

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 20240274.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240274
收稿日期:2024-06-06
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-08-12
通讯作者:
姚栋
E-mail:dongyao@jlu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Binxi, ZHANG Yan, YAO Dong( )
)
Received:2024-06-06
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-08-12
Contact:
YAO Dong
E-mail:dongyao@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
在诊疗一体化大背景下, 通过设计新颖的纳米材料以实现多模式成像备受关注. 其中, 磁共振和荧光成像是临床常用的成像手段, 将这两种成像方法结合起来实现双模式成像, 可为疾病诊断提供更大便利. 本文采用微乳液模板法将具有T2磁共振成像功能的Fe3O4纳米粒子与具有荧光成像功能的CuInS2纳米粒子共组装, 制备了Fe3O4/CuInS2二元超粒子. 使用生物相容性良好的聚乙二醇-聚乳酸-羟基乙酸嵌段共聚物对二元超粒子进行修饰, 提高了其生物安全性. 该二元超粒子除具有双模式成像功能外, 引入的Fe3O4纳米粒子还赋予其光热治疗潜力, 并可以作为载体负载紫杉醇等药物, 为实现成像引导下的肿瘤联合治疗提供了机会.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李滨汐, 张燕, 姚栋. 具有磁共振/荧光双模式成像功能的Fe3O4/CuInS2二元超粒子. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(1): 20240274.
LI Binxi, ZHANG Yan, YAO Dong. Fe3O4/CuInS2 Binary Superparticles for Magnetic Resonance/Fluorescence Dual Mode Imaging. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(1): 20240274.
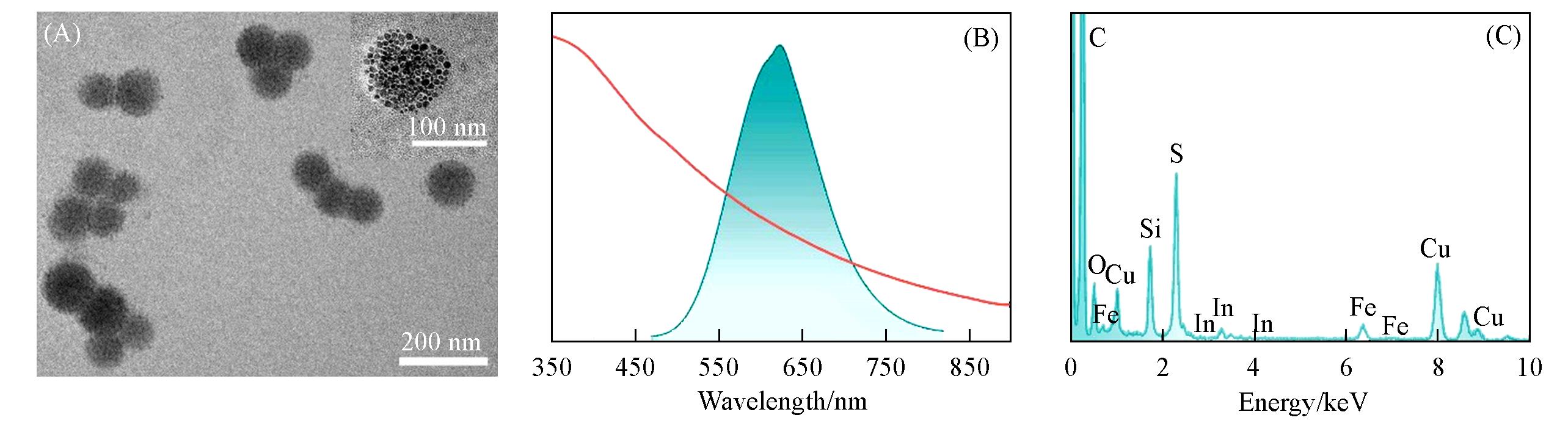
Fig.1 TEM image of Fe3O4/CuInS2 binary SPs(A), UV⁃Vis absorption and PL emission spectra of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs(λex=450 nm)(B), and EDS spectrum of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs(C)Inset of (A): high magnification TEM image of one SP.
