

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 2494.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190206
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jie WANG,Yu ZHANG,Min YU,Jin FANG( )
)
Received:2019-04-08
Online:2019-12-04
Published:2019-12-04
Contact:
Jin FANG
E-mail:jfang@cmu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
Jie WANG,Yu ZHANG,Min YU,Jin FANG. Multiple Analyses of Tumor Invasion Based on an Integrated Microfluidic System with Bi-directional Solute Concentration Gradient †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2494.
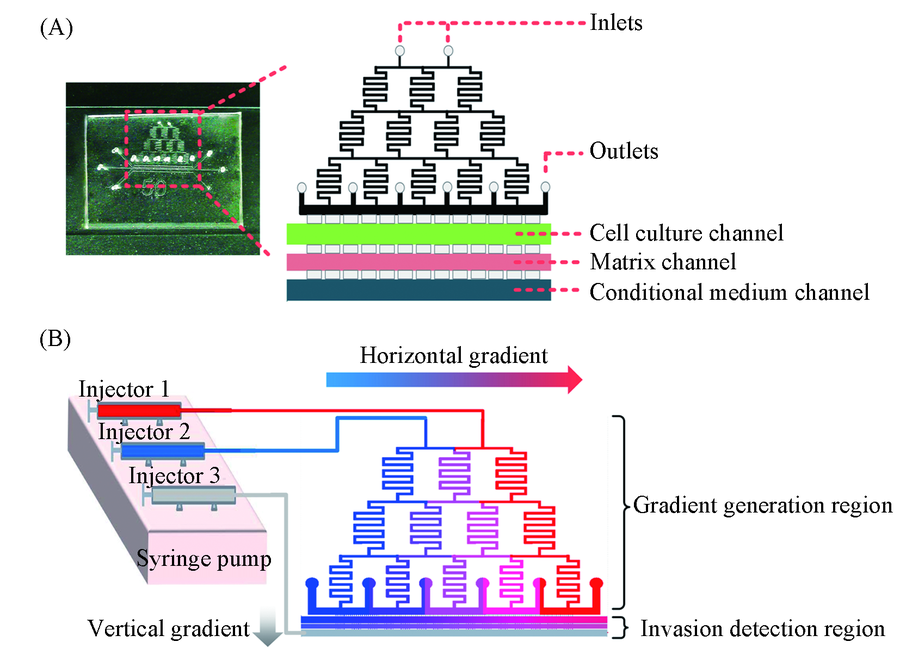
Fig.1 Bi-directional gradient microfluidic system (A) The schematic illustration of microfluidic device; (B) generation principle of the bi-directional gradient device.
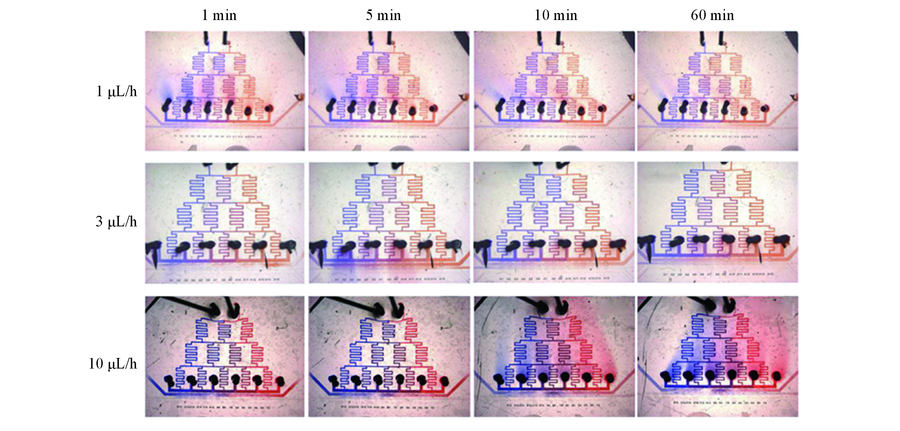
Fig.2 Formation and maintenance of concentration gradients at different flow rates Red, blue water-soluble dye and clear ultrapure water were pumped into device simultaneously. Concentration gradient images were taken under stereomicroscope at a series of time points.
