

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 1430.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200575
刘瀚林1,3,尹琳琳1,2,陈西凤1,李国栋1,3
收稿日期:2020-08-18
出版日期:2021-05-10
发布日期:2021-05-08
基金资助:
LIU Hanlin1,3, YIN Linlin1,2, CHEN Xifeng1, LI Guodong1,3( )
)
Received:2020-08-18
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-08
Contact:
LI Guodong
E-mail:liguodong@nanoctr.cn
Supported by:摘要:
二氧化碳选择性加氢反应不仅能减少二氧化碳排放, 而且能够制备多种含碳产物, 可以作为生产高附加价值化学品与燃料的平台化合物. 然而, 由于二氧化碳的高化学惰性、 碳-碳偶联过程的高能垒和诸多的竞争反应, 开发高效的纳米催化剂以促进二氧化碳的活化并转化为多样性的产物显得至关重要. 最近, 基于氧化铟的纳米催化剂在催化二氧化碳加氢方面受到广泛关注, 主要由于其成本低廉, 且具有丰富的氧缺陷位点, 可有效吸附并活化二氧化碳和氢气. 为深入了解反应机理并设计更高性能的潜在纳米催化剂, 需对氧化铟基纳米催化剂在二氧化碳加氢方面的研究进展进行总结. 本综述首先总结了不同晶型的氧化铟及其与金属氧化物或金属纳米粒子形成的复合催化剂用于催化二氧化碳选择性加氢制备C1产物的性能. 随后, 探讨了氧化铟与不同类型的沸石的复合物用于催化二氧化碳加氢制备C2+产物的性能. 最后, 提出了目前氧化铟基纳米催化剂在催化二氧化碳选择性加氢方面存在的挑战和未来的发展方向. 希望本文能够为设计具有高活性、 高选择性和高稳定性催化二氧化碳加氢的新型氧化铟基纳米催化剂提供一些思路.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
刘瀚林, 尹琳琳, 陈西凤, 李国栋. 氧化铟基纳米催化剂用于二氧化碳选择性加氢的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5): 1430.