| Feed mass ratio | 1∶1 | 1∶2 | 1∶3 | 1∶4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual mass ratio | 1∶0.17 | 1∶0.69 | 1∶1.1 | 1∶5.9 |
Table 1 Actual Fe3O4-to-CuInS2 mass ratios in Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs versus Fe3O4-to-CuInS2 feed mass ratios
| Feed mass ratio | 1∶1 | 1∶2 | 1∶3 | 1∶4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual mass ratio | 1∶0.17 | 1∶0.69 | 1∶1.1 | 1∶5.9 |
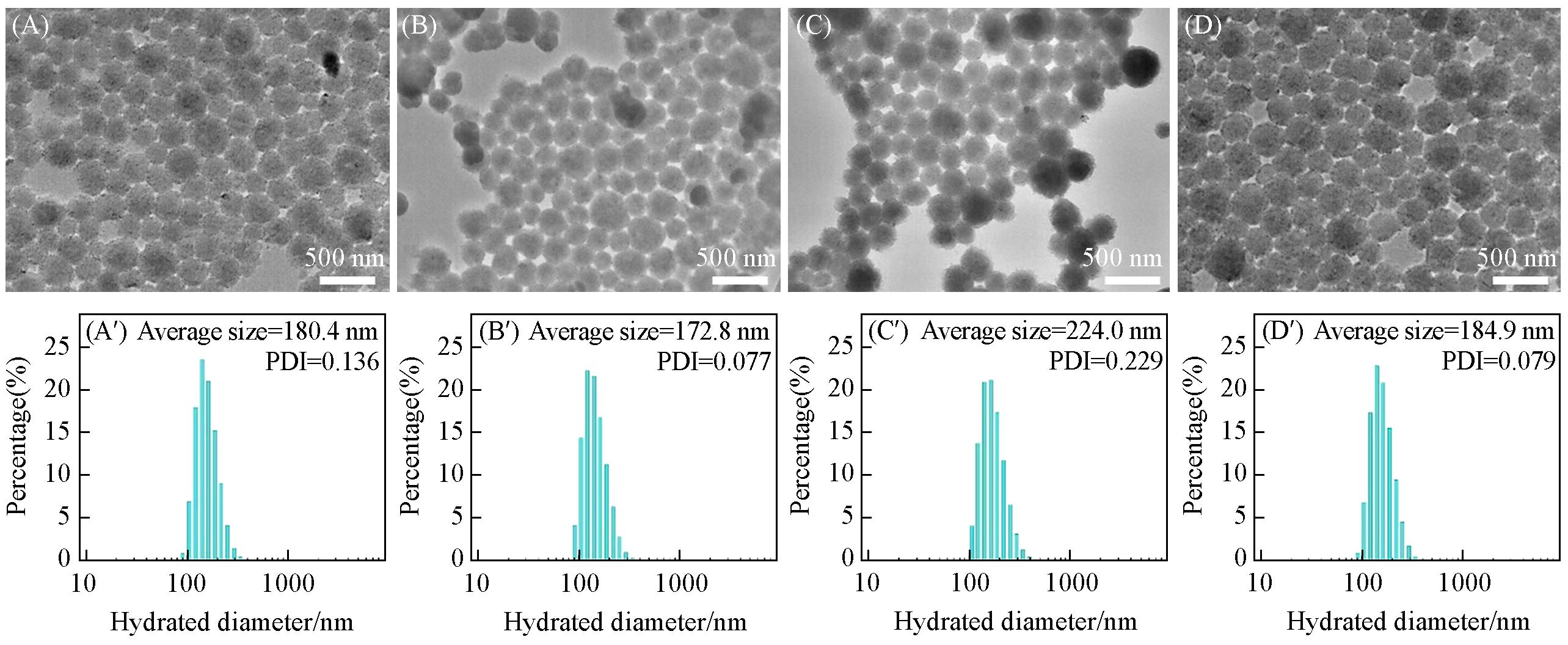
Fig.2 TEM images of Fe3O4/CuInS2 binary SPs prepared with Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed mass ratio of 1∶1(A), 1∶2(B), 1∶3(C) and 1∶4(D), and relative DLS size distributions(A′—D′)
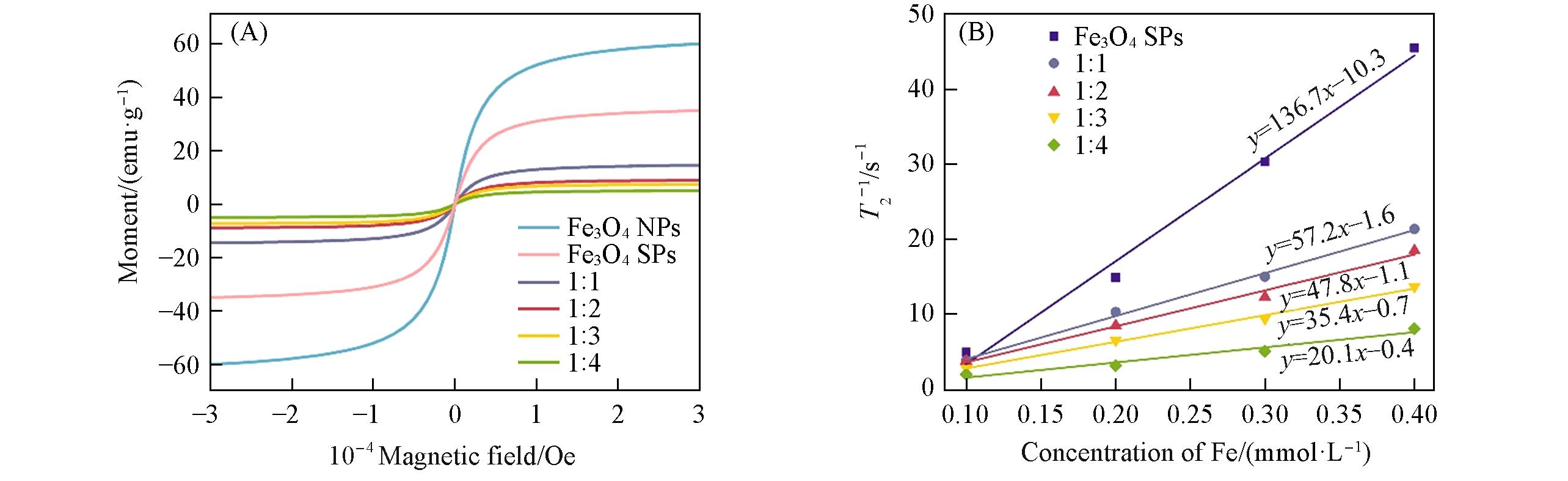
Fig.3 Magnetic hysteresis curves of Fe3O4 NPs, Fe3O4 SPs and Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs with different Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed ratios at 300 K(A) and T2 relaxation rate(r2) of Fe3O4 SPs and the Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs with different Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed ratios(B)1 emu/g=1 A·m2·kg-1.
