

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 1480.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200678
李曈1, 谷思辰1, 林乔伟1, 韩俊伟1, 周光敏1,2( ), 李宝华1, 康飞宇1, 吕伟1(
), 李宝华1, 康飞宇1, 吕伟1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-14
出版日期:2021-05-10
发布日期:2020-12-07
通讯作者:
周光敏,吕伟
E-mail:guangminzhou@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn;lv.wei@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Tong1, GU Sichen1, LIN Qiaowei1, HAN Junwei1, ZHOU Guangmin1,2( ), LI Baohua1, KANG Feiyu1, LYU Wei1(
), LI Baohua1, KANG Feiyu1, LYU Wei1( )
)
Received:2020-09-14
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2020-12-07
Contact:
ZHOU Guangmin,LYU Wei
E-mail:guangminzhou@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn;lv.wei@sz.tsinghua.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
随着电化学储能市场的迅猛发展, 当前商用锂离子电池难以满足人们对高能量密度储能器件的需求. 锂金属具有高比容量和低氧化还原电位等优点, 被认为是下一代二次电池的理想负极材料. 然而, 锂金属负极在充放电过程中会出现体积变化大、 枝晶生长、 界面不稳定等问题, 严重阻碍了其在二次电池中的实际应用. 三维多孔材料具有骨架/空间互穿网络结构、 比表面积大、 孔隙发达和机械性能好等物理特性, 用作金属锂负极的集流体, 在锂沉积/溶解过程中可以起到降低局部有效电流密度、 均匀电场分布和降低锂离子浓度梯度的作用, 有望实现锂的均匀成核和无枝晶沉积, 同时抑制了电极的体积膨胀. 尽管有关三维集流体的研究报道不断出现, 但综合系统评价现有各种三维集流体体系的工作鲜见报道. 本文聚焦锂金属负极三维集流体的构建及应用研究进展, 首先分析了三维集流体抑制锂枝晶生长的基本原理及局限性, 继而重点关注了三维集流体的结构调控、 表面改性和功能化等应对策略对锂成核、 沉积过程的影响, 并对不同材质三维集流体的优缺点进行了归纳总结. 最后, 面向实用化, 分析并展望了三维集流体应用于锂金属电池的发展前景.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李曈, 谷思辰, 林乔伟, 韩俊伟, 周光敏, 李宝华, 康飞宇, 吕伟. 基于三维集流体的无枝晶锂金属负极. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5): 1480.
LI Tong, GU Sichen, LIN Qiaowei, HAN Junwei, ZHOU Guangmin, LI Baohua, KANG Feiyu, LYU Wei. Advanced 3D Current Collectors for Dendrite-free Lithium Metal Anode. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1480.
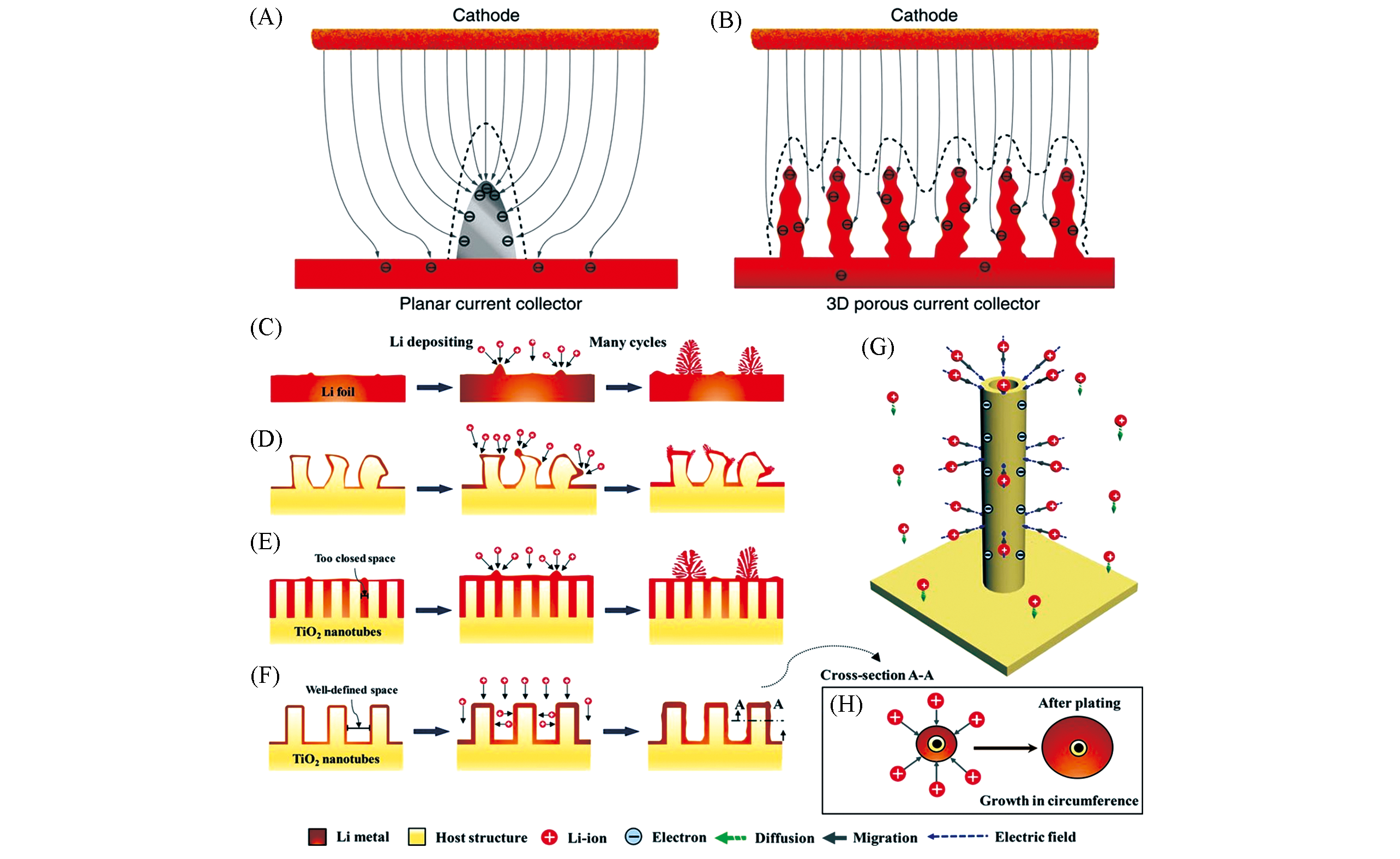
Fig.2 Schematic of the proposed electrochemical deposition processes of Li metal on planar current collector(A) and 3D current collector(B)[9], the proposed electrochemical deposition processes of Li metal on Li foil(C), vertically aligned structure with nonuniform surface curvature(D), closed Li nanotubes(E), and spaced Li nanotubes(F), 3D schematic of Li?ion transport under the influence of diffusion and the uniform electrostatic forces(G) and 2D cross?section of a Li nanotube illustrating the unique electrodeposition manner(H)[21](A, B) Copyright 2015, Nature Publishing Group. (C―H) Copyright 2020, Wiley?VCH.
