

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (12): 20220552.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220552
张钤1, 刘雅薇2( ), 王帆2, 刘凯1,2(
), 王帆2, 刘凯1,2( ), 张洪杰1,2
), 张洪杰1,2
收稿日期:2022-08-19
出版日期:2022-12-10
发布日期:2022-11-08
通讯作者:
刘雅薇,刘凯
E-mail:yaweiliu@ciac.ac.cn;kailiu@tsinghua.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Qian1, LIU Yawei2( ), WANG Fan2, LIU Kai1,2(
), WANG Fan2, LIU Kai1,2( ), ZHANG Hongjie1,2
), ZHANG Hongjie1,2
Received:2022-08-19
Online:2022-12-10
Published:2022-11-08
Contact:
LIU Yawei, LIU Kai
E-mail:yaweiliu@ciac.ac.cn;kailiu@tsinghua.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
荧光成像具有时空分辨率高、 反馈快、 非侵入和无电离辐射等优点, 是一种重要的生物成像技术. 与传统用于荧光成像的可见光和近红外一区(NIR-I, 600~950 nm)相比, 近红外二区(NIR-Ⅱ, 1000~1700 nm)窗口具有低生物组织散射系数和低生物自发荧光, 采用NIR-Ⅱ光进行活体荧光成像能有效提高成像的分辨率、 信噪比和穿透深度. 稀土纳米颗粒(RENPs)具有大斯托克斯位移、 高化学稳定性、 可调的荧光寿命以及较窄的发射带, 是一种重要的荧光成像探针. 近年来, 一系列具有优异的NIR-Ⅱ发光性能的稀土纳米材料被用于高分辨活体荧光成像. 本文综合评述了近年来RENPs用于高分辨活体成像及诊疗中的研究进展, 概述了RENPs的掺杂调控、 基质晶格选择和复合敏化等NIR-Ⅱ发光增强策略, 介绍了其在多种生物医学场景中的靶向聚集、 荧光传感和疾病治疗等功能, 并总结了其在多路成像、 多模态成像和疾病诊疗中的应用. 最后, 简要分析了RENPs在未来生物医学应用中面临的挑战和发展的方向.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
张钤, 刘雅薇, 王帆, 刘凯, 张洪杰. 稀土纳米材料在高分辨活体成像及诊疗中的应用. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220552.
ZHANG Qian, LIU Yawei, WANG Fan, LIU Kai, ZHANG Hongjie. High-resolution in vivo Imaging, Diagnosis and Treatment Applications of Rare-earth-based Nanomaterials. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12): 20220552.
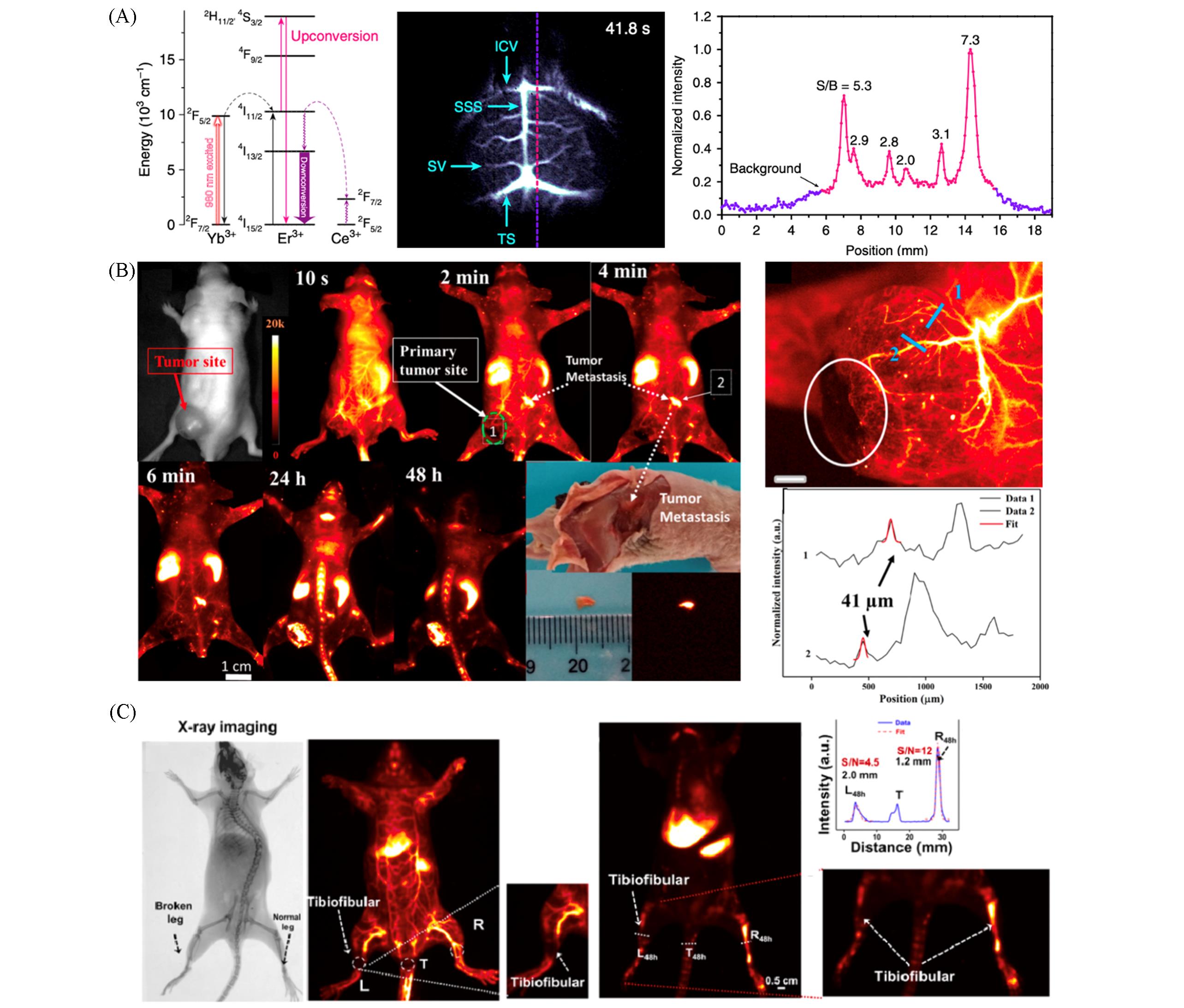
Fig.1 High⁃resolution in vivo fluorescence imaging by using Yb3+⁃sensitized RENPs(A) Energy-level diagram(left) and high-resolution NIR-Ⅱ cerebrovascular imaging(right) of NaYbF4∶Ce,Er@ NaYF4 NPs[22]. Copyright 2017, Springer Nature. (B) NIR-Ⅱb optical image-guided tumor metastasis detection(left) and tumor vessel detection(right) with NaLuF4∶Gd,Yb,Ce,Er@PAA nanorods[27]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. (C) In vivo X-ray and NIR-Ⅱb image-guided bone fracture diagnosis using NaLuF4∶Gd,Yb,Er,Ce@NaYF4@PAA NPs. NIR-Ⅱb images after 1 min(left) and 48 h(right) are shown[28]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society.