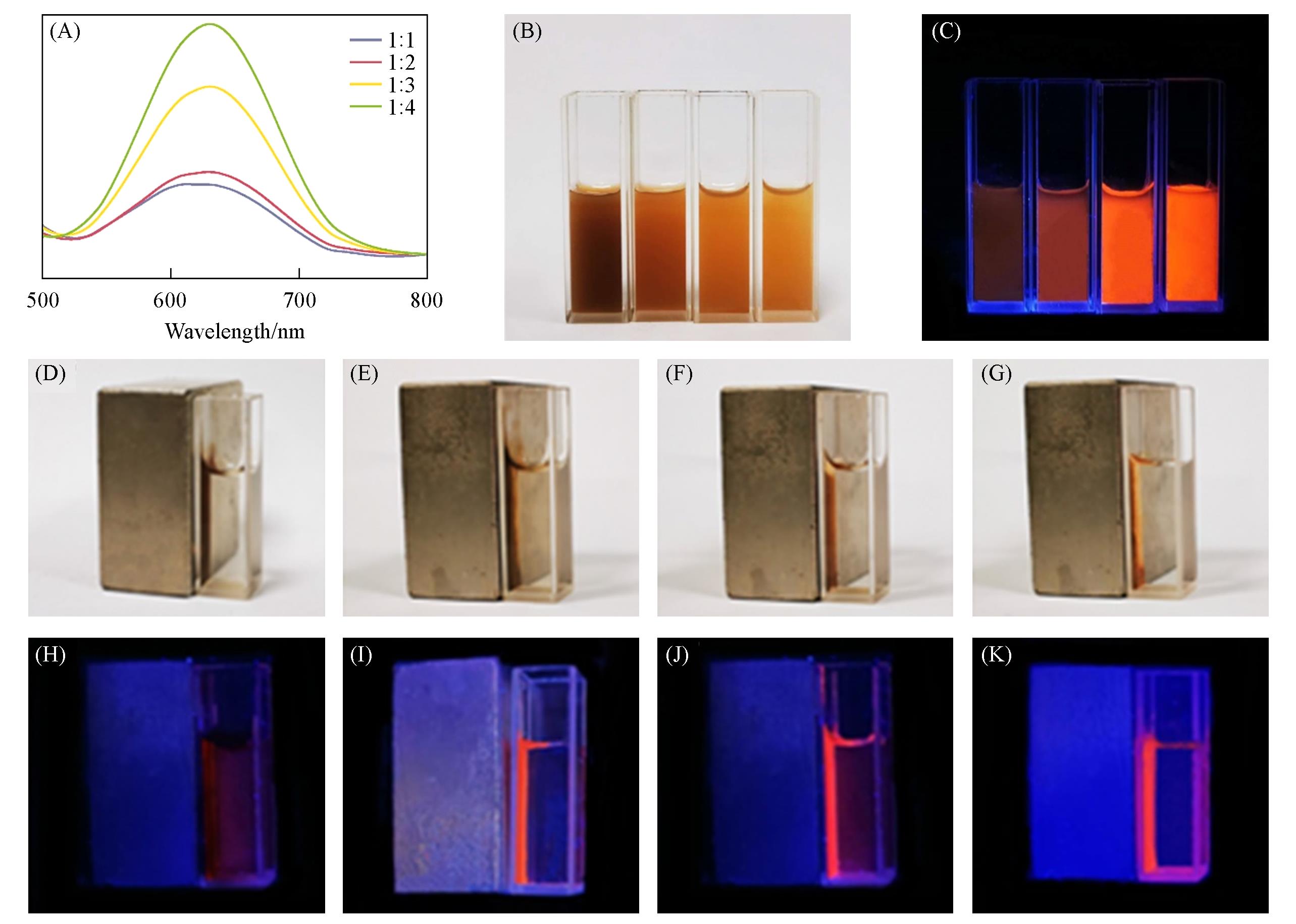
Fig.4 PL emission spectra of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs with different Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed ratios(λex=450 nm)(A), optical photograph(B) and luminescent photograph(C) of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs with different Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed ratios(from left to right∶ 1∶1, 1∶2, 1∶3 and 1∶4), optical photographs(D—G) and luminescent photographs(H—K) of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs with Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed ratios of 1∶1, 1∶2, 1∶3 and 1∶4, respectively, with a magnet
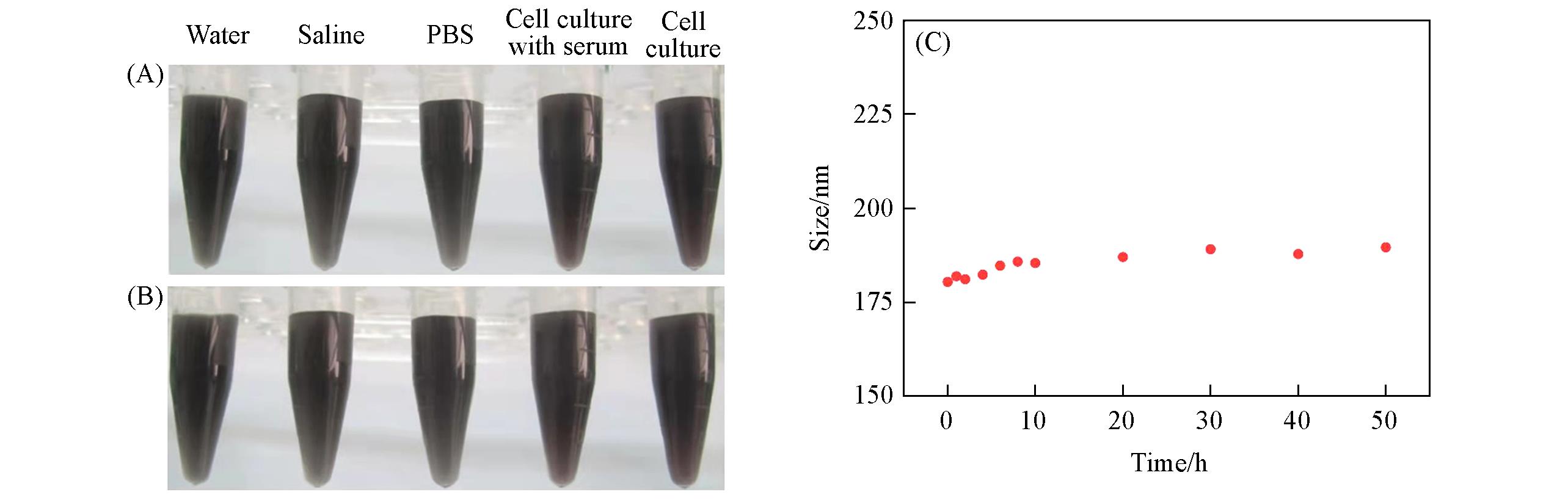
Fig.5 Photographs of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs in water, saline, PBS, and cell culture medium with and without 10% serum tested at 0 h(A) and 48 h(B), DLS size variation of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs measured by incubating in cell culture medium with 10% serum for 50 h(C)The Fe3O4-to-CuInS2 feed ratio is 1∶3.
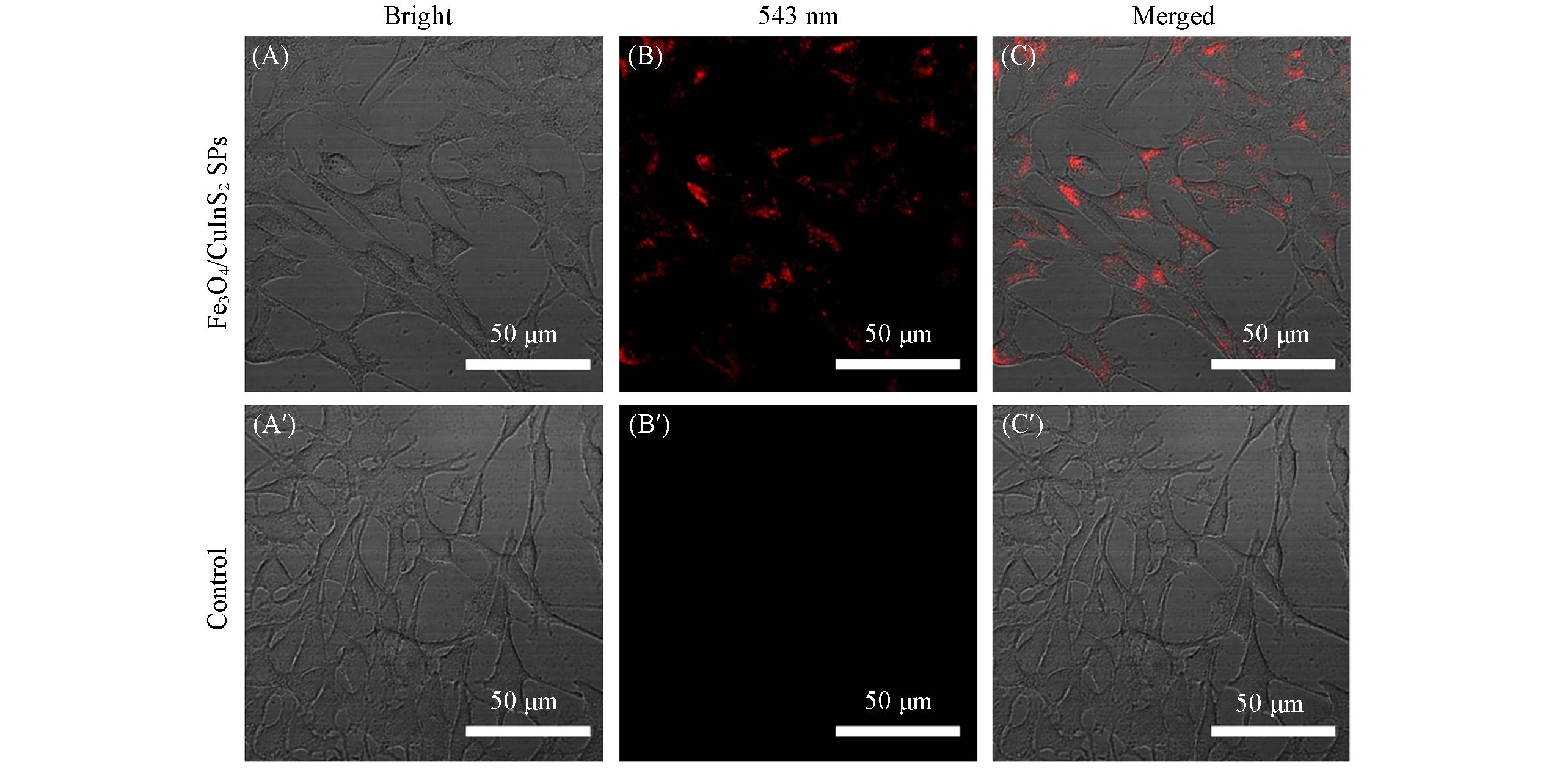
Fig.7 Optical(A, A′), fluorescent(B, B′) and merged(C, C′) images of 4T1 cells after incubation with and without Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs for 24 hThe excitation wavelength is 543 nm; the emission collection range is 570—670 nm.
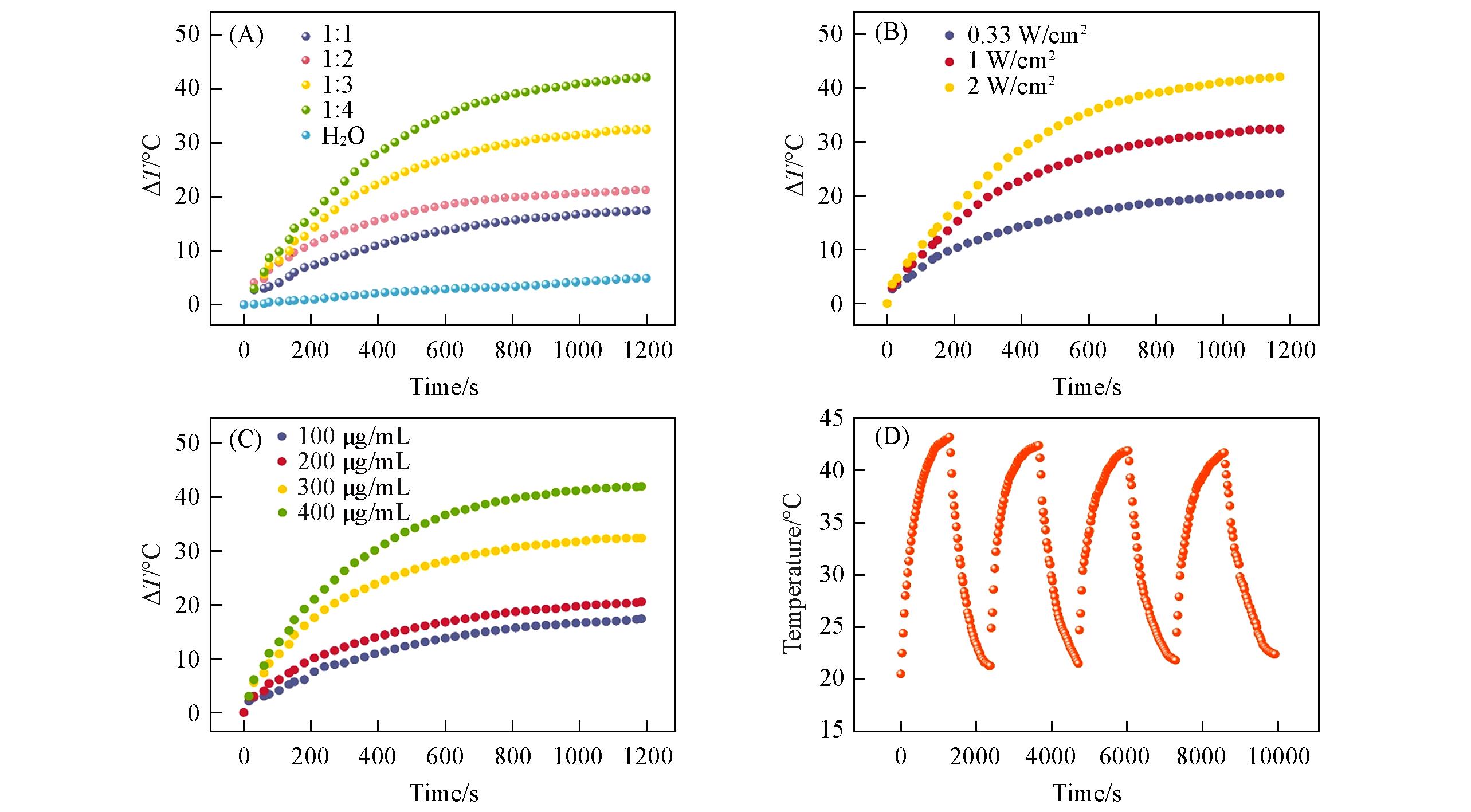
