

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 284.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190496
收稿日期:2019-09-19
出版日期:2020-02-10
发布日期:2019-10-29
通讯作者:
肖杨
E-mail:xiaoyang@scuec.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Bowen,WANG Ruoheng,LI Li,XIAO Yang( )
)
Received:2019-09-19
Online:2020-02-10
Published:2019-10-29
Contact:
Yang XIAO
E-mail:xiaoyang@scuec.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用生物质木质素磺酸钠(SLS)为碳源, 先与硬模板NaCl混合预碳化, 再加入活化剂NaOH在氮气保护下升温至850 ℃碳化, 得到SLS基碱活化的多孔碳吸附剂(SPCN). 将SPCN用于吸附液体石蜡中芳香烃甲苯, 对比研究了不同活化剂加入量对SPCN结构、 性质及吸附效果的影响. 结果表明, SPCN表面具有丰富的官能团和发达的微/介孔结构, 活化剂加入量对比表面积的影响为先增大后减小, 碱/碳质量比为1∶1时比表面积达到最大值(710.4 m 2/g); 吸附量与比表面积呈正相关, 样品SPCN-1的最大吸附量为2875.17 mg/g, 远高于商业吸附剂, 经5次吸附-解吸循环后仍保持92.5%的吸附效率. 探究了活化机理, NaOH、 碳质和气体发生氧化还原反应释放气体留下孔隙, 经充分酸洗、 水洗后得到永久孔道. 最后, 结合扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、 透射电子显微镜(TEM)、 拉曼光谱(Raman)、 X射线衍射(XRD)、 傅里叶变换红外光谱(FTIR)和比表面积分析等结果证明了吸附机理主要是孔隙填充效应、 范德华力、 π-π相互作用及电子供/受体作用的共同作用. 首次报道了SPCN应用的新方向并探究了活化与吸附机理, 制备方法简易、 经济, 产品循环稳定性好、 无污染, 有望用于工业化生产.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李博文,汪若蘅,黎丽,肖杨. 碱活化多孔碳用于分离甲苯及活化/吸附机理. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 284.
LI Bowen,WANG Ruoheng,LI Li,XIAO Yang. Adsorption of Toluene by Alkali Activated Porous Carbons and Activation/Adsorption Mechanism †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 284.
| Sample | Microporosity(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPCN-0 | 316.17 | 0.273 | 0.127 | 46.52 | 3.453 |
| SPCN-1 | 710.44 | 0.564 | 0.256 | 45.39 | 3.175 |
| SPCN-2 | 664.70 | 0.536 | 0.225 | 41.92 | 3.635 |
| SPCN-3 | 625.23 | 0.438 | 0.193 | 44.09 | 3.854 |
| SPCN-4 | 518.29 | 0.442 | 0.208 | 47.06 | 3.412 |
Table 1 Textural parameters of SPCN materials
| Sample | Microporosity(%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPCN-0 | 316.17 | 0.273 | 0.127 | 46.52 | 3.453 |
| SPCN-1 | 710.44 | 0.564 | 0.256 | 45.39 | 3.175 |
| SPCN-2 | 664.70 | 0.536 | 0.225 | 41.92 | 3.635 |
| SPCN-3 | 625.23 | 0.438 | 0.193 | 44.09 | 3.854 |
| SPCN-4 | 518.29 | 0.442 | 0.208 | 47.06 | 3.412 |
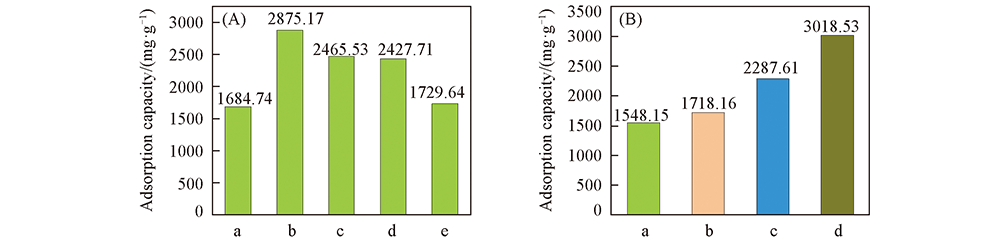
Fig.5 Toluene adsorption capacity of samples and adsorption capacity of SPCN-1 compared to silica gel, 10X molecular sieve and activated carbon particles (A) a. SPCN-0; b. SPCN-1; c. SPCN-2; d. SPCN-3; e. SPCN-4. (B) a. Molecular sieve; b. silica gel; c. activated carbon; d. SPCN-1.
