

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (2): 246.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180452
赵幻希1, 王秋颖1, 孙秀丽1, 李雪1, 苗瑞1, 吴冬雪1, 刘淑莹1,2( ), 修洋1(
), 修洋1( )
)
收稿日期:2018-06-22
出版日期:2019-02-10
发布日期:2018-12-27
作者简介:联系人简介: 修 洋, 男, 博士, 助理研究员, 主要从事中药化学方面的研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
ZHAO Huanxi1, WANG Qiuying1, SUN Xiuli1, LI Xue1, MIAO Rui1, WU Dongxue1, LIU Shuying1,2,*( ), XIU Yang1,*(
), XIU Yang1,*( )
)
Received:2018-06-22
Online:2019-02-10
Published:2018-12-27
Contact:
LIU Shuying,XIU Yang
E-mail:syliu@ciac.ac.cn;ys830805@sina.com
Supported by:摘要:
利用高效液相色谱-质谱联用(HPLC-MS)技术结合多元统计分析方法, 区分中国人参主产区5个不同产地的45个人参样本, 筛选出差异性皂苷类标志物. 根据人参总皂苷在反相C18色谱柱中的洗脱顺序, 结合串联质谱分析和标准品比对, 在提取的人参总皂苷中鉴定出15种原人参三醇型、 24种原人参二醇型和2种齐墩果酸型共41种皂苷. 对人参总皂苷的HPLC-MS全扫描数据进行了多元统计分析. 正交偏最小二乘-判别分析(OPLS-DA)结果表明, 所建立的分析模型具有良好的数据描述能力和预测能力. 所有人参样本能够根据产地被区分, 并筛选得到同时区分5个产地的差异性皂苷类组分18种; 能够区分任意2个产地人参样本的差异性组分主要为在人参中含量较高的人参皂苷Rb1, Rg1, Re, Rc, Rd, Ro和m-Rb1等. 分层聚类分析(HCA)结果显示, 黑龙江和吉林两省的样本能够独自聚类, 但是绥化市的样本更接近于吉林省. 初步推断原因为绥化市地理位置较接近吉林省, 两地人参生长环境相似并可能存在种质资源交换.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
赵幻希, 王秋颖, 孙秀丽, 李雪, 苗瑞, 吴冬雪, 刘淑莹, 修洋. HPLC-MS结合多元统计分析区分人参产地及筛选皂苷类标志物. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(2): 246.
ZHAO Huanxi,WANG Qiuying,SUN Xiuli,LI Xue,MIAO Rui,WU Dongxue,LIU Shuying,XIU Yang. Discrimination of Ginseng Origins and Identification of Ginsenoside Markers Based on HPLC-MS Combined with Multivariate Statistical Analysis†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 246.
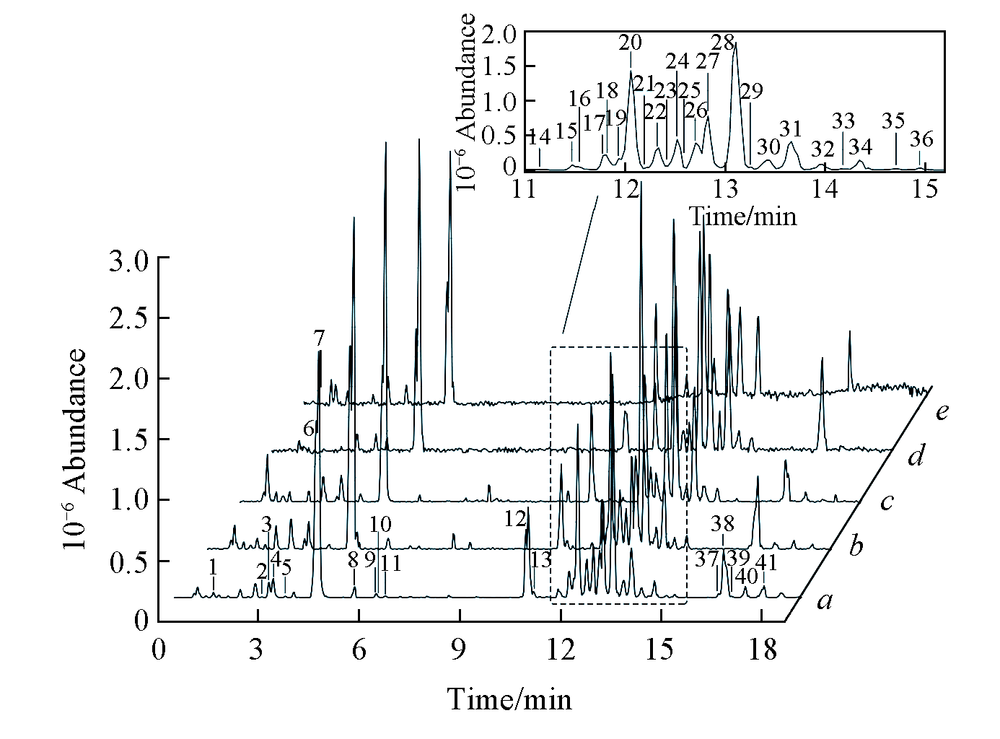
Fig.1 Base peak intensity chromatography of samples WQ1(a), CB1(b), SH1(c), XK1(d), and HL1(e) analyzed by HPLC-MSThe chemical information of the 41 peaks are shown in Table 1.
| No. | tR/min | Ginsenoside | Molecular formula | [M-H]- ion, m/z | Monoisotopic mass | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.14 | Re1 | C48H82O19 | 961.53 | 962.54 | [ |
| 2 | 2.63 | Re4 | C47H80O18 | 931.41 | 932.53 | [ |
| 3 | 2.84 | 20-Glc-Rf | C48H82O19 | 961.52 | 962.54 | [ |
| 4 | 2.97 | NG-R1 isomer | C47H80O18 | 931.55 | 932.53 | [ |