Fig.8 Temperature increment of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs with different Fe3O4⁃to⁃CuInS2 feed ratios(A), temperature increment of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs versus the power of 808 nm laser(B), temperature increment of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs versus concentrations of SPs(C) and real⁃time temperature records of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs solution for 4 heating up and cooling down cycles(D)(B) The Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs solution with the concentration of 200 μg/mL is irradiated by 0.33 W/cm2 808 nm laser; (C) the concentration of Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs solution is 200 μg/mL, the Fe3O4-to-CuInS2 feed ratio of the Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs is 1∶3, the power of 808 nm laser is fixed at 0.33 W/cm2 and the Fe3O4-to-CuInS2 feed ratio of the Fe3O4/CuInS2 SPs is 1∶3.
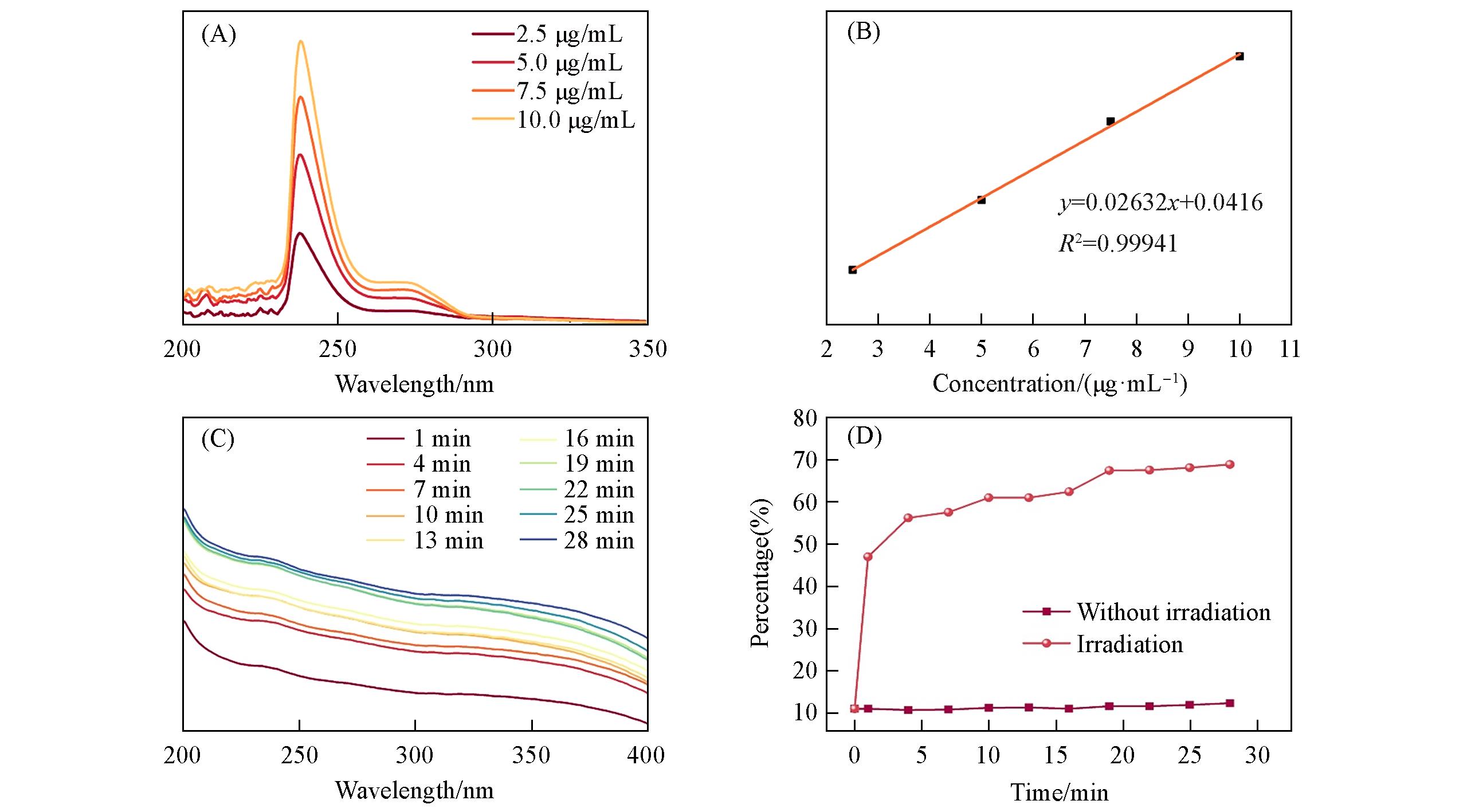
Fig.9 UV⁃Vis absorption spectra of PTX with different concentrations(A), the standard absorption curve of PTX according to the absorbance at 238 nm(B), the release of PTX from Fe3O4/CuInS2/PTX SPs under 808 nm laser irradiation monitored by UV⁃Vis absorption spectra(C) and the released percentage of PTX from Fe3O4/CuInS2/PTX SPs versus the duration of 808 nm laser irradiation(D)
