

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 1093.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131092
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Suqing*( ), ZHAO Yang, ZHANG Qin, GAO Na, YANG Yang, GONG Yongkuan
), ZHAO Yang, ZHANG Qin, GAO Na, YANG Yang, GONG Yongkuan
Received:2013-11-11
Online:2014-05-10
Published:2014-03-26
Contact:
SHI Suqing
E-mail:shisq@nwu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SHI Suqing, ZHAO Yang, ZHANG Qin, GAO Na, YANG Yang, GONG Yongkuan. Fabrication and Surface Properties of Hydrolyticly Function-switchable Polymer Brush†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 1093.
| Glass | C | O | N | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank glass | 12.58 | 58.11 | 29.31 | |
| Glass-OH | 5.51 | 60.99 | 33.49 | |
| Glass-N(CH3)2 | 34.90 | 38.22 | 5.37 | 21.51 |
| Glass-PCBMA-1C2 | 66.52 | 26.38 | 6.04 | 1.06 |
| Glass-PCBMA | 59.39 | 23.03 | 5.74 | 1.84 |
Table 1 Relative atomic contents(%) of glass surface
| Glass | C | O | N | Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank glass | 12.58 | 58.11 | 29.31 | |
| Glass-OH | 5.51 | 60.99 | 33.49 | |
| Glass-N(CH3)2 | 34.90 | 38.22 | 5.37 | 21.51 |
| Glass-PCBMA-1C2 | 66.52 | 26.38 | 6.04 | 1.06 |
| Glass-PCBMA | 59.39 | 23.03 | 5.74 | 1.84 |
| Sample | d/nma | DPb | σ/(Chain·nm-2)c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass-N(CH3)2 | 1.51 | |||
| Glass-PCBMA-1C2 | 10.25 | 40.2 | 9830 | 0.63 |
Table 2 Thickness, grafting density and degree of polymerization(DP) ofPCBMA-1C2 grafted glass surface
| Sample | d/nma | DPb | σ/(Chain·nm-2)c | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass-N(CH3)2 | 1.51 | |||
| Glass-PCBMA-1C2 | 10.25 | 40.2 | 9830 | 0.63 |
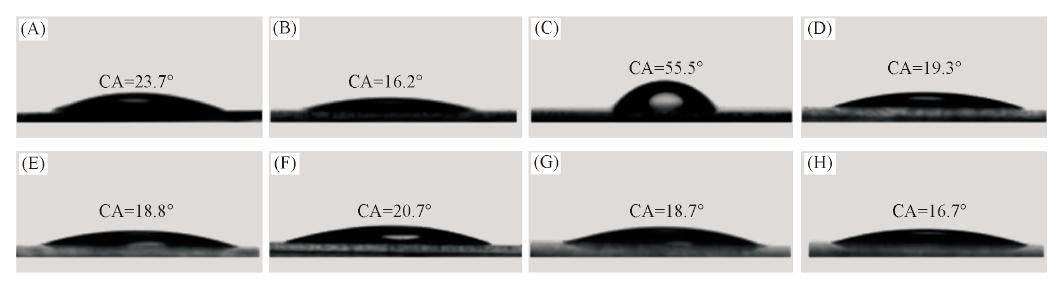
Fig.5 Static water contact angle for the glass surface^(A) Blank glass; (B) Glass-OH; (C) Glass-N(CH3)2; (D) Glass-PCBMA-1C2; (E) Glass-A-PCBMA-1C2;(F) Glass-B-PCBMA-1C2; (G) Glass-C-PCBMA-1C2; (H) Glass-PCBMA.