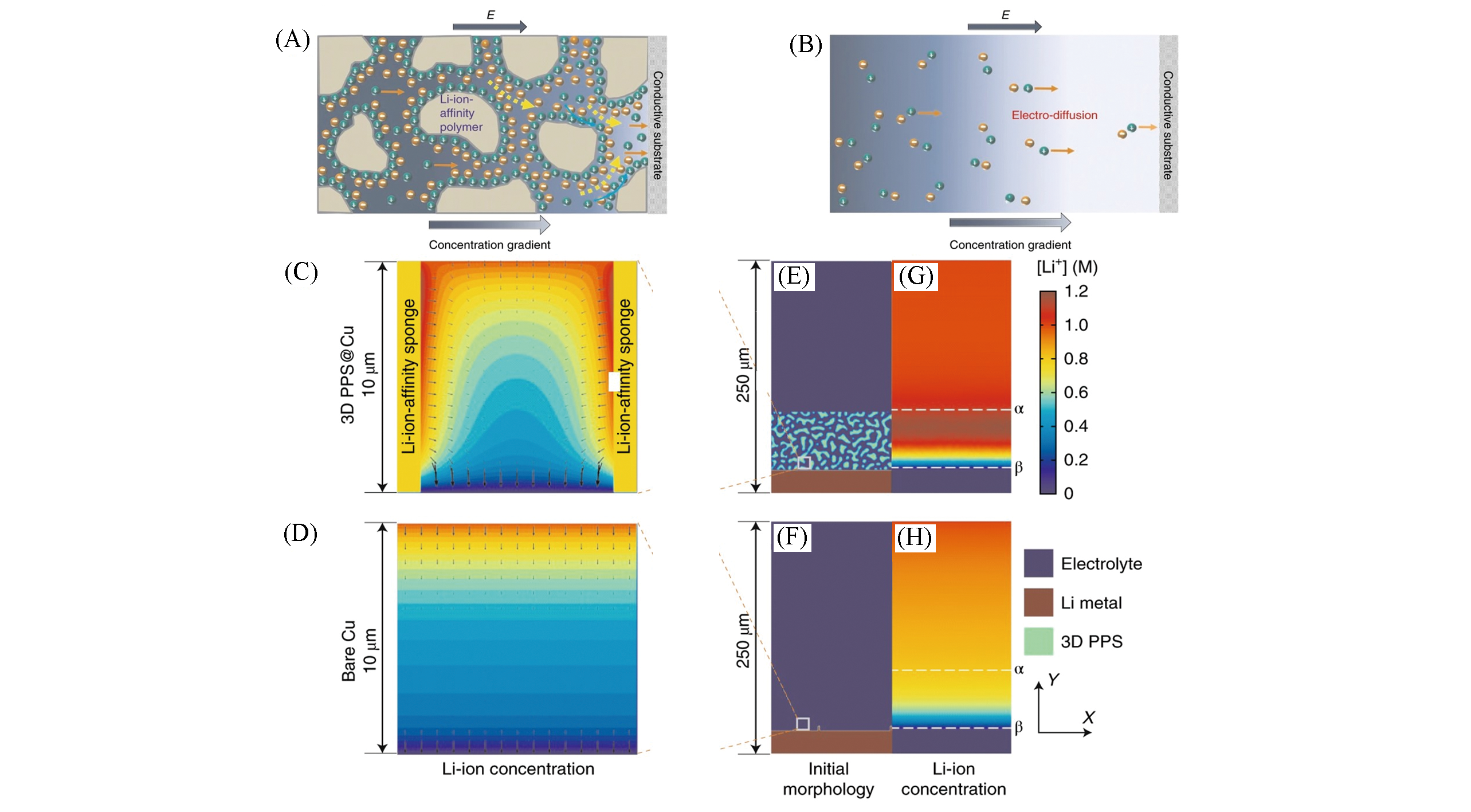
Fig.3 Electrokinetic phenomena in 3D PPS under an electric field(A), electrodiffusion of Li ions in traditional cells under an electric field(B), equilibrium Li?ion concentration profiles with constant?reaction?current electrode surfaces at the enlarged 10 μm×10 μm sponge?pore scale for the 3D PPS@Cu(C) and bare Cu electrodes(D), initial phase morphologies of the 250 μm×250 μm 3D PPS@Cu(E) and bare Cu half?cell systems(F), equilibrium Li?ion concentration profiles with constant?reaction?current electrode surfaces at the 250 μm×250 μm scale for the 3D PPS@Cu(G) and bare Cu electrodes(H)[24]Copyright 2018, Springer Nature.
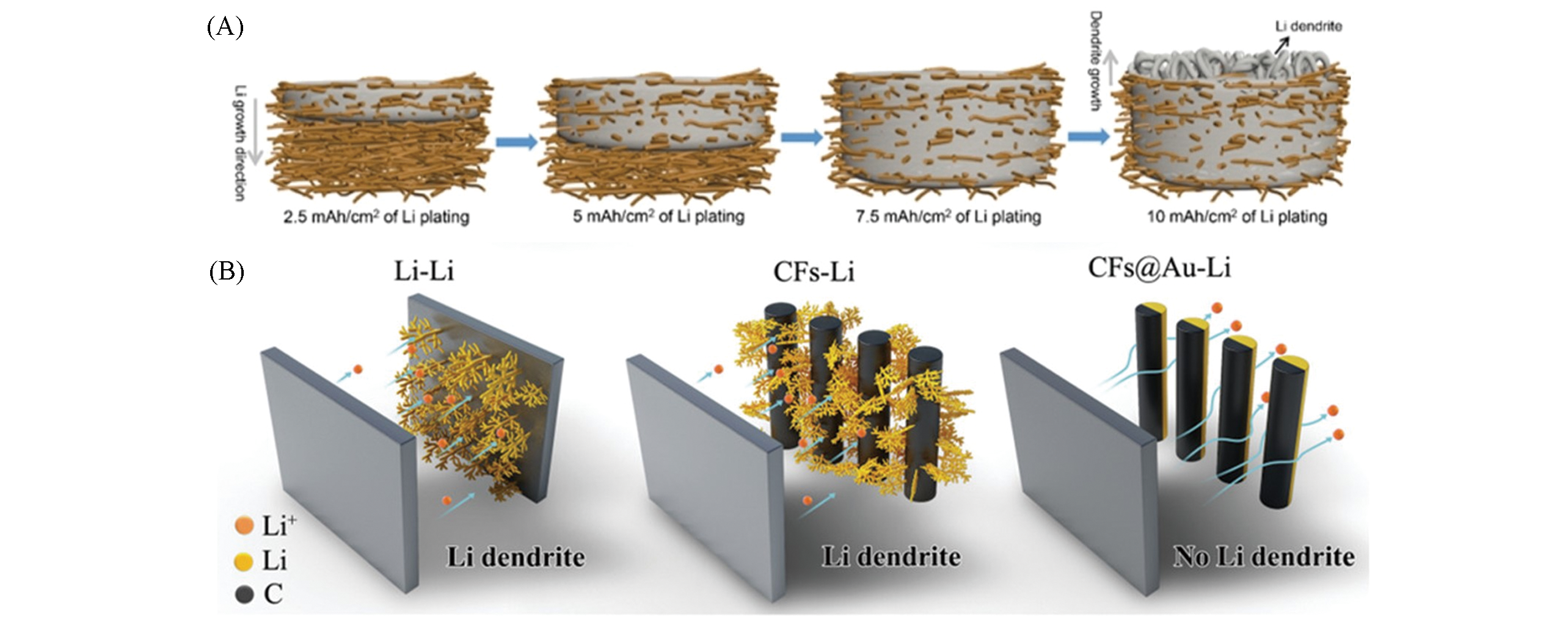
Fig.4 Schematic of the lithium plating direction(A) The top?bottom growth models[26]; (B) selective deposition of Li ions on the back side of the carbon fibers matrix[30].(A) Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2018, Wiley?VCH.
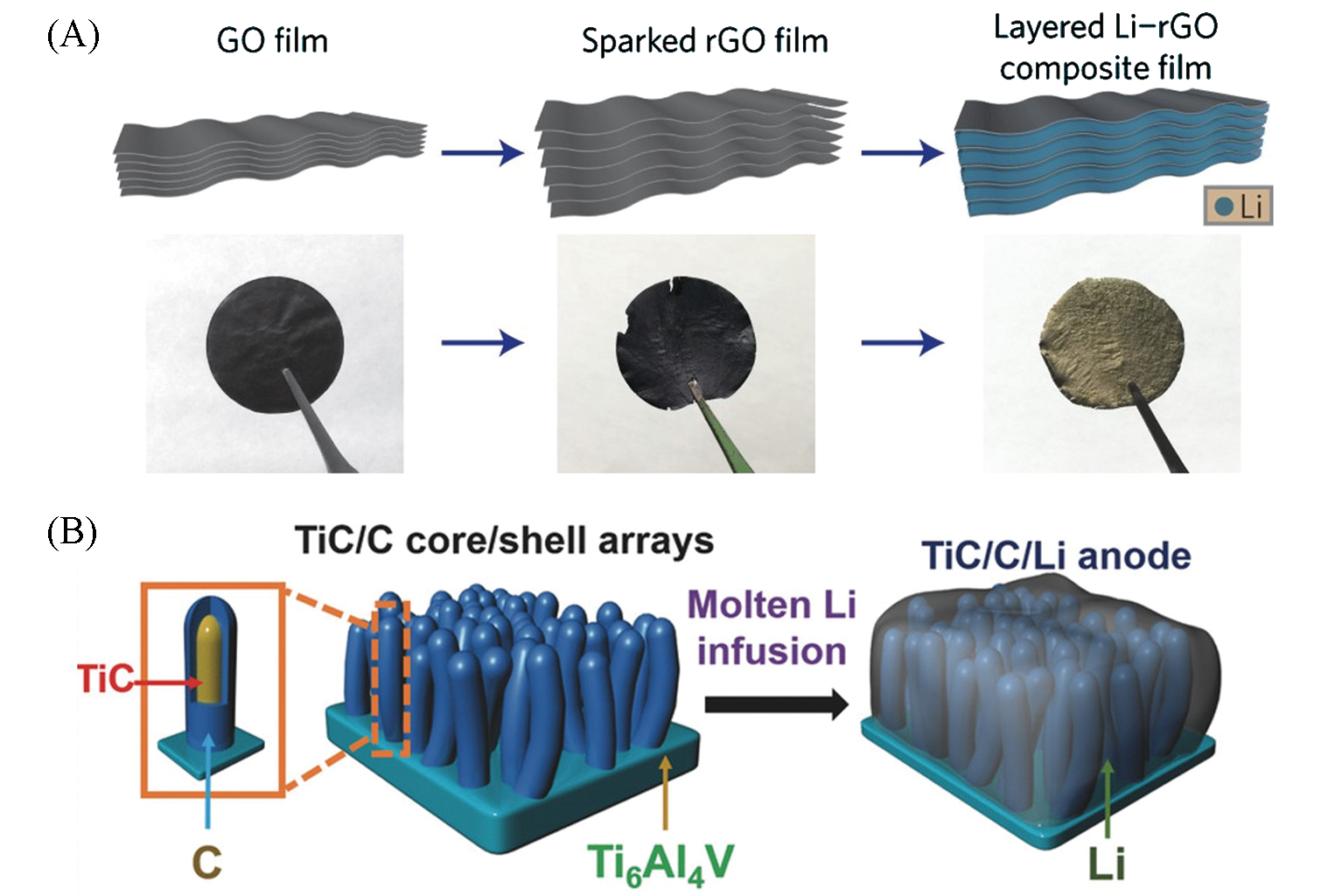
Fig.5 Schematic of the fabrication process of Li/C composite anode: (A) Li?rGO[35], (B) Ti/C?Li[36](A) Copyright 2016, Nature Publishing Group; (B) Copyright 2017, Wiley?VCH.
