

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (10): 1891.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160459
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WU Bo1,2, ZHENG Guo1,2,*( ), LIU Xuzhao2,3, SUN Yu2,4, LIU Huibing2,4, ZHU Jiawen2,4
), LIU Xuzhao2,3, SUN Yu2,4, LIU Huibing2,4, ZHU Jiawen2,4
Received:2016-06-30
Online:2016-10-10
Published:2016-09-20
Contact:
ZHENG Guo
E-mail:zhengguo0703@163.com
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WU Bo, ZHENG Guo, LIU Xuzhao, SUN Yu, LIU Huibing, ZHU Jiawen. Preparation of High Hydrophilic Epoxy Resin and Its Treatment on Carbon Fiber Surface†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1891.
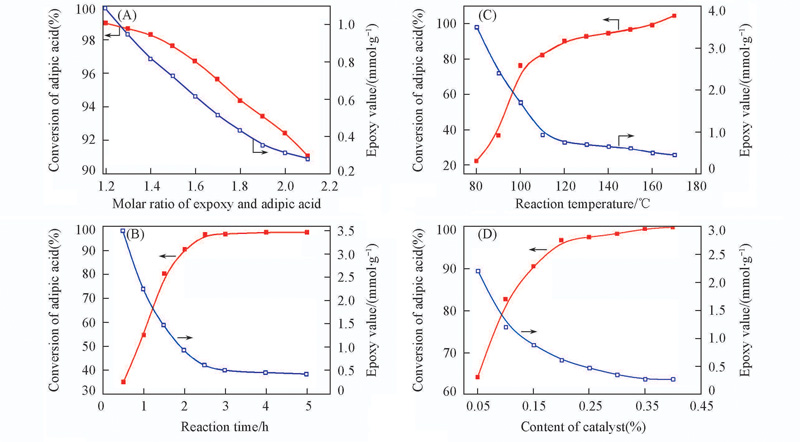
Fig.1 Effect of molar ratio(A), reaction temperature(B), reaction time(C) and content of catalyst(D) on conversion of adipic acid and epoxy value of AAEP
| Epoxy value/(mmol·g-1) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation mass/g | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.056 | 0.093 | 0.125 | 0.180 |
Table 1 Influence of epoxy value of AAEPK on the emulsion centrifugal stability
| Epoxy value/(mmol·g-1) | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Precipitation mass/g | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.056 | 0.093 | 0.125 | 0.180 |
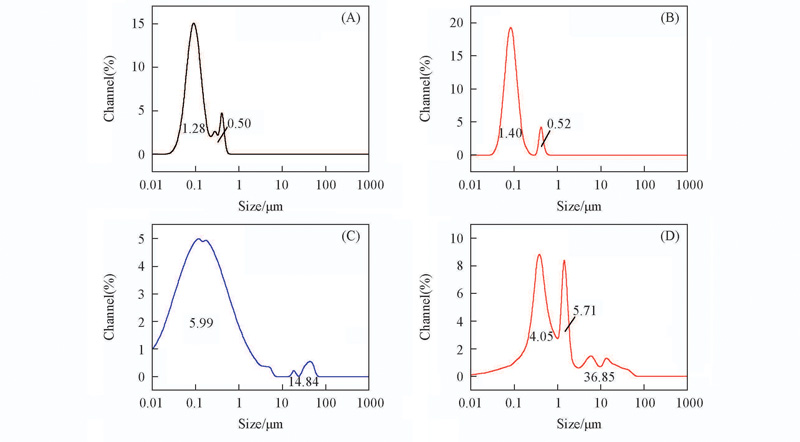
Fig.5 Influence of epoxy value of AAEPK on the emulsion size distributionEpoxy value/(mmol·g-1): (A) 0.4; (B) 0.6; (C) 0.8; (D) 1.0. The peak values are corresponding to the peak areas.
| Sample | Element content(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | |
| CF | 82.95 | 10.99 | 1.92 |
| CF-AAEPK | 72.73 | 22.74 | 1.35 |
Table 2 Element compositions of the surfaces of CF and CF-AAEPK
| Sample | Element content(%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | N | |
| CF | 82.95 | 10.99 | 1.92 |
| CF-AAEPK | 72.73 | 22.74 | 1.35 |
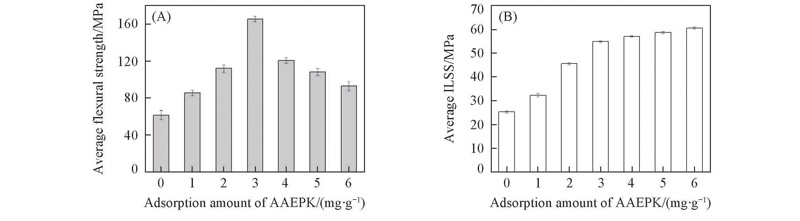
Fig.9 Mechanical property of CF/epoxy resin composites(A) Flexural strength of chopped CF/epoxy resin composites; (B) ILSS of CF cloth/epoxy resin composites. ILSS: interlaminar shear strength.
