

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 1568.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170213
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
DUAN Yongbin1, YIN Yan1,*, MENG Fanli1, ZHAO Lianhua1, LIU Yukun1, YUAN Zhe1, FENG Yangbo2
Received:2017-04-11
Online:2017-09-10
Published:2017-08-22
Contact:
YIN Yan
E-mail:yinyan@sit.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
DUAN Yongbin, YIN Yan, MENG Fanli, ZHAO Lianhua, LIU Yukun, YUAN Zhe, FENG Yangbo. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzothiazoles as Highly Potent ROCK Inhibitors Through Molecular Docking and Free Energy Calculations†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1568.
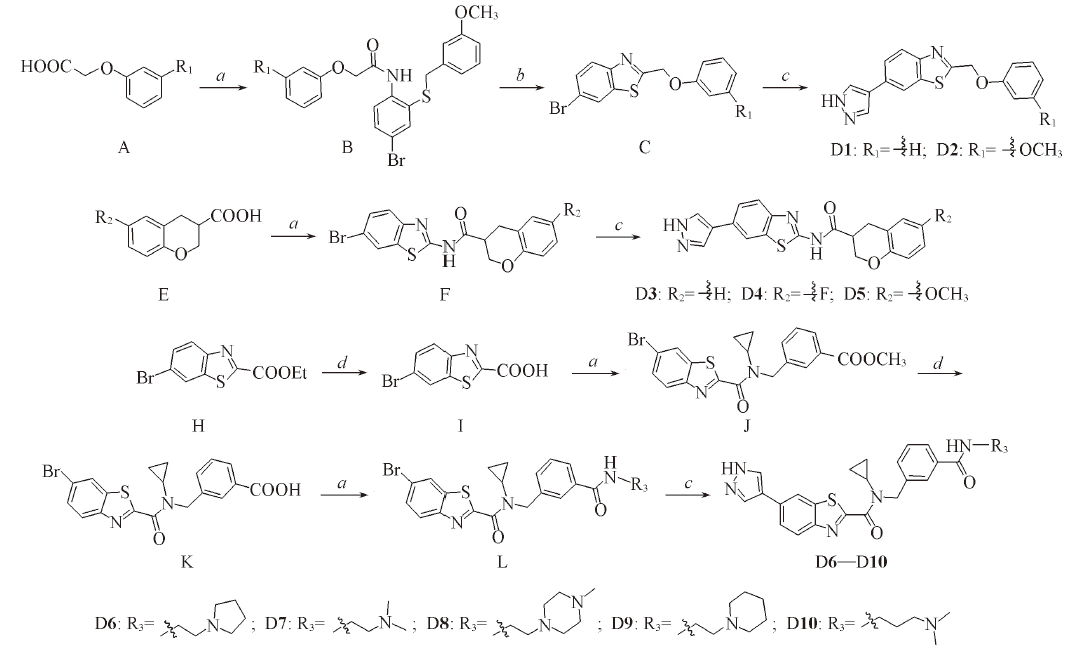
Scheme 1 Synthetic routes of compounds D1—D10Reagents and conditions: a. HATU, amine, DIEA, DMF, r. t. ; b. HOAc, TFA, 100 ℃; c. Pd(PPh3)4, K2CO3, 2-aminopyrid-in-4-ylboronic acid, dioxane/H2O, 95 ℃; d. saturated NaOH solution.