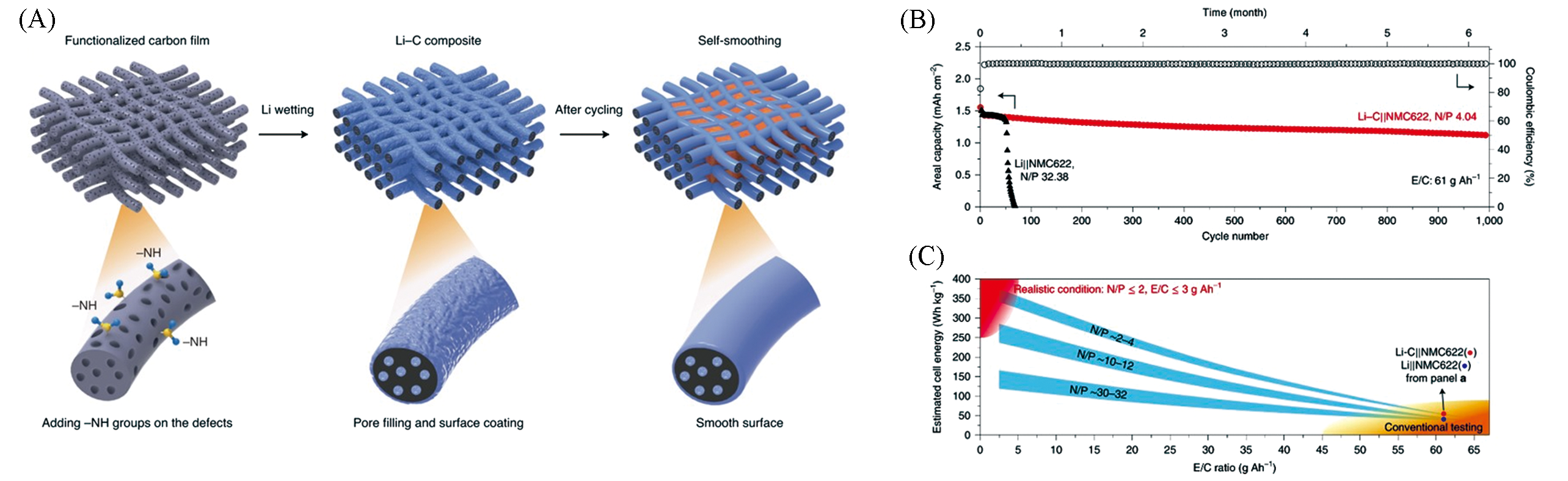
Fig.7 Schematic of self?smoothing behaviour in the lithium?carbon film anode(A) and traditional test of Li?C||NMC622 cell(B, C)[63]Copyright 2019, Nature Publishing Group.
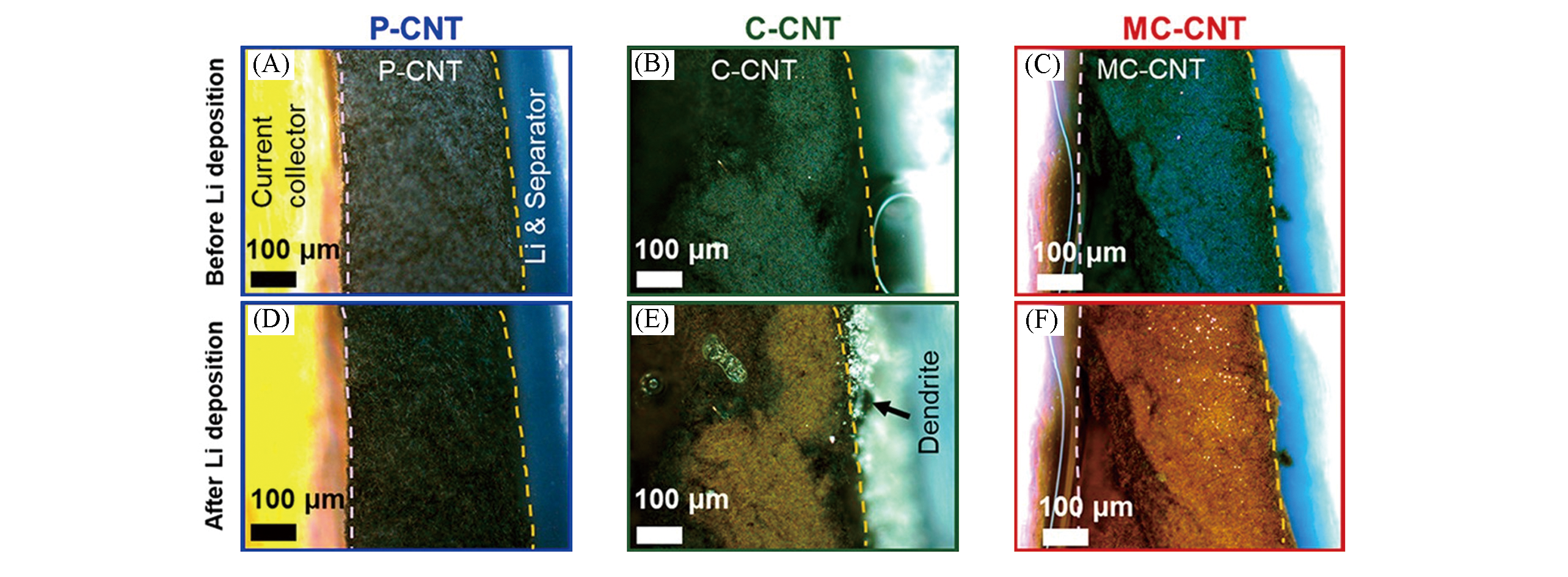
Fig.8 In?operando optical micrographs of P?CNT(A, D), C?CNT(B, E), and MC?CNT(C, F) at the beginning and end of Li insertion processes[65]Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
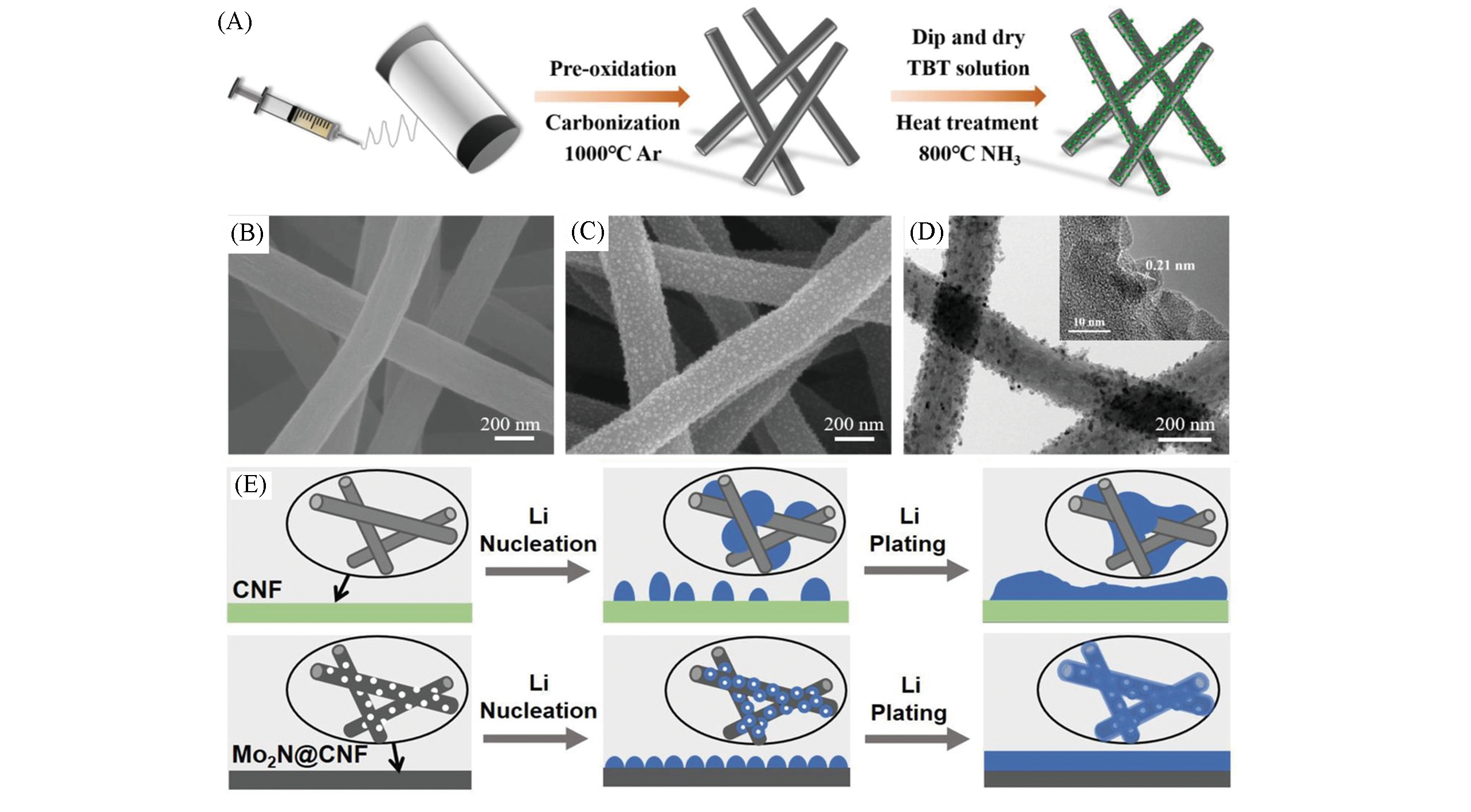
Fig.9 Schematic of the fabrication process of CNF?TiN(A), SEM images of bare CNF(B), CNF?TiN(C) and TEM image of CNF?TiN(D)[67], schematic of the lithium nucleation and deposition process on the bare CNF and Mo2N@CNF(E)[68](A―D) Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH; (E) Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH.
| Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/(mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au@hollow carbon sphere | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 300, 98% | — | — | [ |
Li4.4Sn@hollow graphene spheres | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 150, 97.5% | 1, 1, 600 | LiFePO4(12 mg/cm2), 1C, 100 | [ |
S?doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 220, 97.5% | 0.5, 1, 1600 | LiFePO4, 1C, 300 | [ |
Nitrogen?doped graphitic carbon foams | Electrochemical plating | 2, 2, 300, 99.6% | 2, 1, 200 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 200 | [ |
Hierarchical silver?nanowire? graphene host | Electrochemical plating | — | 40, 1, 1000 | NMC, 10C, 1000 | [ |
| Co@cMOF | Electrochemical plating | 10, 1, 130, 91.5% | 1, 1, 1000 | NMC, 1C, 100 | [ |
| Zn@cMOF | Electrochemical plating | — | 0.2, 0.2, 350 | — | [ |
| Zn@cMOF | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 700 | — | [ |
| Carbon nanotube sponge | Electrochemical plating | 1, 2, 90, 98.5% | — | — | [ |
| Graphite microtubes | Electrochemical plating | 5, 10, 100, 97.5% | 1, 10, 3000 | LiFePO4(2.0 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 1000 | [ |
| Hollow carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 2, 350, 99.5%; 1, 6, 75, 99% | 2, 1, 600 | LiFePO4, 0.2, 150 | [ |
| Carbon nanotube paper | Molten lithium infusion/Electrochemical plating | — | 2, 9.5, 3000 | LiFePO4, 1 mA/cm2, 1000 | [ |
| Layered Li?rGO composite film | Molten lithium infusion | — | 3, 1, >100 | — | [ |
| Nitrogen?doped graphene | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 727 | LiFePO4, 0.2C, 500 | [ |
| Ag@carbon fiber paper | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 2, 110, 98% | — | — | [ |
Vertically grown edge?rich graphene nanosheets@ carbon fiber | Molten lithium infusion | — | 0.5, 1, 1000 | LiFePO4, 1C, 1000 | [ |
| Lithiophilic carbon film | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 600 | Mg/Ti-LiNiO2, 0.2C, 50 | [ |
| Si@carbon fiber | Molten lithium infusion | — | 3, 1, >80 | — | [ |
| Graphitized carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 8, 50, 98% | 2, 1, 170 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 800 | [ |
| TiN@ carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 3, 1, 200, 96.8% | 1, 1, 600 | LiFePO4, 1C, 250 | [ |
| Mo2N@ carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 4, 3, 150, 99.2% | 6, 6, 1500 | NMC811, 3C, 150 | [ |
| Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/(mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Reference |
| Amine?functionalized meso? porous carbon nanofibres | Molten lithium infusion | — | — | NMC622, 353 W·h/kg; NMC811, 381 W·h/kg | [ |
Gradient?distributed ZnO@ carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 0.5, 700,98.1% | 0.5, 0.5, 1400 | LiFePO4, 1C, 300 | [ |
Au modification on one side of the carbon fibers matrix | Electrochemical plating | 2, 4, 99.0%, 400; 5, 5, 98.0%, 100 | 1, 2, 700 | Li—S(2.0 mA·h/cm2), 0.1C, 100(672 mA·h/g) | [ |
Au modification on one side of the carbon fiber paper | Electrochemical plating | 2, 30, 98.7% | 10, 30, 1000 | Li—S(4.0 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 200(933 mA·h/g) | [ |
| LiF@carbonized eggplant | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 2.2, 100, 99.1% | 1, 3, 250 | LiCoO?, 0.2C, 80 | [ |
| ZnO@carbonized wood | Molten lithium infusion | — | 3, 1, 225 | — | [ |
ZnO quantum dots@ carbonized bamboo | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 200, 96.8% | — | LiCoO2, 0.5C, 160 | [ |
表1 分析比较了三维碳基集流体用于锂金属负极的电化学性能.
Table 1 Cycling performance comparison of different 3D carbon-based current collectors
| Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/(mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au@hollow carbon sphere | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 300, 98% | — | — | [ |
Li4.4Sn@hollow graphene spheres | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 150, 97.5% | 1, 1, 600 | LiFePO4(12 mg/cm2), 1C, 100 | [ |
S?doped mesoporous carbon nanospheres | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 220, 97.5% | 0.5, 1, 1600 | LiFePO4, 1C, 300 | [ |
Nitrogen?doped graphitic carbon foams | Electrochemical plating | 2, 2, 300, 99.6% | 2, 1, 200 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 200 | [ |
Hierarchical silver?nanowire? graphene host | Electrochemical plating | — | 40, 1, 1000 | NMC, 10C, 1000 | [ |
| Co@cMOF | Electrochemical plating | 10, 1, 130, 91.5% | 1, 1, 1000 | NMC, 1C, 100 | [ |
| Zn@cMOF | Electrochemical plating | — | 0.2, 0.2, 350 | — | [ |
| Zn@cMOF | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 700 | — | [ |
| Carbon nanotube sponge | Electrochemical plating | 1, 2, 90, 98.5% | — | — | [ |
| Graphite microtubes | Electrochemical plating | 5, 10, 100, 97.5% | 1, 10, 3000 | LiFePO4(2.0 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 1000 | [ |
| Hollow carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 2, 350, 99.5%; 1, 6, 75, 99% | 2, 1, 600 | LiFePO4, 0.2, 150 | [ |
| Carbon nanotube paper | Molten lithium infusion/Electrochemical plating | — | 2, 9.5, 3000 | LiFePO4, 1 mA/cm2, 1000 | [ |
| Layered Li?rGO composite film | Molten lithium infusion | — | 3, 1, >100 | — | [ |