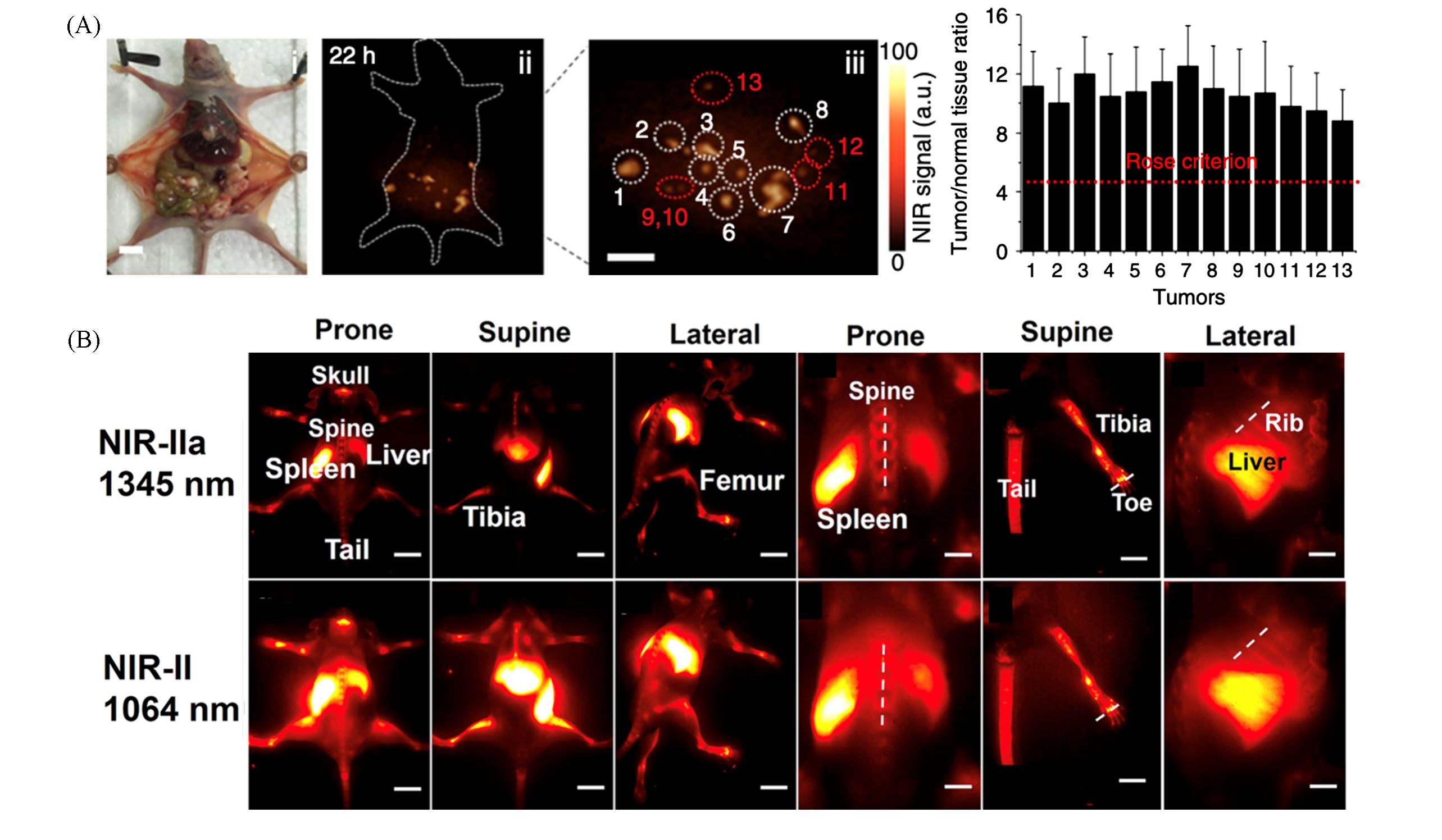
Fig.2 High⁃resolution in vivo fluorescence imaging by using Nd3+⁃sensitized RENPs(A) NIR-Ⅱ image-guided surgery for metastatic ovarian cancer with DNA and targeted peptide modified NaGdF4∶Nd@NaGdF4 NPs[33]. Copyright 2018, Springer Nature. (B) NIR-Ⅱ imaging of various organs and bones with DSPE-mPEG modified NaYF4∶Nd@NaYF4 NPs at various wavelengths[34]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
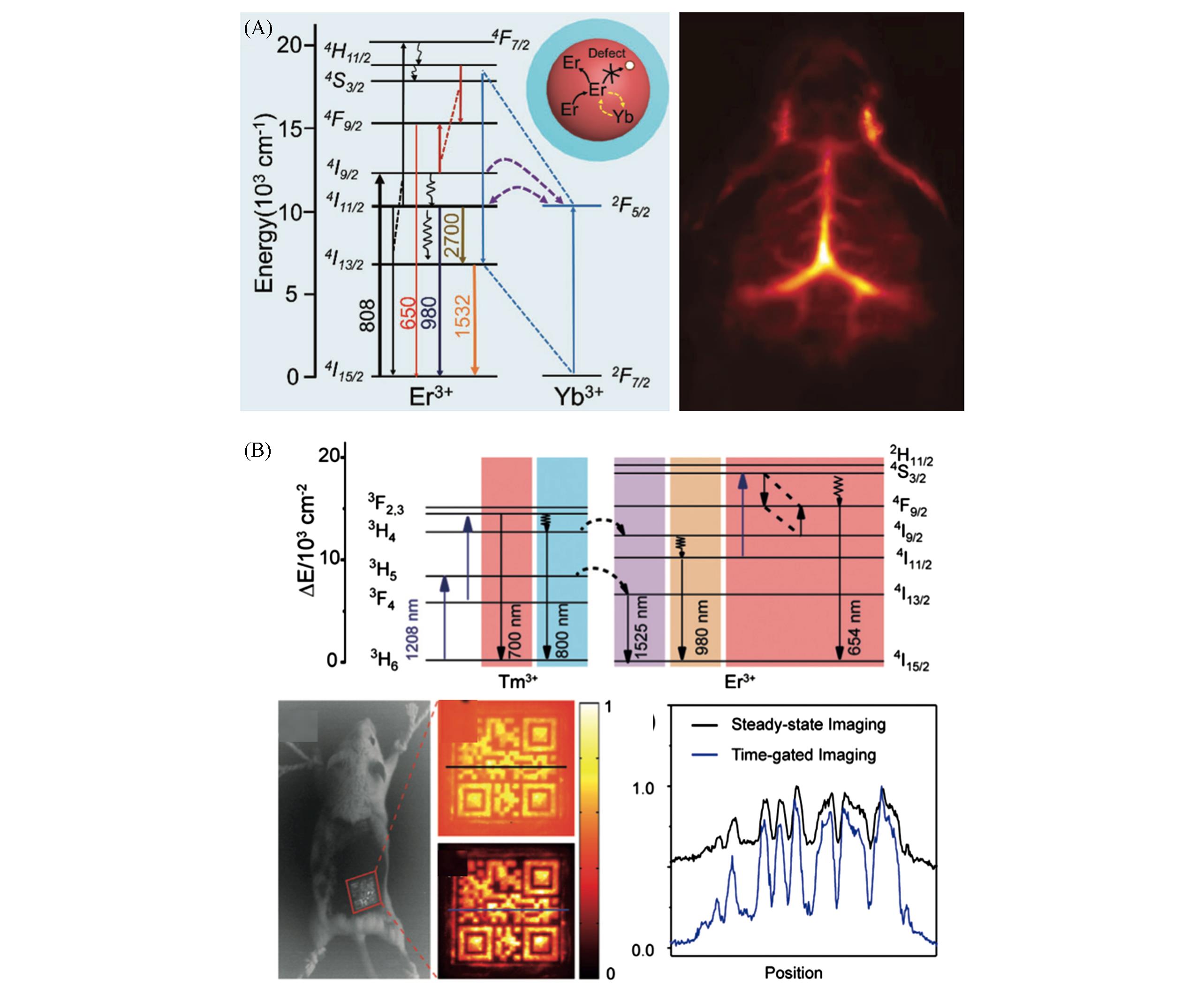
Fig.3 High⁃resolution in vivo imaging applications of Er3+ sensitized RENPs(A) Energy-level diagram of NaErF4∶Yb@NaLuF4 NPs(left), NIR-Ⅱ cerebrovascular imaging with NaErF4∶Yb@NaLuF4@PAA NPs under 808 nm excitation(right)[44]. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. (B) Energy-level diagram of NaErF4@NaYF4∶Tm@NaYF4 NPs(upper), in vivo NIR-Ⅱ information storage with NaErF4@NaYF4∶Tm@NaYF4 NPs under 1208 nm excitation(lower)[45]. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH.
