

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 1012.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20141022
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
PENG Wei1, WANG Lijun1, QIAO Xiuying1,*( ), SHAO Zhengzhong2, SUN Kang1
), SHAO Zhengzhong2, SUN Kang1
Received:2014-11-18
Online:2015-05-10
Published:2015-04-15
Contact:
QIAO Xiuying
E-mail:xyqiao@sjtu.edu.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
PENG Wei, WANG Lijun, QIAO Xiuying, SHAO Zhengzhong, SUN Kang. Emulsification Activity of Natural Silk Fibroin[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(5): 1012.
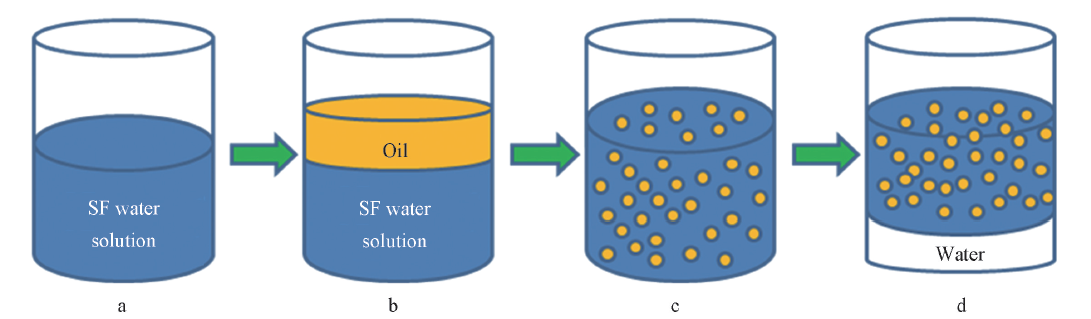
Fig.1 Illustration of the preparation process of the emulsions stabilized by silk fibroina. Silk fibroin water solution with different concentration(φSF); b. adding different oil with different volume fraction(ϕO) on the top; c. polydisperse emulsion; d. final stable emulsion with resolved water on the bottom.
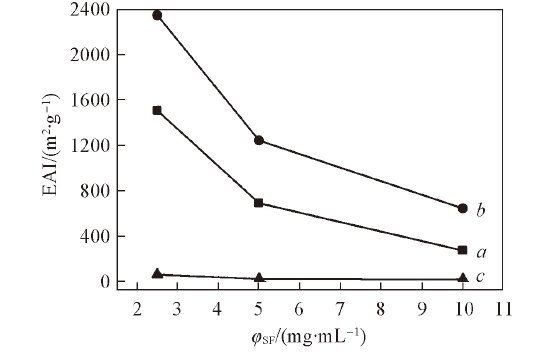
Fig.2 Change of EAI with silk fibroin concentration for the emulsions stabilized by silk fibroin with ϕO=0.3 and different oil phasesa. Dodecane; b. butyl butyrate; c. hexanol.
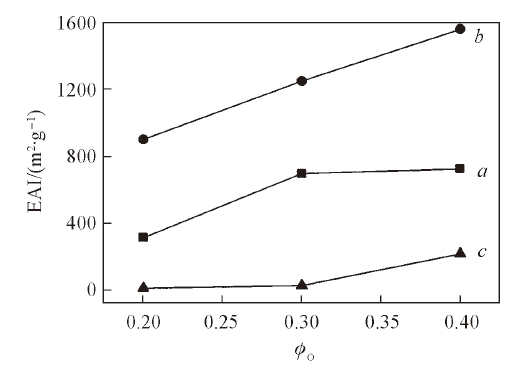
Fig.3 Change of EAI with oil volume fraction for the emulsions stabilized by silk fibroin with φSF=5 mg/mL and different oil phasesa. Dodecane; b. butyl butyrate; c. hexanol.