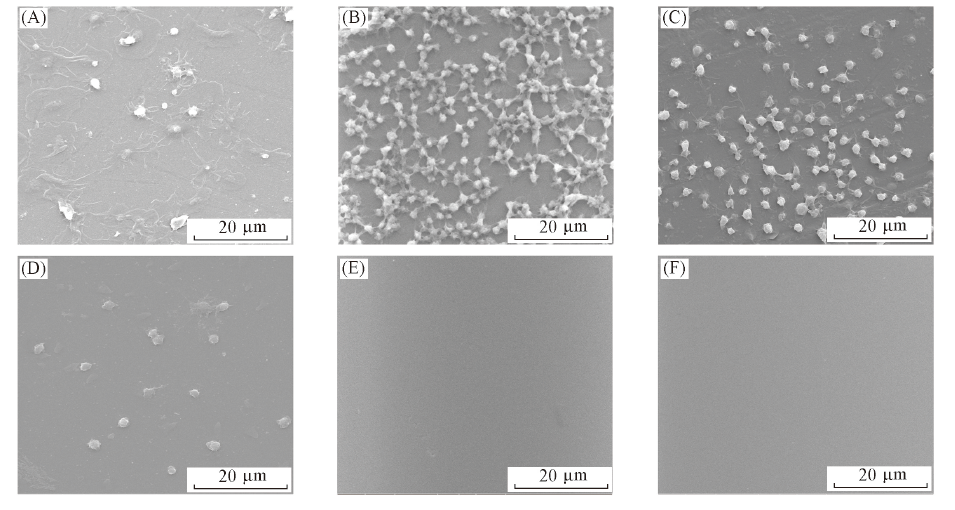
Fig.7 Platelet adhesion for the glass surface^(A) Blank glass; (B) Glass-PCBMA-1C2; (C) Glass-A-PCBMA-1C2; (D) Glass-B-PCBMA-1C2;(E) Glass-C-PCBMA-1C2; (F) Glass-PCBMA.
| [1] | Wu G., Zhang Y., Zhu Y., Friis T., Xiao Y., Biomaterials, 2010, 31, 3429—3438 |
| [2] | Wang D. P., Huang W. H., Materials Review, 2002, 15(5), 36—38 |
| (王德平, 黄文旵.材料导报, 2002,15(5), 36—38) | |
| [3] | Hench L. L., J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1991, 70(2), 240—249 |
| [4] | Hench L. L., Biomaterials, 1998, 19(16), 1419—1423 |
| [5] | Mertz W., Science, 1981, 213, 1332—1338 |
| [6] | Krishnan S., Weinman C. J., Ober C. K., J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18(29), 3405—3413 |
| [7] | Shi Q., Men X. F., Zhao J., Hou J. W., Yang H. W., Luan S. F., Yin J. H., Wan E. N., Chin. J. Blood Transfusion, 2011, 24, 933—935 |
| (石强, 门小菲, 赵杰, 侯建文, 杨华伟, 栾世方, 殷敬华, 宛尔南. 中国输血杂志, 2011, 24, 933—935) | |
| [8] | Chen H., Yuan L., Song W., Wu Z., Li D., Progress in Polymer Science, 2008, 33, 1059—1087 |
| [9] | Liu H. Y., He S. M., Chen C. M., Zhou J., Chemcial Industry and Engineering Progress, 2009, 28, 429—436 |
| (刘荷英, 何淑漫, 陈楚敏, 周健. 化工进展, 2009, 28, 429—436) | |
| [10] | Banerjee I., Pangule R. C., Kane R. S., Adv. Mater., 2011, 23, 690—718 |
| [11] | Cheng G., Li G., Xue H., Chen S., Bryers J. D., Jian S., Biomaterials, 2009, 30, 5234—5240 |
| [12] | Zhang Z., Zhang M., Chen S., Horbett T. A., Ratner B. D., Jiang S., Biomaterials, 2008, 29, 4285—4291 |
| [13] | Yang S., Wang Y. B., Zong M. M., Gong M., Ma J. N., Gong Y. K., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(7), 1579—1585 |
| (杨珊, 王彦兵, 宗明明, 宫铭, 马佳妮, 宫永宽.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(7), 1579—1585) | |
| [14] | Cheng G., Xue H., Zhang Z., Chen S., Jiang S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2008, 47, 8831—8834 |
| [15] | Cao Z., Brault N., Xue H., Keefe A., Jiang S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50, 6102—6104 |
| [16] | Zhang Z., Cheng G., Carr L. R., Vaisocherová H., Chen S., Jiang S., Biomaterials, 2008, 29, 4719—4725 |
| [17] | Cao Z., Mi L., Mendiala J., Ella-Menye J. R., Zhang L., Xue H., Jiang S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51, 2602—2605 |
| [18] | Zhang Q., Gao N., Yang Y., Gong Y. K., Wang Y. B., Zhang S. P., Shi S. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(5), 1270—1276 |
| (张琴, 高娜, 杨扬, 宫永宽, 王彦兵, 张世平, 史素青.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(5), 1270—1276) | |
| [19] | Gam-Derouich S., Lamouri A., Redeuilh C., Decorse P., Maurel F., Carbonnier B., Beyazit S., Yilmaz G., Yagci Y., Chehimi M. M., Langmuir, 2012, 28, 8035—8045 |
| [20] | Dunér G., Anderson H., Myrskog A., Hedlund M., Aastrup T., Ramström O., Langmuir, 2008, 24, 1559—1564 |
| [21] | Popat K. C., Sharma S., Desai T. A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 5185—5188 |