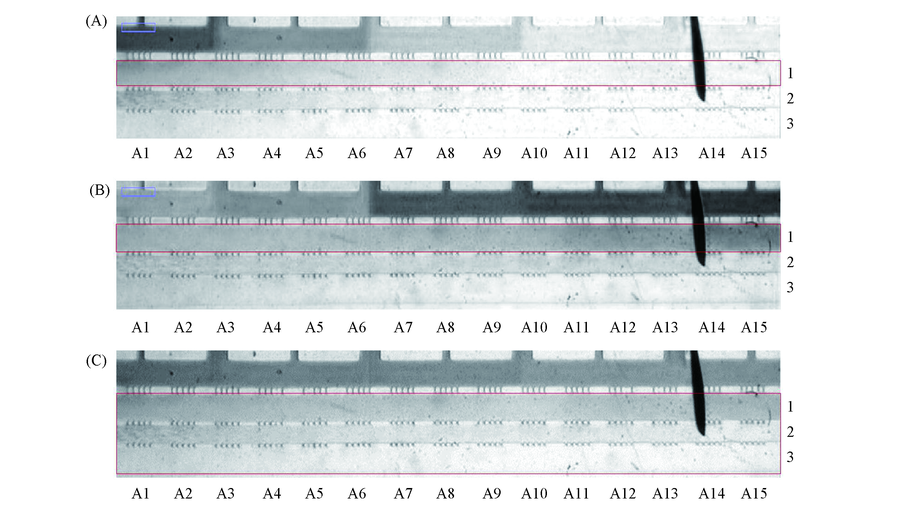
Fig.3 Horizontal and vertical concentration gradient at the flow rate of 3 μL/h Gray value of horizontal red(A), horizontal blue(B) and vertical(C) concentration gradient at 24 h was converted by Image J. 1. Cell culture channel; 2. matrix channel; 3. conditional medium channel.
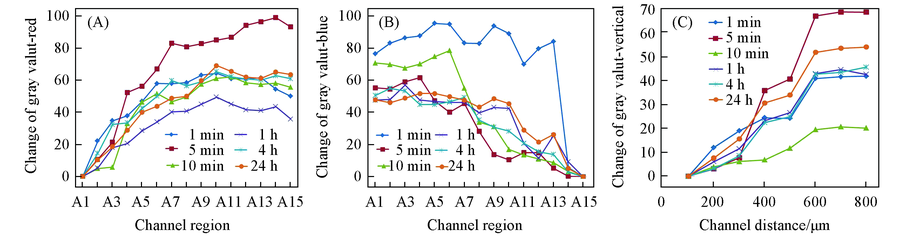
Fig.4 Quantitative evaluation of horizontal and vertical concentration gradient at the flow rate of 3 μL/h (A) Horizontal red; (B) horizontal blue; (C) vertical.
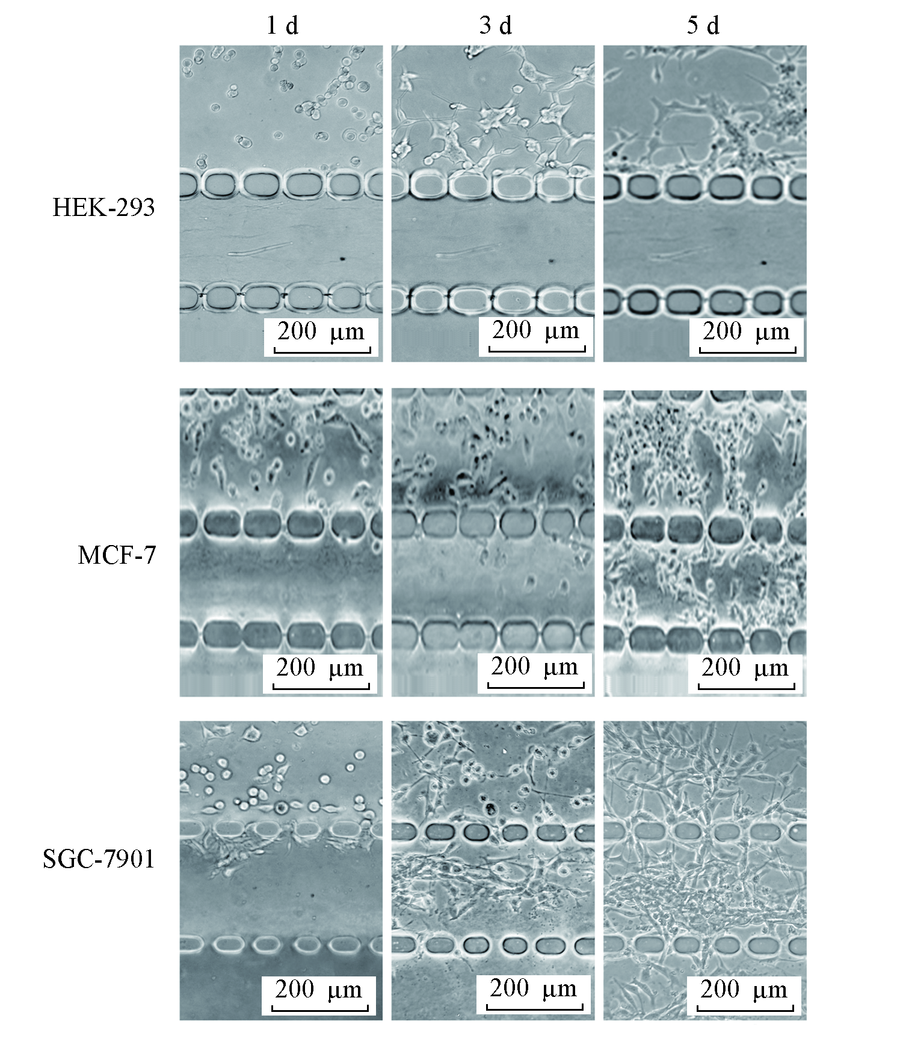
Fig.5 Invasiveness detection of different cell lines Three types of cell lines(HEK-293, MCF-7, SGC-7901) were cultured in the Matrigel-loaded device under a 0—10% FBS gradient.
