

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 277.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190380
蒋静1,2,陈晓丽3,黄亚励3,张奇龙1,3,*( ),徐红3,*(
),徐红3,*( ),杨小生1
),杨小生1
收稿日期:2019-07-06
出版日期:2020-02-10
发布日期:2019-12-04
通讯作者:
张奇龙,徐红
E-mail:gzuqlzhang@126.com;1738943269@qq.com
基金资助:
JIANG Jing1,2,CHEN Xiaoli3,HUANG Yali3,ZHANG Qilong1,3,*( ),XU Hong3,*(
),XU Hong3,*( ),YANG Xiaosheng1
),YANG Xiaosheng1
Received:2019-07-06
Online:2020-02-10
Published:2019-12-04
Contact:
Qilong ZHANG,Hong XU
E-mail:gzuqlzhang@126.com;1738943269@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
利用紫外吸收光谱、 荧光光谱、 核磁共振氢谱及红外光谱等方法考察了八元瓜环(Q[8])对常山碱(Feb)的包结作用; 采用紫外吸收光谱法研究了Q[8]对Feb理化性质的影响及不同pH条件下Q[8]/Feb包合物溶液中Feb的释放及Q[8]/Feb包合物在人工肠液和人工胃液中的释放. 结果表明, 在pH=1.2的盐酸介质中, Q[8]与Feb可形成摩尔比1∶1的稳定主客体包合物, 结合常数为4.20×10 4 L/mol. 在pH=1.2(人工胃液的pH值)时, Feb可与Q[8]形成稳定包合物; 在pH=6.8(人工肠液的pH值)时, Q[8]/Feb包合物可释放出单纯的游离Feb. 因此, Q[8]可作为Feb的一种潜在药物载体为减轻Feb呕吐副反应提供借鉴.
TrendMD:
蒋静,陈晓丽,黄亚励,张奇龙,徐红,杨小生. 八元瓜环与常山碱的相互作用模式. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 277.
JIANG Jing,CHEN Xiaoli,HUANG Yali,ZHANG Qilong,XU Hong,YANG Xiaosheng. Interaction Mode Between Q[8] and Feb †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 277.
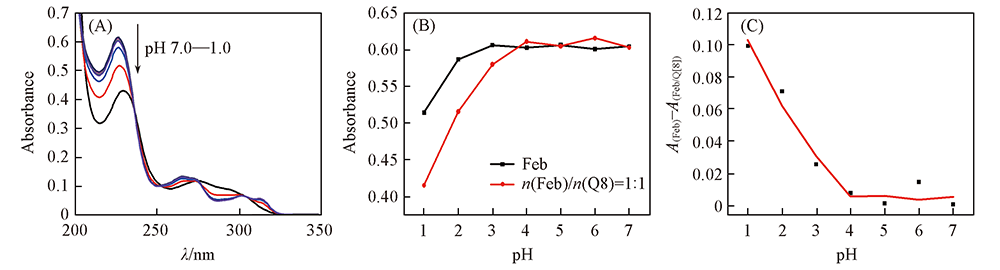
Fig.2 UV spectra of Feb with Q[8] at different pH values(A), trend chart of simple Feb solution and after addition the Q[8](B) and ΔA value(C) of AFeb and AFeb/Q[8] λ=228 nm; c(Feb)=20 μmol/L.
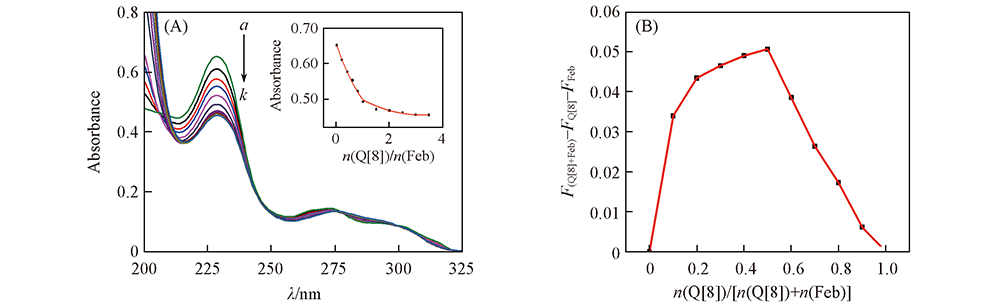
Fig.3 UV spectra(A) and Job’s plot(B) of Feb with Q[8] (A) c(Feb)=20 μmol/L; n(Q[8])/n(Feb), a—k: 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5. Inset of (A): absorption intensity plot at 228 nm of Feb upon addition of increasing concentrations of Q[8].