| [1] | Moret S., Scolaro M., Barp L., Purcaro G., Sander M., Conte L. S., Food Chem., 2014,157, 470— 475 |
| [2] | Urlaub J., Norwig J., Schollmayer C., Holzgrabe U ., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal., 2019,169, 41— 48 |
| [3] | Nash J. F., Gettings S. D., Diembeck W., Chudowski M., Kraus A. L., Food Chem. Toxicol., 1996,34(2), 213— 225 |
| [4] | Wagner M., Oellig C ., J. Chromatogr. A, 2019,1588, 48— 57 |
| [5] | Rawlings A. V., Lombard K. J., Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 2012,34(6), 511— 518 |
| [6] | Kimber I., Carrillo J. C ., Toxicology, 2016, 344—346, 19— 25 |
| [7] | Biles R. W., Mckee R. H., Lewis S. C., Scala R. A., DePass L. R., Toxicology, 1988,53, 301— 314 |
| [8] |
Mackerer C. R., Griffis L. C., Grabowski J. S. Jr., Reitman F. A., Appl. Occup. Environ. Hyg., 2003,18(11), 890— 901
doi: 10.1080/10473220390237467 URL |
| [9] |
Garcia-Cicourel A. R., Janssen H. G., J. Chromatogr. A, 2019,1590, 113— 120
doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2019.01.015 URL |
| [10] |
Zhou X., Qiu S. L., Liu L. X., Xing W. Y., He L. X., Hou Y. B., Fang M. Q., Gui Z., Song L., Hu Y., Composites Part B, 2019,167, 599— 607
doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.03.019 URL |
| [11] |
Petry T., Bury D., Fautz R., Hauser M., Huber B., Markowetz A., Mishra S., Rettinger K., Schuh W., Teichert T., Toxicol. Lett., 2017,280, 70— 78
doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.07.899 URL |
| [12] |
Tennant D. R., Food Chem. Toxicol., 2004,42(3), 481— 492
doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2003.10.011 URL |
| [13] | Nussbaum M. L., Knaggs E. A ., Process for Sulfonation, US 4148821, 1979-04-10 |
| [14] | Joseph M., Dibijak J., Griffith I ., Production of Technical White Mineral Oil, US 3629096, 1971-12-21 |
| [15] | Rausch M. K., , Making a White Oil by Two Stage of Catalytic Hydrogenation, US 3459656A 1969-08-05 |
| [16] |
Nugent P., Belmabkhout Y., Burd S. D., Cairns A. J., Luebke R., Forrest K., Pham T., Ma S., Space B., Wojtas L., Eddaoudi M., Zaworotko M. J., Nature, 2013,495(7439), 80— 84
doi: 10.1038/nature11893 URL |
| [17] |
Woellner M., Hausdorf S., Klein N., Mueller P., Smith M. W., Kaskel S., Adv. Mater., 2018,30(37), 1704679
doi: 10.1002/adma.v30.37 URL |
| [18] |
Yagub M. T., Sen T. K., Afroze S., Ang H. M., Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2014,209, 172— 184
doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2014.04.002 URL |
| [19] |
Ma S., Sun D., Yuan D., Wang X. S., Zhou H. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009,131(18), 6445— 6451
doi: 10.1021/ja808896f URL |
| [20] |
Kresge C. T., Roth W. J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013,42(9), 3663— 3670
doi: 10.1039/c3cs60016e URL |
| [21] |
Wurzbacher J. A., Gebald C., Steinfeld A., Energy Environ. Sci., 2011,4(9), 3584— 3592
doi: 10.1039/c1ee01681d URL |
| [22] |
Chen J., Qu R., Zhang Y., Sun C., Wang C., Ji C., Yin P., Chen H., Niu Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2012,209, 235— 244