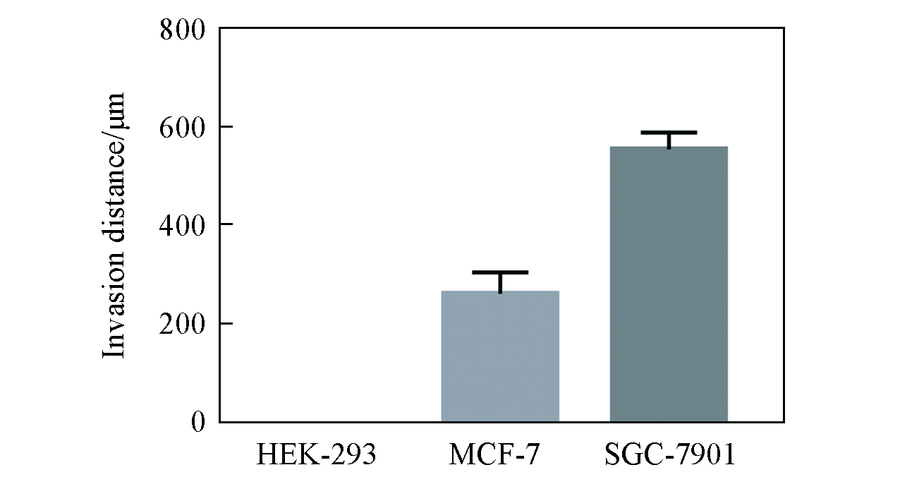
Fig.6 Invasiveness evaluation of different cell lines Invasiveness of different cell lines(HEK-293, MCF-7, SGC-7901) was assessed quantitatively according to the invasion distance of leading cells.
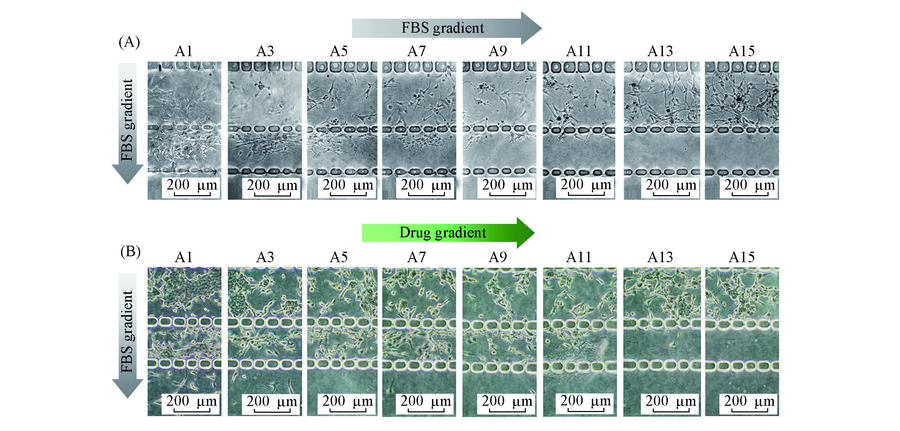
Fig.7 Invasion profile of tumor cells under bi-directional gradient (A) Human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells were cultured and driven to invade into matrix by bi-directional FBS gradient. The invasion was imaged at sequential sites. (B) Under horizontal Staurosporine gradient and vertical FBS gradient, cultured SGC-7901 cells were driven to invade into matrix. The invasion profile was sequential imaged.