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield(%) | m.p./℃ | HRMS(calcd.)[M+H]+ | Elemental analysis(%, calcd.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | |||||
| D1 | White solid | 52% | 204—205 | 308.0872(308.0858) | 66.51(66.43) | 4.36(4.26) | 13.45(13.62) |
| D2 | White solid | 50% | 214—215 | 338.0947(338.0963) | 64.12(64.08) | 4.36(4.48) | 12.71(12.49) |
| D3 | White solid | 70% | 234—235 | 337.1061(337.1072) | 63.99(63.81) | 4.36(4.28) | 14.69(14.81) |
| D4 | White solid | 68% | 248—249 | 395.0959(395.0978) | 60.99(60.90) | 3.96(3.83) | 14.61(14.42) |
| D5 | White solid | 67% | 281—282 | 407.1193(407.1178) | 62.19(62.05) | 4.69(4.46) | 13.92(13.74) |
| D6 | White solid | 31% | 238—239 | 515.2241(515.2229) | 65.51(65.35) | 5.66(5.88) | 16.15(16.13) |
| D7 | White solid | 32% | 244—245 | 489.2059(489.2073) | 63.98(63.91) | 5.53(5.78) | 17.06(17.12) |
| D8 | White solid | 30% | 223—224 | 544.2503(544.2495) | 64.98(64.03) | 6.83(6.62) | 18.06(18.00) |
| D9 | White solid | 31% | 216—217 | 529.2359(529.2386) | 65.98(65.88) | 6.02(6.10) | 15.83(15.90) |
| D10 | White solid | 34% | 254—255 | 503.2247(503.2229) | 64.43(64.52) | 5.97(6.02) | 16.83(16.70) |
Table 1 Appearance, yields, melting points, HRMS and elemental analysis data of compounds D1—D10
| Compd. | Appearance | Yield(%) | m.p./℃ | HRMS(calcd.)[M+H]+ | Elemental analysis(%, calcd.) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | H | O | |||||
| D1 | White solid | 52% | 204—205 | 308.0872(308.0858) | 66.51(66.43) | 4.36(4.26) | 13.45(13.62) |
| D2 | White solid | 50% | 214—215 | 338.0947(338.0963) | 64.12(64.08) | 4.36(4.48) | 12.71(12.49) |
| D3 | White solid | 70% | 234—235 | 337.1061(337.1072) | 63.99(63.81) | 4.36(4.28) | 14.69(14.81) |
| D4 | White solid | 68% | 248—249 | 395.0959(395.0978) | 60.99(60.90) | 3.96(3.83) | 14.61(14.42) |
| D5 | White solid | 67% | 281—282 | 407.1193(407.1178) | 62.19(62.05) | 4.69(4.46) | 13.92(13.74) |
| D6 | White solid | 31% | 238—239 | 515.2241(515.2229) | 65.51(65.35) | 5.66(5.88) | 16.15(16.13) |
| D7 | White solid | 32% | 244—245 | 489.2059(489.2073) | 63.98(63.91) | 5.53(5.78) | 17.06(17.12) |