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.08.030 URL |
| [23] |
Zou H., Wu S., Shen J., Chem. Rev., 2008,108(9), 3893— 3957
doi: 10.1021/cr068035q URL |
| [24] |
Tanhaei B., Ayati A., Lahtinen M., Sillanpää M., Chem. Eng. J., 2015,259, 1— 10
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2014.07.109 URL |
| [25] |
Cai W., Yu J., Jaroniec M ., J. Mater. Chem., 2010,20(22), 4587— 4594
doi: 10.1039/b924366f URL |
| [26] |
Hamon L., Llewellyn P. L., Devic T., Ghoufi A., Clet G., Guillerm V., Pirngruber G. D., Maurin G., Serre C., Driver G., van Beek W., Jolimaitre E., Vimont A., Daturi M., Ferey G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009,131(47), 17490— 17499
doi: 10.1021/ja907556q URL |
| [27] |
An J., Rosi N. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010,132(16), 5578— 5579
doi: 10.1021/ja1012992 URL |
| [28] |
Xue D. X., Belmabkhout Y., Shekhah O., Jiang H., Adil K., Cairns A. J., Eddaoudi M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015,137(15), 5034— 5040
doi: 10.1021/ja5131403 URL |
| [29] | Suo L. L., Juan S., Tao L., Zhang L., Zhang X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016,37(11), 2043— 2049 |
| ( 索路路, 李生娟, 李应涛, 张莉, 张熙 . 高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(11), 2043— 2049) | |
| [30] |
He X., Male K. B., Nesterenko P. N., Brabazon D., Paull B., Luong J. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013,5(17), 8796— 8804
doi: 10.1021/am403222u URL |
| [31] |
Wickramaratne N. P., Xu J., Wang M., Zhu L., Dai L., Jaroniec M., Chem. Mater., 2014,26(9), 2820— 2828
doi: 10.1021/cm5001895 URL |
| [32] |
Zhu X., Liu Y., Zhou C., Luo G., Zhang S., Chen J ., Carbon, 2014,77, 627— 636
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.067 URL |
| [33] |
Siyasukh A., Chimupala Y., Tonanon N ., Carbon, 2018,134, 207— 221
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.03.093 URL |
| [34] |
Lee J., Kim J., Hyeon T., Adv. Mater., 2006,18(16), 2073— 2094
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-4095 URL |
| [35] |
Liang C., Li Z., Dai S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008,47(20), 3696— 3717
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3773 URL |
| [36] |
Stein A., Wang Z., Fierke M. A., Adv. Mater., 2009,21(3), 265— 293
doi: 10.1002/adma.v21:3 URL |
| [37] |
Sevilla M., Valle-Vigón P., Fuertes A. B., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2011,21(14), 2781— 2787
doi: 10.1002/adfm.201100291 URL |
| [38] |
Dutta S., Bhaumik A., Wu K. C. W., Energy Environ. Sci., 2014,7(11), 3574— 3592
doi: 10.1039/C4EE01075B URL |
| [39] |
Luna F. M. T., Pontes-Filho A. A., Trindade E. D., Silva I. J., Azevedo D. C. S., Cavalcante C. L., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2008,47(9), 3207— 3212
doi: 10.1021/ie071476v URL |
| [40] |
Milczarek G., Inganas O ., Science, 2012,335(6075), 1468— 1471
doi: 10.1126/science.1215159 URL |
| [41] |
Xie A., Dai J., Chen X., Ma P., He J., Li C., Zhou Z., Yan Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2016,304, 609— 620
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.06.138 URL |
