

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 20230401.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230401
童大银1,2, 赵耀林1( ), 王禹齐1, 韩子彤1, 王杰1, 张俊1, 喻晨曦1
), 王禹齐1, 韩子彤1, 王杰1, 张俊1, 喻晨曦1
收稿日期:2023-09-07
出版日期:2024-01-10
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
赵耀林
E-mail:zhaoyaolin@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
TONG Dayin1,2, ZHAO Yaolin1( ), WANG Yuqi1, HAN Zitong1, WANG Jie1, ZHANG Jun1, YU Chenxi1
), WANG Yuqi1, HAN Zitong1, WANG Jie1, ZHANG Jun1, YU Chenxi1
Received:2023-09-07
Online:2024-01-10
Published:2023-11-23
Contact:
ZHAO Yaolin
E-mail:zhaoyaolin@mail.xjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用第一性原理和巨正则蒙特卡罗方法, 模拟研究了气态碘分子(I2)在共价有机框架材料(COF-103)中的吸附行为, 并讨论了气态氧化物、 氯化物和挥发性有机化合物(VOCs)等杂质气体的竞争吸附影响. 结果表明, I2偏向以垂直方式吸附于COF-103苯环的碳原子位, 其中, 长程色散相互作用具有重要的贡献, 色散能在吸附能中的占比最多可达46%. I2与COF-103之间存在少量电荷转移, 且可能形成具有弱共价相互作用的次级键. 杂质气体中苯分子(C6H6)的吸附能和等量吸附热最大, 与COF-103的亲和性最强, 并且可以占据I2的吸附位点, 从而引起I2吸附量的显著降低.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
童大银, 赵耀林, 王禹齐, 韩子彤, 王杰, 张俊, 喻晨曦. 气态碘在COF-103上吸附的理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(1): 20230401.
TONG Dayin, ZHAO Yaolin, WANG Yuqi, HAN Zitong, WANG Jie, ZHANG Jun, YU Chenxi. Theoretical Investigation of Volatile Iodine Adsorption onto COF-103. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(1): 20230401.
| Site | Eads/eV | ΔEdisp/eV(proportion) | d(I—I)/nm | d(I—C)/nm | d(I—B)/nm | d(I—O)/nm | d(I—Si)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | -0.70 | -0.32(46%) | 0.269 | 0.337/0.425 | 0.452/0.575 | ||
| PBC | -0.66 | -0.29(44%) | 0.269 | 0.398 | 0.382 | 0.397/0.399 | |
| PBO | -0.63 | -0.26(41%) | 0.268 | 0.369 | 0.387 | ||
| PCC | -0.63 | -0.29(46%) | 0.268 | 0.397/0.399/0.405 | |||
| VB | -0.69 | -0.22(32%) | 0.271 | 0.315 | 0.335 | 0.383/0.387 | |
| VC1 | -0.72 | -0.25(35%) | 0.271 | 0.321/0.331/0.365 | 0.367 | ||
| VC2 | -0.74 | -0.27(36%) | 0.271 | 0.318/0.322 | |||
| VO | -0.61 | -0.21(34%) | 0.269 | 0.360/0.366 | 0.324 |
Table 1 Adsorption energies(Eads), dispersion energy(ΔEdisp) and structural parameters(d) of stable adsorption configurations at different sites
| Site | Eads/eV | ΔEdisp/eV(proportion) | d(I—I)/nm | d(I—C)/nm | d(I—B)/nm | d(I—O)/nm | d(I—Si)/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | -0.70 | -0.32(46%) | 0.269 | 0.337/0.425 | 0.452/0.575 | ||