| 5 | 3.34 | NG-R1 | C47H80O18 | 931.53 | 932.53 | - |
| 6 | 4.24 | Re | C48H82O18 | 945.52 | 946.55 | - |
| 7 | 4.30 | Rg1 | C42H72O14 | 845.44 | 800.49 | - |
| 8 | 5.41 | Ac-Rg1 isomera | C44H74O15 | 841.46 | 842.50 | [ |
| 9 | 6.00 | m-Re | C51H84O21 | 1031.56 | 1032.55 | [ |
| 10 | 6.06 | Ac-Re | C50H84O19 | 987.54 | 988.56 | [ |
| 11 | 6.31 | Ac-Rg1 | C44H74O15 | 841.51 | 542.50 | [ |
| 12 | 10.57 | 20(S)-Rf | C42H72O14 | 799.44 | 800.49 | - |
| 13 | 10.73 | Ra3 | C59H100O27 | 1239.64 | 1240.64 | [ |
| 14 | 11.13 | m-Ra3b | C62H102O30 | 1325.61 | 1326.65 | [ |
| 15 | 11.47 | 20(S)-NG-R2 | C41H70O13 | 769.44 | 770.48 | - |
| 16 | 11.62 | NG-R4 | C59H100O27 | 1239.67 | 1240.64 | [ |
| 17 | 11.78 | Ra2 | C58H98O26 | 1209.66 | 1210.63 | [ |
| 18 | 11.81 | m-NG-R4 | C62H102O30 | 1325.62 | 1236.65 | [ |
| 19 | 11.93 | NG-Fa | C59H100O27 | 1239.66 | 1240.64 | [ |
| 20 | 12.06 | Rb1 | C54H92O23 | 1107.55 | 1108.60 | - |
| No. | tR/min | Ginsenoside | Molecular formula | [M-H]- ion, m/z | Monoisotopic mass | Ref. |
| 21 | 12.21 | m-Ra2 | C61H100O29 | 1295.62 | 1296.63 | [ |
| 22 | 12.33 | 20(S)-Rg2 | C42H72O13 | 783.47 | 784.50 | - |
| 23 | 12.40 | m-NG-Fa | C62H102O30 | 1325.59 | 1326.65 | [ |
| 24 | 12.52 | m-Rb1 | C57H94O26 | 1193.56 | 1194.60 | [ |
| 25 | 12.71 | Ra1 | C58H98O26 | 1209.56 | 1210.63 | [ |
| 26 | 12.80 | 20(S)-Rh1 | C36H62O9 | 637.47 | 638.44 | - |
| 27 | 12.83 | Rc | C53H90O22 | 1077.61 | 1078.59 | - |
| 28 | 13.11 | Ro | C48H76O19 | 955.49 | 956.50 | - |
| 29 | 13.26 | m-Ra1 | C61H100O29 | 1295.66 | 1296.63 | [ |
| 30 | 13.42 | m-Rc | C56H92O25 | 1163.50 | 1164.59 | [ |
| 31 | 13.66 | Rb2 | C53H90O22 | 1077.57 | 1078.59 | - |
| 32 | 13.94 | Rb3 | C53H90O22 | 1077.54 | 1078.59 | - |
| 33 | 14.19 | Ra1 isomer | C58H98O26 | 1209.58 | 1210.63 | [ |
| 34 | 14.34 | m-Rb2 | C56H92O25 | 1163.53 | 1164.59 | [ |
| 35 | 14.65 | m-Rb3 | C56H92O25 | 1163.78 | 1164.59 | [ |
| 36 | 14.96 | Quinquenoside R1 | C56H94O24 | 1149.62 | 1150.61 | [ |
| 37 | 16.20 | Rs2 | C55H92O23 | 1119.54 | 1120.60 | [ |
| 38 | 16.42 | Rd | C48H82O18 | 945.48 | 946.55 | - |