Fig.4 Photos of the vessels containing the O/W emulsions stabilized by silk fibroin with ϕO=0.3 and different φSF initially in water and different oil phases for 7 d (A) Dodecane; (B) butyl butyrate; (C) hexanol. φSF/(mg·mL-1): a. 2.5; b. 5; c. 10.
| Oil phase | φSF /(mg·mL-1) | ϕO | Stable emulsion fraction(%) | Droplet size/μm | Zeta-potential/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dodecane | 2.5 | 0.3 | 47.2 | 27.5 | -28 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 52.8 | 35.4 | -30.7 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 55.6 | 53.8 | -34.2 | |
| 5 | 0.2 | 38.9 | 32.0 | -32.8 | |
| 5 | 0.4 | 65.3 | 37.8 | -29.6 | |
| Butyl butyrate | 2.5 | 0.3 | 60.5 | 30.3 | -19.5 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 78.4 | 26.3 | -21.4 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 84.2 | 21.9 | -25.2 | |
| 5 | 0.2 | 63.2 | 25.0 | -20.4 | |
| 5 | 0.4 | 89.5 | 28.7 | -22.6 | |
| Hexanol | 2.5 | 0.3 | 65.0 | 35.6 | -24.6 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 77.5 | 27.5 | -31.2 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 77.5 | 22.5 | -30.9 | |
| 5 | 0.2 | 45.0 | 23.0 | -27.2 | |
| 5 | 0.4 | 95.0 | 45.5 | -27.6 |
Table 1 Stable emulsion fraction, droplet size and droplet surface charge of different emulsions stabilized by silk fibroin with different φSF initially in water, different ϕO and different oil phases
| Oil phase | φSF /(mg·mL-1) | ϕO | Stable emulsion fraction(%) | Droplet size/μm | Zeta-potential/mV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dodecane | 2.5 | 0.3 | 47.2 | 27.5 | -28 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 52.8 | 35.4 | -30.7 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 55.6 | 53.8 | -34.2 | |
| 5 | 0.2 | 38.9 | 32.0 | -32.8 | |
| 5 | 0.4 | 65.3 | 37.8 | -29.6 | |
| Butyl butyrate | 2.5 | 0.3 | 60.5 | 30.3 | -19.5 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 78.4 | 26.3 | -21.4 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 84.2 | 21.9 | -25.2 | |
| 5 | 0.2 | 63.2 | 25.0 | -20.4 | |
| 5 | 0.4 | 89.5 | 28.7 | -22.6 | |
| Hexanol | 2.5 | 0.3 | 65.0 | 35.6 | -24.6 |
| 5 | 0.3 | 77.5 | 27.5 | -31.2 | |
| 10 | 0.3 | 77.5 | 22.5 | -30.9 | |
| 5 | 0.2 | 45.0 | 23.0 | -27.2 | |
| 5 | 0.4 | 95.0 | 45.5 | -27.6 |
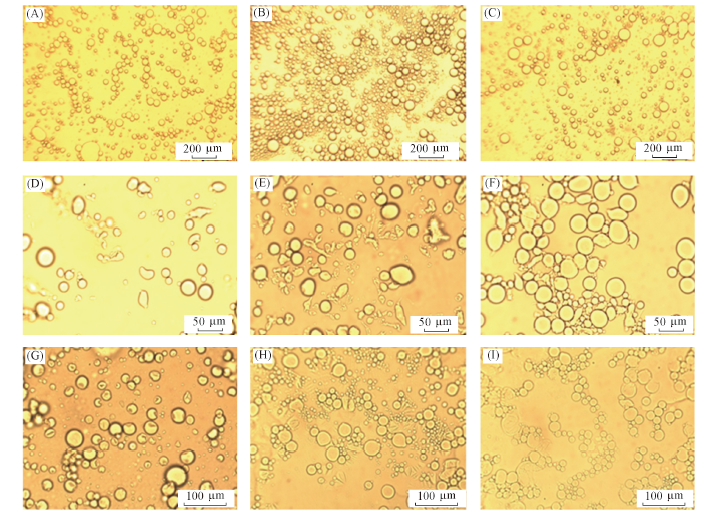
Fig.5 Microscope images for the oil/water emulsions stabilized by silk fibroin with the same φSF initially in water(φSF =5 mg/mL) but different ϕO and oil phases for 7 d(A) ϕO=0.2, dodecane; (B) ϕO=0.3, dodecane; (C) ϕO=0.4, dodecane; (D) ϕO=0.2, butyl butyrate; (E) ϕO=0.3, butyl butyrate; (F) ϕO=0.4, butyl butyrate; (G) ϕO=0.2, hexane; (H) ϕO=0.3, hexane; (I) ϕO=0.4, hexane.