| D8 | White solid | 30% | 223—224 | 544.2503(544.2495) | 64.98(64.03) | 6.83(6.62) | 18.06(18.00) |
| D9 | White solid | 31% | 216—217 | 529.2359(529.2386) | 65.98(65.88) | 6.02(6.10) | 15.83(15.90) |
| D10 | White solid | 34% | 254—255 | 503.2247(503.2229) | 64.43(64.52) | 5.97(6.02) | 16.83(16.70) |
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ |
|---|---|
| D1 | 9.68(s, 1H, NH), 8.46—8.45(m, 1H), 8.20—8.19(m, 1H), 8.09—8.07(m, 1H), 7.90—7.89(m, 1H), 7.65—7.52(m, 4H), 7.32—7.23(m, 2H), 4.02(s, 2H, CH3) |
| D2 | 8.43(s, 1H, NH), 8.09—8.02(m, 2H), 7.89—7.84(m, 1H), 7.32—7.24(m, 2H), 6.93—6.86(m, 4H), 4.00(s, 2H, CH2), 3.75(s, 3H, CH3) |
| D3 | 12.94(s, 1H, NH), 12.63(s, 1H, NH), 8.22(s, 1H), 8.14—8.11(m, 1H), 7.74—7.72(m, 2H), 7.64—7.57(m, 1H), 7.16—7.08(m, 2H), 6.89—6.86(m, 1H), 6.80—6.78(m, 1H), 4.48—4.46(m, 1H, CH2), 4.14—4.10(m, 1H, CH2), 3.25—3.23(m, 1H, CH), 3.11—3.01(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D3 | 12.94(s, 1H, NH), 12.63(s, 1H, NH), 8.22(s, 1H), 8.14—8.11(m, 1H), 7.74—7.72(m, 2H), 7.64—7.57(m, 1H), 7.16—7.08(m, 2H), 6.89—6.86(m, 1H), 6.80—6.78(m, 1H), 4.48—4.46(m, 1H, CH2), 4.14—4.10(m, 1H, CH2), 3.25—3.23(m, 1H, CH), 3.11—3.01(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D4 | 12.63(s, 1H, NH), 8.22(s, 1H, NH), 8.21—8.05(m, 2H), 7.74—7.68(m, 2H), 7.05—7.02(m, 1H), 6.96—6.91(m, 2H), 6.82—6.79(m, 1H), 4.44(dd, J=10.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H, CH2), 4.13(dd, J=10.8, 8.4 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.25—3.23(m, 1H, CH), 3.07—3.02(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D5 | 12.61(s, 1H, NH), 8.25(s, 1H, NH), 8.22—8.21(m, 1H), 8.13—8.10(m, 2H), 7.74—7.68(m, 2H), 6.74—6.67(m, 3H), 4.40(dd, J=10.8, 2.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 4.06(dd, J=10.8, 8.8 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.69(s, 3H, OCH3), 3.09—2.96(m, 3H, CH, CH2) |
| D6 | 9.35(s, 1H, NH), 8.74—8.73(m, 1H, NH), 8.44—8.43(m, 1H), 8.19—8.07(m, 3H), 7.88—7.80(m, 2H), 7.55—7.54(m, 2H), 4.80(s, 2H, CH2), 3.58—3.56(m, 5H, CH, CH2), 3.34—3.30(m, 2H, CH2), 3.10—3.06(m, 2H, CH2), 1.85—1.84(m, 4H, CH2), 0.79—0.69(m, 4H, CH2) |