| 39 | 16.63 | Rs1 | C55H92O23 | 1119.72 | 1120.60 | [ |
| 40 | 17.06 | Chikusetsusaponin Ⅳa | C42H66O14 | 793.41 | 794.44 | [ |
| 41 | 17.56 | m-Rd | C51H84O21 | 1031.51 | 1032.55 | [ |
Table 1 Chemical information of ginsenosides in the 45 ginseng samples identified by HPLC-MS
| No. | tR/min | Ginsenoside | Molecular formula | [M-H]- ion, m/z | Monoisotopic mass | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.14 | Re1 | C48H82O19 | 961.53 | 962.54 | [ |
| 2 | 2.63 | Re4 | C47H80O18 | 931.41 | 932.53 | [ |
| 3 | 2.84 | 20-Glc-Rf | C48H82O19 | 961.52 | 962.54 | [ |
| 4 | 2.97 | NG-R1 isomer | C47H80O18 | 931.55 | 932.53 | [ |
| 5 | 3.34 | NG-R1 | C47H80O18 | 931.53 | 932.53 | - |
| 6 | 4.24 | Re | C48H82O18 | 945.52 | 946.55 | - |
| 7 | 4.30 | Rg1 | C42H72O14 | 845.44 | 800.49 | - |
| 8 | 5.41 | Ac-Rg1 isomera | C44H74O15 | 841.46 | 842.50 | [ |
| 9 | 6.00 | m-Re | C51H84O21 | 1031.56 | 1032.55 | [ |
| 10 | 6.06 | Ac-Re | C50H84O19 | 987.54 | 988.56 | [ |
| 11 | 6.31 | Ac-Rg1 | C44H74O15 | 841.51 | 542.50 | [ |
| 12 | 10.57 | 20(S)-Rf | C42H72O14 | 799.44 | 800.49 | - |
| 13 | 10.73 | Ra3 | C59H100O27 | 1239.64 | 1240.64 | [ |
| 14 | 11.13 | m-Ra3b | C62H102O30 | 1325.61 | 1326.65 | [ |
| 15 | 11.47 | 20(S)-NG-R2 | C41H70O13 | 769.44 | 770.48 | - |
| 16 | 11.62 | NG-R4 | C59H100O27 | 1239.67 | 1240.64 | [ |
| 17 | 11.78 | Ra2 | C58H98O26 | 1209.66 | 1210.63 | [ |
| 18 | 11.81 | m-NG-R4 | C62H102O30 | 1325.62 | 1236.65 | [ |
| 19 | 11.93 | NG-Fa | C59H100O27 | 1239.66 | 1240.64 | [ |
| 20 | 12.06 | Rb1 | C54H92O23 | 1107.55 | 1108.60 | - |
| No. | tR/min | Ginsenoside | Molecular formula | [M-H]- ion, m/z | Monoisotopic mass | Ref. |
| 21 | 12.21 | m-Ra2 | C61H100O29 | 1295.62 | 1296.63 | [ |
| 22 | 12.33 | 20(S)-Rg2 | C42H72O13 | 783.47 | 784.50 | - |
| 23 | 12.40 | m-NG-Fa | C62H102O30 | 1325.59 | 1326.65 | [ |
| 24 | 12.52 | m-Rb1 | C57H94O26 | 1193.56 | 1194.60 | [ |
| 25 | 12.71 | Ra1 | C58H98O26 | 1209.56 | 1210.63 | [ |
| 26 | 12.80 | 20(S)-Rh1 | C36H62O9 | 637.47 | 638.44 | - |
| 27 | 12.83 | Rc | C53H90O22 | 1077.61 | 1078.59 | - |