| PBC | -0.66 | -0.29(44%) | 0.269 | 0.398 | 0.382 | 0.397/0.399 | |
| PBO | -0.63 | -0.26(41%) | 0.268 | 0.369 | 0.387 | ||
| PCC | -0.63 | -0.29(46%) | 0.268 | 0.397/0.399/0.405 | |||
| VB | -0.69 | -0.22(32%) | 0.271 | 0.315 | 0.335 | 0.383/0.387 | |
| VC1 | -0.72 | -0.25(35%) | 0.271 | 0.321/0.331/0.365 | 0.367 | ||
| VC2 | -0.74 | -0.27(36%) | 0.271 | 0.318/0.322 | |||
| VO | -0.61 | -0.21(34%) | 0.269 | 0.360/0.366 | 0.324 |
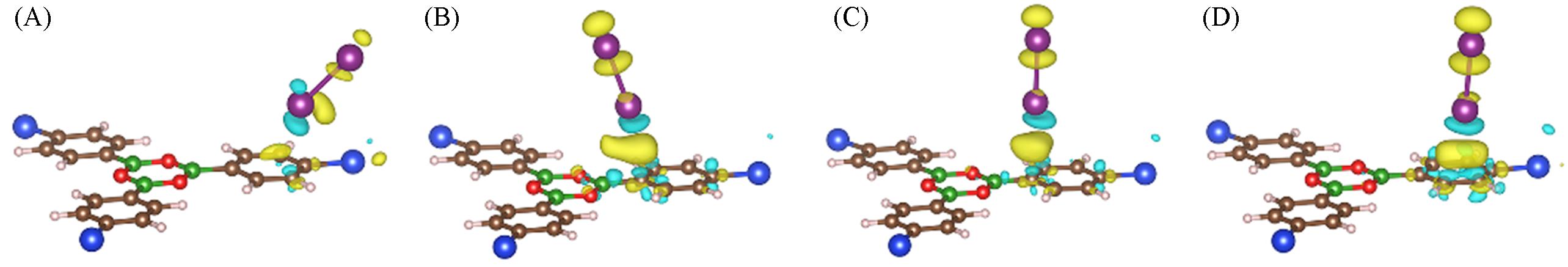
Fig.3 Charge density difference at favorable adsorption sites of S(A), VB(B), VC1(C) and VC2(D)The isosurface value is set as 0.0008 e/Bohr3. I: purple, C: brown, B: green, O: red, H: pink, Si: blue.
| Site | Qads(I1)/e | Qads(I2)/e | ΔQ(I2)/e | ΔQ(COF)/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 6.99 | 7.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| VB | 6.98 | 7.07 | 0.05 | -0.05 |
| VC1 | 6.98 | 7.07 | 0.05 | -0.05 |
| VC2 | 6.99 | 7.08 | 0.07 | -0.07 |
Table 2 Bader charge results(Q and ΔQ) at favorable adsorption sites
| Site | Qads(I1)/e | Qads(I2)/e | ΔQ(I2)/e | ΔQ(COF)/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S | 6.99 | 7.03 | 0.02 | -0.02 |
| VB | 6.98 | 7.07 | 0.05 | -0.05 |
| VC1 | 6.98 | 7.07 | 0.05 | -0.05 |
| VC2 | 6.99 | 7.08 | 0.07 | -0.07 |
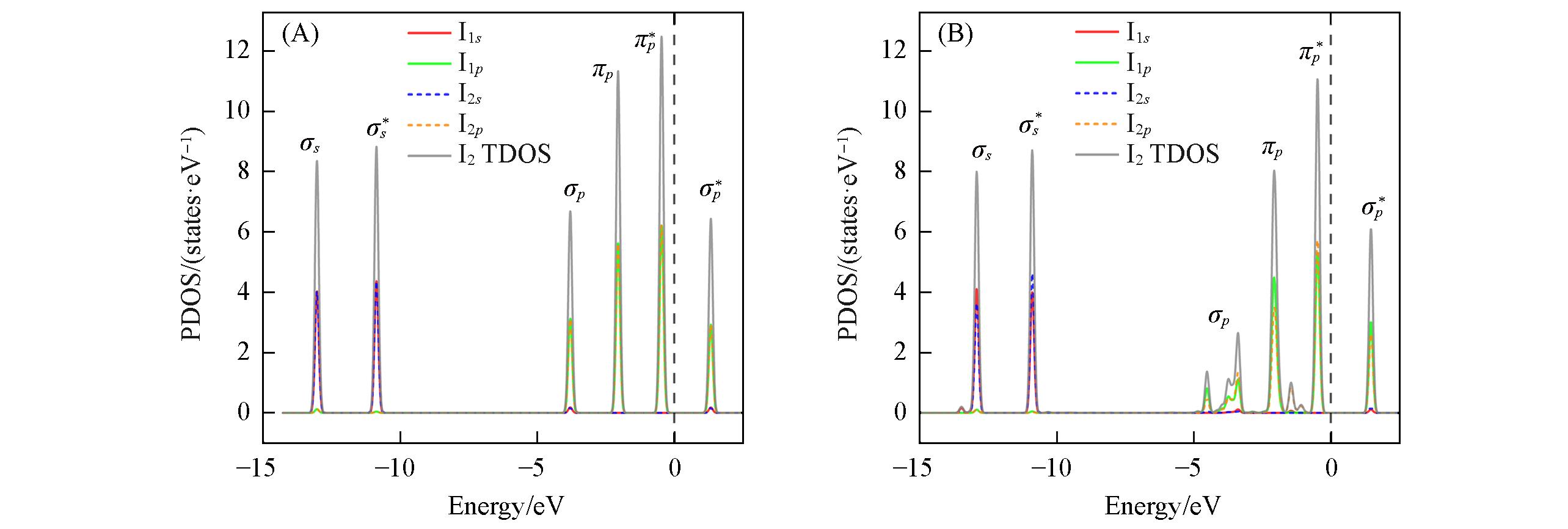
Fig.4 Electronic projected density of states of I2 before(A) and after adsorption(B) onto COF⁃103 at VC2 siteTDOS: the total density of states. The black dash line denotes the Fermi level.
| Contaminant | Eads(B3O3 ring)/eV | Eads(Phenyl ring)/eV | Contaminant | Eads(B3O3 ring)/eV | Eads(Phenyl ring)/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6H6 | -0.74 | -0.72 | C2H6 | -0.56 | -0.59 |
| C2H5OH | -0.65 | -0.60 | Cl2 | -0.55 | -0.56 |
| H2O | -0.57 | -0.61 | NO | -0.48 | -0.54 |
| CH3OH | -0.61 | -0.56 | CO | -0.49 | -0.52 |
| CH3Cl | -0.58 | -0.60 | CH4 | -0.52 | -0.50 |
Table 3 Adsorption energies(Eads) of contaminants at phenyl and B3O3 ring site on COF-103
| Contaminant | Eads(B3O3 ring)/eV | Eads(Phenyl ring)/eV | Contaminant | Eads(B3O3 ring)/eV | Eads(Phenyl ring)/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C6H6 | -0.74 | -0.72 | C2H6 | -0.56 | -0.59 |
| C2H5OH | -0.65 | -0.60 | Cl2 | -0.55 | -0.56 |
| H2O | -0.57 | -0.61 | NO | -0.48 | -0.54 |
| CH3OH | -0.61 | -0.56 | CO | -0.49 | -0.52 |
| CH3Cl | -0.58 | -0.60 | CH4 | -0.52 | -0.50 |