LIU Hanlin, YIN Linlin, CHEN Xifeng, LI Guodong. Recent Advances in Indium Oxide Based Nanocatalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of CO2. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1430.
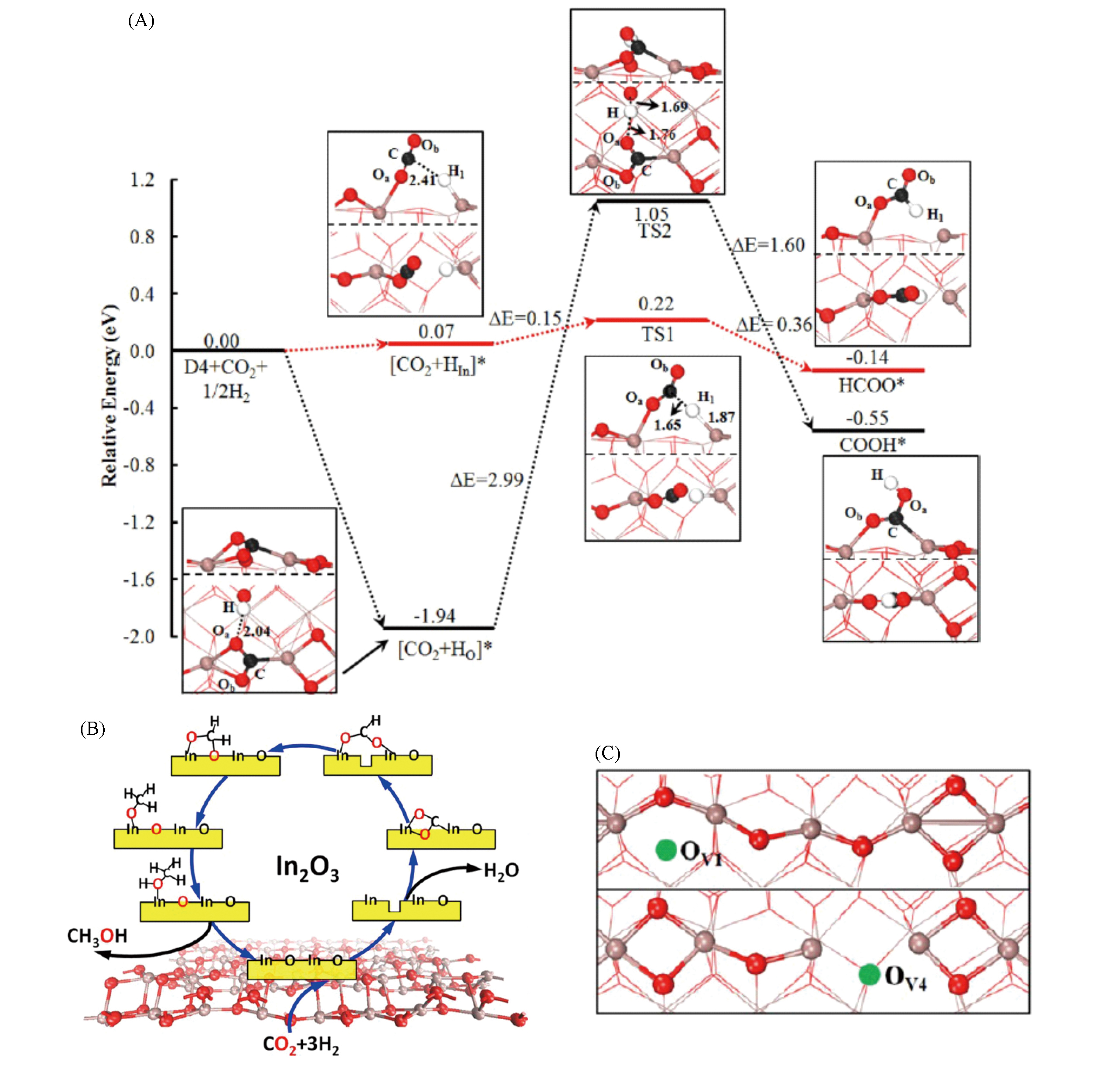
Fig.2 Potential energy profiles of CO2 hydrogenation on the defective (110) surface of In2O3(A),a possible reaction route for CO2 hydrogenation into methanol(B) and two different types of oxygen vacancies on defective (110) surface of In2O3(C)[29]Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
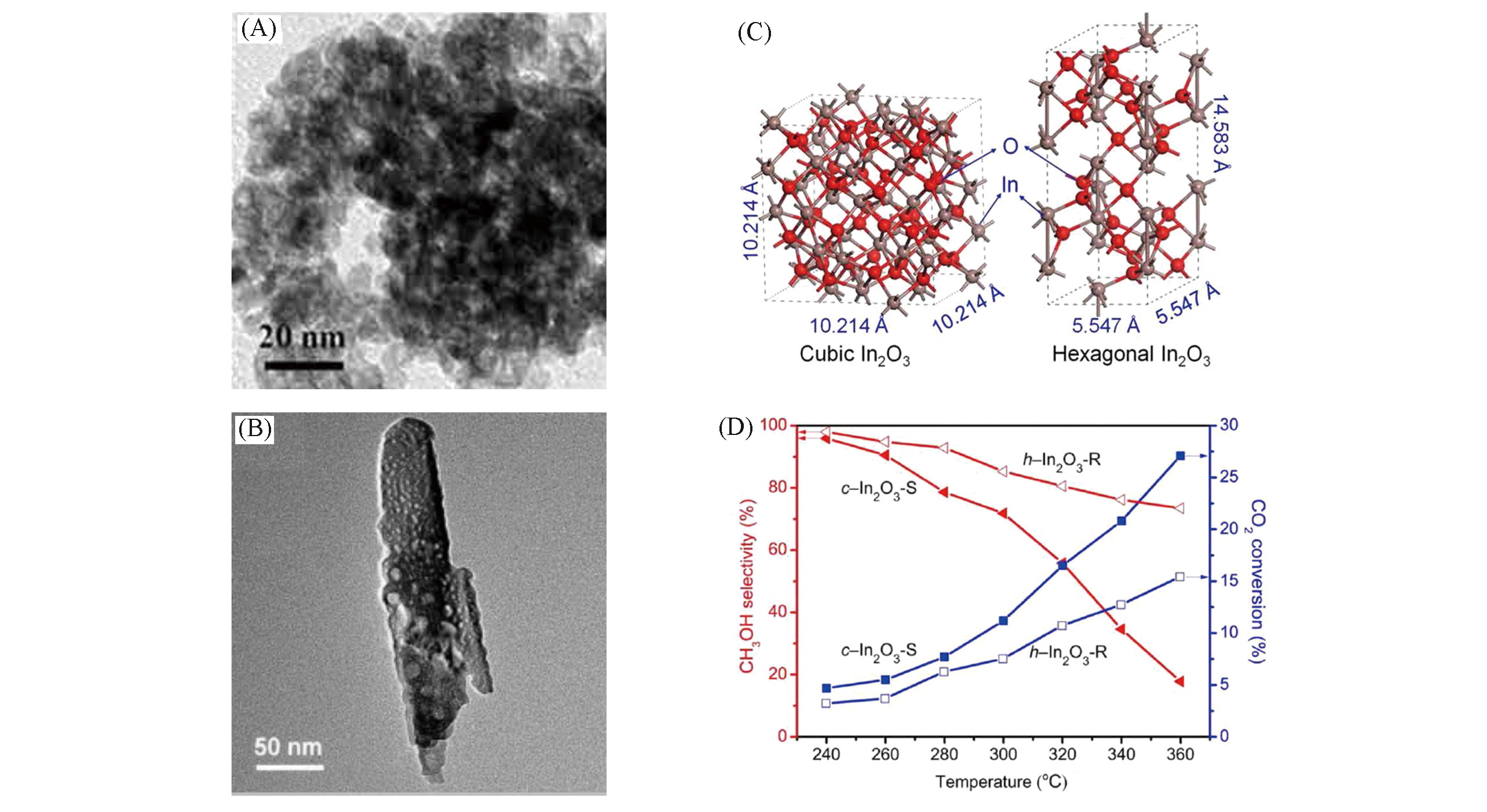
Fig.3 Characterizations and catalytic tests of c?In2O3 and h?In2O3[33](A) TEM image of c-In2O3 nanoparticles; (B) TEM image of h-In2O3 nanorods; (C) schematic models of c-In2O3 and h-In2O3 unit cells; (D) CO2 conversion and methanol selectivity over c-In2O3 and h-In2O3 at different temperatures. Reaction conditions: 5.0 MPa, GHSV=9000 mL?gcat-1?h-1, n(H2)∶n(CO2)∶n(N2)=73∶24∶3. Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