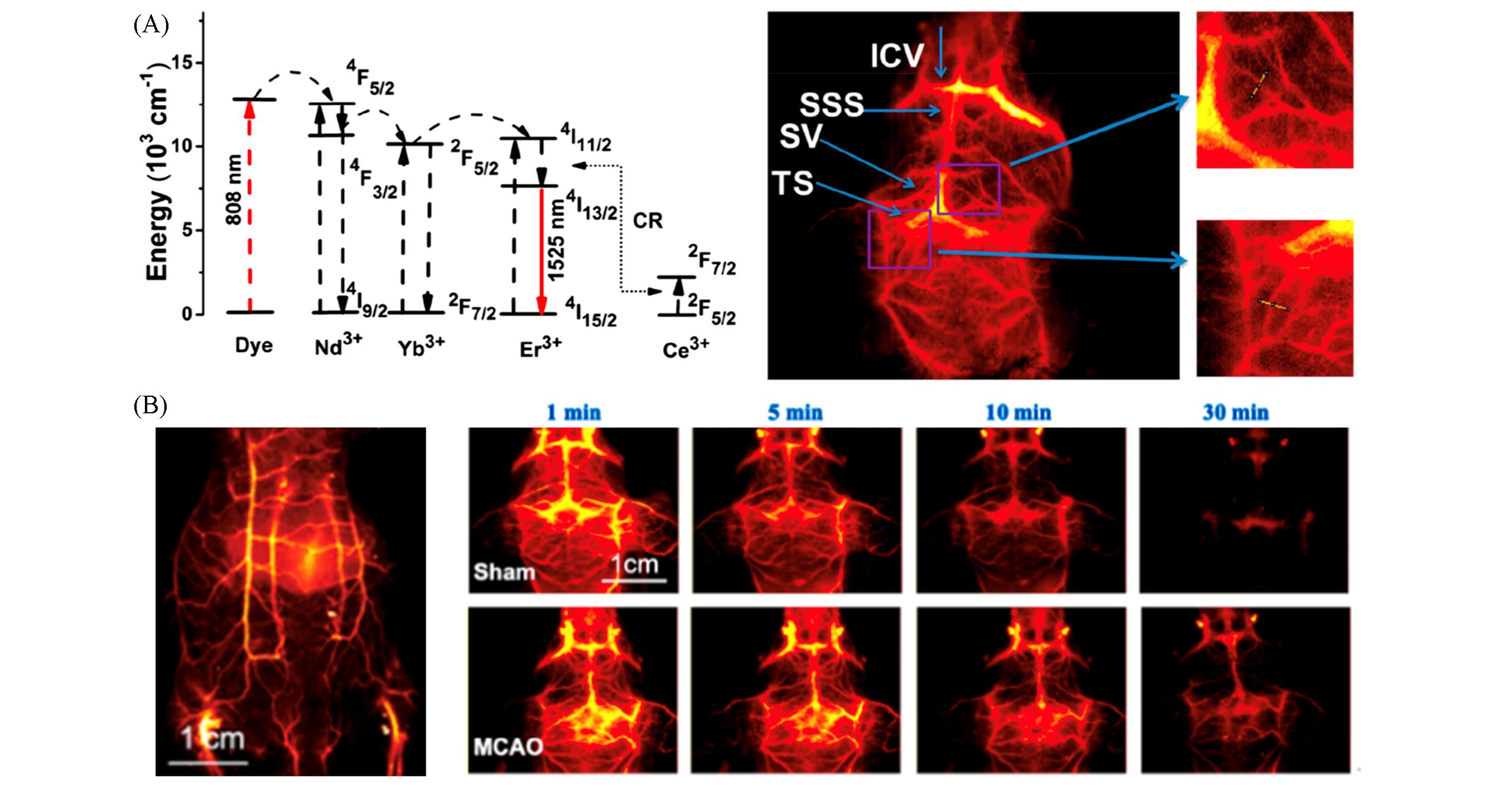
Fig.4 High⁃resolution in vivo imaging by using organic dyes and QDs sensitized RENPs(A) Energy-level diagram(left) and NIR-Ⅱ cerebrovascular imaging(right) of NaYF4∶Yb,Er@NaYF4∶Nd@Alk-pi NPs under 808 nm excitation[49]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (B) NIR-Ⅱ imaging of abdomen(left) and dynamic NIR-Ⅱ cerebrovascular imaging in MCAO model with NaYbF4∶Gd,Ce,Er@NaYF4∶Yb@Ag2Se NPs under 808 nm excitation(right)[50]. Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society.