| [42] |
Saito T., Brown R. H., Hunt M. A., Pickel D. L., Pickel J. M., Messman J. M., Baker F. S., Keller M., Naskar A. K., Green Chem., 2012,14(12), 3295— 3303
doi: 10.1039/c2gc35933b URL |
| [43] |
Lillo-Ródenas M. A., Lozano-Castelló D., Cazorla-Amorós D., Linares-Solano A., Carbon, 2001,39, 751— 759
doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(00)00186-X URL |
| [44] |
Lillo-Ródenas M. A., Juan-Juan J., Cazorla-Amorós D., Linares-Solano A., Carbon, 2004,42(7), 1371— 1375
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.01.008 URL |
| [45] |
Lillo-Ródenas M. A., Cazorla-Amorós D., Linares-Solano A., Carbon, 2003,41, 267— 275
doi: 10.1016/S0008-6223(02)00279-8 URL |
| [46] |
Raymundo-Piñero E., Azaïs P., Cacciaguerra T., Cazorla-Amorós D., Linares-Solano A., Béguin F ., Carbon, 2005,43(4), 786— 795
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2004.11.005 URL |
| [47] |
Foo K. Y., Hameed B. H., Chem. Eng. J., 2012,187, 53— 62
doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.01.079 URL |
| [48] | Chen H., Wang H., Xue Z., Yang L., Xiao Y., Zheng M., Lei B., Liu Y., Sun L., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2012,37(24), 18888— 18894 |
| [49] | Byamba-Ochir N., Shim W. G., Balathanigaimani M. S., Moon H., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016,379, 331— 337 |
| [50] | Yamashita Y., Ouchi K ., Carbon, 1982,20(1), 41— 45 |
| [51] | Yamashita Y., Ouchi K ., Carbon, 1982,20(1), 47— 53 |
| [52] | Su F., Poh C. K., Chen J. S., Xu G., Wang D., Li Q., Lin J., Lou X. W., Energy Environ. Sci., 2011,4(3), 717— 724 |
| [53] | Qie L., Chen W. M., Wang Z. H., Shao Q. G., Li X., Yuan L. X., Hu X. L., Zhang W. X., Huang Y. H., Adv. Mater., 2012,24(15), 2047— 2050 |
| [54] | Chen Z., Ma L., Li S., Geng J., Song Q., Liu J., Wang C., Wang H., Li J., Qin Z., Li S., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2011,257(20), 8686— 8691 |
| [55] | Milczarek G ., Langmuir, 2009,25(17), 10345— 10353 |
| [56] |
Li X., Chen S., Fan X., Quan X., Tan F., Zhang Y., Gao J ., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015,447, 120— 127
doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.01.042 URL |
| [57] |
Si Y., Ren T., Li Y., Ding B., Yu J ., Carbon, 2012,50(14), 5176— 5185
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.06.059 URL |
| [58] | Thomas W. J., Crittenden B., Adsorption Technology and Design, Butterworth-Heinemann Oxford, 1998, 66—86, 146— 162 |
| [59] |
Yuan M., Tong S., Zhao S., Jia C. Q., J. Hazard. Mater., 2010,181(1—3), 1115— 1120
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.130 URL |
| [60] |
Cardoso N. F., Pinto R. B., Lima E. C., Calvete T., Amavisca C. V., Royer B., Cunha M. L., Fernandes T. H. M., Pinto I. S., Desalination, 2011,269(1—3), 92— 103
doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2010.10.047 URL |
| [61] |
Chang B., Guan D., Tian Y., Yang Z., Dong X ., J. Hazard. Mater., 2013,262(15), 256— 264
doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2013.08.054 URL |
| [62] | Polanyi M., Verh. Deutsch. Phys . Ges., 1914,16, 1012 |