| D7 | 9.19(s, 1H, NH), 8.65—8.64(m, 1H), 8.37—8.36(m, 1H), 8.13—8.12(m, 1H), 8.02—8.00(m, 1H), 7.81—7.73(m, 3H), 7.48—7.47(m, 2H), 4.76(s, 2H), 3.62—3.61(m, 1H), 3.53—3.52(m, 2H), 3.20—3.10(m, 2H), 2.78(s, 3H), 2.77(s, 3H), 1.82—1.79(m, 2H), 0.83—0.79(m, 2H) |
| D8 | 9.17(s, 1H, NH), 8.6—8.58(m, 1H), 8.33—8.31(m, 1H), 8.10—8.08(m, 1H), 8.05—8.03(m, 1H), 7.85—7.76(m, 3H), 7.45—7.43(m, 2H), 4.72(s, 2H, CH2), 3.62—3.61(m, 1H, CH), 3.53—3.52(m, 6H, CH2), 3.20—3.10(m, 6H, CH2), 2.78(s, 3H, CH3), 1.80—1.79(m, 2H, CH2), 0.87—0.84(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D9 | 9.32(s, 1H, NH), 8.71—8.69(m, 1H), 8.47—8.45(m, 1H), 8.10—8.07(m, 3H), 7.88—7.64(m, 4H), 4.81(s, 2H, CH2), 3.65—3.63(m, 1H, CH), 3.58—3.56(m, 2H, CH2), 3.34—3.30(m, 2H, CH2), 3.10—3.06(m, 2H, CH2), 2.01—1.99(m, 2H, CH2), 1.85—1.84(m, 4H, CH2), 0.79—0.69(m, 6H, CH2) |
| D10 | 9.10(s, 1H, NH), 8.78—8.79(m, 1H), 8.34—8.30(m, 1H), 8.10—7.98(m, 2H), 7.85—7.74(m, 3H), 7.55—7.47(m, 2H), 4.75(s, 2H, CH2), 3.67—3.65(m, 1H, CH), 3.60—3.58(m, 2H, CH2), 3.56—3.54(m, 2H, CH2), 3.19—3.08(m, 2H, CH2), 2.80(s, 3H, CH3), 2.78(s, 3H, CH3), 1.80—1.78(m, 2H, CH2), 1.45—1.41(m, 2H, CH2), 0.84—0.83(m, 2H, CH2) |
Table 2 1H NMR data of compounds D1—D10
| Compd. | 1H NMR(400 MHz, DMSO-d6), δ |
|---|---|
| D1 | 9.68(s, 1H, NH), 8.46—8.45(m, 1H), 8.20—8.19(m, 1H), 8.09—8.07(m, 1H), 7.90—7.89(m, 1H), 7.65—7.52(m, 4H), 7.32—7.23(m, 2H), 4.02(s, 2H, CH3) |
| D2 | 8.43(s, 1H, NH), 8.09—8.02(m, 2H), 7.89—7.84(m, 1H), 7.32—7.24(m, 2H), 6.93—6.86(m, 4H), 4.00(s, 2H, CH2), 3.75(s, 3H, CH3) |
| D3 | 12.94(s, 1H, NH), 12.63(s, 1H, NH), 8.22(s, 1H), 8.14—8.11(m, 1H), 7.74—7.72(m, 2H), 7.64—7.57(m, 1H), 7.16—7.08(m, 2H), 6.89—6.86(m, 1H), 6.80—6.78(m, 1H), 4.48—4.46(m, 1H, CH2), 4.14—4.10(m, 1H, CH2), 3.25—3.23(m, 1H, CH), 3.11—3.01(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D3 | 12.94(s, 1H, NH), 12.63(s, 1H, NH), 8.22(s, 1H), 8.14—8.11(m, 1H), 7.74—7.72(m, 2H), 7.64—7.57(m, 1H), 7.16—7.08(m, 2H), 6.89—6.86(m, 1H), 6.80—6.78(m, 1H), 4.48—4.46(m, 1H, CH2), 4.14—4.10(m, 1H, CH2), 3.25—3.23(m, 1H, CH), 3.11—3.01(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D4 | 12.63(s, 1H, NH), 8.22(s, 1H, NH), 8.21—8.05(m, 