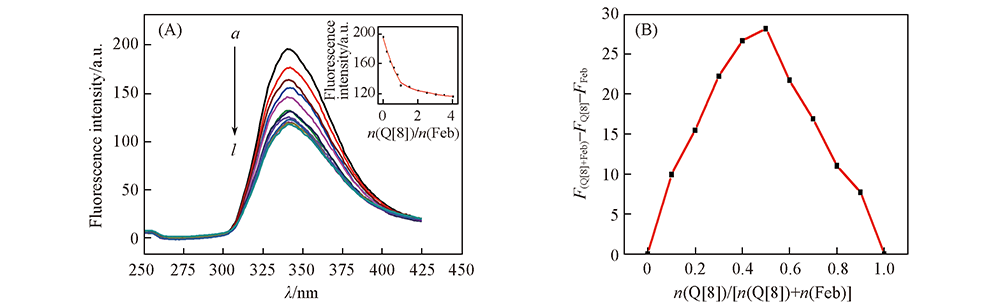
Fig.4 Fluorescence emission spectra(A), and Job’s plot(B) of Feb with Q[8] (A) c(Feb)=20 μmol/L; n(Q[8])/n(Feb), a—l: 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, 3.5, 4.0. Inset of (A): the fluorescence intensity plot at 340 nm of Feb upon addition of increasing concentrations of Q[8].
| [1] | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2015, Section One, China Medical Science and Technology Press, Beijing, 2015,313 |
| ( 国家药典委员会. 中国药典2015年版一部, 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015,313) | |
| [2] | Li Y., Liu M. C., Jin L. H., Hu D. Y., Yang S., Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2011,39(9), 7— 9 |
| ( 李燕, 刘明川, 金林红, 胡德禹, 杨松 . 广州化工, 2011,39(9), 7— 9) | |
| [3] | Guo Z. T., Liu X. L., Liang J. P., Shang R. F., Liu Y., Qiang Z., Journal of Traditional Chinese Veterinary Medicine, 2013,32(2), 17— 19 |
| ( 郭志廷, 刘晓璐, 梁剑平, 尚若锋, 刘宇, 强哲 . 中兽医医药杂志, 2013,32(2), 17— 19) | |
| [4] | Zhang J. Y., Liu X. Q., Yang L. X., Feng W. H., China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2017,42(16), 3178— 3184 |
| ( 张继远, 刘晓谦, 杨立新, 冯伟红 . 中国中药杂志, 2017,42(16), 3178— 3184) | |
| [5] | Zhu S., Chandrashekar G., Meng L., Robinson K., Chatterji D., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2012,20(2), 927— 932 |
| [6] |
Kaur K., Jain M., Kaur T., Jain R., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2009,17(9), 3229— 3256
doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.02.050 URL |
| [7] | Gao Z. R., Luo Y., Su K. X., Pan J. C., Xie X. Y., Gao Y. J., Chinese Journal of Practical Stomatology, 2018,11(6), 343— 346 |
| ( 高峥嵘, 罗银, 苏楷欣, 潘军臣, 谢小燕, 高义军 . 中国实用口腔科杂志, 2018,11(6), 343— 346) | |
| [8] |
Jonge M. J. A. D., Dumez H., Verweij J., Yarkoni S., Snyder D., Lacombe D., Marréaud S., Yamaguchi T., Punt C. J. A., van Oosterom A., Eur. J. Cancer, 2006,42(12), 1768— 1764
doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.12.027 URL |
| [9] | Guo Z. Y., Liang J. P., Wei X. B., Shang R. F., Guo W. Z., Wang X. H., Hao B. C., Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2013,33(7), 1083— 1085, 1118 |
| ( 郭志廷, 梁剑平, 韦旭斌, 尚若锋, 郭文柱, 王学红, 郝宝成 . 中国兽医学报, 2013,33(7), 1083— 1085, 1118) | |
| [10] | Jiang W. D., Acta Physiologica Sinica, 1961,24(3), 180— 186 |
| ( 江文德 . 生理学报, 1961,24(3), 180— 186) | |
| [11] | Nanjing University Of Chinese Medicine, Chinese Medicine Dictionary Volume Ⅱ(Second Edition), Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers, Shanghai, 2006, 2942— 2944 |
| ( 南京中医药大学. 中药大辞典下册(第2版), 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2006, 2942— 2944) | |
| [12] |
Assaf K. I., Nau W. M., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,44(2), 394— 418
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00273C URL |
| [13] |
Mandadapu V., Day A. I., Ghanem A., Chirality, 2014,26(11), 712— 723
doi: 10.1002/chir.22363 URL |
| [14] |
Day A. I. D., Blanch R. J. B., Arnold A. P., Lorenzo S., Lewis G. R., Dance I., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2010,41(2), 275— 277
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020118)41:2<275::AID-ANIE275>3.0.CO;2-M URL |
| [15] | Huang Y., Tao Z., Xue S. F., Zhu Q. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011,32(9), 2022— 2031 |
| ( 黄英, 陶朱, 薛赛凤, 祝黔江 . 高等学校化学学报, 2011,32(9), 2022— 2031) | |
| [16] |