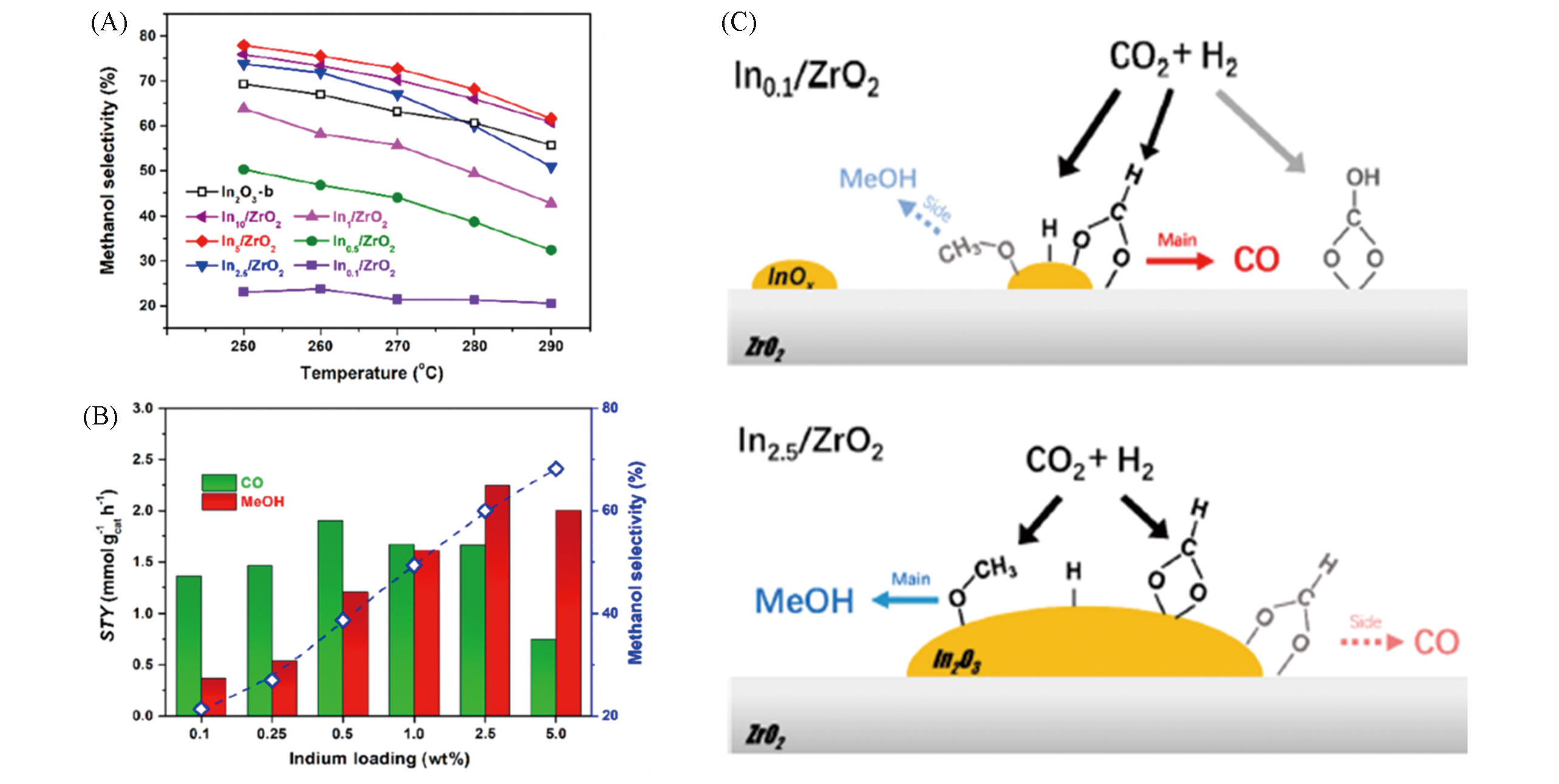
Fig.4 Catalytic tests and possible reaction pathways of CO2 hydrogenation over In2O3/ZrO2 with different indium mass?loading[41](A) Methanol selectivity over different Inx/ZrO2 at different temperatures; (B) STY of CO and methanol, and methanol selectivity at 280 ℃ over Inx/ZrO2. Reaction conditions: 5.0 MPa, n(CO2)∶n(H2)∶n(N2)=4∶1∶1.67, GHSV= 24000 h-1; (C) schematic pathways for CO2 hydrogenation over In0.1/ZrO2 and In2.5/ZrO2. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
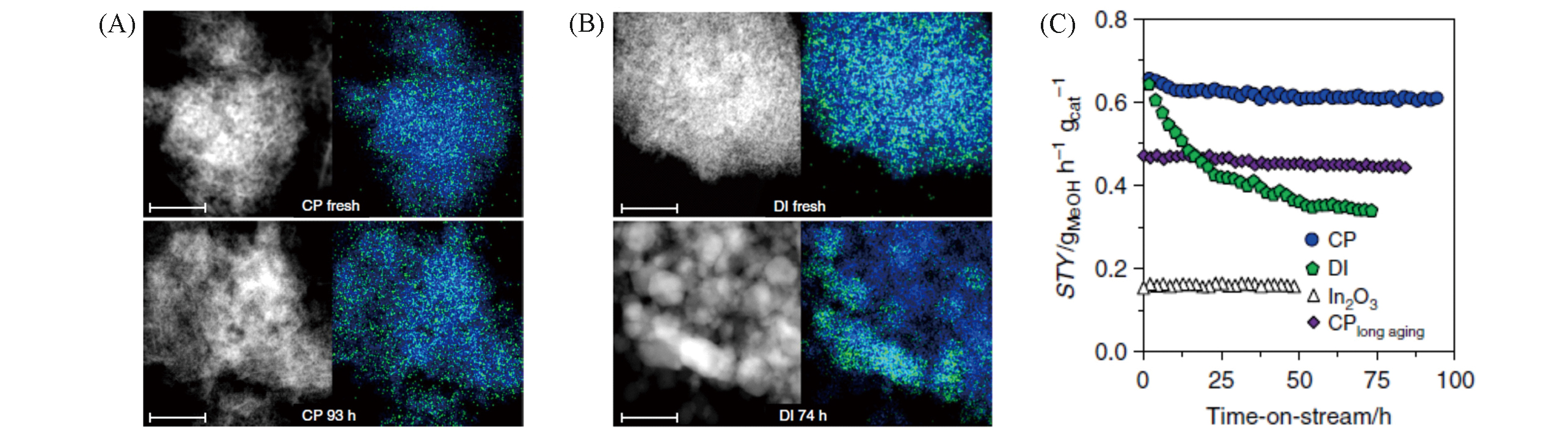
Fig.5 Characterizations and catalytic tests of 0.75wt% Pd/In2O3 catalysts[46](A, B) HAADF?STEM images and EDX maps of indium(blue) and palladium(green) for CP and DI catalysts produced by co?precipitation(A) and dry impregnation(B) methods before and after catalytic tests; (C) methanol STY for CP and DI catalysts, with pure In2O3 and 200 h aged CP catalyst as references. Reaction conditions: 553 K, 5 MPa, n(H2)∶n(CO2)=4∶1, and WHSV=24000 cm3?h-1?gcat-1.Copyright 2019, Nature Publishing Group.