| 28 | 13.11 | Ro | C48H76O19 | 955.49 | 956.50 | - |
| 29 | 13.26 | m-Ra1 | C61H100O29 | 1295.66 | 1296.63 | [ |
| 30 | 13.42 | m-Rc | C56H92O25 | 1163.50 | 1164.59 | [ |
| 31 | 13.66 | Rb2 | C53H90O22 | 1077.57 | 1078.59 | - |
| 32 | 13.94 | Rb3 | C53H90O22 | 1077.54 | 1078.59 | - |
| 33 | 14.19 | Ra1 isomer | C58H98O26 | 1209.58 | 1210.63 | [ |
| 34 | 14.34 | m-Rb2 | C56H92O25 | 1163.53 | 1164.59 | [ |
| 35 | 14.65 | m-Rb3 | C56H92O25 | 1163.78 | 1164.59 | [ |
| 36 | 14.96 | Quinquenoside R1 | C56H94O24 | 1149.62 | 1150.61 | [ |
| 37 | 16.20 | Rs2 | C55H92O23 | 1119.54 | 1120.60 | [ |
| 38 | 16.42 | Rd | C48H82O18 | 945.48 | 946.55 | - |
| 39 | 16.63 | Rs1 | C55H92O23 | 1119.72 | 1120.60 | [ |
| 40 | 17.06 | Chikusetsusaponin Ⅳa | C42H66O14 | 793.41 | 794.44 | [ |
| 41 | 17.56 | m-Rd | C51H84O21 | 1031.51 | 1032.55 | [ |
| No. | Variable | m/z@tR | VIP | Molecular ion | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1107.55@12.06 | 6.42 | [M-H]- | Rb1 |
| 2 | 3 | 955.47@13.11 | 6.03 | [M-H]- | Ro |
| 3 | 7 | 1077.61@12.96 | 5.58 | [M-H]- | Rc |
| 4 | 4 | 991.46@4.29 | 4.70 | [M+HCOO]- | Re |
| 5 | 1 | 845.46@4.36 | 4.62 | [M-H]- | Rg1 |
| 6 | 9 | 991.49@16.43 | 4.45 | [M+HCOO]- | Rd |
| 7 | 6 | 1123.50@12.56 | 4.10 | [M+HCOO]- | Rc |
| 8 | 14 | 1193.53@12.52 | 3.87 | [M-H]- | m-Rb1 |
| 9 | 16 | 1163.49@13.43 | 3.73 | [M-H]- | m-Rc |
| 10 | 15 | 945.52@16.41 | 3.56 | [M-H]- | Rd |
| 11 | 12 | 1209.58@12.71 | 3.50 | [M-H]- | Ra1 |
| 12 | 5 | 799.49@10.57 | 3.27 | [M-H]- | 20(S)-Rf |
| 13 | 20 | 835.43@4.35 | 3.02 | [M+Cl]- | Rg1 |
| 14 | 34 | 1143.57@12.08 | 2.74 | [M+Cl]- | Rb1 |
| 15 | 18 | 1239.63@11.96 | 2.65 | [M-H]- | NG-Fa |
| 16 | 32 | 1113.64@12.85 | 2.58 | [M+Cl]- | Rc |
| 17 | 11 | 769.44@11.50 | 2.48 | [M-H]- | 20(S)-NG-R2 |
| 18 | 8 | 1153.51@12.09 | 2.38 | [M+HCOO]- | Rb1 |
| 19 | 19 | 1255.63@11.76 | 2.34 | [M+HCOO]- | Ra2 |
| 20 | 39 | 981.41@16.66 | 2.25 | [M+Cl]- | Rd |
| 21 | 36 | 793.41@17.00 | 2.20 | [M-H]- | Chikusetsusaponin Ⅳa |
| 22 | 26 | 1285.55@11.98 | 2.19 | [M+HCOO]- | NG-Fa |
| 23 | 10 | 945.50@4.28 | 2.14 | [M-H]- | Re |
| 24 | 31 | 981.43@4.25 | 2.09 | [M+Cl]- | Re |