| [63] |
Manes M., Hofer L. J. E., J. Phys. Chem., 1969,73(3), 584— 590
doi: 10.1021/j100723a018 URL |
| [64] |
Ji L., Wan Y., Zheng S., Zhu D., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2011,45(13), 5580— 5586
doi: 10.1021/es200483b URL |
| [65] |
Ji L., Chen W., Duan L., Zhu D., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2009,43(7), 2322— 2327
doi: 10.1021/es803268b URL |
| [66] |
Bernal V., Giraldo L., Moreno-Pirajan J. C., Balsamo M., Erto A., Molecules, 2019,24(3), 413— 433
doi: 10.3390/molecules24030413 URL |
| [67] |
McGaughey G. B., Gagné M., Rappé A. K., J. Biol. Chem., 1998,273(25), 15458— 15463
doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.25.15458 URL |
| [68] |
Sinnokrot M. O., Valeev E. F., Sherrill C. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2002,124(36), 10887— 10893
doi: 10.1021/ja025896h URL |
| [69] |
Moreno-Castilla C ., Carbon, 2004,42(1), 83— 94
doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2003.09.022 URL |
| [70] |
Mattson J. S., Mark H. B., J. R., Malbin M. D., Weber W. J., Crittenden J. C., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 1969,31(1), 116— 130
doi: 10.1016/0021-9797(69)90089-7 URL |
| [1] | 罗昪, 周芬, 潘牧. 层级多孔碳载铂催化剂的制备及可达性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [2] | 方基永, 姜振华, 岳喜贵. 聚芳醚酮基复合吸波材料的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1994. |
| [3] | 李敏, 赵纯, 冯钦忠, 冯建, 孟晓静. 硫脲基纳米螯合纤维对水溶液中Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附和密度泛函理论计算[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(12): 3680. |
| [4] | 李晨光, 花儿, 刘天霞. 异辛基乙二胺-CF3SO3型质子化离子液体作为液体石蜡添加剂的摩擦学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(7): 1411. |
| [5] | 王秀利, 何兴权. 氮/硫双掺多孔碳负载Fe9S10纳米粒子的氧还原电催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(7): 1524. |
| [6] | 张保海, 罗民, 杨顺, 付蓉蓉, 马金福. 用金属生物大分子配合物前驱体制备多孔碳球及其电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(2): 310. |
| [7] | 栾敬德, 刘亚伟, 张成玉, 可欣. 蒙脱石复合材料对Zn2+和对硝基苯酚的同步捕集[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(2): 270. |
| [8] | 王小兵, 石秀仪, 周星均, 丘秀珍, 卢文贯. 金属-有机骨架材料NH2-MIL-53(Al)对水中双氯芬酸钠的吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(2): 206. |
| [9] | 李常青, 杨东杰, 席跃宾, 秦延林, 邱学青. 二氧化硅/木质素多孔碳复合材料的制备及作为锂离子电池负极材料的性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(12): 2725. |
| [10] | 韩雪, 邹博, 顾小雪, 庞丽云, 曹礼媛, 刘琦, 郭玉鹏. 糖蜜基多孔碳球电极材料的制备及应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6): 1135. |
| [11] | 严山, 张胜建, 赵迎宪, 李显明, 张永明, 张洪, 王健, 符建琼. TMPDO和4-NOH-TMPD在HTS/H2O2催化体系中的吸附机理及对Ti—OOH的稳定作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(5): 946. |
| [12] | 索路路, 李生娟, 李应涛, 张莉, 张熙. 三维全碳多孔结构对亚甲基蓝吸附性能的动力学探究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(11): 2043. |
| [13] | 李娃, 李凤云, 史志胜, 黄珏, 蔡强, 张伟. 毫米级轻质高强度多孔二氧化硅球的制备与表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(9): 1655. |
| [14] | 孟宪斌, 高秋明. 由含铝金属有机骨架材料制备的多孔碳在锂硫电池中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(8): 1715. |
| [15] | 肖小雨, 盛光遥, 邱宇平. 海水体系中黑碳吸附三丁基锡的行为与机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(1): 84. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||