| 1 | Schneider M., Froggatt A., World Nuclear Industry Status Report 2022, A Mycle Schneider Consulting Project, Paris, 2022, 38—39 |
| 2 | Grossman C. M., Nussbaum R. H., Nussbaum F. D., Arch. Environ. Health, 2003, 58(5), 267—274 |
| 3 | Grossman C. M., Nussbaum R. H., Nussbaum F. D., Arch. Environ. Health, 2002, 57(1), 9—15 |
| 4 | Xie W., Cui D., Zhang S. R., Xu Y. H., Jiang D. L., Mater. Horiz., 2019, 6(8), 1571—1595 |
| 5 | Riley B. J., Vienna J. D., Strachan D. M., McCloy J. S., Jerden J. L., J. Nucl. Mater., 2016, 470, 307—326 |
| 6 | Huve J., Ryzhikov A., Nouali H., Lalia V., Augé G., Daou T. J., RSC Adv., 2018, 8(51), 29248—29273 |
| 7 | Li L., Li P. F., Wang B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9), 1917—1932 |
| 李丽, 李鹏飞, 王博. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(9), 1917—1932 | |
| 8 | Geng K., He T., Liu R., Dalapati S., Tan K. T., Li Z., Tao S., Gong Y., Jiang Q., Jiang D., Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(16), 8814—8933 |
| 9 | Wang J. L., Zhuang S. T., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 400, 213046 |
| 10 | He L. W., Chen L., Dong X. L., Zhang S. T., Zhang M. X., Dai X., Liu X. J., Lin P., Li K. F., Chen C. L., Pan T. T., Ma F. Y., Chen J. C., Yuan M. J., Zhang Y. G., Chen L., Zhou R. H., Han Y., Chai Z. F., Wang S. A., Chem, 2021, 7(3), 699—714 |
| 11 | Wang P., Xu Q., Li Z. P., Jiang W. M., Jiang Q. H., Jiang D. L., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(29), 1801991 |
| 12 | Yin Z. J., Xu S. Q., Zhan T. G., Qi Q. Y., Wu Z. Q., Zhao X., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(53), 7266—7269 |
| 13 | Li J. H., Zhang H. X., Zhang L. Y., Wang K., Wang Z. K., Liu G. Y., Zhao Y. L., Zeng Y. F., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2020, 8(19), 9523—9527 |
| 14 | Zhang L. Y., Li J. H., Zhang H. X., Liu Y., Cui Y. M., Jin F. C., Wang K., Liu G. Y., Zhao Y. L., Zeng Y. F., Chem. Commun., 2021, 57(45), 5558—5561 |
| 15 | Pan X. W., Qin X. H., Zhang Q. H., Ge Y. S., Ke H. Z., Cheng G. E., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2020, 296, 109990 |
| 16 | Zhai L. P., Han D. D., Dong J. H., Jiang W. Q., Nie R. M., Yang X. B., Luo X. L., Li Z. P., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2021, 42(13), 2100032 |
| 17 | Xu G. J., Chang J. H., Fang Q. R., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12), 2667—2672 |