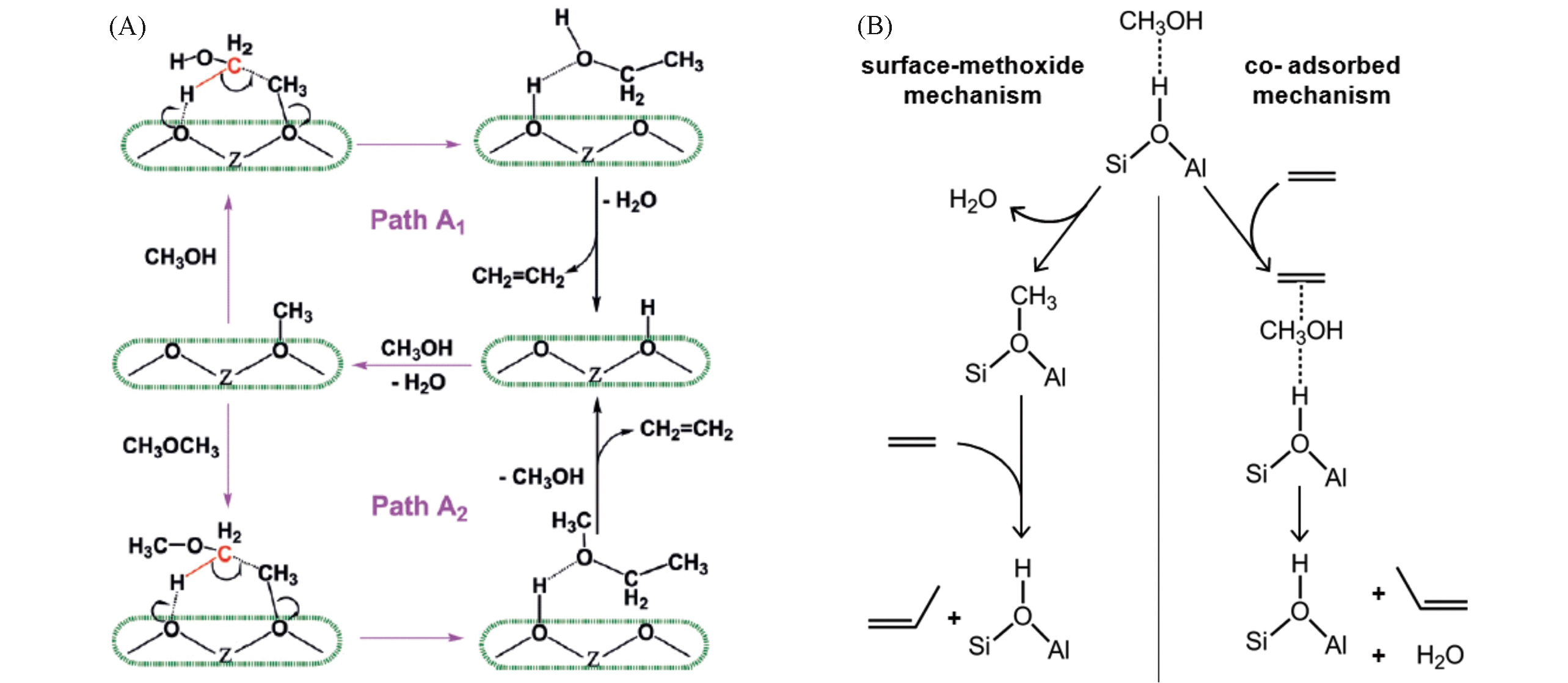
Fig.7 Probable mechanisms of the first C—C bond formation step over zeolites[58](A) and probable mechanisms of olefin methylation with methanol over zeolites[59](B)(A) Copyright 2017, Wiley; (B) Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
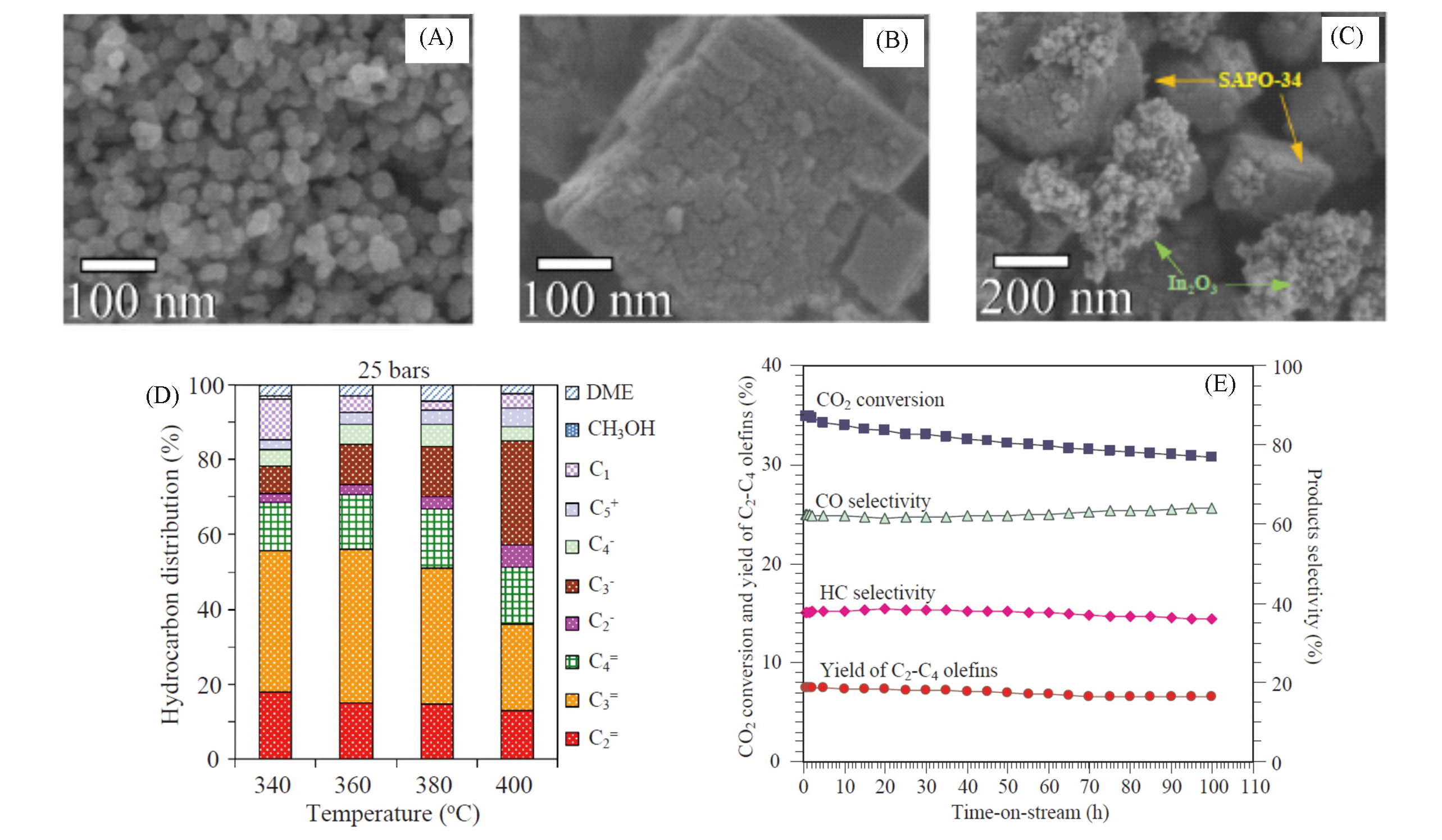
Fig.8 Characterizations and catalytic tests of In2O3/SAPO?34[63] TEM images of In2O3(A), SAPO?34(B) and hybrid In2O3/SAPO?34 catalyst(C); (D) product distribution of CO2 hydrogenation over In2O3/SAPO?34 at different temperatures under 2.5 MPa, n(H2)∶n(CO2)∶n(N2)=3∶1∶1; (E) stability test of In2O3/SAPO?34 at 380 ℃ under 25 bar.Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
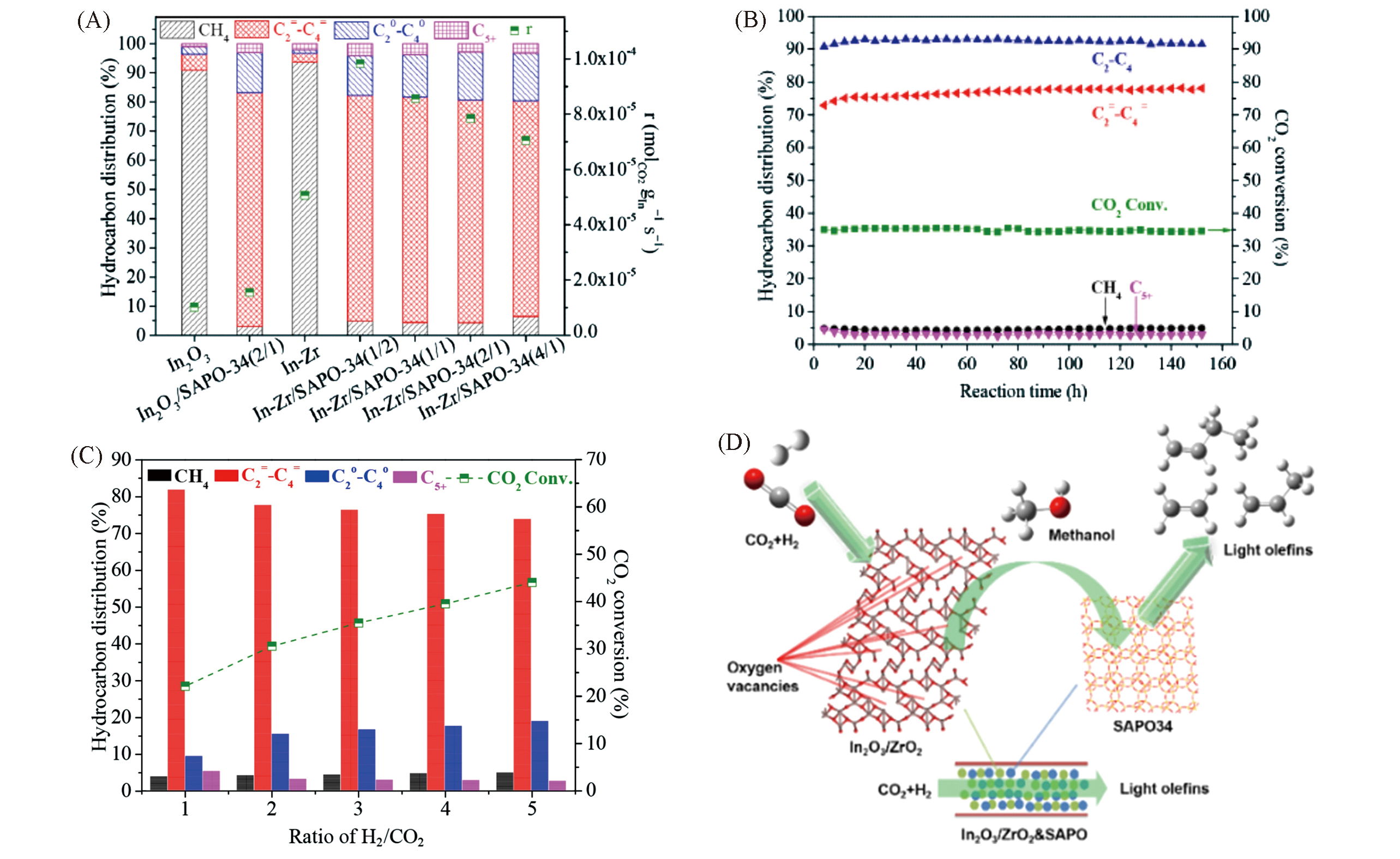
Fig.9 Catalytic tests for In?Zr?O/SAPO?34 catalysts and the reaction pathway[64, 67](A) Hydrocarbon distribution and reaction rate over In?Zr/SAPO?34 catalysts with different In/Zr ratios at 400 ℃, as well as over In2O3 and In?Zr oxide references; (B) stability test of In?Zr/SAPO?34 at 400 ℃; GHSV=9000 mL?gcat-1?h-1, n(H2)∶n(CO2)∶n(N2)=73∶24∶3; (C) catalytic tests for In?Zr/SAPO?34 at different H2/CO2 ratios[64]; (D) schematic reaction pathway of CO2 hydrogenation into light olefins over In?Zr/SAPO?34[67].(A)―(C) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (D) Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
| 1 | Wang L., Chen W., Zhang D., Du Y., Amal R., Qiao S., Wu J., Yin Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(21), 5310—5349 |
| 2 | Ding M., Flaig R. W., Jiang H. L., Yaghi O. M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48(10), 2783—2828 |
| 3 | Hepburn C., Adlen E., Beddington J., Carter E. A., Fuss S., Mac Dowell N., Minx J. C., Smith P., Williams C. K., Nature, 2019, 575(7781), 87—97 |
| 4 | Grim R. G., Huang Z., Guarnieri M. T., Ferrell J. R., Tao L., Schaidle J. A., Energ. Environ. Sci.,2020, 13(2), 472—494 |
| 5 | Bao J., Yang G., Yoneyama Y., Tsubaki N., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(4), 3026—3053 |
| 6 | Podrojková N., Sans V., Oriňak A., Oriňaková R., ChemCatChem, 2020, 12(7), 1802—1825 |
| 7 | Tan L., Xu S. M., Wang Z., Xu Y., Wang X., Hao X., Bai S., Ning C., Wang Y., Zhang W., Jo Y. K., Hwang S. J., Cao X., Zheng X., Yan H., Zhao Y., Duan H., Song Y. F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(34), 11860—11867 |
