

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 1044.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131144
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Yao, LIANG Wenjing, LI Cheng, SHANG Xu, CONG Lina*( )
)
Received:2013-11-25
Online:2014-05-10
Published:2014-04-18
Contact:
CONG Lina
E-mail:congln@dlpu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Yao, LIANG Wenjing, LI Cheng, SHANG Xu, CONG Lina. Effects of Temperature on the Antibacterial Activity and Structural Change of the C-terminal Polypeptide of the Sea Cucumber Lysozyme†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 1044.
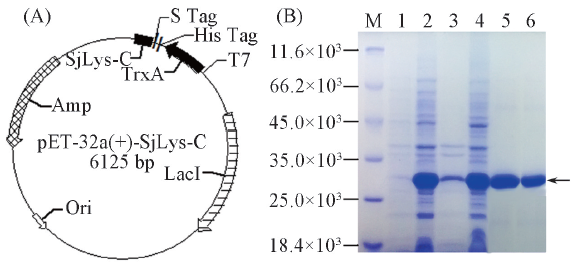
Fig.1 Map of the recombination plasmid(A) and the expression of recombination SjLys-C on SDS-PAGE(B)^M: Protein markers; lane 1: control; lane 2: total cellular protein; lane 3: sample in precipitation after ultrasonication; lane 4: sample in supernatant after ultrasonication; lane 5: recombinant SjLys-C after Ni2+-NTA affinity chromatography; lane 6: recombinant SjLys-C after G-25 desalination column.
| Tested bacteria | Diameter of inhibition zonea/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosetta(DE3)pLysSb | Rosetta-gamiB(DE3)pLysS | |||
| SjLys-C | Heat-treated SjLys-C | SjLys-C | Heat-treated SjLys-C | |
| M. lysodeikticus | 19 | 23 | 18 | 22 |
| S. aureus | 10 | 10 | 19 | 19 |
| P. aeruginosa | 8 | 8 | 14 | 15 |
| V. parahaemolyticus | 20 | 21 | 20 | 21 |
Table 1 Antimicrobial activities of the recombinant SjLys-C expressed in different host strains
| Tested bacteria | Diameter of inhibition zonea/mm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rosetta(DE3)pLysSb | Rosetta-gamiB(DE3)pLysS | |||
| SjLys-C | Heat-treated SjLys-C | SjLys-C | Heat-treated SjLys-C | |
| M. lysodeikticus | 19 | 23 | 18 | 22 |
| S. aureus | 10 | 10 | 19 | 19 |
| P. aeruginosa | 8 | 8 | 14 | 15 |
| V. parahaemolyticus | 20 | 21 | 20 | 21 |
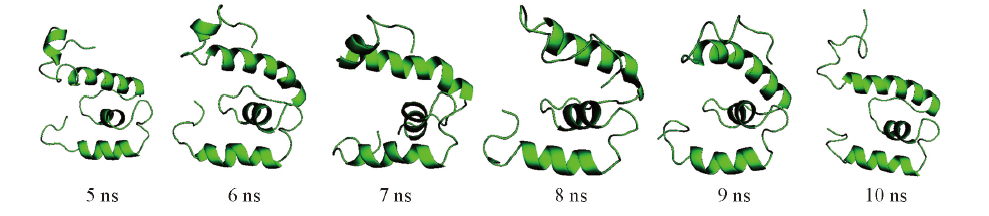
Fig.6 Comparision of the structures from simulated annealing^The native sructures were selected from the MD structure of SjLys-C at 100 ℃ at different time points 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 ns.