| [1] | McClements D . J., Food Emulsions: Principles, Practice, and Techniques, CRC Press, Florida, USA, 1999, 1- 16 |
| [2] | Perrechil F., A. , Cunha R., L. , J. Food Eng., 2010, 97( 4), 441- 448 |
| [3] | 刘国鹏, 王君, 李伟, 刘尚营, 孙德军. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34( 2), 386- 393 |
| Liu G., P. , Wang, J. , Li, W. , Liu S., Y. , Sun D., J. , Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34( 2), 386- 393 | |
| [4] | 喻火贵, 易英. 武汉大学学报, 2013, 59( 1), 61- 65 |
| Yu H., G. , Yi, Y. , J. Wuhan University, 2013, 59( 1), 61- 65 | |
| [5] | Bos M., A. , van Vliet, T. , Adv. Colloid Interface Sci., 2001, 91( 3), 437- 471 |
| [6] | Dickinson, E. , Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces, 2001, 20( 3), 197- 210 |
| [7] | Mirhosseini, H. , Tan C., P. , Hamid N. S., A. , Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp., 2008, 315( 1-3), 47- 56 |
| [8] | Wongpanit, P. , Tabata, Y. , Rujiravanit, R. , Macromol. Biosci., 2007, 7( 12), 1258- 1271 |
| [9] | Jin H., J. , Park, J. , Valluzzi, R. , Cebe, P. , Kaplan D., L. , Biomacromolecules, 2004, 5( 3), 711- 717 |
| [10] | Altman G., H. , Horan R., L. , Lu H., H. , Moreau, J. , Martin, I. , Richmond J., C. , Kaplan D., L. , Biomaterials, 2002, 23( 20), 4131- 4141 |
| [11] | Kim U., J. , Park, J. , Kim H., J. , Wada, M. , Kaplan D., L. , Biomaterials, 2005, 26( 15), 2775- 2785 |
| [12] | Rao J., J. , Chen Z., M. , Chen B., C. , Food Technol. Biotechnol., 2009, 47( 4), 413- 420 |
| [13] | Alamed, J. , McClements D., J. , Decker E., A. , Food Chem., 2006, 95( 4), 585- 590 |
| [14] | Gu Y., S. , Regnier, L. , McClements D., J. , J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2005, 286( 2), 551- 558 |
| [15] | Krstonošic' V gt;evic' T ., Food Hydrocolloids, 2009, 23, 2212- 2218 |
| [16] | Figueiredo E., N. , Arê, as J. A. G. , Arê, as E. P. G. , J. Brazil Chem. Soc., 2008, 19, 1336- 1346 |
| [17] | Pearce K., N. , Kinsella J., E. , J. Agr. Food Chem., 1978, 26( 3), 716- 723 |
| [18] | Cameron D., R. , Weber M., E. , Idziak E., S. , Neufeld R., J. , Cooper D., G. , J. Agr. Food Chem., 1991, 39( 4), 655- 659 |
| [19] | Guo, Q. , Mu T., H. , Food Hydrocolloids, 2011, 25( 1), 98- 106 |
| [20] | Agyare K., K. , Addo, K. , Xiong Y., L. , Food Hydrocolloids, 2009, 23( 1), 72- 81 |
| [21] | Sze T., K. , Sathe, S. , Food Chem., 2000, 69( 2), 153- 160 |
| [22] | Dagorn S., C. , Gueguen, J. , Lefebvre, J. , J. Food Sci., 1987, 52( 2), 335- 341 |
| [23] | Joshi, M. , Adhikari, B. , Aldred, P. , Panozzo J., F. , Kasapis, S. , Barrow C., J. , Food Chem., 2012, 134, 1343- 1353 |
| [24] | Wang, B. , Li, D. , Wang L., J. , Ö, zkan N. , J. Food Eng., 2010, 96( 4), 555- 561 |
| [25] | White D., A. , Fisk I., D. , Mitchell J., R. , Wolf, B. , Hill S., E. , Gray D., A. , Food Hydrocolloids, 2008, 22( 7), 1224- 1232 |
| [26] | Derkatch S., R. , Levachov S., M. , Kuhkushkina A., N. , Novosyolova N., V. , Kharlov A., E. , Matveenko V., N. , Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp., 2007, 298( 3), 225- 234 |
| [27] | Dickinson, E. , Protein Polysaccharide Interactions in Food, Colloids , Royal Soc., Chemistry , Cambridge, 1993, 77-93 |
| [28] | Bengoechea, C. , Cordobé, s F. , Guerrero, A. , Rheol. Acta, 2006, 46( 1), 13- 21 |
| [29] | Floury, J. , Desrumaux, A. , Lardieres, J. , Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol., 2000, 1( 2), 127- 134 |
| [30] | Sun, C. , Gunasekaran, S. , Food Hydrocolloids, 2009, 23( 1), 165- 174 |
| [31] | El-Mahrab-Robert, M. , Rosilio, V. , Bolzinger M., A. , Chaminade, P. , Grossiord J., L. , Int. J. Pharm., 2008, 348( 1/2), 89- 94 |