2H), 7.74—7.68(m, 2H), 7.05—7.02(m, 1H), 6.96—6.91(m, 2H), 6.82—6.79(m, 1H), 4.44(dd, J=10.8, 2.4 Hz, 1H, CH2), 4.13(dd, J=10.8, 8.4 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.25—3.23(m, 1H, CH), 3.07—3.02(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D5 | 12.61(s, 1H, NH), 8.25(s, 1H, NH), 8.22—8.21(m, 1H), 8.13—8.10(m, 2H), 7.74—7.68(m, 2H), 6.74—6.67(m, 3H), 4.40(dd, J=10.8, 2.0 Hz, 1H, CH2), 4.06(dd, J=10.8, 8.8 Hz, 1H, CH2), 3.69(s, 3H, OCH3), 3.09—2.96(m, 3H, CH, CH2) |
| D6 | 9.35(s, 1H, NH), 8.74—8.73(m, 1H, NH), 8.44—8.43(m, 1H), 8.19—8.07(m, 3H), 7.88—7.80(m, 2H), 7.55—7.54(m, 2H), 4.80(s, 2H, CH2), 3.58—3.56(m, 5H, CH, CH2), 3.34—3.30(m, 2H, CH2), 3.10—3.06(m, 2H, CH2), 1.85—1.84(m, 4H, CH2), 0.79—0.69(m, 4H, CH2) |
| D7 | 9.19(s, 1H, NH), 8.65—8.64(m, 1H), 8.37—8.36(m, 1H), 8.13—8.12(m, 1H), 8.02—8.00(m, 1H), 7.81—7.73(m, 3H), 7.48—7.47(m, 2H), 4.76(s, 2H), 3.62—3.61(m, 1H), 3.53—3.52(m, 2H), 3.20—3.10(m, 2H), 2.78(s, 3H), 2.77(s, 3H), 1.82—1.79(m, 2H), 0.83—0.79(m, 2H) |
| D8 | 9.17(s, 1H, NH), 8.6—8.58(m, 1H), 8.33—8.31(m, 1H), 8.10—8.08(m, 1H), 8.05—8.03(m, 1H), 7.85—7.76(m, 3H), 7.45—7.43(m, 2H), 4.72(s, 2H, CH2), 3.62—3.61(m, 1H, CH), 3.53—3.52(m, 6H, CH2), 3.20—3.10(m, 6H, CH2), 2.78(s, 3H, CH3), 1.80—1.79(m, 2H, CH2), 0.87—0.84(m, 2H, CH2) |
| D9 | 9.32(s, 1H, NH), 8.71—8.69(m, 1H), 8.47—8.45(m, 1H), 8.10—8.07(m, 3H), 7.88—7.64(m, 4H), 4.81(s, 2H, CH2), 3.65—3.63(m, 1H, CH), 3.58—3.56(m, 2H, CH2), 3.34—3.30(m, 2H, CH2), 3.10—3.06(m, 2H, CH2), 2.01—1.99(m, 2H, CH2), 1.85—1.84(m, 4H, CH2), 0.79—0.69(m, 6H, CH2) |
| D10 | 9.10(s, 1H, NH), 8.78—8.79(m, 1H), 8.34—8.30(m, 1H), 8.10—7.98(m, 2H), 7.85—7.74(m, 3H), 7.55—7.47(m, 2H), 4.75(s, 2H, CH2), 3.67—3.65(m, 1H, CH), 3.60—3.58(m, 2H, CH2), 3.56—3.54(m, 2H, CH2), 3.19—3.08(m, 2H, CH2), 2.80(s, 3H, CH3), 2.78(s, 3H, CH3), 1.80—1.78(m, 2H, CH2), 1.45—1.41(m, 2H, CH2), 0.84—0.83(m, 2H, CH2) |
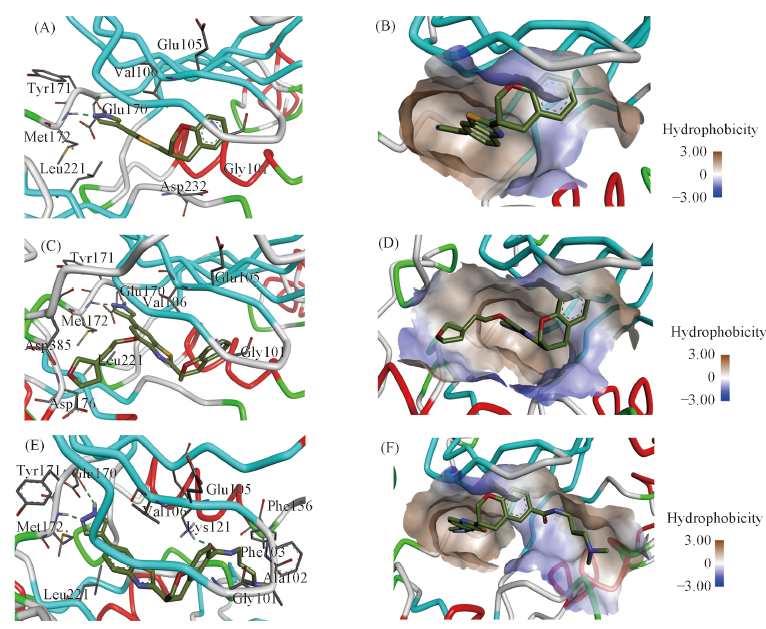
Fig.3 Docking results of compounds 1—3 and the catalytic domain of ROCK2(A), (C) and (E): interaction of compounds 1—3 and ROCK2, respectively; (B), (D) and (F): the hydrophobic pocket of ROCK2 with compounds 1—3, respectively.