| Nitrogen?doped graphene | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 727 | LiFePO4, 0.2C, 500 | [ |
| Ag@carbon fiber paper | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 2, 110, 98% | — | — | [ |
Vertically grown edge?rich graphene nanosheets@ carbon fiber | Molten lithium infusion | — | 0.5, 1, 1000 | LiFePO4, 1C, 1000 | [ |
| Lithiophilic carbon film | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 600 | Mg/Ti-LiNiO2, 0.2C, 50 | [ |
| Si@carbon fiber | Molten lithium infusion | — | 3, 1, >80 | — | [ |
| Graphitized carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 8, 50, 98% | 2, 1, 170 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 800 | [ |
| TiN@ carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 3, 1, 200, 96.8% | 1, 1, 600 | LiFePO4, 1C, 250 | [ |
| Mo2N@ carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 4, 3, 150, 99.2% | 6, 6, 1500 | NMC811, 3C, 150 | [ |
| Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/(mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Reference |
| Amine?functionalized meso? porous carbon nanofibres | Molten lithium infusion | — | — | NMC622, 353 W·h/kg; NMC811, 381 W·h/kg | [ |
Gradient?distributed ZnO@ carbon fibers | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 0.5, 700,98.1% | 0.5, 0.5, 1400 | LiFePO4, 1C, 300 | [ |
Au modification on one side of the carbon fibers matrix | Electrochemical plating | 2, 4, 99.0%, 400; 5, 5, 98.0%, 100 | 1, 2, 700 | Li—S(2.0 mA·h/cm2), 0.1C, 100(672 mA·h/g) | [ |
Au modification on one side of the carbon fiber paper | Electrochemical plating | 2, 30, 98.7% | 10, 30, 1000 | Li—S(4.0 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 200(933 mA·h/g) | [ |
| LiF@carbonized eggplant | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 2.2, 100, 99.1% | 1, 3, 250 | LiCoO?, 0.2C, 80 | [ |
| ZnO@carbonized wood | Molten lithium infusion | — | 3, 1, 225 | — | [ |
ZnO quantum dots@ carbonized bamboo | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 200, 96.8% | — | LiCoO2, 0.5C, 160 | [ |
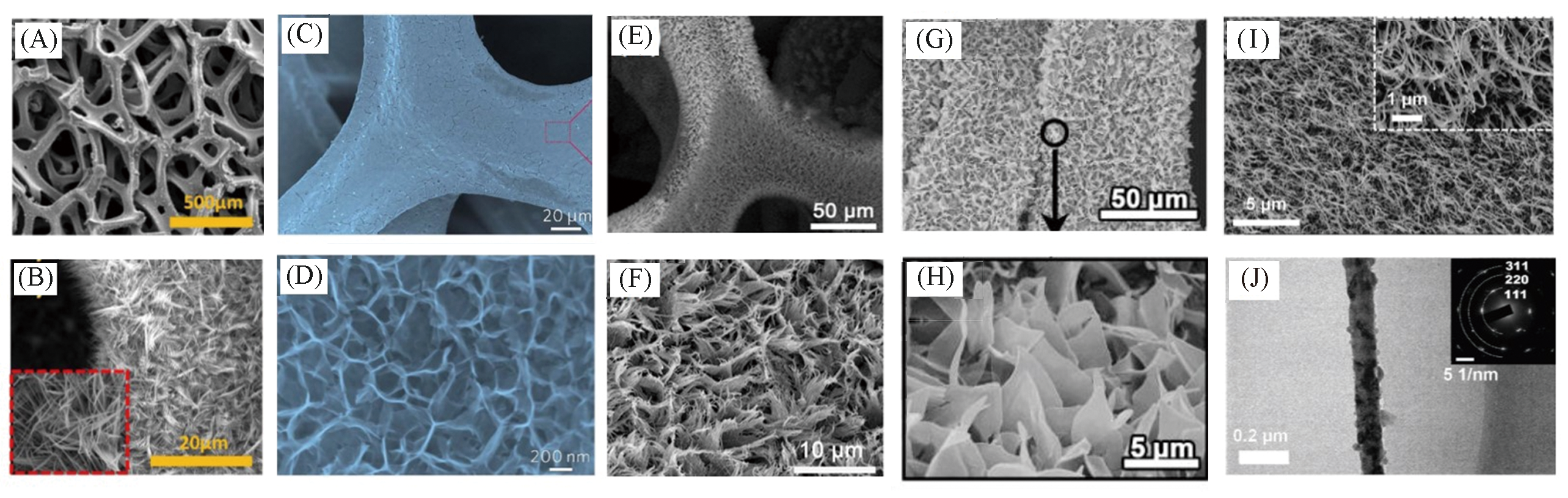
Fig.10 SEM images of nanofiber@Ni foam(A, B)[40], nanowall@Cu foam(C, D)[82], nanobrush@Ni foam(E, F)[81], nanosheets@Ni foam(G, H)[83]; SEM(I) and TEM(J) images of Cu?CuO?Ni[84](A, B) Copyright 2018, Elsevier; (C, D) Copyright 2019, The Royal Society of Chemistry; (E, F) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society; (G, H) Copyright 2019, Elsevier; (I, J) Copyright 2018, Wiley?VCH.
| Metal?base | Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/ (mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal foam | Cu2S nanowire@Cu foam | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 500, 99.2%; 4, 4, 100, 98% | — | LiFePO4(6.0 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 300 | [ |
| Cu nanowire@Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | — | 10, 1, 200 | LiFePO4(7.5 mg/cm2), 2C, 400 | [ | |
Cu nanowire@Li2O@ Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 300, 98.5%; 2, 2, 100, 93% | 3, 1, 600 | LiFePO4, 1C, 500 | [ | |
| CuON nanoarray@Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | 0.5, 1, 200, 98.8%; 2, 1, 100, >98% | 2, 1, 2100 | LiFePO4, 2C, 300 | [ | |
| CoO nanofiber@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 130 | NCA, 4C, 500 | [ | |
| Co3N nanobrush@Ni foam | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 200, 98.3% | 0.5, 1, 1600 | LiFePO4(2.5 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 600 | [ | |
Nitrogen?doped graphdiyne nanowall@Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 250, 98%; 5, 1, 150, 99.6%; 1, 5, 70, >99% | 1, 1, 719 | NCM, 0.2C, 440 | [ | |
Vertically aligned ZnO nanosheets@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 150, 98.5% | 1, 1, 400; 5, 1, 250 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 100 | [ | |
| Cu?CuO@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 250, >95%; 3, 1, 100, >90% | 0.5, 0.5, 580 | — | [ | |
CuBr? and Br?doped graphene?like film@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 2, 2, 300, 98.9% | 1, 1, 850 | LiFePO4(20.3 mg/cm2), 0.7 mA/cm2, 200 | [ | |
| Metal?base | Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/ (mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Ref. |
Restructured rimous Cu foam | Electrochemical plating | 3, 1, 220, 98.8% | 3, 1, 200 | LiFePO4, 1C, 330 | [ | |
| g?C3N4@Ni foam | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 300, 98%; 1, 2, 140, 97% | 1, 1, 900 | LiCoO2, 1C, 200 | [ | |
| AuLi3@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 0.5, 1, 98%, 100 | 0.5, 1, 740 | LiFePO4, 1C, 500 | [ | |
Compact porous Cu | 3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 140, >97% | 0.2, 1, 1000 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 300 | [ |
| Compact 3D Cu | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 200, 97.9% | 1, 1, 400 | LiFePO4, 1C, 350 | [ | |
| 3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 250, >98% | 1, 1, 800 | LiFePO4, 2C, 200 | [ | |
| 3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.52, 0.26, 120, ca. 81% | 0.52, 0.26, 120 | NCM, 50 mA/g, 300 | [ | |
| Zn@3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 220, 95% | 1, 1, 450 | — | [ | |