| [32] | Wang L., J. , Xie H., E. , Qiao X., Y. , Goffin, A. , Hodgkinson, T. , Yuan X., F. , Sun, K. , Fuller G., G. , Langmuir, 2012, 28( 1), 459- 467 |
| [1] | WANG Hong, SAN Khin Nyein Ei, FANG Yun, ZHANG Xinyu, FAN Ye. Pickering Emulsion Stabilization and Interfacial Catalytic Oxidation by Janus Nano-Au [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220105. |
| [2] | HUANG Yi, LYU Lingling, PAN Xiaopeng, SUN Guangdong, LI Yongqiang, YAO Juming, SHAO Jianzhong. Three-dimensional Printing of Photocrosslinked Self-supporting Silk Fibroin Hydrogels [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210841. |
| [3] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [4] | QIAO Zhenghua, FAN Qi, HAO Jingcheng. Silicone Surfactant-enhanced Dual Networks and High Temperature Resistance Porous Silicone Elastomers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220384. |
| [5] | ZHENG Zirui, LI Zilu, ZHAO Kefei, WU Tianyue, ZHANG Chenhui, GAO Yuxia, DU Fengpei. Interfacial Behaviors of Bio-based Surfactant Escin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3107. |
| [6] | LI Boxin, YANG Junge, YIN Dezhong, GAO Chengqian, ZHANG Qiuyu. Preparation of Large-sized Microencapsulated Phase Change Materials Through Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Monodisperse Polymer Microspheres [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2085. |
| [7] | REN Wen, ZHANG Guoli, YAN Han, HU Xinghua, LI Kun, WANG Jingfeng, LI Ruiqi. Preparation of Superhydrophobic Polyaniline/Polytetrafluoroethylenethylene Composite Membrane and Its Separation Ability for Oil-Water Emulsion † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 846. |
| [8] | LI Ming,CUI Xiaoqian,WANG Xuan,LI Zaijun. Synthesis of Amphiphilic Graphene Quantum Dots and Their Sustained Release Effect on L-Menthol † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 324. |
| [9] | ZHANG Xinyu, WANG Hong, FANG Yun, FAN Ye. Stimuli-responsive Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Modified by Conjugated Linoleic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2519. |
| [10] | CHEN Jing,CHEN Jinhua,YIN Dezhong,ZHANG Wei. Phase Inversion of Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Adipate-functionalized SiO2 Particles † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 140. |
| [11] | FAN Ye,LIU Tingting,FANG Yun,XIA Yongmei. Vesiculation and Stability: Oligomer of Conjugated Linoleate Acids Prepared by High Internal Phase Self-emulsion Polymerization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1193. |
| [12] | LIU Yaoshan,WU Hailin,JIA Zhi,DU Bo,LIU Dayong,ZHOU Zhimin. Silk Fibroin-modified Ploylactic Acid-glycolic Acid Copolymer Porous Microspheres as Gingival Mesenchymal Stem Cells Delivery Carrier † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(11): 2419. |
| [13] | LIU Zihao,XIAO Han,YAO Yuan,WANG Ting,WU Liguang,ZHANG Xueyang. Fabrication of PVDF Hybrid Blending Membrane via Microemulsion Polymerization Coupling with Blending Method † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2248. |
| [14] | XIAO Zuoxu, CAO Hongyan, JIANG Xubao, KONG Xiangzheng. Preparation of Pickering Emulsion of Paraffin Wax and Microspheres Using Polymer Particles as Pickering Stabilizer† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1797. |
| [15] | TONG Yongchun, WANG Qingyun, BAI Qingling, LI Zhen, JIA Chuanming. Preparation of Inorganic-organic Composite Hollow Microspheres by Double Pickering Emulsion Template† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1462. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||