| 25 | 37 | 1031.49@17.61 | 2.05 | [M-H]- | m-Rd |
| 26 | 52 | 835.41@10.57 | 1.81 | [M+Cl]- | 20(S)-Rf |
| 27 | 54 | 1008.49@2.69 | 1.72 | - | Unknown |
Table 2 Identification of differential components from ginseng samples from 5 different origins
| No. | Variable | m/z@tR | VIP | Molecular ion | Identity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 1107.55@12.06 | 6.42 | [M-H]- | Rb1 |
| 2 | 3 | 955.47@13.11 | 6.03 | [M-H]- | Ro |
| 3 | 7 | 1077.61@12.96 | 5.58 | [M-H]- | Rc |
| 4 | 4 | 991.46@4.29 | 4.70 | [M+HCOO]- | Re |
| 5 | 1 | 845.46@4.36 | 4.62 | [M-H]- | Rg1 |
| 6 | 9 | 991.49@16.43 | 4.45 | [M+HCOO]- | Rd |
| 7 | 6 | 1123.50@12.56 | 4.10 | [M+HCOO]- | Rc |
| 8 | 14 | 1193.53@12.52 | 3.87 | [M-H]- | m-Rb1 |
| 9 | 16 | 1163.49@13.43 | 3.73 | [M-H]- | m-Rc |
| 10 | 15 | 945.52@16.41 | 3.56 | [M-H]- | Rd |
| 11 | 12 | 1209.58@12.71 | 3.50 | [M-H]- | Ra1 |
| 12 | 5 | 799.49@10.57 | 3.27 | [M-H]- | 20(S)-Rf |
| 13 | 20 | 835.43@4.35 | 3.02 | [M+Cl]- | Rg1 |
| 14 | 34 | 1143.57@12.08 | 2.74 | [M+Cl]- | Rb1 |
| 15 | 18 | 1239.63@11.96 | 2.65 | [M-H]- | NG-Fa |
| 16 | 32 | 1113.64@12.85 | 2.58 | [M+Cl]- | Rc |
| 17 | 11 | 769.44@11.50 | 2.48 | [M-H]- | 20(S)-NG-R2 |
| 18 | 8 | 1153.51@12.09 | 2.38 | [M+HCOO]- | Rb1 |
| 19 | 19 | 1255.63@11.76 | 2.34 | [M+HCOO]- | Ra2 |
| 20 | 39 | 981.41@16.66 | 2.25 | [M+Cl]- | Rd |
| 21 | 36 | 793.41@17.00 | 2.20 | [M-H]- | Chikusetsusaponin Ⅳa |
| 22 | 26 | 1285.55@11.98 | 2.19 | [M+HCOO]- | NG-Fa |
| 23 | 10 | 945.50@4.28 | 2.14 | [M-H]- | Re |
| 24 | 31 | 981.43@4.25 | 2.09 | [M+Cl]- | Re |
| 25 | 37 | 1031.49@17.61 | 2.05 | [M-H]- | m-Rd |
| 26 | 52 | 835.41@10.57 | 1.81 | [M+Cl]- | 20(S)-Rf |
| 27 | 54 | 1008.49@2.69 | 1.72 | - | Unknown |
| Origin | Identity | Origin | Identity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XK | HL | Rb1, Rc, Rd, Rg1, Ro | HL | WQ | Rg1, Rb1, m-Rc, m-Rb1 |
| SH | Rd, Rc, Ro, Rg1 | CB | Rg1, Rb1, Rc, Re, m-Rc, m-Rb1 | ||
| WQ | Rb1, Rc, Rf, Ra1, Re, m-Rb1 | SH | WQ | Rb1, Rc, Rg1, Ro, Ra1, Re | |
| CB | Rc, Rb1, Rd, Rg1, m-Rc, m-Rb1, Ro | CB | Rb1, Rc, Rd, Rg1, Ra1, Rc, m-Rc | ||