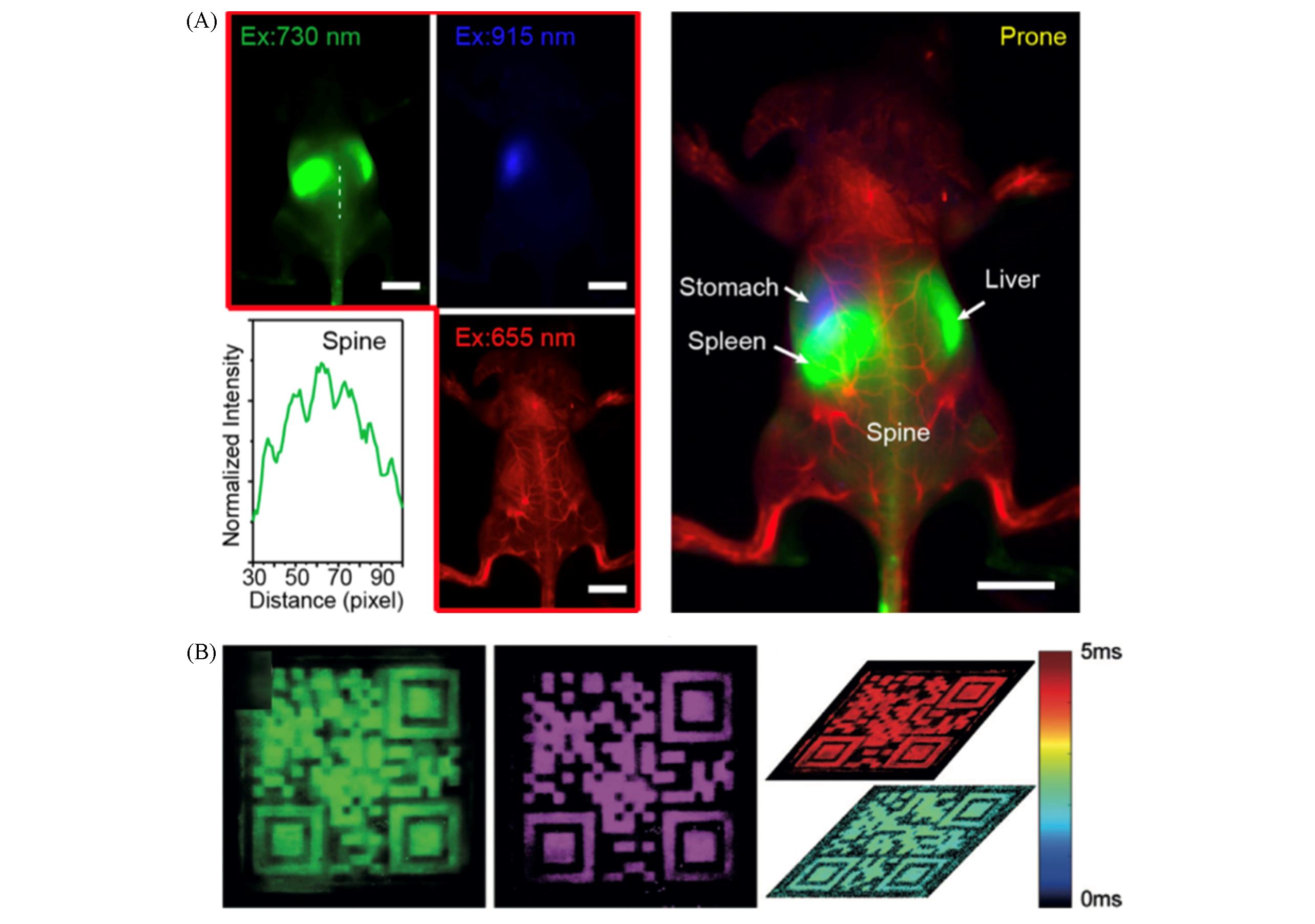
Fig.5 High⁃resolution in vivo multiplexed imaging with RENPs(A) Orthogonal three-color NIR-Ⅱ imaging of vessels, stomach and liver/spleen/spine with NaErF4@NaYF4, α-NaYF4∶Nd@NaYF4 and α-NaYbF4∶Ho@NaYF4 NPs[55]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society. (B) Multiplex(left) and decoded QR code(right) prined with Er-τ1 and Er-τ10 NPs[45]. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH.
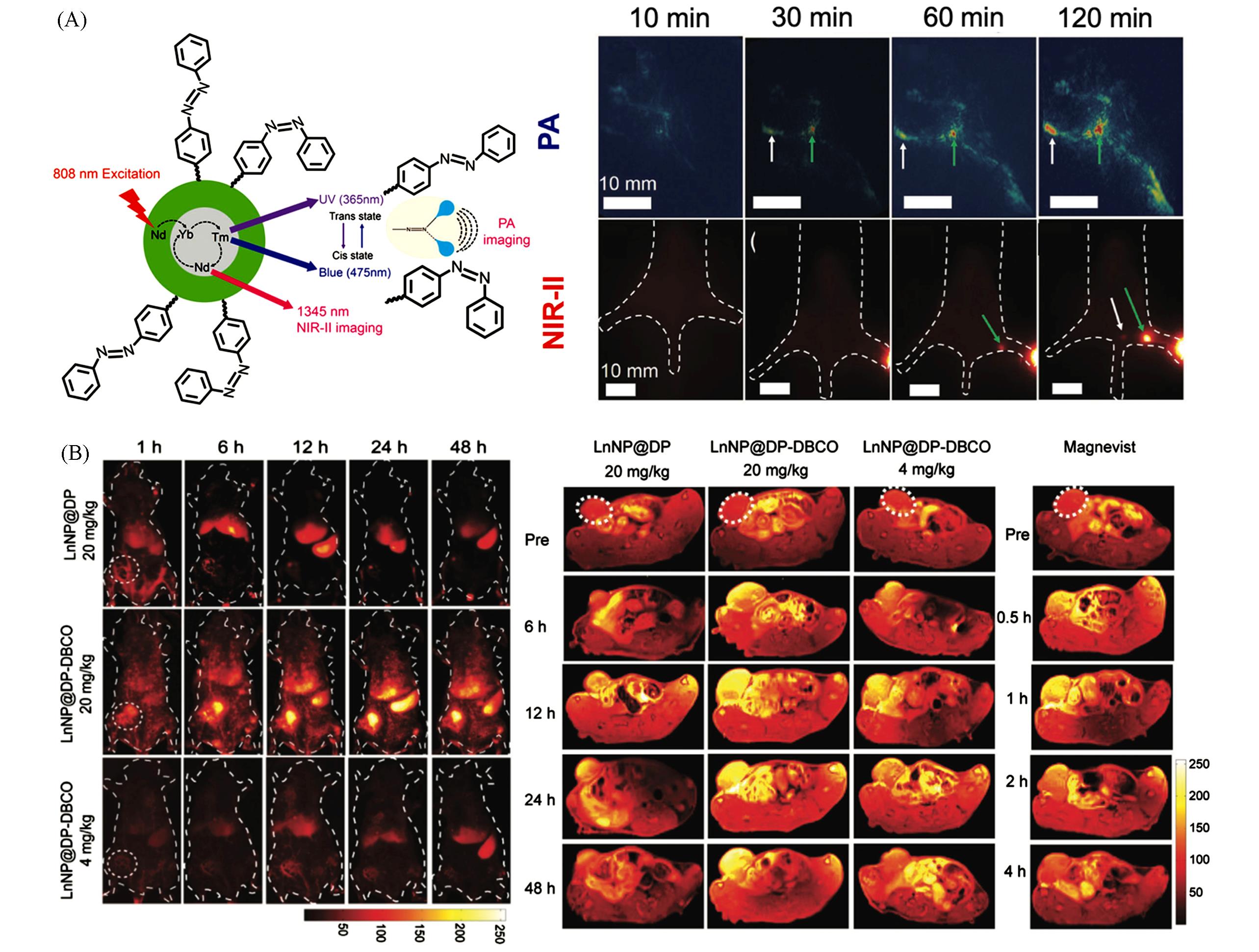
Fig.6 High⁃resolution in vivo multimodal imaging with RENPs(A) Schematic illustration(left) and images(right) of PA/NIR-Ⅱ dual-modal imaging with NaYF4∶Yb,Nd,Tm@NaYF4@NaYF4∶Nd@PAA-Azo NPs. Arrows indicate lymph nodes[66]. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (B) Significant enhancement of NIR-Ⅱ(left) and MR(right) imaging with biorthogonal NaYF4∶Yb,Er,Ce@NaYF4∶Nd@NaGdF4@DP-DBCO NPs. Dotted circles indicate tumor sites[67]. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH.