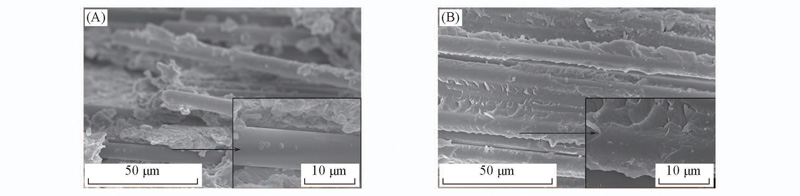
Fig.10 FE-SEM images of the fractured surfaces of the CF cloth/epoxy resin composites(A) CF composite; (B) AAEPK-CF composite. Insets are the partial enlangement to the FE-SM images.
| [1] | Vishkaei M. S., Salleh M. A. M., Yunus R., Biak D. R. A., Danafar F., Mirjalili F., J. Compos. Mater., 2011, 45(18), 1885—1891 |
| [2] | Ren F.Z., Fabrication and Performance of Short Carbon Fiber Reinforced Magnesium-based Composite, Chongqing University, Chongqing, 2011 |
| (任富忠. 短碳纤维增强镁基复合材料的制备及其性能的研究, 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011) | |
| [3] | Tiedje E. W., Guo P., J. Mater. Civil. Eng., 2014, 26(7), 06014013-1—06014013-4 |
| [4] | Giraud I., Franceschi-Messant S., Perez E., Lacabanne C., Dantras E., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 266, 94—99 |
| [5] | Wen J., Xia Z., Choy F., Compos. Part B: Eng., 2011, 42(1), 77—86 |
| [6] | Vogt-Birnbrich B., Awokola M. G., Beyers H., Aqueous Dispersions of Epoxy Resins, US 6258875 B1, 2001-07-10 |
| [7] | Li J., Li P., Cai Q., Yang X. P., New Chemical Materials, 2015, 43(1), 178—181 |
| (李晋, 李鹏, 蔡晴, 杨小平. 化工新型材料 2015, 43(1), 178—181) | |
| [8] | Su Y. Q., Tang B. J., Dong A. Q., Zhao Y., Zhang Z. G., Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2011, 28(6), 80—85 |
| (苏玉芹, 汤冰洁, 董安琪, 肇研, 张佐光.复合材料学报, 2011,28(6), 80—85) | |
| [9] | Yuan C. D., Duan C. H., Xu Y. S., Cao T. Y., Thermosetting Resin, 2007, 22(2), 19—22 |
| (袁才登, 段春华, 许涌深, 曹同玉.热固性树脂, 2007,22(2), 19—22) | |
| [10] | Zhang Z. Y., Huang Y. H., Liao B., Cong G. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(5), 974—978 |
| (张肇英, 黄玉惠, 廖兵, 丛广民.高等学校化学学报, 2002,23(5), 974—978) | |
| [11] | Huang X.X., Preparation of Hydrophobic and Oleophilic Waterborne Epoxy Emulsion and Its Application to Water/Oil Separation Filter Paper, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2012 |
| (黄相璇. 超疏水/超亲油水性环氧树脂乳液涂层的制备及在油水分离滤纸中的应用研究, 广州: 华南理工大学, 2012) | |
| [12] | Li C., Guo L. M., Technical Textiles, 2011, 29(6), 40—42 |
| (李超, 郭腊梅.产业用纺织品, 2011,29(6), 40—42) | |
| [13] | GB/T2895-2008, Plastics-polyester Resin-determination of Partial Acid Value and Total Acid Value, Standard Press of China, Beijing, 2008 |
| (GB/T2895-2008GB/T2895-2008. 塑料聚酯树脂部分酸值和总酸值的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [14] | GB/T1677-2008, Determinating the Epoxy Value of Plasticizers, Standard Press of China, Beijing, 2008 |
| (GB/T1677-2008.增塑剂环氧值的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [15] | GB/T22237-2008, Surface Active Agents-determination of Surface Tension, Standard Press of China, Beijing, 2008 |
| (GB/T22237-2008GB/T22237-2008. 表面活性剂表面张力的测定, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008) | |
| [16] | GB/T24368-2009, Test Method for Hydrophobic Contamination on Glass by Contact Angle Measurement, Standard Press of China, Beijing, 2009 |
| (GB/T24368-2009GB/T24368-2009. 玻璃表面疏水污染物检测接触角测量法, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009) | |
| [17] | Jung M. J., Ju W. K., Ji S. I., Park S. J., Lee Y. S., J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2009, 15(3), 410—414 |
| [18] | Yang Y., Cement. Concrete. Res., 2002, 32(5), 747—750 |
| [19] | GB/T1449-2005, Fiber-reinforced Plastic Composites-determination of Flexural Properties, Standard Press of China, Beijing, 2005 |
| (GB/T1449-2005. 纤维增强塑料弯曲性能试验方法, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005) | |
| [20] | JC/T773-2010, Fibre-reinforced Plastics Composites-Determination of Apparent Interlaminar Shear Strength by Short-beam Method, Standard Press of China, Beijing, 2010 |
| (JC/T773-2010. 纤维增强塑料短梁法测定层间剪切强度, 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010) | |
| [21] | Deng X., Mammen L., Butt H. J., Vollmer D., Science, 2012, 335(6064), 67—70 |