| 8 | Xu W., Lu Z., Sun X., Jiang L., Duan X., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51(7), 1590—1598 |
| 9 | Burkart M. D., Hazari N., Tway C. L., Zeitler E. L., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(9), 7937—7956 |
| 10 | Liang J., Xie Y. Q., Wang X. S., Wang Q., Liu T. T., Huang Y. B., Cao R., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(4), 342—345 |
| 11 | Saeidi S., Amin N. A. S., Rahimpour M. R., J. CO2 Util., 2014, 5, 66—81 |
| 12 | Kattel S., Liu P., Chen J. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(29), 9739—9754 |
| 13 | Alvarez A., Bansode A., Urakawa A., Bavykina A. V., Wezendonk T. A., Makkee M., Gascon J., Kapteijn F., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(14), 9804—9838 |
| 14 | Bowker M., ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(17), 4238—4246 |
| 15 | Roy S., Cherevotan A., Peter S. C., ACS Energ. Lett., 2018, 3(8), 1938—1966 |
| 16 | Ma Z., Porosoff M. D., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(3), 2639—2656 |
| 17 | Ye R. P., Ding J., Gong W., Argyle M. D., Zhong Q., Wang Y., Russell C. K., Xu Z., Russell A. G., Li Q., Fan M., Yao Y. G., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 5698 |
| 18 | Wang Y., Kattel S., Gao W., Li K., Liu P., Chen J. G., Wang H., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1166 |
| 19 | Liao F., Wu X. P., Zheng J., Li M. M. J., Kroner A., Zeng Z., Hong X., Yuan Y., Gong X. Q., Tsang S. C. E., Green Chem., 2017, 19(1), 270—280 |
| 20 | Chen Y., Li H., Zhao W., Zhang W., Li J., Li W., Zheng X., Yan W., Zhang W., Zhu J., Si R., Zeng J., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1885 |
| 21 | Wang L., He S., Wang L., Lei Y., Meng X., Xiao F. S., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(12), 11335—11340 |
| 22 | An B., Li Z., Song Y., Zhang J., Zeng L., Wang C., Lin W., Nat. Catal., 2019, 2(8), 709—717 |
| 23 | Han F. Q., Zhang Z., Niu N., Li J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2018, 34(4), 635—642 |
| 24 | Yao L., Shen X., Pan Y., Peng Z., J. Catal., 2019, 372, 74—85 |
| 25 | Jiang X., Nie X., Gong Y., Moran C. M., Wang J., Zhu J., Chang H., Guo X., Walton K. S., Song C., J. Catal., 2020, 383, 283—296 |
| 26 | Martin O., Martin A. J., Mondelli C., Mitchell S., Segawa T. F., Hauert R., Drouilly C., Curulla⁃Ferre D., Pérezv⁃Ramírez J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(21), 6261—6265 |