N?doped graphene@ compact porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 4, 100, 97.8% | — | LiFePO4(6.4 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 100 | [ | |
Cu mesh | Cu mesh | Mechanical press/ Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 100, 97.5% | 0.5, 1, 230 | Li4Ti5O12, 4C, 500 | [ |
| U?LDH?O@Cu mesh | Electrochemical plating | 1, 6, 80, >95% | 2, 1, 200 | — | [ | |
Faceted Cu(100)@Cu mesh | Electrochemical plating | 4, 1, 400, 97% | 2, 1, 300 | LiFePO4, 1C, 120 | [ | |
| Cu nanowires network | Electrochemical plating | 1, 2, 200, 98.6% (Average) | 1, 2, 550 | LiCoO2, 5C, 100 | [ | |
Cu nanowires | Cu nanowire network with phosphidation gradient | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 150, 97.4% | 1, 1, 1000 | LiFePO4(3 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 300 | [ |
| Cu3P nanowires | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 200, 98% | 2, 2, 450 | LiFePO4(9.4 mg/cm2), 1C, 700 | [ |
Table 2 Cycling performance comparison of different 3D metal-based current collectors
| Metal?base | Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/ (mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Metal foam | Cu2S nanowire@Cu foam | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 500, 99.2%; 4, 4, 100, 98% | — | LiFePO4(6.0 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 300 | [ |
| Cu nanowire@Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | — | 10, 1, 200 | LiFePO4(7.5 mg/cm2), 2C, 400 | [ | |
Cu nanowire@Li2O@ Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 300, 98.5%; 2, 2, 100, 93% | 3, 1, 600 | LiFePO4, 1C, 500 | [ | |
| CuON nanoarray@Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | 0.5, 1, 200, 98.8%; 2, 1, 100, >98% | 2, 1, 2100 | LiFePO4, 2C, 300 | [ | |
| CoO nanofiber@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | — | 1, 1, 130 | NCA, 4C, 500 | [ | |
| Co3N nanobrush@Ni foam | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 200, 98.3% | 0.5, 1, 1600 | LiFePO4(2.5 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 600 | [ | |
Nitrogen?doped graphdiyne nanowall@Cu foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 250, 98%; 5, 1, 150, 99.6%; 1, 5, 70, >99% | 1, 1, 719 | NCM, 0.2C, 440 | [ | |
Vertically aligned ZnO nanosheets@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 150, 98.5% | 1, 1, 400; 5, 1, 250 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 100 | [ | |
| Cu?CuO@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 250, >95%; 3, 1, 100, >90% | 0.5, 0.5, 580 | — | [ | |
CuBr? and Br?doped graphene?like film@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 2, 2, 300, 98.9% | 1, 1, 850 | LiFePO4(20.3 mg/cm2), 0.7 mA/cm2, 200 | [ | |
| Metal?base | Current collector | Method for loading lithium | Half cell performance [current density/ (mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h, CE] | Symmetry cell performance [current density/(mA·cm-2), areal capacity/ (mA·h·cm-2), cycle number/h] | Full cell performance (cathode, rate performance and lifespan) | Ref. |
Restructured rimous Cu foam | Electrochemical plating | 3, 1, 220, 98.8% | 3, 1, 200 | LiFePO4, 1C, 330 | [ | |
| g?C3N4@Ni foam | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 300, 98%; 1, 2, 140, 97% | 1, 1, 900 | LiCoO2, 1C, 200 | [ | |
| AuLi3@Ni foam | Molten lithium infusion | 0.5, 1, 98%, 100 | 0.5, 1, 740 | LiFePO4, 1C, 500 | [ | |
Compact porous Cu | 3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 140, >97% | 0.2, 1, 1000 | LiFePO4, 0.5C, 300 | [ |
| Compact 3D Cu | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 200, 97.9% | 1, 1, 400 | LiFePO4, 1C, 350 | [ | |
| 3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 250, >98% | 1, 1, 800 | LiFePO4, 2C, 200 | [ | |
| 3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.52, 0.26, 120, ca. 81% | 0.52, 0.26, 120 | NCM, 50 mA/g, 300 | [ | |
| Zn@3D porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 220, 95% | 1, 1, 450 | — | [ | |
N?doped graphene@ compact porous Cu | Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 4, 100, 97.8% | — | LiFePO4(6.4 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 100 | [ | |
Cu mesh | Cu mesh | Mechanical press/ Electrochemical plating | 0.5, 1, 100, 97.5% | 0.5, 1, 230 | Li4Ti5O12, 4C, 500 | [ |
| U?LDH?O@Cu mesh | Electrochemical plating | 1, 6, 80, >95% | 2, 1, 200 | — | [ | |
Faceted Cu(100)@Cu mesh | Electrochemical plating | 4, 1, 400, 97% | 2, 1, 300 | LiFePO4, 1C, 120 | [ | |
| Cu nanowires network | Electrochemical plating | 1, 2, 200, 98.6% (Average) | 1, 2, 550 | LiCoO2, 5C, 100 | [ | |
Cu nanowires | Cu nanowire network with phosphidation gradient | Electrochemical plating | 1, 1, 150, 97.4% | 1, 1, 1000 | LiFePO4(3 mg/cm2), 0.5C, 300 | [ |
| Cu3P nanowires | Molten lithium infusion | 1, 1, 200, 98% | 2, 2, 450 | LiFePO4(9.4 mg/cm2), 1C, 700 | [ |
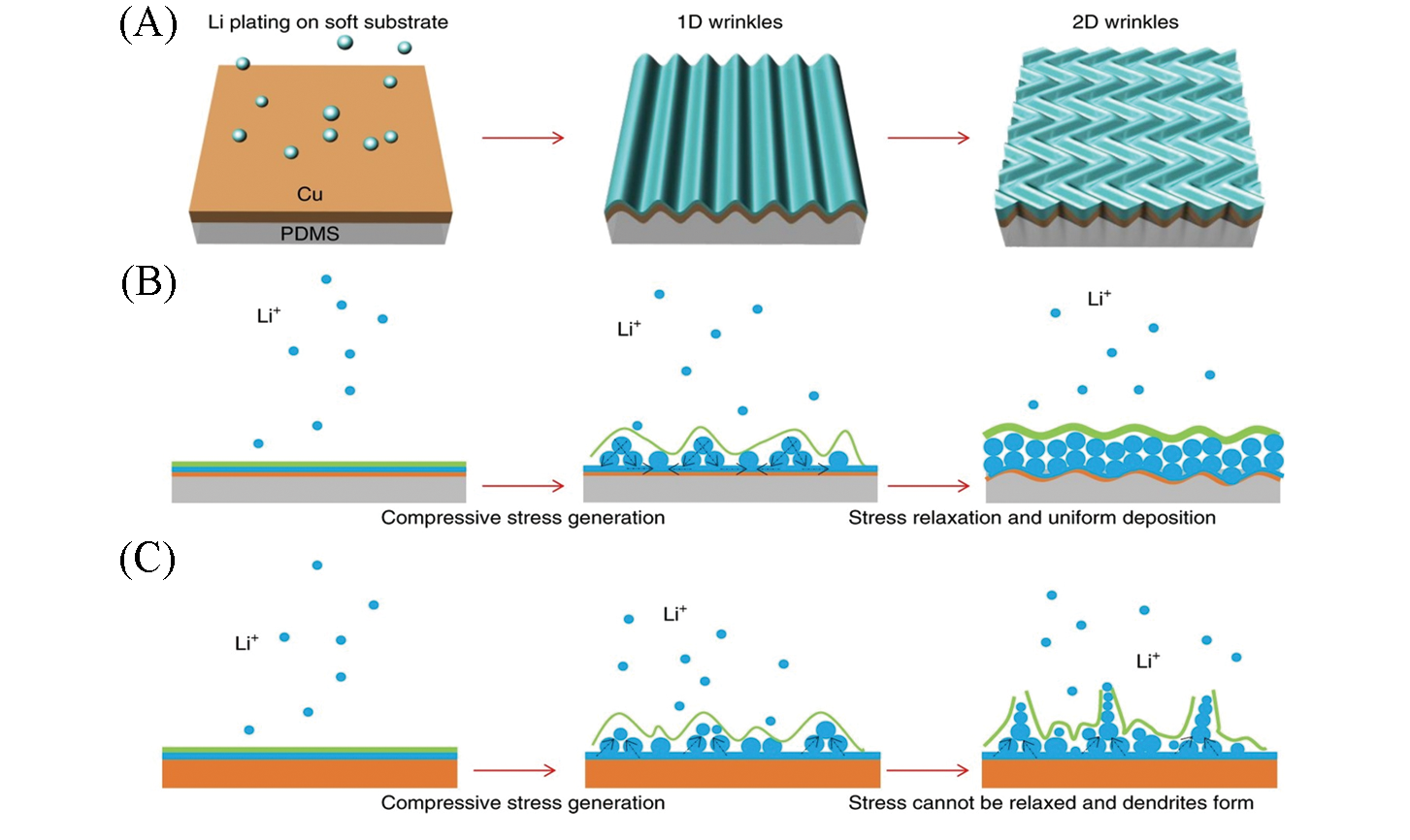
Fig.14 Schematic illustration of Cu thin film wrinkles due to the compressive stress generated during Li plating(A), upon Li electroplating, compressive stress is generated, and soft substrate releases compressive stress, and thus mitigates Li dendrite growth(B), Li?plating?induced compressive stress cannot be relaxed on hard Cu foil, and causes the formation of Li dendrites(C)[110]Copyright 2018, Springer Nature.