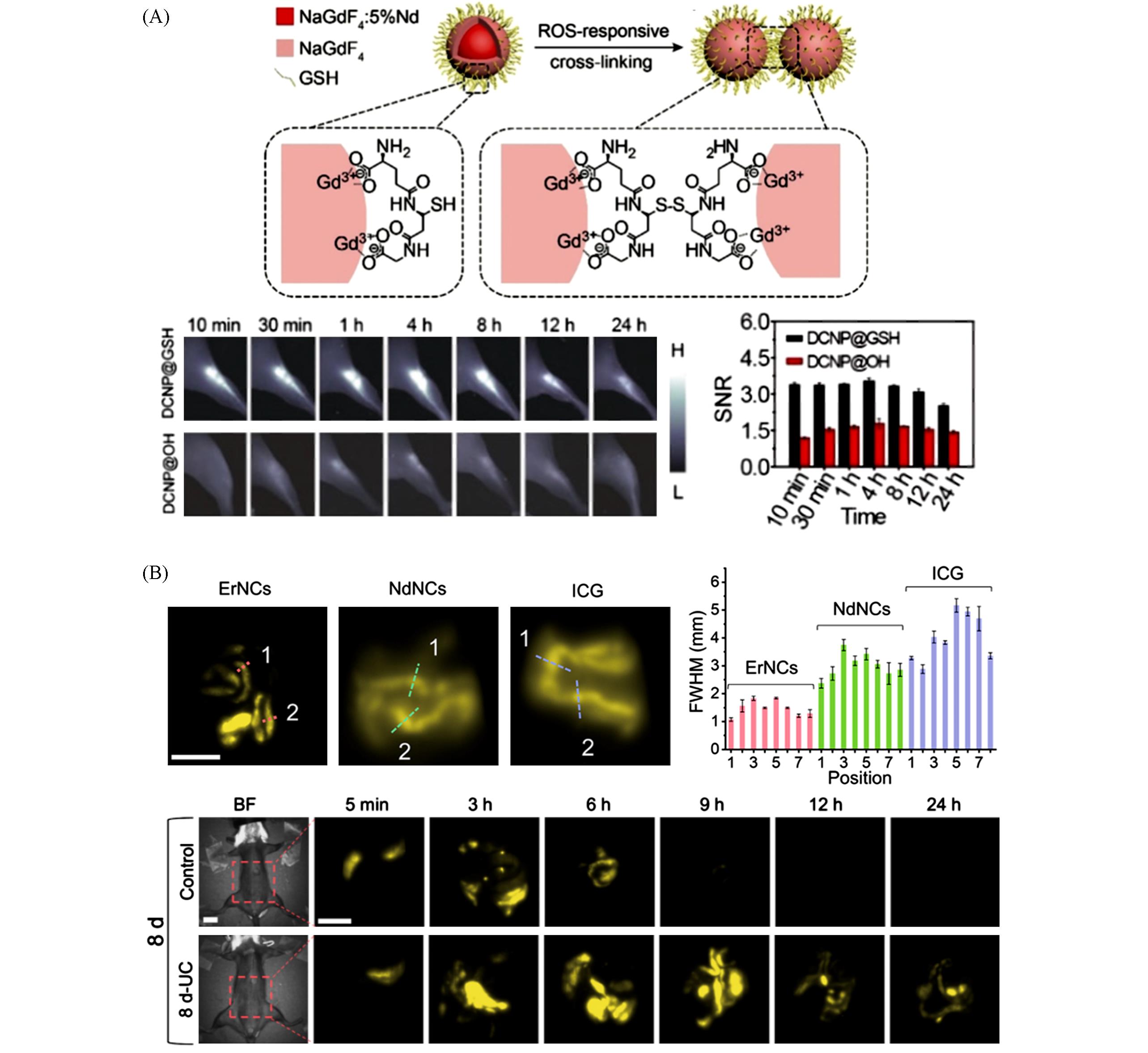
Fig.7 High⁃resolution in vivo fluorescence image⁃guided diagnosis by using RENPs(A) Schematic illustration of NaGdF4∶Nd@NaGdF4@GSH NPs cross-linking in the presence of ROS(left), NIR-Ⅱ imaging of inflammation with various nanoparticles(right)[70]. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH. (B) Resolution comparison of NaYbF4∶Ce,Er@CaF2, NaYF4∶Nd@NaYF4 and ICG in mice GI tract(upper); high-resolution NIR-Ⅱb image-guided diagnosis of ulcerative colitis(UC) with NaYbF4∶Ce,Er@CaF2@CMC-Na NPs(bottom)[30]. Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society.
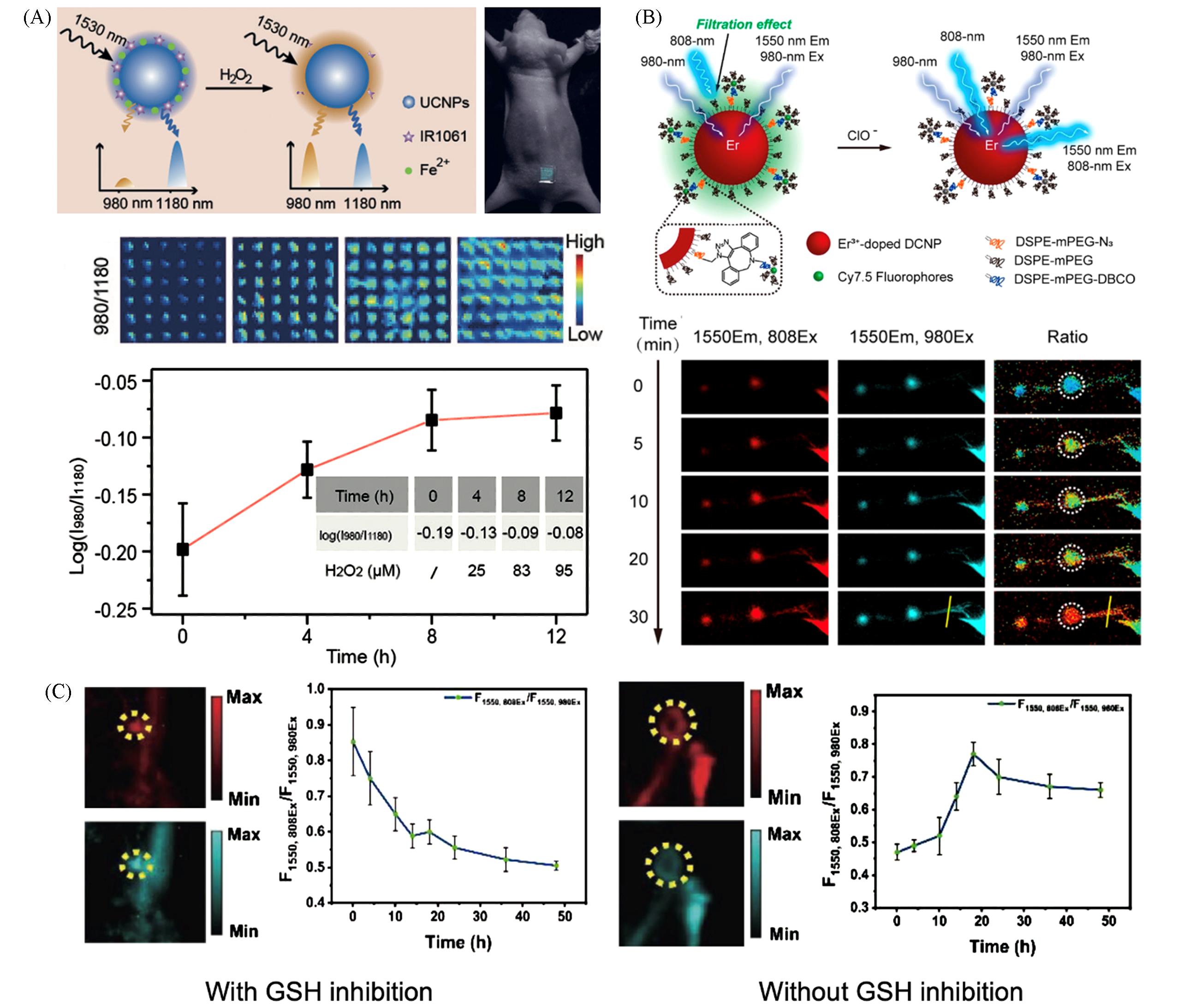
Fig.8 High⁃resolution biosensing applications of RENPs(A) Schematic illustration of H2O2 biosensing with NaErF4∶Ho@NaYF4-Fe2+-IR1061 nanoprobe(left), in vivo biosensing of H2O2 in the inflammation site(right)[41]. Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH. (B) Schematic illustration of ClO- biosensing with NaY0.5Er0.5F4@NaYF4@Cy7.5 NPs(left), NIR-Ⅱ ratiometric fluorescence imaging of lymphatic inflammation(right). Dotted circles indicate tumor sites[72]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society. (C) NIR-Ⅱ image-guided diagnosis based on GSH biosensing. NIR-Ⅱ images and fluorescence intensity ratios of tumor-bearing mice with(left) and without(right) GSH inhibition. Dashed circles indicate tumor sites[75]. Copyright 2021, Wiley-VCH.