Uzunova V. D., Cullinane C., Brix K., Nau W. M., Day A. I., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2010,8(9), 2037— 2042
doi: 10.1039/b925555a URL |
| [17] |
Chen H., Chan J. Y. W., Xue Y., Wyman I. W., Bardelang D., Macartney D. H., Lee S. M. Y., Wang R., RSC Advances, 2015,5(38), 30067— 30074
doi: 10.1039/C5RA04335B URL |
| [18] | Fu Y. Z., Shen X. C., Huang Y., Tao Z., Xue S. F., Zhu Q. J., Journal of Guizhou University(Natural Sciences), 2007,24(6), 650— 652 |
| ( 傅晓钟, 沈祥春, 黄英, 陶朱, 薛赛凤, 祝黔江 . 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2007,24(6), 650— 652) | |
| [19] | Du P., Zhang Y. P., Journal of Guiyang University of Chinese Medicine, 2016,38(6), 9— 11 |
| ( 杜鹏, 张永萍 . 贵阳中医学院学报, 2016,38(6), 9— 11) | |
| [20] | Jiang J., Huang Y. L., Zhang Q. L., Xu H., Sun X. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(1), 76— 82 |
| ( 蒋静, 黄亚励, 张奇龙, 徐红, 孙晓红 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(1), 76— 82) | |
| [21] |
Held B., Tang H., Natarajan P., Da S. C., De O. S. V., Bohne C., Quina F. H., Photochem. Photobiol. Sci., 2016,15(6), 832— 832
doi: 10.1039/C6PP90018F URL |
| [22] |
Basílio N., Petrov V., Pina F . ChemPlusChem, 2016,80(12), 1779— 1785
doi: 10.1002/cplu.201500304 URL |
| [23] | Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission, Chinese Pharmacopoeia, 2015, Section Two, China Medicai Science and Technology Press, Beijing, 2015,119 |
| ( 国家药典委员会. 中国药典 2015年版二部, 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2015,119) |
| [1] | 蒋静, 黄亚励, 张奇龙, 徐红, 孙晓红. 八元瓜环对氯化矢车菊素溶解性、稳定性及抗氧化性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 76. |
| [2] | 方超, 朱焓毓, 刘晔, 赵外欧, 李亚鹏, 王静媛. 过氧化氢敏感的靶向荧光载药纳米粒子的制备及在动脉粥样硬化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(9): 2071. |
| [3] | 叶慧, 刘亚博, 贾玉玺. 弱聚电解质水凝胶溶胀释药的数值模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(4): 817. |
| [4] | 练小卫, 黄净净, 陶朱, 周清娣, 张前军, 卫钢. 八元瓜环与乔松素的主客体作用及对乔松素性质的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(2): 226. |
| [5] | 杨梅, 刘青, 唐青, 王成会, 杨梅香, 孙涛, 黄英, 陶朱. 水溶性超分子荧光探针对多菌灵的识别及细胞成像[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(12): 2665. |
| [6] | 黄净净, 许志玲, 练小卫, 张晓东, 陶朱, 周清娣, 张前军, 卫钢. 八元瓜环与黄岑苷的主客体相互作用及对黄岑苷性质的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2425. |
| [7] | 张海鹏, 韩冰, 贾致真, 丁荣波, 徐斌, 徐蔚青, 范志民. 载药荧光纳米粒子的制备及在乳腺癌MCF-7细胞系的应用及效果评价[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(5): 860. |
| [8] | 王晓丹, 徐丹丹, 吕维忠, 刘婧媛, 刘琦, 景晓燕, 王君. 抗癌载药体系Fe3O4@ZIF-8@PA的合成及药物释放[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(11): 1927. |
| [9] | 朱寿进, 刘法谦, 王璟朝, 宿烽, 李速明. 新型羧甲基壳聚糖水凝胶的合成与表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(4): 863. |
| [10] | 郝和群, 姚萍. 葡聚糖分子量和接枝度对阿霉素/白蛋白-葡聚糖纳米粒子体外抗肿瘤效果的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(3): 652. |
| [11] | 易平贵, 阳习春, 于贤勇, 刘峥军, 刘金, 汪朝旭, 李筱芳. 八元瓜环超分子作用下2-(2-氨基-3-吡啶基)苯并咪唑的质子转移[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(12): 2657. |
| [12] | 张同艳, 孙世国, 彭孝军, 陶彬彬. 紫精与八元瓜环的超分子组装及光切割质粒DNA[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(02): 292. |
| [13] | 张静哲, 李冬冬, 刘桂锋, 吴琼, 王金成. 新型介孔羟基磷灰石/壳聚糖-万古霉素药物释放系统复合材料的制备及体外抗菌和成骨能力[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(02): 219. |
| [14] | 魏雨, 纪璎, 计剑. REDV/雷帕霉素复合涂层构建内皮细胞选择性功能界面[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(01): 193. |
| [15] | 刘源岗, 毛鸿浩, 王士斌, 孙学战. 栓塞型新型微包纳药物控释载体的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(11): 2574. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||