| 1 | Cheng X. B., Zhang R., Zhao C. Z., Zhang Q., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(15), 10403―10473 |
| 2 | Qian J., Henderson W. A., Xu W., Bhattacharya P., Engelhard M., Borodin O., Zhang J., Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 6362 |
| 3 | He X., Liu X., Han Q., Zhang P., Song X., Zhao Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(16), 6397―6405 |
| 4 | Cha E., Patel M. D., Park J., Hwang J., Prasad V., Cho K., Choi W., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13(4), 337―344 |
| 5 | Zhao Y., Ye Y., Wu F., Li Y., Li L., Chen R., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(12), e1806532 |
| 6 | Liu Y., Lin D., Yuen P. Y., Liu K., Xie J., Dauskardt R. H., Cui Y., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(10), 1605531 |
| 7 | Liu S., Xia X., Deng S., Xie D., Yao Z., Zhang L., Zhang S., Wang X., Tu J., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(3), e1806470 |
| 8 | Liu Y., Lin D., Liang Z., Zhao J., Yan K., Cui Y., Nat. Commun., 2016, 7, 10992 |
| 9 | Yang C., Yin Y., Zhang S., Li N. , Guo Y., Nat. Commun., 2015, 6, 8058 |
| 10 | Li G., Gao Y., He X., Huang Q., Chen S., Kim S. H., Wang D., Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 850 |
| 11 | Zheng J., Engelhard M. H., Mei D., Jiao S., Polzin B. J., Zhang J. G., Xu W., Nat. Energy, 2017, 2(3), 17012 |
| 12 | Zhang X., Wang S., Xue C., Xin C., Lin Y., Shen Y., Li L., Nan C. W., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(11), e1806082 |
| 13 | Zhou D., Tkacheva A., Tang X., Sun B., Shanmukaraj D., Li P., Zhang F., Armand M., Wang G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(18), 6001―6006 |
| 14 | Cohen Y. S., Cohen. Y., Aurbach. D., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104, 12282―12291 |
| 15 | Jun⁃ichi Y., Shin⁃ichi T., Katsuya H., Keiichi S., Yasue N., Masayasu A., J. Power Sources, 1998, 74, 219―227 |
| 16 | Sand H. J. S., Philos. Mag., 2010, 1(1), 45―79 |
| 17 | Rosso M., Brissot C., Teyssot A., Dollé M., Sannier L., Tarascon J. M., Bouchet R., Lascaud S., Electrochim. Acta, 2006, 51(25), 5334―5340 |
| 18 | Cheng X., Zhang R., Zhao C., Zhang Q., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(15), 10403―10473 |
| 19 | Jin S., Jiang Y., Ji H., Yu Y., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(48), e1802014 |
| 20 | Lee B., Paek E., Mitlin D., Lee S. W., Chem. Rev., 2019, 119(8), 5416―5460 |
| 21 | Tantratian K., Cao D., Abdelaziz A., Sun X., Sheng J., Natan A., Chen L., Zhu H., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 10(5), 1902819 |
| 22 | Chen K. H., Sanchez A. J., Kazyak E., Davis A. L., Dasgupta N. P., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(4), 1802534 |
| 23 | Brady R. M., Ball R. C., Nature, 1984, 309(17), 225―229 |
| 24 | Li G., Liu Z., Huang Q., Gao Y., Regula M., Wang D., Chen L. Q., Wang D., Nat. Energy, 2018, 3(12), 1076―1083 |
| 25 | Pu J., Li J., Zhang K., Zhang T., Li C., Ma H., Zhu J., Braun P. V., Lu J., Zhang H., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 1896 |
| 26 | Lu L., Ge J., Yang J., Chen S., Yao H., Zhou F., Yu S., Nano. Lett., 2016, 16(7), 4431―4437 |
| 27 | Ke X., Liang Y., Ou L., Liu H., Chen Y., Wu W., Cheng Y., Guo Z., Lai Y., Liu P., Shi Z., Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 23, 547―555 |
| 28 | Zou P., Chiang S. W., Li J., Wang Y., Wang X., Wu D., Nairan A., Kang F., Yang C., Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 18, 155―164 |
| 29 | Li J., Zou P., Chiang S. W., Yao W., Wang Y., Liu P., Liang C., Kang F., Yang C., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 24, 700―706 |
| 30 | Xiang J., Yuan L., Shen Y., Cheng Z., Yuan K., Guo Z., Zhang Y., Chen X., Huang Y., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(36), 1802352 |
| 31 | Nan Y., Li S., Shi Y., Yang S., Li B., Small, 2019, 15(45), e1903520 |
| 32 | Liao Y., Yuan L., Xiang J., Zhang W., Cheng Z., He B., Li Z., Huang Y., Nano Energy, 2020, 69, 104471 |
| 33 | Deng W., Zhu W., Zhou X., Zhao F., Liu Z., Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 23, 693―700 |
| 34 | Wang S., Yue J., Dong W., Zuo T., Li J., Liu X., Zhang X., Liu L., Shi J., Yin Y., Guo Y., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 4930 |
| 35 | Lin D., Liu Y., Liang Z., Lee H. W., Sun J., Wang H., Yan K., Xie J., Cui Y., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2016, 11(7), 626―632 |
| 36 | Liu S., Xia X., Zhong Y., Deng S., Yao Z., Zhang L., Cheng X. B., Wang X., Zhang Q., Tu J., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(8), 1702322 |
| 37 | Liang Z., Lin D., Zhao J., Lu Z., Liu Y., Liu C., Lu Y., Wang H., Yan K., Tao X., Cui Y., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2016, 113(11), 2862―2867 |
| 38 | Zhao B., Li B., Wang Z., Xu C., Liu X., Yi J., Jiang Y., Li W., Li Y., Zhang J., ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(17), 19530―19538 |
| 39 | Chi S. S., Liu Y., Song W. L., Fan L. Z., Zhang Q., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(24), 1700348 |
| 40 | Yue X. Y., Wang W. W., Wang Q. C., Meng J. K., Zhang Z. Q., Wu X. J., Yang X. Q., Zhou Y. N., Energy Storage Mater., 2018, 14, 335―344 |
| 41 | Liang X., Pang Q., Kochetkov I. R., Sempere M. S., Huang H., Sun X., Nazar L. F., Nat. Energy, 2017, 2(9), 17119 |
| 42 | Deng W., Liang S., Zhou X., Zhao F., Zhu W. , Liu Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(11), 6267―6274 |
| 43 | Yang G., Li Y., Tong Y., Qiu J., Liu S., Zhang S., Guan Z., Xu B., Wang Z., Chen L., Nano. Lett., 2019, 19(1), 494―499 |
| 44 | Jin S., Sun Z., Guo Y., Qi Z., Guo C., Kong X., Zhu Y. , Ji H., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(38), 1700783 |
| 45 | Liu L., Yin Y. X., Li J. Y., Li N. W., Zeng X. X., Ye H., Guo Y. G., Wan L. J., Joule, 2017, 1(3), 563―575 |
| 46 | Zhang Y., Luo W., Wang C., Li Y., Chen C., Song J., Dai J., Hitz E. M., Xu S., Yang C., Wang Y., Hu L., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2017, 114(14), 3584―3589 |
| 47 | Cui J., Yao S., Ihsan⁃Ul⁃Haq M., Wu J., Kim J. K., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(1), 1802777 |
| 48 | Xue P., Liu S., Shi X., Sun C., Lai C., Zhou Y., Sui D., Chen Y., Liang J., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(44), e1804165 |
| 49 | Wang H., Lin D., Xie J., Liu Y., Chen H., Li Y., Xu J., Zhou G., Zhang Z., Pei A., Zhu Y., Liu K., Wang K., Cui Y., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(7), 1802720 |
| 50 | Liu L., Yin Y., Li J., Wang S., Guo Y., Wan L., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(10), 1706216 |
| 51 | Deng W., Zhou X., Fang Q., Liu Z., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(12), 1703152 |
| 52 | Huang G., Han J., Zhang F., Wang Z., Kashani H., Watanabe K., Chen M., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(2), e1805334 |
| 53 | Phattharasupakun N., Wutthiprom J., Duangdangchote S., Sawangphruk M., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(40), 5689―5692 |
| 54 | Chen Q., Yang Y., Zheng H., Xie Q., Yan X., Ma Y., Wang L., Peng D. L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(19), 11683―11689 |
| 55 | Zhao J., Zhou G., Yan K., Xie J., Li Y., Liao L., Jin Y., Liu K., Hsu P., Wang J., Cheng H., Cui Y., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12(10), 993―999 |
| 56 | Li X., Yang G., Zhang S., Wang Z., Chen L., Nano Energy, 2018, 66, 104144 |
| 57 | Chen Y., Ke X., Cheng Y., Fan M., Wu W., Huang X., Liang Y., Zhong Y., Ao Z., Lai Y., Wang G., Shi Z., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 26, 56―64 |
| 58 | Yan K., Lu Z., Lee H. W., Xiong F., Hsu P. C., Li Y., Zhao J., Chu S. , Cui Y., Nat. Energy, 2016, 1(3), 16010 |
| 59 | Wang T. S., Liu X., Zhao X., He P., Nan C. W. , Fan L. Z., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(16), 2000786 |
| 60 | Kim J., Lee J., Yun J., Choi S. H., Han S. A., Moon J., Kim J. H., Lee J. W. , Park M. S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(15), 1910538 |
| 61 | Zhu M., Li B., Li S., Du Z., Gong Y. , Yang S., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(18), 1703505 |
| 62 | Zhang R., Chen X., Chen X., Cheng X., Zhang X., Yan C. , Zhang Q., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(27), 7764―7768 |
| 63 | Niu C., Pan H., Xu W., Xiao J., Zhang J., Luo L., Wang C., Mei D., Meng J., Wang X., Liu Z., Mai L. , Liu J., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2019, 14(6), 594―601 |