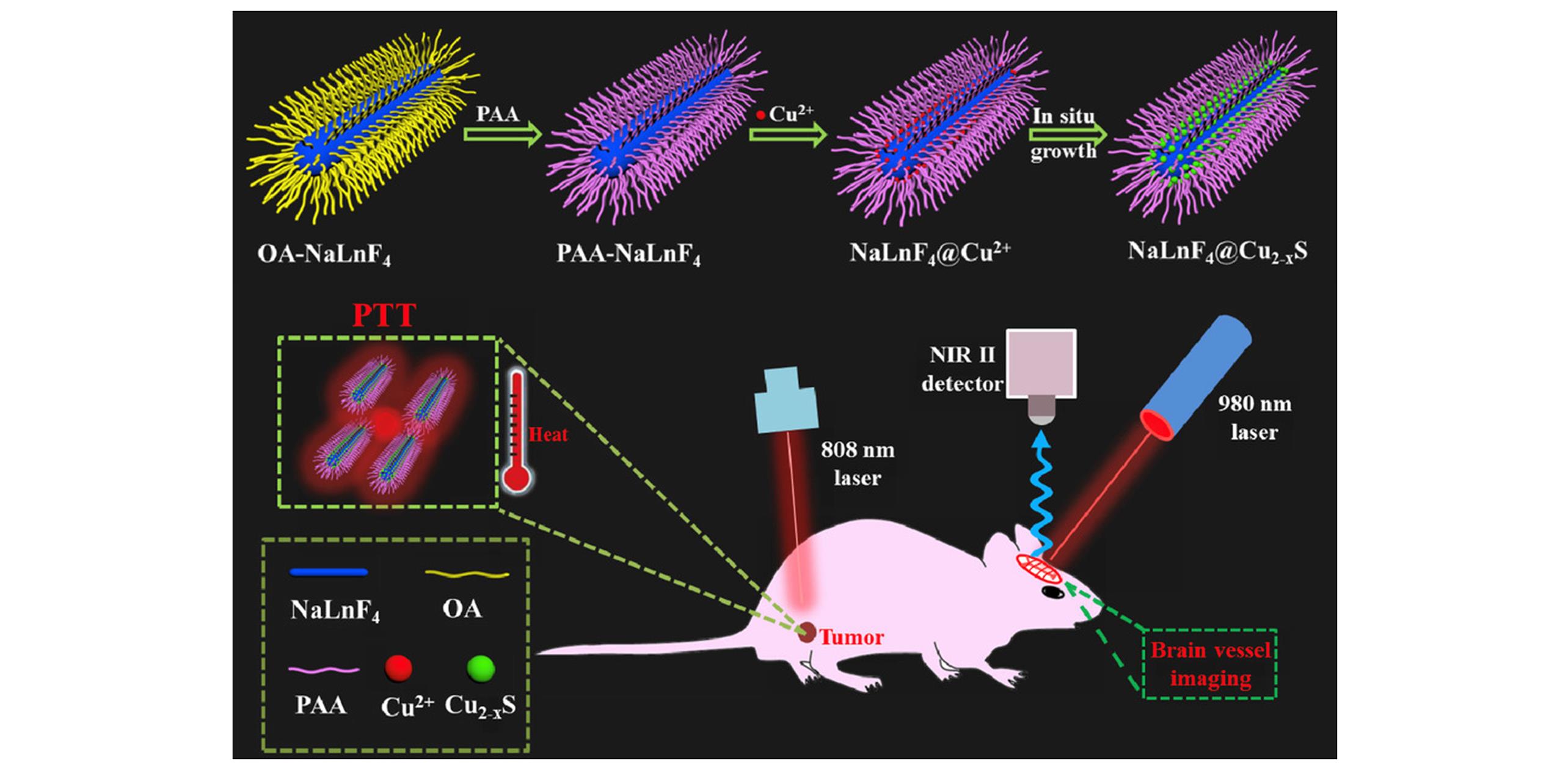
Fig.9 Theranostics applications of RENPs[80]Upper: schematic illustration of designing PAA-NaYF4∶Gd,Yb,Er@Cu2‒x S nanorods; lower: schematic illustration of PTT and NIR-Ⅱ imaging of tumor using PAA-NaYF4∶Gd,Yb,Er@Cu2‒x S nanorods under 808 nm excitation. Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH.