| 1 | Xie J., Lee S., Chen X. Y., Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 2010, 62(11), 1064—1079 |
| 2 | He X. H., Shen X., Li D. M., Liu Y. Y., Jia K., Liu X. B., ACS Appl. Bio. Mater., 2018, 1(2), 520—528 |
| 3 | Banerjee A., Bertolesi G. E., Ling C. C., Blasiak B., Purchase A., Calderon O., Tomanek B., Trudel S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(14), 13069—13078 |
| 4 | Li H. M., Liu Y., Huang B., Zhang C. J, Wang Z. C., She W. Y., Liu Y., Jiang P., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(29), 10470—10478 |
| 5 | Yao Y., Li N., Zhang X., Machuki J. O., Yang D. Z., Yu Y. Y., Li J. J., Tang D. Q., Tian J. W., Gao F. L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(15), 13991—14003 |
| 6 | Choi K. Y., Liu G., Lee S., Chen X. Y., Nanoscale, 2012, 4(2), 330—342 |
| 7 | Sumer B., Gao J. M., Nanomedicine, 2008, 3(2), 137—140 |
| 8 | Cai Y., Chen X. Y., Si J. X., Mou X. Z., Dong X. C., Small, 2021, 17(52), 2103072 |
| 9 | Kunjachan S., Ehling J., Storm G., Kiessling F., Lammers T., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(19), 10907—10937 |
| 10 | Dasgupta A., Biancacci I., Kiessling F., Lammers T., Theranostics, 2020, 10(3), 956—967 |
| 11 | Jokerst J. V., Gambhir S. S., Acc. Chem. Res., 2011, 44(10), 1050—1060 |
| 12 | Hartwig V., Giovannetti G., Vanello N., Lombardi M., Landini L., Simi S., Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health, 2009, 6(6), 1778—1798 |