| 27 | Ye J., Liu C., Ge Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(14), 7817—7825 |
| 28 | Tsoukalou A., Abdala P. M., Stoian D., Huang X., Willinger M. G., Fedorov A., Muller C. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(34), 13497—13505 |
| 29 | Ye J., Liu C., Mei D., Ge Q., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(6), 1296—1306 |
| 30 | Sun K., Fan Z., Ye J., Yan J., Ge Q., Li Y., He W., Yang W., Liu C. J., J. CO2 Util., 2015, 12, 1—6 |
| 31 | Frei M. S., Capdevila⁃Cortada M., García⁃Muelas R., Mondelli C., López N., Stewart J. A., Curulla⁃Ferré D.,Pérez⁃Ramírez J., J. Catal., 2018, 361, 313—321 |
| 32 | Yang B., Li L., Jia Z., Liu X., Zhang C., Guo L., Chinese Chem. Lett., 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.cclet.2020.05.031 |
| 33 | Dang S., Qin B., Yang Y., Wang H., Cai J., Han Y., Li S., Gao P., Sun Y., Sci. Adv.,2020,6(25),eaaz2060 |
| 34 | Chen P., Tao L., Zhu J., Zhao G., Liu Y.,Lu Y., Energy Technol., 2019, 7(3), 1800747—1800756 |
| 35 | Pan Y. X., You Y., Xin S., Li Y., Fu G., Cui Z., Men Y. L., Cao F. F., Yu S. H., Goodenough J. B., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2017, 139(11), 4123—4129 |
| 36 | Ghuman K. K., Hoch L. B., Wood T. E., Mims C., Singh C. V., Ozin G. A., ACS Catal.,2016, 6(9), 5764—5770 |
| 37 | Ghuman K. K., Hoch L. B., Szymanski P., Loh J. Y., Kherani N. P., El⁃Sayed M. A., Ozin G. A., Singh C. V., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2016, 138(4), 1206—1214 |
| 38 | Yan T., Li N., Wang L., Liu Q., Jelle A., Wang L., Xu Y., Liang Y., Dai Y., Huang B., You J., Ozin G. A., Energ. Environ. Sci.,2020, 13, 3054—3063 |
| 39 | Ben S. G., Yuan F. L., Zhu Y. J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(6), 1005—1009 |
| 40 | Frei M. S., Mondelli C., Cesarini A., Krumeich F., Hauert R., Stewart J. A., Curulla⁃Ferré D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., ACS Catal., 2019, 10(2), 1133—1145 |
| 41 | Chen T. Y., Cao C., Chen T. B., Ding X., Huang H., Shen L., Cao X., Zhu M., Xu J., Gao J., Han Y. F., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(9), 8785—8797 |
| 42 | Chou C. Y., Lobo R. F., Appl. Catal. A, 2019, 583, 117144 |
| 43 | Wang H., Jia J., Wang L., Butler K., Song R., Casillas G., He L., Kherani N. P., Perovic D. D., Jing L., Walsh A., Dittmeyer R., Ozin G. A., Adv. Sci.,2019, 6(22), 1902170 |