| 1 | Fan Y., Zhang F., Adv. Opt. Mater., 2019, 7(7), 1801417 |
| 2 | Xu J., Gulzar A., Yang P., Bi H., Yang D., Gai S., He F., Lin J., Xing B., Jin D., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 381, 104—134 |
| 3 | Li C., Chen G., Zhang Y., Wu F., Wang Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(35), 14789—14804 |
| 4 | Zhong Y., Dai H., Nano. Res., 2020, 13(5), 1281—1294 |
| 5 | Diao S., Hong G., Antaris A. L., Blackburn J. L., Cheng K., Cheng Z., Dai H., Nano Res., 2015, 8(9), 3027—3034 |
| 6 | Welsher K., Liu Z., Sherlock S. P., Robinson J. T., Chen Z., Daranciang D., Dai H., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2009, 4(11), 773—780 |
| 7 | Zhang Y., Yang H., An X., Wang Z., Yang X., Yu M., Zhang R., Sun Z., Wang Q., Small, 2020, 16(14), e2001003 |
| 8 | Li B., Zhao M., Feng L., Dou C., Ding S., Zhou G., Lu L., Zhang H., Chen F., Li X., Li G., Zhao S., Jiang C., Wang Y., Zhao D., Cheng Y., Zhang F., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 3102 |
| 9 | Liu M. H., Zhang Z., Yang Y. C., Chan Y. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(2), 983—989 |
| 10 | Qi J., Alifu N., Zebibula A., Wei P., Lam J. W. Y., Peng H. Q., Kwok R. T. K., Qian J., Tang B. Z., Nano Today, 2020, 34, 100893 |
| 11 | Yi Z., Luo Z., Qin X., Chen Q., Liu X., Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53(11), 2692—2704 |
| 12 | Ding S., Lu L., Fan Y., Zhang F., J. Rare Earths, 2020, 38(5), 451—463 |
| 13 | Wei Z., Liu Y., Li B., Li J., Lu S., Xing X., Liu K., Wang F., Zhang H., Light. Sci. Appl., 2022, 11(1), 175 |
| 14 | Liu Y., Lu Y., Yang X., Zheng X., Wen S., Wang F., Vidal X., Zhao J., Liu D., Zhou Z., Ma C., Zhou J., Piper J. A., Xi P., Jin D., Nature, 2017, 543(7644), 229—233 |
| 15 | Chen C., Wang F., Wen S., Su Q. P., Wu M. C. L., Liu Y., Wang B., Li D., Shan X., Kianinia M., Aharonovich I., Toth M., Jackson S. P., Xi P., Jin D., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 3290 |
| 16 | Chen C., Liu B., Liu Y., Liao J., Shan X., Wang F., Jin D., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(23), e2008847 |
| 17 | Naczynski D. J., Tan M. C., Zevon M., Wall B., Kohl J., Kulesa A., Chen S., Roth C. M., Riman R. E., Moghe P. V., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 2199 |
| 18 | Wang R., Li X., Zhou L., Zhang F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(45), 12086—12090 |
| 19 | Haase M., Schafer H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(26), 5808—5829 |
| 20 | Menyuk N., Dwight K., Pierce J. W., Appl. Phys. Lett., 1972, 21(4), 159—161 |
| 21 | Shi R., Brites C. D. S., Carlos L. D., Small Struct., 2022, 3(3), 2100194 |
| 22 | Zhong Y., Ma Z., Zhu S., Yue J., Zhang M., Antaris A. L., Yuan J., Cui R., Wan H., Zhou Y., Wang W., Huang N. F., Luo J., Hu Z., Dai H., Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 737 |
| 23 | Franke D., Harris D. K., Chen O., Bruns O. T., Carr J. A., Wilson M. W. B., Bawendi M. G., Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 12749 |
| 24 | Zhong Y., Ma Z., Wang F., Wang X., Yang Y., Liu Y., Zhao X., Li J., Du H., Zhang M., Cui Q., Zhu S., Sun Q., Wan H., Tian Y., Liu Q., Wang W., Garcia K. C., Dai H., Nat. Biotechnol., 2019, 37(11), 1322—1331 |
| 25 | Yi G. S., Chow G. M., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2006, 16(18), 2324—2329 |
| 26 | Xue Z., Zeng S., Hao J., Biomaterials, 2018, 171, 153—163 |
| 27 | Li Y., Zeng S., Hao J., ACS Nano, 2019, 13(1), 248—259 |
| 28 | Li Y., Wen X., Deng Z., Jiang M., Zeng S., Nano. Lett., 2022, 22(7), 2691—2701 |
| 29 | Li Y., Zhang P., Ning H., Zeng J., Hou Y., Jing L., Liu C., Gao M., Small, 2019, 15(51), e1905344 |
| 30 | Mi C., Guan M., Zhang X., Yang L., Wu S., Yang Z., Guo Z., Liao J., Zhou J., Lin F., Ma E., Jin D., Yuan X., Nano. Lett., 2022, 22(7), 2793—2800 |
| 31 | Deng Z., Li X., Xue Z., Jiang M., Li Y., Zeng S., Liu H., Nanoscale, 2018, 10(19), 9393—9400 |
| 32 | Dibaba S. T., Xiaoqian G., Ren W., Sun L., J. Rare Earths, 2019, 37(8), 791—805 |
| 33 | Wang P., Fan Y., Lu L., Liu L., Fan L., Zhao M., Xie Y., Xu C., Zhang F., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1), 2898 |
| 34 | He S., Chen S., Li D., Wu Y., Zhang X., Liu J., Song J., Liu L., Qu J., Cheng Z., Nano. Lett., 2019, 19(5), 2985—2992 |
| 35 | Li D., He S., Wu Y., Liu J., Liu Q., Chang B., Zhang Q., Xiang Z., Yuan Y., Jian C., Yu A., Cheng Z., Adv. Sci., 2019, 6(23), 1902042 |
| 36 | Yang J., He S., Hu Z., Zhang Z., Cao C., Cheng Z., Fang C., Tian J., Nano Today, 2021, 38, 101120 |
| 37 | Cao C., Wu N., Yuan W., Gu Y., Ke J., Feng W., Li F., Nanoscale, 2020, 12(15), 8248—8254 |
| 38 | Li Y., Jiang M., Xue Z., Zeng S., Theranostics, 2020, 10(15), 6875—6885 |
| 39 | Chen Q., Xie X., Huang B., Liang L., Han S., Yi Z., Wang Y., Li Y., Fan D., Huang L., Liu X., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(26), 7605—7609 |
| 40 | Cheng X., Pan Y., Yuan Z., Wang X., Su W., Yin L., Xie X., Huang L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28(22), 1800208 |
| 41 | Liu L., Wang S., Zhao B., Pei P., Fan Y., Li X., Zhang F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(25), 7518—7522 |
| 42 | Huang B., Sun M., Dougherty A. W., Dong H., Xu Y. J., Sun L. D., Yan C. H., Nanoscale, 2017, 9(46), 18490—18497 |
| 43 | Wang W., Feng Z., Li B., Chang Y., Li X., Yan X., Chen R., Yu X., Zhao H., Lu G., Kong X., Qian J., Liu X., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2021, 9(12), 2899—2908 |
| 44 | Wang X., Yakovliev A., Ohulchanskyy T. Y., Wu L., Zeng S., Han X., Qu J., Chen G., Adv. Opt. Mater., 2018, 6(20), 1800690 |
| 45 | Zhang H., Fan Y., Pei P., Sun C., Lu L., Zhang F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(30), 10153—10157 |
| 46 | Zhang H., Chen Z. H., Liu X., Zhang F., Nano Res., 2020, 13(7), 1795—1809 |
| 47 | Shao W., Chen G., Kuzmin A., Kutscher H. L., Pliss A., Ohulchanskyy T. Y., Prasad P. N., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(50), 16192—16195 |