| 13 | Thangudu S., Huang E. Y., Su C. H., Biomater. Sci., 2022, 10(18), 5032—5053 |
| 14 | Brito B., Price T. W., Gallo J., Bañobre-López M., Stasiuk G. J., Theranostics, 2021, 11(18), 8706—8737 |
| 15 | Chang T. H., Cheng Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12), 20220430 |
| 常通航, 程震. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12), 20220430 | |
| 16 | Wang L. C., Li N., Wang W. L., Mei A. Q., Shao J. J., Wang W. J., Dong X. C., ACS Nano, 2024, 18(6), 4683—4703 |
| 17 | Etrych T., Lucas H., Janoušková O., Chytil P., Mueller T., Mäder K., J. Control. Release, 2016, 226, 168—181 |
| 18 | Zhu S. J., Tian R., Antaris A. L., Chen X. Y., Dai H. J., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(24), 1900321 |
| 19 | Seah D., Cheng Z. M., Vendrell M., ACS Nano, 2023, 17(20), 19478—19490 |
| 20 | Han X. J., Xu K., Taratula O., Farsad K., Nanoscale, 2019, 11(3), 799—819 |
| 21 | Liu L. W., Hu R., Law W. C., Roy I., Zhu J., Ye L., Hu S. Y., Zhang X. H., Yong K. T., Analyst, 2013, 138(20), 6144—6153 |
| 22 | Meng X. D., Pang X. J., Zhang K., Gong C. C., Yang J. Y., Dong H. F., Zhang X. J., Small, 2022, 18(31), 2202035 |
| 23 | Zhang X., Han J. S., Yao T. J., Wu J., Zhang H., Zhang H., Zhang X. D., Yang B., CrystEngComm, 2011, 13(19), 5674—5676 |
| 24 | Wang Z., Zhang X. Y., Xin W., Yao D., Liu Y., Zhang L. N., Liu W. Y., Zhang W., Zheng W. T., Yang B., Zhang H., Chem. Mater., 2018, 30(24), 8939—8947 |