| 44 | Ye G., Gong Y., Lin J., Li B., He Y., Pantelides S. T., Zhou W., Vajtai R., Ajayan P. M., Nano Lett., 2016, 16(2), 1097—1103 |
| 45 | Rui N., Wang Z., Sun K., Ye J., Ge Q., Liu C. J., Appl. Catal. B, 2017, 218, 488—497 |
| 46 | Frei M. S., Mondelli C., Garcia⁃Muelas R., Kley K. S., Puertolas B., Lopez N., Safonova O. V., Stewart J. A., Curulla⁃Ferre D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 3377 |
| 47 | Sun K., Rui N., Zhang Z., Sun Z., Ge Q., Liu C. J., Green Chem., 2020, 22(15), 5059—5066 |
| 48 | Wang J., Sun K., Jia X., Liu C. J., Catal. Today, 2020, DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.05.020 |
| 49 | Jia X., Sun K., Wang J., Shen C., Liu C. J., J. Energ. Chem., 2020, 50, 409—415 |
| 50 | Shi Z., Tan Q., Tian C., Pan Y., Sun X., Zhang J., Wu D., J. Catal., 2019, 379, 78—89 |
| 51 | Bavykina A., Yarulina I., Al Abdulghani A. J., Gevers L., Hedhili M. N., Miao X., Galilea A. R., Pustovarenko A., Dikhtiarenko A., Cadiau A., Aguilar⁃Tapia A., Hazemann J. L., Kozlov S. M., Oud⁃Chikh S., Cavallo L., Gascon J., ACS Catal.,2019, 9(8), 6910—6918 |
| 52 | Shi Z., Tan Q., Wu D., AIChE J., 2018, 65(3), 1047—1058 |
| 53 | Pustovarenko A., Dikhtiarenko A., Bavykina A., Gevers L., Ramírez A., Russkikh A., Telalovic S., Aguilar A., Hazemann J. L., Ould⁃Chikh S., Gascon J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(9), 5064—5076 |
| 54 | Kubelková L., Nováková J., Nedomová K., J. Catal., 1990, 124(2), 441—450 |
| 55 | Narula C. K., Li Z., Casbeer E. M., Geiger R. A., Moses⁃Debusk M., Keller M., Buchanan M. V., Davison B. H., Sci. Rep.,2015, 5, 16039 |
| 56 | Chen Y., Gong K., Jiao F., Pan X., Hou G., Si R., Bao X., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2020, 59(16), 6529—6534 |
| 57 | Yarulina I., Chowdhury A. D., Meirer F., Weckhuysen B. M., Gascon J., Nat. Catal.,2018, 1(6), 398—411 |
| 58 | Wu X., Xu S., Zhang W., Huang J., Li J., Yu B., Wei Y., Liu Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2017, 56(31), 9039—9043 |
| 59 | Ilias S., Bhan A., ACS Catal.,2012, 3(1), 18—31 |
| 60 | Dessau R. M., LaPierre R. B., J. Catal., 1982, 78(1), 136—141 |
| 61 | Gao P., Li S., Bu X., Dang S., Liu Z., Wang H., Zhong L., Qiu M., Yang C., Cai J., Wei W., Sun Y., Nat. Chem., 2017, 9(10), 1019—1024 |
