

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (4): 714.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170683
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Gang1, ZHANG Heng1, SUN Heng2, ZHU Hongxia1, ZHANG Yuhan1, ZHU Qingzeng1,*( ), YUAN Shiling2,*(
), YUAN Shiling2,*( )
)
Received:2017-10-31
Online:2018-04-10
Published:2018-03-20
Contact:
ZHU Qingzeng,YUAN Shiling
E-mail:qzzhu@sdu.edu.cn;shilingyuan@sdu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Gang, ZHANG Heng, SUN Heng, ZHU Hongxia, ZHANG Yuhan, ZHU Qingzeng, YUAN Shiling. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on the Structure of Cellulose Inclusion Complexes and Interactions Between Cellulose Chains and Solvent Molecules in Alkali/urea Aqueous Solution†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 714.
| Atom | Charge/e | Atom | Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.340 | O2, O3, O6 | -0.650 |
| C2, C3, C4 | 0.140 | O1 | -0.650 |
| C5 | 0.110 | O5 | -0.400 |
| C6 | 0.050 | HO2, HO3, HO6 | 0.420 |
| H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6 | 0.090 |
Table 1 Partial atomic charges of cellulose
| Atom | Charge/e | Atom | Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.340 | O2, O3, O6 | -0.650 |
| C2, C3, C4 | 0.140 | O1 | -0.650 |
| C5 | 0.110 | O5 | -0.400 |
| C6 | 0.050 | HO2, HO3, HO6 | 0.420 |
| H1, H2, H3, H4, H5, H6 | 0.090 |
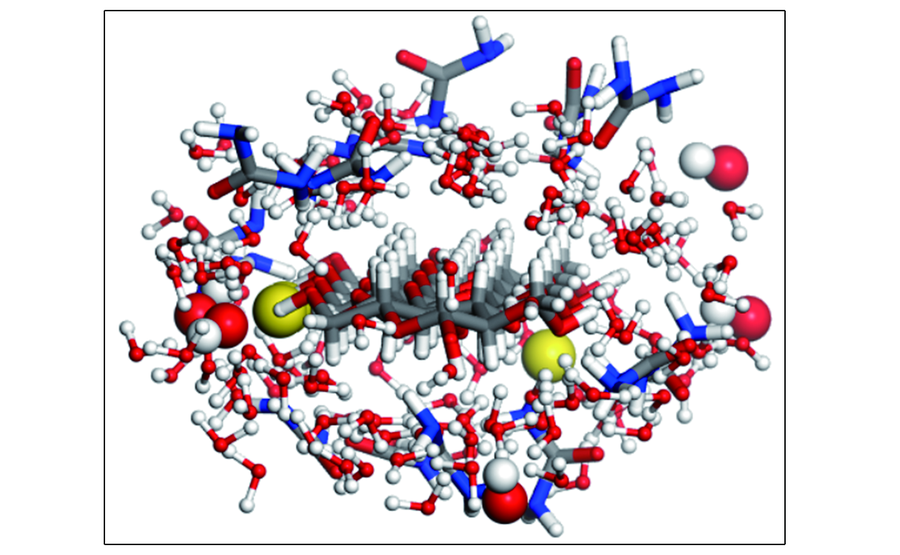
Fig.3 Side view of cellulose inclusion complexesThe cellulose and urea molecules are displayed in stick mode. Water molecules are displayed in ball and stick mode. Sodium ions and hydroxide ions are displayed in CPK mode.
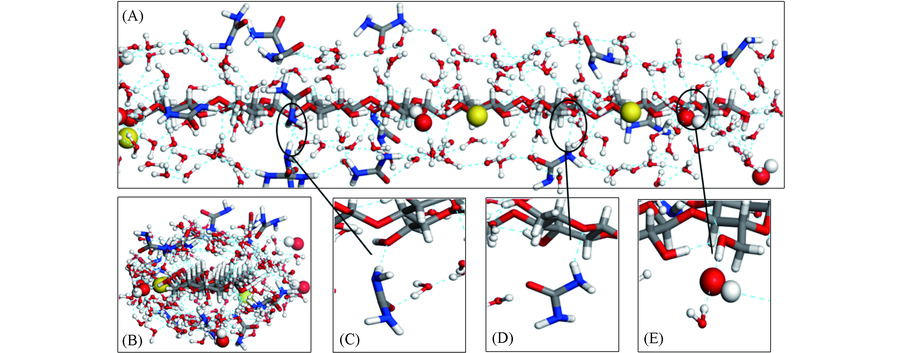
Fig.6 Hydrogen-bonding network of cellulose inclusion complexes(A, B), and the typical hydrogen-bonding structure(C-E)(A) Top view; (B) side view. The hydroxide ions and sodium ions are displayed in CPK mode. The cellulose molecule is displayed in stick mode. Water molecules are displayed in line mode.