| HL | SH | Rg1, Rb1, Rc, Re, m-Rb1 | WQ | CB | Re, Rd, Rg1, m-Rc, Ro |
Table 3 Differential components in ginseng samples from any two of the five origins
| Origin | Identity | Origin | Identity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XK | HL | Rb1, Rc, Rd, Rg1, Ro | HL | WQ | Rg1, Rb1, m-Rc, m-Rb1 |
| SH | Rd, Rc, Ro, Rg1 | CB | Rg1, Rb1, Rc, Re, m-Rc, m-Rb1 | ||
| WQ | Rb1, Rc, Rf, Ra1, Re, m-Rb1 | SH | WQ | Rb1, Rc, Rg1, Ro, Ra1, Re | |
| CB | Rc, Rb1, Rd, Rg1, m-Rc, m-Rb1, Ro | CB | Rb1, Rc, Rd, Rg1, Ra1, Rc, m-Rc | ||
| HL | SH | Rg1, Rb1, Rc, Re, m-Rb1 | WQ | CB | Re, Rd, Rg1, m-Rc, Ro |
| [1] | Yun T. K., Lancet Oncol., 2001, 2(1), 49-55 |
| [2] | Kim D. H., J. Ginseng Res., 2012, 36(1), 1-15 |
| [3] | Liu Z. Q., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(6), 3329-3355 |
| [4] | Wong A. S. T., Che C. M., Leung K. W., Nat. Prod. Rep.,2015, 32(2), 256-272 |
| [5] | Liu Z., Wang C. Z., Zhu X. Y., Wan J. Y., Zhang J., Li W., Ruan C. C., Yuan C. S., Molecules,2017, 22(5), 734 |
| [6] | Pace R., Martineli E. M., Sardone N., Combarieu E. D. E., Fitoterapia,2015, 101, 80-91 |
| [7] | Xiao D., Yue H., Xiu Y., Sun X. L., Wang Y. B., Liu S. Y., J. Ginseng Res.,2015, 39(4), 338-344 |
| [8] | Cheng C., Yuan Q., Zhou H., Huang L., Microsc. Res. Tech.,2016, 79(2), 98-105 |
| [9] | Chen Y., Zhao Z., Chen H., Brand E., Yi T., Qin M., Liang Z., J. Ginseng Res.,2017, 41(1), 10-22 |
| [10] | Kwon S. W., Han S. B., Park I. H., Kim J. M., Park M. K., Park J. H., J. Chromatogr. A,2001, 921(2), 335-339 |
| [11] | Luo Z. Y., Zhou G., Zhou S. Q., Chen X. H., Luo J. Q., Hu W. X., Acta Pharm. Sin.,2000, 35(8), 626-629 |
| [12] | Wen J., Zimmer E. A., Mol. Phylogenet. Evol.,1996, 6(2), 167-177 |
| [13] | Kim J. H., Yi Y. S., Kim M. Y., Cho J. Y., J. Ginseng Res.,2016, 41(4), 435-443 |
| [14] | Li K. K., Gong X. J., RSC Adv.,2015, 5, 47353-47366 |
| [15] | Li X., Zhao H. X., Miao R., Li W. Y., Xiu Y., Liu S. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(10), 1730-1736 |
| (李雪, 赵幻希, 苗瑞, 李文影, 修洋, 刘淑莹. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(10), 1730-1736) | |
