enantioselective Mannich-type Addition of 5H-Oxazol-4-ones to Isatin Derived Ketimines [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220131. |
| [14] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [15] | HAN Fuchao, LI Fujin, CHEN Liang, HE Leiyi, JIANG Yunan, XU Shoudong, ZHANG Ding, QI Lu. Enhance of CoSe2/C Composites Modified Separator on Electrochemical Performance of Li-S Batteries at High Sulfur Loading [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||