| [1] | Ghanbari D., Salavati-Niasari M., Beshkar F., Amiri O., J. Mater. Sci-Mater. El., 2015, 26, 8358-8366 |
| [2] | Vega B., Wondraczek H., Bretschneider L., Nareoja T., Fardim P., Heinze T., Carbohyd. Polym., 2015, 132, 261-273 |
| [3] | Jiang G. S., Yuan Y., Wang B. C., Mukuze K. S., Huang W. F., Zhang Y. M., Wang H. P., Cellulose,2012, 19, 1075-1083 |
| [4] | Jimenez de la Parra C., Zambrano J. R., Dolores Bermejo M,, Martin A., Segovia J. J., Cocero M. J., Carbohyd. Polym., 2015, 91, 8-16 |
| [5] | Luo X. G., Zeng J., Liu S. L., Zhang L. N., Bioresour. Technol., 2015, 194, 403-406 |
| [6] | Zhou H. Y., Cao P. P., Li J. B., Zhang F. L., Ding P. P., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2015, 132, 42152 |
| [7] | Kolakovic R., Peltonen L., Laukkanen A., Hirvonen J., Laaksonen T., Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 2012, 82, 308-315 |
| [8] | He M., Zhao Y., Duan J., Wang Z., Chen Y., Zhang L., ACS Appl. Mat. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 1872-1878 |
| [9] | Huang C. F., Chen J. K., Tsai T. Y., Hsieh Y. A., Lin K. Y. A., Polymer,2015, 72, 195-200 |
| [10] | Han H., Liang Y., Wang F., Zhang Y., Food Science and Technology,2011, 36, 48-53 |
| (韩浩, 梁琰, 王凤, 张勇. 食品科技, 2011, 36, 50-53) | |
| [11] | Liu T., Liu N., Fang G. Z., Food Science, 2009, 30, 376-280 |
| (刘涛, 刘宁, 方桂珍. 食品科学, 2009, 30, 276-280) | |
| [12] | Fink H. P., Weigel P., Purz H. J., Ganster J., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2001, 26, 1473-1524 |
| [13] | Liu R. G., Shen Y. Y., Shao H. L., Wu C. X., Hu X. C., Cellulose,2001, 8, 13-21 |
| [14] | Morgenstern B., Kammer H. W., Berger W., Skrabal P., Acta Poly., 1992, 43, 356-357 |
| [15] | Zhang C., Liu R. G., Xiang J. F., Kang H. L., Liu Z. J., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118, 9507-9514 |
| [16] | Wang H., Gurau G., Rogers R. D., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 1519-1537 |
| [17] | Aaltonen O., Jauhiainen O., Carbohyd. Polym., 2009, 75, 125-129 |
| [18] | Cai J., Zhang L., Zhou J., Li H., Chen H., Jin H., Macromol. Rapid Comm., 2004, 25, 1558-1562 |
| [19] | Cai J., Zhang L., Biomacromolecules,2006, 7, 183-189 |
| [20] | Cai J., Zhang L., Zhou J., Qi H., Chen H., Kondo T., Chen X., Chu B., Adv. Mater., 2007, 19, 821-825 |
| [21] | Cai J., Zhang L., Chang C., Cheng G., Chen X., Chu B., Chem. Phys. Chem., 2007, 8, 1572-1579 |
| [22] | Lue A., Zhang L., Ruan D., Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2007, 208, 2359-2366 |
| [23] | Cai J., Zhang L., Macromol. Biosci., 2005, 5, 539-548 |
| [24] | Cai J., Zhang L., Liu S., Liu Y., Xu X., Chen X., Chu B., Guo X., Xu J., Cheng H., Macromolecules,2008, 41, 9345-9351 |
| [25] | Qin X., Lu A., Cai J., Zhang L., Carbohyd. Polym., 2013, 92, 1315-1320 |
| [26] | Jiang Z., Fang Y., Xiang J., Ma Y., Lu A., Kang H., Huang Y., Guo H., Liu R., Zhang L., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118, 10250-10257 |
| [27] | Cai L., Liu Y., Liang H., Polymer,2012, 53, 1124-1130 |
| [28] | Wernersson E., Stenqvist B., Lund M., Cellulose,2015, 22, 991-1001 |
| [29] | Miyamoto H., Ueda K., Yamane C., Nord. Pulp Pap. Res. J., 2015, 30, 67-77 |
| [30] | Guvench O., Hatcher E., Venable R. M., Pastor R. W., MacKerell A. D. Jr., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2009, 5, 2353-2370 |
| [31] | Weerashinghe S., Smith P. E., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 7, 3891-3898 |
| [32] | Hess B., Kutzner C., van der Spoel D., Lindahl E., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2008, 4,435-447 |
| [33] | Durell S. R., Brooks B. R., Ben-Naim A., J. Chem. Phys., 1994, 98, 2198-2202 |
| [34] | Gomes T. C., Skaf M. S., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33, 1338-1346 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [3] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [4] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [5] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [6] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [7] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [8] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [9] | QU Siying, XU Qin. Different Roles of Some Key Residues in the S4 Pocket of Coagulation Factor Xa for Rivaroxaban Binding † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| [10] | MA Yucong, FAN Baomin, WANG Manman, YANG Biao, HAO Hua, SUN Hui, ZHANG Huijuan. Two-step Preparation of Trazodone and Its Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism for Carbon Steel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| [11] | ZHANG Zhang,WANG Dong,WANG Xiaolei,XU Yan. Regulation of Ester Synthesis Activity of Rhizopus chinensis Lipase† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 747. |
| [12] | MA Lan,RONG Jingjing,ZHU Youliang,HUANG Yineng,SUN Zhaoyan. Simulation on the Dynamic Process of Formation of Particle Cluster by Generalized Exponential Model† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 195. |
| [13] | ZHU Jingxuan,YU Zhengfei,LIU Ye,ZHAN Dongling,HAN Jiarui,TIAN Xiaopian,HAN Weiwei. Exploration of Increasing the Non-specificity Substrates Activity for the Phosphotriesterase-like Lactonase Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 138. |
| [14] | WU Hongmei,LI Huiting,LI Yongcheng,WANG Hongqing,WANG Meng. Using Group Contribution Method and Molecular Dynamics to Predict the Glass Transition Temperature of Poly(p-phenylene isophthalamide)† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 180. |
| [15] | LIU Yanfang, YANG Hua, ZHANG Hui. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on the Orientation of Alkane Mixture on Graphene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1729. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||