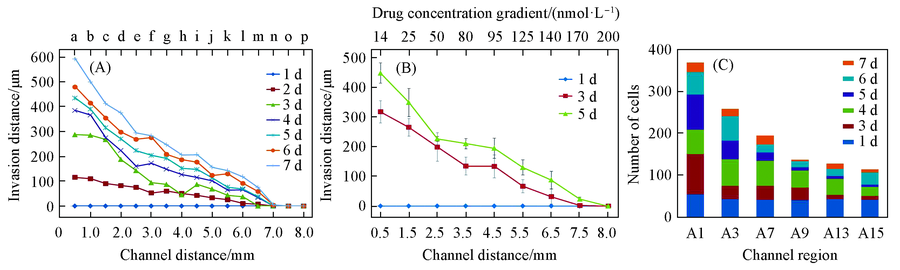
Fig.8 Quantitative invasion analysis of tumor cells under bi-directional gradient (A) Quantitative analysis of invasion distances at different sites over a 7 d period of time. The corresponding drug concentrations at different sites were also demonstrated. (B) Invasion distances at different sites were quantified on the third day and the fifth day. (C) Cell numbers within channels were also quantified accordingly for proliferation evaluation. (A) Drug concentration gradient/(nmol·L-1): a. 14; b. 16; c. 25; d. 45; e. 50; f. 60; g. 80; h. 90; i. 95; j. 110; k. 125; l. 135; m. 140; n. 160; o. 170; p. 200.
| [1] |
Hanahan D., Weinberg R. A ., Cell, 2011,144(5), 646— 674
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013 URL |
| [2] |
Nangami G. N., Watson K., Parker-Johnson K., Okereke K. O., Sakwe A., Thompson P., Frimpong N., Ochieng J ., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2013,438(4), 660— 665
doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.125 URL pmid: 23933250 |
| [3] |
Eslami Amirabadi H., SahebAli S., Frimat J. P., Luttge R., den Toonder J. M. J ., Biomed. Microdevices, 2017,19(4), 92
doi: 10.1007/s10544-017-0234-8 URL pmid: 29038872 |
| [4] | Dai J., Fan X. F., Fang Z. L ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004,25(S1), 41— 42 |
| ( 戴敬, 樊晓峰, 方肇伦 . 高等学校化学学报, 2004,25(S1), 41— 42) | |
| [5] |
Huang Y. L., Segall J. E., Wu M ., Lab Chip, 2017,17(19), 3221— 3233
doi: 10.1039/c7lc00623c URL pmid: 28805874 |
| [6] |
Wang S. J., Saadi W., Minh-Canh Nguyen C., Lin F., Jeon N. L ., Exp. Cell Res., 2004,300(1), 180— 189
doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.06.030 URL pmid: 15383325 |
| [7] | Huang Y. Z., Fang Q., Li D. N ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004,25(9), 1628— 1631 |
| ( 黄艳贞, 方群, 李丹妮 . 高等学校化学学报, 2004,25(9), 1628— 1631) | |
| [8] |
Shang M., Soon R. H., Lim C. T., Khoo B. L., Han J ., Lab Chip, 2019,19(3), 369— 386
doi: 10.1039/c8lc00970h URL pmid: 30644496 |
| [9] |
Chaw K. C., Manimaran M., Tay F. E., Swaminathan S ., Biomed. Microdevices, 2007,9(4), 597— 602
doi: 10.1007/s10544-007-9071-5 URL pmid: 17505887 |
| [10] |
Chen Z. Z., Li W. M., Zhang Y., Yu M., Shan L. F., Yuan D. Z., Liu F. R., Fang J ., Sci. Rep., 2016,6, 38376
doi: 10.1038/srep38376 URL pmid: 27917905 |
| [11] |
Yan X. H., Hu L., Li Y., Feng X. J., Liu B. F ., Chinese J. Anal. Chem., 2015,43(10), 1520— 1525
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(15)60868-4 URL |
|
( 鄢兴华, 胡亮, 李颖, 冯晓均, 刘笔锋 . 分析化学, 2015,43(10), 1520— 1525)
doi: 10.1016/S1872-2040(15)60868-4 URL |
|
| [12] |
Hu S. W., Xu B. Y., Xu J. J., Chen H. Y ., Biomicrofluidics, 2013,7(6), 64116
doi: 10.1063/1.4847815 URL pmid: 24396550 |
| [13] |
Chi C. W., Ahmed A. R., Dereli-Korkut Z., Wang S ., Bioanalysis, 2016,8(9), 921— 937
doi: 10.4155/bio-2016-0028 URL pmid: 27071838 |
| [14] |
Wang Y., Yang H., Liu H., Huang J., Song X ., BMC Cancer, 2009,9, 174
doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-9-174 URL pmid: 19500428 |
| [15] |
Malsy M., Bitzinger D., Graf B., Bundscherer A ., Eur. J. Med. Res., 2019,24(1), 5
doi: 10.1186/s40001-019-0365-x URL pmid: 30686270 |
| [16] |
Yadav S. S., Prasad C. B., Prasad S. B., Pandey L. K., Singh S., Pradhan S., Narayan G ., Life Sci., 2015,133, 21— 28
doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.04.019 URL pmid: 26006035 |
| [17] |
Harmalkar M. N., Shirsat N. V ., Neurochem. Res., 2006,31(5), 685— 692
doi: 10.1007/s11064-006-9068-0 URL |