| [16] | Shin B. K., Kwon S. W., Park J. H., J. Ginseng Res.,2015, 39(4), 287-298 |
| [17] | Chen S., Kong H., Lu X., Li Y., Yin P., Zeng Z., Xu G., Anal. Chem.,2013, 85(17), 8326-8333 |
| [18] | Cheng Y., Liu Y. M., Huang F. J., Chen T. L., Zheng X. J., Zhao A. H., He P. G., Jia W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(1), 77-83 |
| (成玉, 刘玉敏, 黄凤杰, 陈天璐, 郑晓皎, 赵爱华, 何品刚, 贾伟. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(1), 77-83) | |
| [19] | Huang Y., Gu C. Y., Wu H. Z., Xia X. S., Li X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(10), 1742-1750 |
| (黄玉, 谷彩云, 吴翰钟, 夏晓爽, 李新. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(10), 1742-1750) | |
| [20] | Chen Y., Zhao Z., Chen H., Yi T., Qin M., Liang Z., Phytochem. Anal.,2015, 26(2), 145-160 |
| [21] | Sun X., Chen P., Cook S. L., Jackson G. P., Harnly J. M., Harrington P. B., Anal. Chem.,2012, 84(8), 3628-3634 |
| [22] | Cho I. H., Lee H. J., Kim Y. S., J. Agric. Food Chem.,2012, 60(31), 7616-7622 |
| [23] | Wang H. P., Zhang Y. B., Yang X. W., Zhao D. Q., Wang Y. P., J. Ginseng Res.,2016, 40(4), 382-394 |
| [24] | Song H. H., Moon J. Y., Ryu H. W., Noh B. S., Kim J. H., Lee H. K., Oh S. R., J. Ginseng Res.,2014, 38(3), 187-193 |
| [25] | Xu X., Cheng X., Lin Q., Li S., Jia Z., Han T., Lin R., Wang D., Wei F., Li X., J. Ginseng Res.,2016, 40(4), 344-350 |
| [26] | Shan S. M., Luo J. G., Huang F., Kong L. Y., J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal.,2014, 89, 76-82 |
| [27] | Xiu Y., Li X., Sun X., Xiao D., Miao R., Zhao H., Liu S.,J. Ginseng Res., 2017, DOI: 10.1016/j.jgr.2017.12.001 |
| [28] | Xiu Y., Zhao H., Gao Y., Liu W., Liu S., New J. Chem.,2016, 40(11), 9073-9080 |
| [29] | Song F., Liu Z., Liu S., Cai Z., Anal. Chim. Acta,2005, 531(1), 69-77 |
| [30] | Xu X. F., Xu S. Y., Zhang Y., Zhang H., Liu M. N., Liu H., Gao Y., Xue X., Xiong H., Lin R. C., Li X. R., Molecules,2017, 22(5), 717 |
| [31] | Worley B., Powers R., Curr. Metabolomics,2013, 1(1), 92-107 |
| [32] | Triba M. N., Moyec L. L., Amathieu R., Goossens C., Bouchemal N., Nahon P., Rutledge D. N., Savarin P., Mol. Bio. Syst.,2015, 11(1), 13-19 |