| [1] | Blake C. C. F., Koenig D. F., Mair G. A., North A. C. T., Philips D. C., Sarma V. R., Nature, 1965, 206(4986), 757—761 |
| [2] | Fujimoto S., Toshimori-Tsuda I., Kishimoto K., Yamano Y., Morishima I., Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2001, 128(4), 709—718 |
| [3] | Fleming A., Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. B: Biol. Sci., 1922, 93(653), 306—317 |
| [4] | Jollès P., Lysozymes: Model Enzymes in Biochemistry and Biology, Birkhäuser Press, Berlin, 1995, 9—31 |
| [5] | Huang S., Xiao Q., He Z. K., Liu Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(10), 1951—1955 |
| (黄珊, 肖琦, 何治柯, 刘义.高等学校化学学报, 2009,30(10), 1951—1955) | |
| [6] | Xue Q., Hellberg M. E., Schey K. L., Li Y. L., Cooper R. K., La Peyre J. F., Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2007, 64(1), 82—95 |
| [7] | Olsen Ø. M., Nilsen I. W., Sletten K., Myrnes B., Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol., 2003, 136(1), 107—115 |
| [8] | Nilsen I. W., Myrnes B., Gene, 2001, 16,269(1/2), 27—32 |
| [9] | Cong L., Yang X., Wang X., Tada M., Lu M., Liu H., Zhu B., J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2009, 107(6), 583—588 |
| [10] | Wang X. X., Cong L. N., Wang D., Chin. J. Biotech., 2009, 25(2), 189—194 |
| (王秀霞, 丛丽娜, 王丹.生物工程学报, 2009,25(2), 189—194) | |
| [11] | Chang Y. H., Cong L. N., Lu D., Journal of Agricultural Biotechnology, 2012, 20(4), 443—450 |
| (常艺海, 丛丽娜, 卢冬.农业生物技术学报, 2012,20(4), 443—450) | |
| [12] | Düring K., Porsch P., Mahn A., Brinkmann O., Gieffers W., FEBS Letters, 1999, 449(2), 93—100 |
| [13] | Spoel D., Lindahl E., Hess B., Gromacs 4.6, Royal Institute of Technology and Uppsala University, Uppsala, 2012 |
| [14] | Lemkul J., GROMACS Tutorial: Lysozyme in Water, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Virginia, 2010 |
| [15] | Feng X. L., Zhao X., Yu H., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2012, 70(5), 606—610 |
| (冯献礼, 赵熹, 于辉.化学学报, 2012,70(5), 606—610) | |
| [16] | Hess B., Bekker H., Berendsen H. J., Fraaije J. G., J. Comput. Chem., 1997, 18(12), 1463—1472 |
| [17] | Zhao J., Yan C. L., Xiu Z. L., Computers and Applied Chemistry, 2008, 25(10), 1185—1188 |
| (赵军, 闰春丽, 修志龙.计算机与应用化学, 2008,25(10), 1185—1188) | |
| [18] | Parrinello M., Rahman A., J. Appl. Phys., 1981, 52, 7182 |
| [19] | Essmann U., Perera L., Berkowitz M. L., Darden T., Lee H., Pedersen L. G., J. Chem. Phys., 1995, 103(19), 8577—8593 |
| [20] | Jorge R. M. C., Carlos A. F., Léo D., J. Biol. Chem., 2011, 3, 244—257 |
| [21] | Chen F., Liu S. S., Duan X., T., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2013, 71, 1035—1040 |
| (陈浮, 刘树深, 段欣甜. 化学学报, 2013, 71, 1035—1040) | |
| [22] | Case D. A., Cheatham T. E., Darden T., Gohlke H., Luo R., Merz K. M., Onufriev A., Simmerling C., Wang B., Woods R. J., J. Comput. Chem., 2005, 26, 1668 |
| [23] | Khuntawee W., Rungrotmongkol T., Hannongbua S. J., Chem. Inf. Model, 2012, 52, 76 |
| [24] | Zhan D. L., Gao N., Han W. W., Feng Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(1), 146—153 |
| (詹冬玲, 高楠, 韩葳葳, 冯雁.高等学校化学学报, 2014,35(1), 146—153) | |
| [25] | Studier F.W., Davanloo P., Rosenberg A. H., Moffatt B. A., Dunn J. J., pET System Manual, 11th ed., Merck KGaA Press, Darmstadt, 2010, 49—51 |
| [26] | Drets M.E., Bandscan 5.0, BioMarin Pharmaceutical Inc., San Francisco, 2003 |
| [27] | Ibrahim H. R., Thomas U., Pellegrini A., J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276(47), 43767—43774 |
| [28] | Ruda V. M., Akopov S. B., Trubetskoy D. O., Manuylov N. L., Vetchinova A. S., Zavalova L. L., Nikolaev L. G., Sverdlov E. D., Virus Res., 2004, 104(1), 11—16 |