| 徐国杰, 常建红, 方千荣. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(12), 2667—2672 | |
| 18 | Lan Y. S., Tong M. M., Yang Q. Y., Zhong C. L., CrystEngComm, 2017, 19(33), 4920—4926 |
| 19 | Tong D. Y., Zhao Y. L., Chen Z. C., Wang Y. Q., Jia Z. Q., Nie X. M., Xiao S. T., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2021, 23(44), 25365—25373 |
| 20 | Jabraoui H., Hessou E. P., Chibani S., Cantrel L., Lebègue S., Badawi M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 485, 56—63 |
| 21 | Chebbi M., Chibani S., Paul J. F., Cantrel L., Badawi M., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2017, 239, 111—122 |
| 22 | Auvinen A., Zilliacus R., Jokiniemi J., Nucl. Technol., 2005, 149(2), 232—241 |
| 23 | Bosland L., Dickinson S., Glowa G. A., Herranz L. E., Kim H. C., Powers D. A., Salay M., Tietze S., Ann. Nucl. Energy, 2014, 74, 184—199 |
| 24 | Yuan Y., Dong X. Q., Chen Y. F., Zhang M. H., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(33), 23246—23256 |
| 25 | Tong D. Y., Zhao Y. L., Wang Y. Q., Nie S. W., Xiao S. T., Comput. Mater. Sci., 2023, 229, 112417 |
| 26 | Kresse G., Furthmüller J., Phys. Rev. B, 1996, 54(16), 11169—11186 |
| 27 | Kresse G., Hafner J., J. Phys.: Condens.Matter, 1994, 6(40), 8245—8257 |
| 28 | Kresse G., Hafner J., Phys. Rev. B, 1994, 49(20), 14251—14269 |
| 29 | Kresse G., Hafner J., Phys. Rev. B, 1993, 47(1), 558—561 |
| 30 | Kresse G., Phys. Rev. B: Condens. Matter Mater. Phys., 1999, 59(3), 1758—1775 |
| 31 | Blöchl P. E., Phys. Rev. B, 1994, 50(24), 17953—17979 |
| 32 | Perdew J. P., Burke K., Ernzerhof M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77(18), 3865—3868 |
| 33 | Hessou E. P., Jabraoui H., Khalil I., Dziurla M. A., Badawi M., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 541, 148515 |
| 34 | Chibani S., Badawi M., Loiseau T., Volkringer C., Cantrel L., Paul J. F., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018, 20(24), 16770—16776 |
| 35 | Chibani S., Chiter F., Cantrel L., Paul J. F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(45), 25283—25291 |
| 36 | Grimme S., Antony J., Ehrlich S., Krieg H., J. Chem. Phys., 2010, 132(15), 154104 |
| 37 | Tong M. M., Lan Y. S., Yang Q. Y., Zhong C. L., Chem. Eng. Sci., 2017, 168, 456—464 |
| 38 | Dubbeldam D., Calero S., Ellis D. E., Snurr R. Q., Mol. Simul., 2016, 42(2), 81—101 |