| [1] | 朱铃,王雨辰,赵江源,文孟良,李铭刚,韩秀林. 重组β-木糖苷酶转化人参皂苷Rb3及C-Mx[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(5): 1010. |
| [2] | 王天琦,余琼卫,冯钰锜. 基于氧化镍沉积硅胶固相萃取与液相色谱-质谱联用技术的2型糖尿病血清中咪唑丙酸的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 262. |
| [3] | 肖永坤, 刘春莹, 鱼红闪, 李泰厚, 徐龙权, 宋建国, 林完泽, 孙长凯, 金凤燮. 人参二醇类皂苷的生物转化动态及人参稀有皂苷C-K或F2的制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(6): 1184. |
| [4] | 乔梦丹, 刘尚, 张琰, 李晶, 郑飞, 戴雨霖, 越皓. 基于UPLC-Q-Orbitrap MS/MS研究人参皂苷在发酵过程中的生物转化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(2): 219. |
| [5] | 刘欣茹, 刘春莹, 徐龙权, 宋建国, 鱼红闪. 人参皂苷β-葡萄糖苷酶基因的毕赤酵母载体构建及生物转化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2451. |
| [6] | 刘迎, 陈妍心, 吴谦, 黎鹏, 李绪文, 时晓磊, 金永日. 20(S/R)-人参皂苷Rg3的制备及调节Th1/Th2免疫失衡活性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11): 2419. |
| [7] | 苗瑞, 吴冬雪, 王秋颖, 赵幻希, 李雪, 修洋, 刘淑莹. 基于多壁碳纳米管的人参皂苷快速分离[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10): 2178. |
| [8] | 李瑞刚, 朱娜, 赵幻希, 王楠, 孙红梅, 越皓, 李晶. 人参多糖对人参皂苷Re体内代谢和体外转化的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10): 2192. |
| [9] | 李雪, 赵幻希, 苗瑞, 李文影, 修洋, 刘淑莹. 基于HPLC-HRMS/MSn/QqQ技术的人参皂苷Rb1化学转化产物的结构与途径分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(10): 1730. |
| [10] | 李兰杰, 李绪文, 丁健, 刘迎, 吴谦, 王晓中, 李敏, 金永日. 超声辅助结合离子液体双水相提取-高效液相色谱法测定三七中5种稀有人参皂苷的含量[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3): 454. |
| [11] | 许春春, 于渤浩, 王红蕾, 李晶, 刘淑莹, 于珊珊. 重组嗜热β-葡萄糖苷酶转化稀有人参皂苷Rd和CK[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2): 281. |
| [12] | 王一博, 肖丹, 李晓宇, 戴雨霖, 越皓, 刘淑莹. 液相色谱-质谱联用技术结合多探针底物法研究人参皂苷Rb1的体外代谢[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(10): 1894. |
| [13] | 姚华, 金永日, 杨洁, 李兰杰, 孙婷, 时晓磊, 李绪文. 密闭式微波降解法促进常见人参皂苷向稀有人参皂苷转化的规律[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(11): 2317. |
| [14] | 齐瑶, 李世哲, 朱洪彬, 宋凤瑞, 林娜, 刘志强. 复方乌头汤配伍贝母化学成分变化研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(6): 1374. |
| [15] | 刘跃芹, 皮子凤, 宋凤瑞, 刘志强, 刘忠英. 阿卡波糖对Ⅱ型糖尿病大鼠尿液代谢轮廓的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(09): 1932. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||