| [1] | HU Haocheng, LI Wenli, ZHANG Jianing, LIU Yubo. Extraction, Structure Characterization and Biological Activities of Oligosaccharides from Auricularia heimuer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2465. |
| [2] | MAO Long, LIU Yuejun, FAN Shuhong. Preparation and Properties of Polypyrrole Modified Layered Clay/poly(ε-caprolactone) Antibacterial Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1726. |
| [3] | LI Pu,CHEN Ying,XIA Rongjiao,GUO Tao,ZHANG Min,JIANG Shichun,ANG Xu,HE Ming,XUE Wei. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Myricetin Derivatives Containing Quinoxaline† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 909. |
| [4] | LI Bing,WANG Xuemin,BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing. Synthesises, Structures and Antibacterial Activities of a Series of Rare Earth Nitrogen Heterocyclic Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 632. |
| [5] | WAN Jinlin, WU Shouqun, GAN Yiyuan, MENG Jiao, WANG Zhenchao*, OUYANG Guiping*. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities Evaluation of Chalconesemicarbazone Derivatives Bearing 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Moiety† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1683. |
| [6] | JIA Yunjing, SHI Wensi, HU Feiliu, ZHU Huajie, LIU Li, MA Zhengyue. Cytotoxic Activity of Trichothecene Compounds and Derivatives from Myrothecium sp.† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1668. |
| [7] | ZHANG Bingyang, MA Yangyang, GUO Hua, ZHU Huajie, LI Wan. Absolute Configuration Determination of Two Drimane Sesquiterpenoids from the Endophytic Fungi Talaromyces Purpureogenus of Panax notoginseng† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 1046. |
| [8] | DONG Xiaoming, YUAN Baoming, CHEN Bingpeng, HE Chaoliang, WANG Jincheng, CHEN Xuesi. In vitro Antibacterial Activity of PLGA-PEG-PLGA Thermosensitive Hydrogels Loaded with Vancomycin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 866. |
| [9] | FU Ranran, JI Xiujie, LIU Chao, REN Yanfei, WANG Gang, CHENG Bowen. Fabrication of Cellulose/Nano Lamellar ZnO Composite Antibacterial Fibers Using Ionic Liquid† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2344. |
| [10] | MA Yangyang, CAI Hui, DU Min, CAO Fei, ZHU Huajie. Fractionation of Azaphilones from Secondary Metabolites of Marine-Derived Fungus Penicillim pinophilum and Their Antibacterial Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1963. |
| [11] | XIAO Wei, RUAN Xianghui, LI Qin, ZHANG Juping, ZHONG Xinmin, XIE Yan, WANG Xiaobin, HUANG Minguo, XUE Wei. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of Myricetin Derivatives ontaining Acidamide Moiety† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(1): 35. |
| [12] | GAO Tong, CAI Siyuan, XU Lanlan, CAO Fei, ZHU Huajie. Citrinin Derivatives from Marine-derived Fungus Penicillim Grisefulvum and Antibacterial Activity† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1282. |
| [13] | WANG Hongyun, LIU Jinbiao, LU Junrui, YING Ming, YANG Xuyun, YANG Shuxun, MA Yao. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of 5-Methyl-1,2,4-triazole-3-thione Glucosides Compounds† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(2): 246. |
| [14] | XU Lanlan, ZHAO Qiqi, YU He, WANG Jingchen, WANG Huijun, YANG Qin, ZHU Huajie, LI Yan. Absolute Configuration Determination of One New Compound Trichoderol A from Trichoderma sp. Fungus† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 1972. |
| [15] | ZHANG Ruibo, LU Junrui, LIU Jinbiao, MU Jiangbei, YANG Xuyun, WANG Hongyun, WANG Meijun, ZHANG He, ZHANG Mei. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities of 3-S-(β-D-Glucosides)-1,2,4-triazole† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8): 1521. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||