| 25 | Mo J. T., Da X. B., Li Q. X., Huang J. J., Lu L., Lu H. W., J. Oncol., 2022, 2022(1), 4234116 |
| 26 | Hu X. M., Tang Y. F., Hu Y. X., Lu F., Lu X. M., Wang Y. Q., Li J., Li Y. Y., Ji Y., Wang W. J., Ye D. J., Fan Q. L., Huang W., Theranostics, 2019, 9(14), 4168—4181 |
| 27 | Dong Y. S., Dong S. M., Wang Z., Feng L. L., Sun Q. Q., Chen G. Y., He F., Liu S. K., Li W. T., Yang P. P., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(47), 52479—52491 |
| 28 | Wei W. F., Zhang X. Y., Zhang S., Wei G., Su Z. Q., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2019, 104, 109891 |
| 29 | Wang Y. K., Li W. J., Lin B., Yuan Y., Ning P. B., Tao X. F., Lv R. C., Biomater. Sci., 2023, 11(15), 5177—5185 |
| 30 | Duan S. F., Hu Y. L., Zhao Y., Tang K. Y., Zhang Z. J., Liu Z. L., Wang Y., Guo H. Y., Miao Y. C., Du H. D., Yang D. L., Li S. K., Zhang J. J., RSC. Adv., 2023, 13(21), 14443—14460 |
| 31 | Cai W., Fan G. H., Zhou H., Chen L., Ge J. X., Huang B. X., Zhou D. D., Zeng J. F., Miao Q. Q., Hu C. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(44), 49407—49415 |
| [1] | 朱宣祺, 崔丽影, 赵欣宇, 姜玲, 张雪. Fe3+掺杂的聚氨基吡咯纳米粒子用于原位乳腺癌的磁共振成像和光热治疗[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(1): 20240156. |
| [2] | 孙菁华, 郭春燕, 董杰, 张瑞平. 黑色素基靶向纳米药物用于乳腺癌的光热治疗[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230044. |
| [3] | 徐若韬, 王强, 鲍庆嘉, 王伟宇, 张志, 刘朝阳, 徐君, 邓风. γ -Al2O3颗粒溶液浸润过程的原位磁共振成像[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220587. |