| Compd. | ΔEVDW/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGSA/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔEELE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGGB/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGbind/ (kJ·mol-1) | IC50/ (nmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -181.4458 | -21.8627 | -152.2825 | 170.4642 | -185.1268 | 11 |
| 2 | -214.9761 | -26.5596 | -67.0682 | 140.4793 | -168.1246 | 500 |
| 3 | -226.3453 | -26.0829 | -141.0213 | 191.2943 | -202.1552 | 0.9 |
Table 3 Predicted binding free energies and individual energy components
| Compd. | ΔEVDW/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGSA/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔEELE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGGB/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔGbind/ (kJ·mol-1) | IC50/ (nmol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -181.4458 | -21.8627 | -152.2825 | 170.4642 | -185.1268 | 11 |
| 2 | -214.9761 | -26.5596 | -67.0682 | 140.4793 | -168.1246 | 500 |
| 3 | -226.3453 | -26.0829 | -141.0213 | 191.2943 | -202.1552 | 0.9 |
| Compd. | Structure | IC50/(nmol·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROCK1 | ROCK2 | |||
| 1 | 64 | 11 | 18 | |
| 3 | 2 | 0.9 | 34 | |
| D1 | 72 | 44 | 60 | |
| D2 | 64 | 42 | 19 | |
| D3 | 72 | 14 | 45.9 | |
| D4 | 171 | 22 | 56.4 | |
| D5 | 288 | 105 | 91 | |
| D6 | 60 | 21 | 30 | |
| D7 | 95 | 35 | 12 | |
| D8 | 11 | 2 | 9 | |
| D9 | 58 | 37 | 13 | |
| D10 | 45 | 19 | 45 | |
Table 4 Inhibitory activities and metabolic stabilities of newly designed inhibitors
| Compd. | Structure | IC50/(nmol·L-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROCK1 | ROCK2 | |||
| 1 | 64 | 11 | 18 | |
| 3 | 2 | 0.9 | 34 | |
| D1 | 72 | 44 | 60 | |
| D2 | 64 | 42 | 19 | |
| D3 | 72 | 14 | 45.9 | |
| D4 | 171 | 22 | 56.4 | |
| D5 | 288 | 105 | 91 | |
| D6 | 60 | 21 | 30 | |
| D7 | 95 | 35 | 12 | |
| D8 | 11 | 2 | 9 | |
| D9 | 58 | 37 | 13 | |
| D10 | 45 | 19 | 45 | |
| [1] | Nakagawa O., Fujisawa K., Ishizaki T., Saito Y., Nakao K., Narumiya S., FEBS Lett., 1996, 392(2), 189—193 |
| [2] | Uehata M., Ishizaki T., Satoh H., Ono T., Kawahara T., Morishita T., Narumiya S., Nature,1997, 389(6654), 990—994 |
| [3] | Sato M., Tani E., Fujikawa H., Kaibuchi K., Circ. Res., 2000, 87(3), 195—200 |
| [4] | Kajikawa M., Noma K., Nakashima A., Maruhashi T., Iwamoto Y., Matsumoto T., Aibara Y., Hypertension,2015, 66(4), 892—899 |
| [5] | del Re D. P., Miyamoto S., Brown J. H., J. Biol. Chem., 2007, 282(11), 8069—8078 |
| [6] | Fernández-Gamba A., Leal M. C., Maarouf C. L., Richter-Landsberg C., Wu T., Morelli L., Castaño E. M., J. Neurochem., 2012, 121(6), 985—995 |
| [7] | Challa P., Arnold J. J., Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs, 2014, 23(1), 81—95 |
| [8] | Surma M., Wei L., Shi J., Future Cardiol., 2011, 7(5), 657—671 |
| [9] | Huentelman M. J., Stephan D. A., Talboom J., Corneveaux J. J., Reiman D. M., Gerber J. D., Bimonte-Nelson H. A., Behav. Neurosci., 2009, 123(1), 218—223 |
| [10] | Rath N., Olson M. F., EMBO Rep., 2012, 13(10), 900—908 |
| [11] | Shimizu Y., Dobashi K., Sano T., Yamada M., Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol., 2014, 27(1), 37—44 |
| [12] | Schirok H., Paulsen H., Kroh W., Chen G., Gao P., Org. Process Res. Dev., 2009, 13(2), 168—173 |
| [13] | Shen M., Zhou S., Li Y., Pan P., Zhang L., Hou T., Mol. BioSyst., 2013, 9(3), 361—374 |
| [14] | Sumi K., Inoue Y., Nishio M., Naito Y., Hosoya T., Suzuki M., Hidaka H., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2014, 24(3), 831—834 |
| [15] | Yin Y., Lin L., Ruiz C., Khan S., Cameron M. D., Grant W., LoGrasso P. V., J. Med. Chem., 2013, 56(9), 3568—3581 |
| [16] | Green J., Cao J., Bandarage U. K., Gao H., Court J., Marhefka C., Shah S., J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58(12), 5028—5037 |
| [17] | Boland S., Bourin A., Alen J., Geraets J., Schroeders P., Castermans K., Vanormelingen J., J. Med. Chem., 2015, 58(10), 4309—4324 |
| [18] | Ding M., Yin Y., Wu F., Cui J., Zhou H., Sun G., Feng Y., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2015, 23(10), 2505—2517 |