| 39 | Liu Y. L., Hu C. J., Zhao C. C., Comput. Phys. Commun., 2011, 182(5), 1111—1119 |
| 40 | Chen B., Potoff J. J., Siepmann J. I., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105(15), 3093—3104 |
| 41 | Ongari D., Boyd P. G., Barthel S., Witman M., Haranczyk M., Smit B., Langmuir, 2017, 33(51), 14529—14538 |
| 42 | Willems T. F., Rycroft C. H., Kazi M., Meza J. C., Haranczyk M., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2012, 149(1), 134—141 |
| 43 | El⁃Kaderi H. M., Hunt J. R., Mendoza⁃Cortés J. L., Côté A. P., Taylor R. E., Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2007, 316(5822), 268—272 |
| 44 | Manz T. A., Limas N. G., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(53), 47771—47801 |
| 45 | Limas N. G., Manz T. A., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(51), 45727—45747 |
| 46 | Banerjee D., Chen X., Lobanov S. S., Plonka A. M., Chan X., Daly J. A., Kim T., Thallapally P. K., Parise J. B., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(13), 10622—10626 |
| 47 | Tong D. Y., Zhao Y. L., Chen Z. C., Bo T., Nie S. W., Xiao S. T., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2021, 317, 111017 |
| 48 | Haynes W. M., Bruno T. J., Lide D. R., CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 96th Edition(Internet Version 2016), CRC press/ Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton, Florida, 2016, 949—950 |
| 49 | Zhou G. D., Duan L. Y., Fundamentals of Structural Chemistry(5th Edition), Peking University Press, Beijing, 2017, 354—357 |
| 周公度, 段连运. 结构化学基础(第5版), 北京: 北京大学出版社, 2017, 354—357 | |
| 50 | Tang W., Sanville E., Henkelman G., J. Phys.: Condens.Matter, 2009, 21(8), 084204 |
| 51 | Sanville E., Kenny S. D., Smith R., Henkelman G., J. Comput. Chem., 2007, 28(5), 899—908 |
| 52 | Ubaid M., Aziz A., Pujari B. S., New J. Chem., 2021, 45(28), 12647—12654 |
| 53 | Music D., Schneider J. M., Phys. Rev. B, 2006, 74(17), 174110 |
| 54 | Wang Y. X., Wang C. L., Zhao M. L., Zhang J. L., Chin. Phys. Lett., 2005, 22(2), 469—471 |
| 55 | Hebel W., Cottone G., Management Modes for Iodine⁃129, Harwood Academic Publishers, Luxembourg, 1982, 282—283 |
| 56 | Stull D. R., Ind. Eng. Chem., 1947, 39(4), 517—540 |