| [4] | 顾亚琴, 丁劲峰, 陈金娥, 谢文娜, 肖林霞. 咔唑近红外荧光探针可视化线粒体及体内成像应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230367. |
| [5] | 陈尚钰, 沈清明, 孙鹏飞, 范曲立. 小分子基温敏聚合物纳米粒子的制备及在近红外二区荧光成像与光热治疗中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220392. |
| [6] | 常通航, 程震. 整合荧光成像和化疗的有机小分子诊疗探针的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220430. |
| [7] | 马小飞, 胡山, 李俊彬, 杨盛, 谌委菊, 卿志和, 周怡波, 杨荣华. 细胞内源性分子辅助荧光信号放大策略及细胞成像[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220320. |
| [8] | 李奥, 李凌轩, 左翠翠, 陈传凯, 樊一凡, 步逸凡, 林泓域, 高锦豪. 基于硼酸酯的19F磁共振分子探针的设计合成及活体深组织活性氧物种的激活响应成像[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220545. |
| [9] | 汪诗琪, 罗博文, 俞计成, 顾臻. 近红外二区活体荧光成像在肿瘤诊疗中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220577. |
| [10] | 张钤, 刘雅薇, 王帆, 刘凯, 张洪杰. 稀土纳米材料在高分辨活体成像及诊疗中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220552. |
| [11] | 赵雪琪, 赵越, 薛静, 白敏, 陈锋, 孙颖, 宋大千, 赵永席. 单细胞核酸编码扩增成像分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220572. |
| [12] | 刘苗, 刘瑞波, 刘巴蒂, 钱鹰. 溶酶体靶向吲哚氟硼二吡咯光敏剂的合成、 双光子荧光成像及光动力治疗[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [13] | 陈宏达, 张婳, 王振新. 用于小动物活体的荧光-光热双模成像系统[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 725. |
| [14] | 王萌萌, 栾天骄, 杨铭焱, 吕佳佳, 高杰, 李洪玉, 卫钢, 袁泽利. 肿瘤乏氧靶向响应的罗丹明荧光探针及其成像介导手术治疗[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3071. |
| [15] | 孙启睿, 赵楠, 刘树威, 辛华, 张皓, 张乐宁. 用于磁性靶向治疗肺纤维化的聚多巴胺包覆的Fe3O4/甲强龙/环磷酰胺复合超粒子[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||