| 48 | Liu Z., Ren F., Zhang H., Yuan Q., Jiang Z., Liu H., Sun Q., Li Z., Biomaterials, 2019, 219, 119364 |
| 49 | Wang Q., Liang T., Wu J., Li Z., Liu Z., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 29303—29312 |
| 50 | Song D., Zhu M., Chi S., Xia L., Li Z., Liu Z., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(22), 7949—7957 |
| 51 | Xi J., Chen N., Yang Y. B., Yuan Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 41(11), 3247—3264 |
| 席京, 陈娜, 杨雁冰, 袁荃. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11), 3247—3264 | |
| 52 | Jiang M., Deng Z., Zeng S., Hao J., View, 2021, 2(4), 20200128 |
| 53 | Ou X., Qin X., Huang B., Zan J., Wu Q., Hong Z., Xie L., Bian H., Yi Z., Chen X., Wu Y., Song X., Li J., Chen Q., Yang H., Liu X., Nature, 2021, 590(7846), 410—415 |
| 54 | Pei P., Chen Y., Sun C., Fan Y., Yang Y., Liu X., Lu L., Zhao M., Zhang H., Zhao D., Liu X., Zhang F., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2021, 16(9), 1011—1018 |
| 55 | Xu H., Yang Y., Lu L., Yang Y., Zhang Z., Zhao C. X., Zhang F., Fan Y., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(8), 3661—3668 |
| 56 | Liao J., Yang L., Wu S., Yang Z., Zhou J., Jin D., Guan M., J. Lumin., 2022, 242, 118597 |
| 57 | Zhang X., He S., Ding B., Qu C., Chen H., Sun Y., Zhang R., Lan X., Cheng Z., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2021, 9(44), 9116—9122 |
| 58 | Wang T., Wang S., Liu Z., He Z., Yu P., Zhao M., Zhang H., Lu L., Wang Z., Wang Z., Zhang W., Fan Y., Sun C., Zhao D., Liu W., Bunzli J. G., Zhang F., Nat. Mater., 2021, 20(11), 1571—1578 |
| 59 | Zhang Z., Yang Y., Zhao M., Lu L., Zhang F., Fan Y., ACS Appl. Bio. Mater., 2022, 5(6), 2935—2942 |
| 60 | Fan Y., Wang P., Lu Y., Wang R., Zhou L., Zheng X., Li X., Piper J. A., Zhang F., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13(10), 941—946 |
| 61 | Lee D. E., Koo H., Sun I. C., Ryu J. H., Kim K., Kwon I. C., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(7), 2656—2672 |
| 62 | Zhang Y., Zhao K., He H., Wan S., Martins A. F., Zhang L., Liu K., Dalton Trans., 2021, 50(6), 2014—2017 |
| 63 | Wan S. K., Cui F. Z., Li B., Zhao K. L., He H. N., Zhang Y., Liu J. H., Zhang L., Liu K., ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2020, 3(9), 9433—9439 |
| 64 | Lei P., Feng J., Zhang H., Nano Today, 2020, 35, 100952 |
| 65 | Zhao S., Tian R. R., Shao B. Q., Feng Y., Yuan S. W., Dong L. P., Zhang L., Liu K., Wang Z. X., You H. P., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(1), 394—402 |
| 66 | He S., Song J., Liu J., Liu L., Qu J., Cheng Z., Adv. Opt. Mater., 2019, 7(12), 1900045 |
| 67 | Luo Z., Hu D., Gao D., Yi Z., Zheng H., Sheng Z., Liu X., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(49), e2102950 |
| 68 | Zhou J., Liu Z., Li F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41(3), 1323—1349 |
| 69 | Ansari A. A., Parchur A. K., Chen G., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2022, 457, 214423 |
| 70 | Zhao M., Wang R., Li B., Fan Y., Wu Y., Zhu X., Zhang F., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(7), 2050—2054 |
| 71 | Zhu J., Jin Q., Zhao H., Zhu W., Liu Z., Chen Q., Small Struct., 2021, 2(7), 2100002 |
| 72 | Wang S., Liu L., Fan Y., El⁃Toni A. M., Alhoshan M. S., Li D., Zhang F., Nano Lett., 2019, 19(4), 2418—2427 |
| 73 | Sun C., Zhao M., Zhu X., Pei P., Zhang F., CCS Chem., 2022, 4(2), 476—486 |
| 74 | Gamcsik M. P., Kasibhatla M. S., Teeter S. D., Colvin O. M., Biomarkers, 2012, 17(8), 671—691 |
| 75 | Wang C., Lin H., Ge X., Mu J., Su L., Zhang X., Niu M., Yang H., Song J., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(16), 2009942 |
| 76 | Wang Y., Song S., Zhang S., Zhang H., Nano Today, 2019, 25, 38—67 |
| 77 | Liu B., Sun J., Zhu J., Li B., Ma C., Gu X., Liu K., Zhang H., Wang F., Su J., Yang Y., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(39), e2004460 |
| 78 | Liu B., Gu X., Sun Q., Jiang S., Sun J., Liu K., Wang F., Wei Y., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2021, 31(19), 2010779 |
| 79 | Zhao K., Sun J., Wang F., Song A., Liu K., Zhang H., ACS Appl. Bio. Mater., 2020, 3(7), 3975—3986 |
| 80 | Jiang M., Liu H., Zeng S., Hao J., Adv. Therap., 2019, 2(6), 1800153 |
| 81 | Li X., Jiang M., Zeng S., Liu H., Theranostics, 2019, 9(13), 3866—3878 |
| 82 | Carrasco E., del Rosal B., Sanz⁃Rodríguez F., de la Fuente Á. J., Gonzalez P. H., Rocha U., Kumar K. U., Jacinto C., Solé J. G., Jaque D., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(4), 615—626 |
| 83 | Marciniak L., Pilch A., Arabasz S., Jin D., Bednarkiewicz A., Nanoscale, 2017, 9(24), 8288—8297 |
| 84 | Yu Z., Hu W., Zhao H., Miao X., Guan Y., Cai W., Zeng Z., Fan Q., Tan T. T. Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(25), 8536—8540 |
| 85 | Wang X., Li H., Li F., Han X., Chen G., Nanoscale, 2019, 11(45), 22079—22088 |
| 86 | Feng M., Wang Y., Lin B., Peng X., Yuan Y., Tao X., Lv R., Dalton Trans., 2020, 49(27), 9444—9453 |
| 87 | Peng P., Wu N., Ye L., Jiang F., Feng W., Li F., Liu Y., Hong M., ACS Nano, 2020, 16672—16680 |
| 88 | Ding B., Sheng J., Zheng P., Li C., Li D., Cheng Z., Ma P., Lin J., Nano Lett., 2021, 21(19), 8281—8289 |
| 89 | Zhang X., Li Y., Ge J., Qin L., Zheng Y., Lei B., Zheng Z., Du Y., CCS Chem., 2022, 4(3), 926—937 |
| 90 | Zhang X., Wang S., Cheng G., Yu P., Chang J., Engineering, 2022, 13, 18—30 |
| 91 | Chen Y., Zhang H., Lei Z., Zhang F., Small Struct., 2020, 1(1), 2000036 |
| 92 | Ren F., Jiang Z., Han M., Zhang H., Yun B., Zhu H., Li Z., View, 2021, 2(6), 20200122 |
| 93 | Xue D., Wu D., Lu Z., Neuhaus J., Zebibula A., Feng Z., Cheng S., Zhou J., Qian J., Li G., Engineering, doi:10.1016/j.eng. 2021.07.032 |
| [1] | 沙蒙, 许维庆, 吴志超, 顾文玲, 朱成周. 单原子材料类酶催化及生物医学应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220077. |
| [2] | 张庆鹏, 关国强, 刘慧怡, 陆畅, 周颖, 宋国胜. 磁粒子成像示踪剂的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12): 20220375. |
| [3] | 冯玮 赵光耀 孙聆东 严纯华. Au@SiO2/LaF3∶Ce,Tb复合结构的发光共振能量转移[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(3): 635. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||