| [22] | Cheng Q., Tang J., Zhang H., Qin L. C., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2014, 616/617, 35—39 |
| [23] | Sun H., Guo G., Memon S. A., Xu W., Zhang Q., Zhu J. H., Compos. Part A: Appl. S., 2015, 78, 10—17 |
| [24] | Song H. H., Oh H. J., Lee H. C., Kim S. S., Compos. Part. B: Eng., 2013, 45(1), 172—177 |
| [1] | YANG Zhaohua, CHENG Hongjing, YANG Yi, LIU Hui, DU Feipeng, ZHANG Yunfei. Preparation of Silver-loaded Polyvinyl Alcohol Sponge and Its Interfacial Photothermal Driven Water Evaporation Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220181. |
| [2] | ZHAO Lingyun, HUANG Hanxiong, LUO Duyu, SU Fengchun. Effect of Flexibility of Composites on Performances of Sensors with Micro-structured Inverted Pyramid Arrays [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2953. |
| [3] | DONG Luming, SU Yanyue, WANG Chunzheng, QIAO Yafei, CHEN Yajun, MA Haiyun. Synthesis of Micro- to Nano-scale Perovskite Calcium Hydroxytinate and Its Performance as a Flame Retardant in Epoxy Resin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 937. |
| [4] | WANG Peng, MAO Dan, WAN Jiawei, QI Qi, DU Jiang, WANG Dan. Effect of Hollow Multi-shelled TiO2 on Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3218. |
| [5] | SHA Di, YU Xumin, ZHAO Jiang, MA Xiaofei, WANG Hanfu, LIU Fangfang, QIU Xuepeng. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Triaxial Woven Fabric/Epoxy Composites † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 838. |
| [6] | WANG Zhenyu, LI Jianhua, GUO Huijun, YANG Chuncai. In situ Synthesis of Nano-sized Silica Enforced Anionic Polyester Sizing Agent and Its Effect on ILSS of Carbon Fiber Composites † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 2005. |
| [7] | HAN Tao,CAI Xiaoxia,LI Cong,QIAO Congde,ZHAO Hui. Preparation and Properties Characterization of Biobased Dihydrocoumarin Toughened Epoxy Resin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1043. |
| [8] | WANG Na,YANG Fei,ZHANG Jing,FANG Qinghong. Inflame-retardant Water-borne Epoxy Resin of APP Microsphere with Carrageenan Cladding† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 385. |
| [9] | Minwen JIANG,Chenhui YIN,Sheng LI,Xiaoli LI. Synthesis of DOPO-based Cyclotriphosphazene Macromolecule Flame Retardant and Its Performance in Flame-retarded Epoxy Resin † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2615. |
| [10] | YE Longqiang,KANG Shuo,ZHANG Weihao,ZHANG Yulu,HUI Zhenzhen,JIANG Bo. Sol-gel Preparation of Anti-Fogging SiO2/SiO2-TiO2 Double-layer Antireflective Coating † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2274. |
| [11] | QIAN Yihao, ZHANG Dongjie, CHENG Zhongjun, KANG Hongjun, LIU Yuyan. Preparation of Hydrophilic Epoxy Resin and Its Wettability Regulation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1823. |
| [12] | LI Yuan, WANG Tingting, LI Mei, CHENG Han. Determination of Dopamine Based on RO/Gold Nanoparticles-poly(dienedimethylammonium chloride) Modified Carbon Fiber Microelectrode† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1656. |
| [13] | WANG Yingnan, DAI Xueyan, XU Tianlu, QU Lijie, ZHANG Chunling. Preparation and Anticorrosion Properties of Silane Grafted Nano-silica/Epoxy Composite Coating† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1564. |
| [14] | LI Yuan,WANG Tingting,LI Mei,GU Fei,BAO Changhao,HUANG Rongping,MA Jingfang,CHENG Han. Quantitative Determination of 5-HT by Electrochemical Current-correction Method† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 876. |
| [15] | KANG Hongjun,YU Xiaoyan,LAI Hua,CHENG Zhongjun,LIU Yuyan. Reversible Control of Under-oil Superhydrophobicity to Superhydrophilicity on TiO2 Nanostructured Thin Film† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2621. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||