| 64 | Zhang F., Liu X., Yang M., Cao X., Huang X., Tian Y., Zhang F. , Li H., Nano Energy, 2020, 69, 104443 |
| 65 | Noh J., Tan J., Yadav D., Wu P., Xie K. Y. , Yu C., Nano. Lett., 2020, 20(5), 3681―3687 |
| 66 | Zuo T., Wu X., Yang C., Yin Y., Ye H., Li N. , Guo Y., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(29), 1700389 |
| 67 | Lin K., Qin X., Liu M., Xu X., Liang G., Wu J., Kang F., Chen G. , Li B., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(46), 1903229 |
| 68 | Luo L., Li J., Yaghoobnejad Asl H. , Manthiram A., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(48), e1904537 |
| 69 | Sun Y., Zheng G., Seh Zhi W., Liu N., Wang S., Sun J., Lee Hye R. , Cui Y., Chem, 2016, 1(2), 287―297 |
| 70 | Ye H., Xin S., Yin Y., Li J. Y., Guo Y. , Wan L. J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(16), 5916―5922 |
| 71 | Jiang Y., Jiang J., Wang Z., Han M., Liu X., Yi J., Zhao B., Sun X. , Zhang J., Nano Energy, 2020, 70, 104504 |
| 72 | Sun Z., Jin S., Jin H., Du Z., Zhu Y., Cao A., Ji H. , Wan L., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(32), e1800884 |
| 73 | Song Q., Yan H., Liu K., Xie K., Li W., Gai W., Chen G., Li H., Shen C., Fu Q., Zhang S., Zhang L. , Wei B., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(22), 1800564 |
| 74 | Tao L., Hu A., Yang Z., Xu Z., Wall C. E., Esker A. R., Zheng Z. , Lin F., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 2000585 |
| 75 | Jin C., Sheng O., Luo J., Yuan H., Fang C., Zhang W., Huang H., Gan Y., Xia Y., Liang C., Zhang J. , Tao X., Nano Energy, 2017, 37, 177―186 |
| 76 | Zhang X., Wang A., Lv R. , Luo J., Energy Storage Mater., 2019, 18, 199―204 |
| 77 | Zhai P., Wei Y., Xiao J., Liu W., Zuo J., Gu X., Yang W., Cui S., Li B., Yang S. , Gong Y., Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(8), 1903339 |
| 78 | Adair K. R., Iqbal M., Wang C., Zhao Y., Banis M. N., Li R., Zhang L., Yang R., Lu S. , Sun X., Nano Energy, 2018, 54, 375―382 |
| 79 | Tan L., Li X., Cheng M., Liu T., Wang Z., Guo H., Yan G., Li L., Liu Y. , Wang J., J. Power Sources, 2020, 463, 228178 |
| 80 | Lei M., You Z., Ren L., Liu X. , Wang J. G., J. Power Sources, 2020, 463, 228191 |
| 81 | Lei M., Wang J. G., Ren L., Nan D., Shen C., Xie K. , Liu X., ACS. Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(34), 30992―30998 |
| 82 | Jiang T., Chen K., Wang J., Hu Z., Wang G., Chen X. D., Sun P., Zhang Q., Yan C. , Zhang L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(48), 27535―27546 |
| 83 | Zhao F., Zhou X., Deng W. , Liu Z., Nano Energy, 2019, 62, 55―63 |
| 84 | Wu S., Zhang Z., Lan M., Yang S., Cheng J., Cai J., Shen J., Zhu Y., Zhang K. , Zhang W., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(9), 1705830 |
| 85 | Yun Q., He Y. B., Lv W., Zhao Y., Li B., Kang F. , Yang Q., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(32), 6932―6939 |
| 86 | Zhao H., Lei D., He Y. B., Yuan Y., Yun Q., Ni B., Lv W., Li B., Yang Q. H., Kang F. , Lu J., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(19), 1800266 |
| 87 | Qiu H., Tang T., Asif M., Huang X. , Hou Y., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(19), 1808468 |
| 88 | An Y., Fei H., Zeng G., Xu X., Ci L., Xi B., Xiong S., Feng J. , Qian Y., Nano Energy, 2018, 47, 503―511 |
| 89 | Lin K., Li T., Chiang S. W., Liu M., Qin X., Xu X., Zhang L., Kang F., Chen G. , Li B., Small, 2020, 2001784 |
| 90 | Li Q., Zhu S. , Lu Y., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(18), 1606422 |
| 91 | Lu Z., Liang Q., Wang B., Tao Y., Zhao Y., Lv W., Liu D., Zhang C., Weng Z., Liang J., Li H. , Yang Q. H., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(7), 1803186 |
| 92 | Zhang R., Wen S., Wang N., Qin K., Liu E., Shi C. , Zhao N., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(23), 1800914 |
| 93 | Chen X., Chen X., Hou D., Li B., Cheng X., Zhang R. , Zhang Q., Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaau7728 |
| 94 | Duan H., Zhang J., Chen X., Zhang X., Li J., Huang L., Zhang X., Shi J., Yin Y., Zhang Q., Guo Y., Jiang L. , Wan L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(51), 18051―18057 |
| 95 | Xu P., Lin X., Hu X., Cui X., Fan X., Sun C., Xu X., Chang J. K., Fan J., Yuan R., Mao B., Dong Q. , Zheng M., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 28, 188―195 |
| 96 | Sun C., Lin A., Li W., Jin J., Sun Y., Yang J. , Wen Z., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 10(3), 1902989 |
| 97 | Huang K., Li Z., Xu Q., Liu H., Li H. , Wang Y., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(29), 1900853 |
| 98 | Li Z., Liu K., Fan K., Yang Y., Shao M., Wei M. , Duan X., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(12), 3962―3966 |
| 99 | Zhang C., Lyu R., Lv W., Li H., Jiang W., Li J., Gu S., Zhou G., Huang Z., Zhang Y., Wu J., Yang Q. , Kang F., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(48), e1904991 |
| 100 | Lin K., Xu X., Qin X., Zhang G., Liu M., Lv F., Xia Y., Kang F., Chen G. , Li B., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 26, 250―259 |
| 101 | Zhang D., Dai A., Wu M., Shen K., Xiao T., Hou G., Lu J. , Tang Y., ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 5(1), 180―186 |
| 102 | Gu Y., Xu H., Zhang X., Wang W., He J., Tang S., Yan J., Wu D., Zheng M., Dong Q. , Mao B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(10), 3092―3096 |
| 103 | Zhang X., Lv R., Wang A., Guo W., Liu X. , Luo J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(46), 15028―15033 |
| 104 | Zhang D., Wang S., Li B., Gong Y. , Yang S., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31(33), e1901820 |
| 105 | Gu J., Zhu Q., Shi Y., Chen H., Zhang D., Du Z. , Yang S., ACS Nano, 2020, 14(1), 891―898 |
| 106 | Shi H., Zhang C. J., Lu P., Dong Y., Wen P. , Wu Z., ACS Nano, 2019, 13(12), 14308―14318 |
| 107 | Cao Z., Zhu Q., Wang S., Zhang D., Chen H., Du Z., Li B. , Yang S., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 30(5), 1908075 |
| 108 | Yoon I., Jurng S., Abraham D. P., Lucht B. L., Guduru P. R., Nano Lett., 2018, 18(9), 5752―5759 |
| 109 | Lopez J., Pei A., Oh J. Y., Wang G. J. N., Cui Y. , Bao Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(37), 11735―11744 |
| 110 | Wang X., Zeng W., Hong L., Xu W., Yang H., Wang F., Duan H., Tang M. , Jiang H., Nat. Energy, 2018, 3(3), 227―235 |
| 111 | Chen J., Zhao J., Lei L., Li P., Chen J., Zhang Y., Wang Y., Ma Y. , Wang D., Nano Lett., 2020, 20(5), 3403―3410 |
| 112 | Ye L., Feng P., Chen X., Chen B., Gonzalez K., Liu J., Kim I. , Li X., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 26, 371―377 |
| [1] | 李威, 罗飘, 黄廉湛, 崔志明. 基于聚苯乙烯磺酸的锂金属负极界面保护层的设计[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220166. |
| [2] | 李伟辉, 李浩博, 曾诚, 梁昊樾, 陈佳俊, 李俊勇, 李会巧. 热压法构筑锂负极聚偏氟乙烯基双功能保护层的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210629. |
| [3] | 姜宝正, 黄文婷, 刘文宝, 郭荣胜, 徐成俊, 康飞宇. 纳米铜修饰三维锌网电极的制备及锌离子电池负极的电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220257. |
| [4] | 詹迎新, 石鹏, 张学强, 魏俊宇, 张乾魁, 黄佳琦. 锂金属负极亲锂骨架的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5): 1569. |
| [5] | 王增强, 孙一翎, 钱正芳, 王任衡. 基于表界面反应及优化的锂金属电池研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1017. |
| [6] | 王凤春, 周万里. 离子型添加剂四丁基胺-双(氟磺酰)亚胺对锂电池性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2529. |
| [7] | 郭爱红,毕成良,焦丽芳,张宝贵 . 全氟二异丙基膦酸锂的合成及其电化学性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(1): 106. |
| [8] | 张存中, 刘震, 林丽君, 齐菲, 吴锋. 高铁酸盐在SnO2-Sb2O3/Ti电极上的选择性电化学合成[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(5): 927. |
| [9] | 黄宗浩, 阚玉和, 徐栋, 马淑荣, 杨桂霞, 孟素慈, 苏忠民. 石墨负极充放电过程的DFT研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(12): 2289. |
| [10] | 黄宗浩 阚玉和 徐栋 马淑荣 杨桂霞 孟素慈 苏忠民. 石墨负极充放电过程的DFT研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(12): 2289. |
| [11] | 万传云, 努丽燕娜, 江志裕. 掺稀土的LiM0.02Mn1.98O4锂离子电池正极材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2002, 23(1): 126. |
| [12] | 林东风, 陈霜睿, 蔡蓉, 宋德瑛, 申泮文. 正交表诸因素对铁电极充电效率的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2001, 22(S1): 13. |
| [13] | 谢德民, 傅玉洁, 王荣顺, 王存国, 张喜艳. 硫化类聚乙炔电池的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1992, 13(9): 1233. |
| [14] | 张喜艳, 谢德民, 王荣顺, 傅玉杰, 王存国, 赵成大, 李长志, 王宝忱. 聚并苯二次电池的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 1991, 12(9): 1275. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||