| 57 | Zhang Z. Y., Dong X. L., Yin J., Li Z. G., Li X., Zhang D. L., Pan T. T., Lei Q., Liu X. L., Xie Y. Q., Shui F., Li J. L., Yi M., Yuan J., You Z. F., Zhang L. Y., Chang J. H., Zhang H. B., Li W., Fang Q. R., Li B. Y., Bu X. H., Han Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144(15), 6821—6829 |
| 58 | Xie Y. Q., Pan T. T., Lei Q., Chen C. L., Dong X. L., Yuan Y. Y., Maksoud W. A., Zhao L., Cavallo L., Pinnau I., Han Y., Nat. Commun., 2022, 13(1), 2878 |
| 59 | Chen W., Li M., Peng W. L., Huang L., Zhao C., Acharya D., Liu W. T., Zheng A. M., Green Energy Environ., 2022, 7(2), 296—306 |
| 60 | Karavias F., Myers A. L., Langmuir, 1991, 7(12), 3118—3126 |
| [1] | 曹圣哲, 黄欣, 杨志红. 直接Z型In2SSe/Sb范德华异质结光催化水分解的第一性原理研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230145. |
| [2] | 胡平澳, 张琪, 张会茹. 锂硫电池中硒缺陷WSe2催化性能的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220595. |
| [3] | 孔祥宇, 廖力, 卢灿忠, 方千荣. 共价有机框架-杂多酸复合材料用于非均相催化烯烃环氧化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230282. |
| [4] | 王迪, 钟克利, 汤立军, 侯淑华, 吕春欣. 席夫碱共价有机框架的合成及对I ‒ 的识别[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220115. |
| [5] | 王凯旋, 黎子平, 陈先阳, 崔勇. 一种基于二氢吩嗪的三维共价有机框架的合成、 结构与表征[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220210. |
| [6] | 陈铭苏, 张会茹, 张琪, 刘家琴, 吴玉程. 锂硫电池中钴磷共掺杂MoS2催化性能的第一性原理研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2540. |
| [7] | 李义山, 郭亮, 彭思凡, 张庆茂, 张瑜皓, 徐诗淇. 钴掺杂锰酸镧光催化剂的第一性原理与可见光响应光催化性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1881. |
| [8] | 颜艳红, 吴锶敏, 严逸伦, 汤西豪, 蔡松亮, 郑盛润, 章伟光, 顾凤龙. 具有超高阳离子染料去除能力的磺酸功能化球形共价有机框架[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 956. |
| [9] | 颜艳红, 李舒晴, 汤西豪, 郑盛润, 蔡松亮, 章伟光, 顾凤龙. 阳离子共价有机框架对水中非甾体药物的强化去除[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(10): 3091. |
| [10] | 李丽, 李鹏飞, 王博. 共价有机框架材料在光催化领域中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(9): 1917. |
| [11] | 严逸伦, 黄晓玲, 范军, 蔡松亮, 郑盛润, 章伟光. β-酮烯胺类手性共价有机框架的合成及在毛细管气相色谱中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(9): 1996. |
| [12] | 常建红, 徐国杰, 李辉, 方千荣. 基于醌基的共价有机框架用于电催化析氧反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(7): 1609. |
| [13] | 张丹维, 王辉, 黎占亭. 水溶性三维有序超分子和共价有机聚合物[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1139. |
| [14] | 李闪闪, 赵文娟, 李辉, 方千荣. 偶氮苯功能化的光响应共价有机框架材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1384. |
| [15] | 徐国杰, 常建红, 方千荣. 具有高气态碘吸附的二维介孔共价有机框架[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(12): 2667. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||