| [19] | Cui J., Ding M., Deng W., Yin Y., Wang Z., Zhou H., Feng Y., Bioorg. Med. Chem., 2015, 23(23), 7464—7477 |
| [20] | Zhao Z., Cui J., Yin Y., Zhang H., Liu Y., Zeng R., Wu F., Chin. J. Chem., 2016, 34(8), 801—808 |
| [21] | Yin Y., Lin L., Ruiz C., Cameron M. D., Pocas J., Grant W., LoGrasso P., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2009, 19(23), 6686—6690 |
| [22] | Huang Y. L., Gao X. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5), 928—931 |
| (黄义玲, 高雪峰.高等学校化学学报,2016, 37(5), 928—931) | |
| [23] | Li H., Zou H., Liu L., Zhao D., Yang Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2017, 33(2), 239—247 |
| [24] | Yang H., Ren Y., Gao X., Gao Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(6), 973—978 |
| [25] | Maier J. A., Martinez C., Kasavajhala K., Wickstrom L., Hauser K. E., Simmerling C., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2015, 11(8), 3696—3713 |
| [26] | Homeyer N., Gohlke H., Mol. Inf., 2012, 31(2), 114—122 |
| [27] | Huo S., Wang J., Cieplak P., Kollman P. A., Kuntz I. D., J. Med. Chem., 2002, 45(7), 1412—1419 |
| [28] | Onufriev A., Bashford D., Case D. A., Proteins,2004, 55(2), 383—394 |
| [29] | Weiser J., Shenkin P. S., Still W. C., J. Comput. Chem., 1999, 20(2), 217—230 |
| [30] | Hou T., Wang J., Li Y., Wang W., J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2010, 51(1), 69—82 |
| [31] | Hou T., Li N., Li Y., Wang W., J. Proteome Res., 2012, 11(5), 2982—2995 |
| [32] | Gohlke H., Kiel C., Case D. A., J. Mol. Biol., 2003, 330(4), 891—913 |
| [33] | Yin Y., Ruiz C., Khan S., Cameron M. D., Grant W., Pocas J., Eid N., Park H., Schröter T., LoGrasso P. V., Feng Y. B., J. Med. Chem., 2013, 56(21), 3568—3581 |
| [34] | Kamenecka T., Jiang R., Song X., Duckett D., Chen W., Ling Y. Y., Cameron M. D., J. Med. Chem., 2010, 53(1), 419—431 |
| [35] | Sessions E. H., Yin Y., Bannister T. D., Weiser A., Griffin E., Pocas J., Schröter T., Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett., 2008, 18(24), 6390—6393 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [3] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [4] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [5] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [6] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [7] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [8] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [9] | SHUAI Die, ZHAO Meijuan, CHEN Bingnian, WANG Li. Inhibitory Effect of Four Kinds of Keegin-type Phosphomolybdate on Tyrosinase and Melanin Formation and Its Antioxidant Activities [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3579. |
| [10] | YANG Ju, SU Lijiao, LI Canhua, LU Jiajia, YANG Junli, GU Jie, YANG Li, YANG Lijuan. Host-guest Complexation Behavior of Nardosinone and Water-soluble Phosphate Salt Pillar[6]arene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3099. |
| [11] | ZHANG Aiqin, WANG Man, SHEN Gangyi, JIN Jun. Interactions Between Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Using SPR and Molecular Docking [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2054. |
| [12] | WANG Lianping,LI Qingjie,LIU Xiaoyan,REN Yueying,YANG Xiuwei. Screening of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Fructus Evodiae Alkaloids Based on UFLC-MS/molecular Simulation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 111. |
| [13] | WANG Xiaoxia, MA Litong, NIE Zhihua, WANG Zhengde, CUI Jinlong, ZHAO Wenyuan, SAI Huazheng. Interaction Between Fulvic Acid and Pepsin Investigated by Multispectral and Molecular Docking Simulation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1840. |
| [14] | QU Siying, XU Qin. Different Roles of Some Key Residues in the S4 Pocket of Coagulation Factor Xa for Rivaroxaban Binding † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| [15] | MA Yucong, FAN Baomin, WANG Manman, YANG Biao, HAO Hua, SUN Hui, ZHANG Huijuan. Two-step Preparation of Trazodone and Its Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism for Carbon Steel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||