| [1] | WANG Fangyuan, ZHANG Fenxian, LI Yi, GAO Jianhua, NIU Yanbing, SHEN Shaofei. Fabrication of Bionic Leaf Model and Its Application in Agarose Microfluidic Chip [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220445. |
| [2] | LUO Cheng, PENG Yamei, SHEN Hong, FANG Qun, PAN Jianzhang. Research Progress of Multiplex Immunoassay [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3421. |
| [3] | WANG Mengmeng, LUAN Tianjiao, YANG Mingyan, LYU Jiajia, GAO Jie, LI Hongyu, WEI Gang, YUAN Zeli. Rhodamine Fluorescent Probe for Tumor Targeted Hypoxia-imaging as Intra-operative Navigators [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3071. |
| [4] | PENG Huo, GAO Zehang, LIAO Chengyue, WANG Xiaodong, ZHOU Hongbo, ZHAO Jianlong. Robust Droplet Digital PCR Chip for Absolute Quantitative Detection of Nucleic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1760. |
| [5] | ZHANG Kaixiang, LIU Junjie, SONG Qiaoli, WANG Danyu, SHI Jinjin, ZHANG Haiyue, LI Jinghong. Multifunctional DNA Nanoflowers for Autophagy Inhibition and Enhanced Antitumor Chemotherapy† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1461. |
| [6] | ZHANG Zuoran, ZHANG Li, ZHANG Zhiling. On-chip Sorting of Beads with Different Magnetic Responsiveness by Lateral Magnetophoresis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1243. |
| [7] | BAI Bing,WANG Long,XU Gaigai,YANG Pengfei,ZHANG Gaihong,MAO Duobin. Synthesis and Antitumor Activities of α-2,7,11-Cembratriene-4,6-diol Derivatives † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 481. |
| [8] | YUAN Zhongwen, HE Lizhen, CHEN Tianfeng. Biomedical Applications of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12): 2690. |
| [9] | XIAO Yanhua, ZHANG Guangjie, ZONG Liang, LIU Guohong, REN Lijun, DONG Junxing. Chemical Constituents and Antitumor Activity of Tupistra chinensis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1897. |
| [10] | SHENG Bingchen, LI Cong, LIU Yingya, WANG Anjie, WANG Yao, ZHANG Jian, LIU Weixu. Microfluidic Synthesis of UiO-66 Metal-organic Frameworks Modified with Different Functional Groups† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7): 1365. |
| [11] | LÜ Mingjun,LI Wen,YANG Xinying,FANG Hao. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of N9 Position Aromatic Substituted Purine-8-one Derivatives† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 254. |
| [12] | FANG Fang,XUE Liangmin,CONG Jing,TIAN Chao,WANG Xiaowei,LIU Junyi,ZHANG Zhili. Synthesis and Anti-tumor Activity Evaluation of a Series of 2- or 4-Substituted Pyrido[3,2-d]pyrimidines as Nonclassical Antifolates † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2111. |
| [13] | ZHANG Peiquan,YANG Qianqian,LONG Huidan,CHEN Xin. Synthesis and Antitumor Activity of Auranofin Derivatives † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2097. |
| [14] | YANG Mingming,NAN Lijing,JIN Wanjun,WANG Chengjian,HUANG Linjuan,ZHANG Ying,WANG Zhongfu. Quali-quantitative Profiling of Mucin-type O-Glycans in Normal and Tumor Cell Lines Based on Oligosaccharide Metabolic Engineering Combined with Mass Spectrometry† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1904. |
| [15] | GUAN Qingxiang, JI Danyang, SUN Bo, QIAO Jin, HE Tong, ZHANG Guangyuan, YU Zhenjing, YIN Jianyuan, YANG Wei. Synthesis of Folate-conjugated Stearic Acid Grafted Bletilla striata Polysaccharides Copolymers and Application for Delivering Antitumor Drugs as a Drug Delivery Carrier† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1815. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||