| 62 | Remi J. C. S., Lauerer A., Chmelik C., Vandendael I., Terryn H., Baron G. V., Denayer J. F. M., Kärger J., Nat. Mater., 2016, 15(4), 401—406 |
| 63 | Numpilai T., Wattanakit C., Chareonpanich M., Limtrakul J., Witoon T., Energ. Convers. Manage., 2019, 180, 511—523 |
| 64 | Gao P., Dang S., Li S., Bu X., Liu Z., Qiu M., Yang C., Wang H., Zhong L., Han Y., Liu Q., Wei W., Sun Y., ACS Catal., 2017, 8(1), 571—578 |
| 65 | Dang S., Gao P., Liu Z., Chen X., Yang C., Wang H., Zhong L., Li S., Sun Y., J. Catal., 2018, 364, 382—393 |
| 66 | Gao J., Jia C., Liu B., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2017, 7(23), 5602—5607 |
| 67 | Tan L., Zhang P., Cui Y., Suzuki Y., Li H., Guo L., Yang G., Tsubaki N., Fuel Sci. Technol., 2019, 196, 106174 |
| 68 | Wang J., Zhang A., Jiang X., Song C., Guo X., J. CO2 Util., 2018, 27, 81—88 |
| 69 | Dang S., Li S., Yang C., Chen X., Li X., Zhong L., Gao P., Sun Y., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(15), 3582—3591 |
| 70 | Shen Q., Cao C., Huang R., Zhu L., Zhou X., Zhang Q., Gu L., Song W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(3), 1216—1219 |
| [1] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | 张昕昕, 许狄, 王艳秋, 洪昕林, 刘国亮, 杨恒权. CO2加氢制低碳醇CuFe基催化剂中的Mn助剂效应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [3] | 周紫璇, 杨海艳, 孙予罕, 高鹏. 二氧化碳加氢制甲醇多相催化剂研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [4] | 张维中,温月丽,宋镕鹏,王斌,张倩,黄伟. 催化剂表面Cu0含量对二氧化碳加氢合成C2+醇性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1297. |
| [5] | 李振华, 施润, 赵家琦, 张铁锐. 光驱动C1转换到高附加值化学品的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4): 604. |
| [6] | 张怡青, 刘家祥. 立方形貌ITO粉体的水热法制备及光电性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(7): 1110. |
| [7] | 汤儆, 田晓春, 刘跃强, 林建航. ITO上电沉积Pd的成核机理及电催化性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(05): 1011. |
| [8] | 晏晓晖 刁鹏 项民. 形貌可控的钯纳米粒子的电化学制备及电催化性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(11): 2650. |
| [9] | 吴志勇, 田晓溪, 渠柏艳, 陈坤, 方芳. 透明导电玻璃(ITO)基材自加热传感静态芯片聚合酶链反应(PCR)[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(12): 2259. |
| [10] | 杨秀娟, 剑菊, 陆天虹. 马心血红蛋白在氧化铟电极上的直接电子传递反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1996, 17(12): 1932. |
| [11] | 林仲华, 罗瑾, 陈海漪, 田昭武. 阳极氧化膜In2O3(Ⅰ)——膜的形成和电子性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1993, 14(7): 978. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||