| [22] | Ray S., Shard A. G., Analytical Chemistry, 2011, 83, 8659—8666 |
| [23] | Blmberg E., Classon P. M., Fröberg J. C., Biomaterials, 1998, 19, 371—386 |
| [24] | Ma Q., Zhang H., Zhao J., Gong Y. K., Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258, 9711—9717 |
| [25] | Chen Y.L., Zeng Z. H., Yang J. W., Radiation Curable Material and Its Application, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2003, 107—108 |
| (陈用烈, 曾兆华, 杨建文. 辐射固化材料及其应用, 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2003, 107—108) |
| [1] | TAN Yan, YU Shen, LYU Jiamin, LIU Zhan, SUN Minghui, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Efficient Preparation of Mesoporous γ-Al2O3 Microspheres and Performance of Pd-loaded Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220133. |
| [2] | CAO Meiqi, LIU Xia, CUI Shuxun. Single-molecule Mechanics of Polyacrylamide Under Different Liquid Environments [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2982. |
| [3] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [4] | WANG Longjie, FAN Hongchuan, QIN Yu, CAO Qiue, ZHENG Liyan. Research Progress of Metal-organic Frameworks in the Field of Chemical Separation and Analysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [5] | LIU Siming, WANG Jiannan, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, WANG Zhao, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Preparation of High-surface-area Hierarchically Porous γ-Al2O3 by One-step Hydrolysis of Metal Alkoxide and Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1208. |
| [6] | WANG Xinghuo,TANG Jun,YANG Yingwei. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles-Based Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems Gated by Polymers † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 28. |
| [7] | WANG Chenfeng, XU Qiuyu, WANG Lincai, ZHANG Ruiqi, PAN Xinxin, WANG Jingwei, HAO Weiju. Preparation of a Sandwich-like Ni-P@Ni-B/Ni Catalytic Electrode for pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution Reaction † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2156. |
| [8] | GUO Zhenhao, GUI Qifeng, ZHANG Bo, REN Shuaizhen, ZHANG Shupeng, LI Xinzhong, REN Tianrui. Application of Polycarboxylate and Naphthalenesulfonate Dispersants in High Concentration Suspension Concentrate† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1278. |
| [9] | GENG Lihua, JIN Weihua, WANG Jing, ZHANG Quanbin. Fucoidan Degradation and Preparation of Fuco-oligosaccharides from Saccharina japonica† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2193. |
| [10] | WANG Meiyi, MA Yi, WANG Haiying, CAO Gang, LI Zhengming. Kinetics of the Chemical Hydrolysis and 3D-QSAR Study of 5-Substituted Benzenesulfonylurea Compounds† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1636. |
| [11] | ZHANG Xiao, SHAN Xindi, ZHAO Xiaoliang, LI Guoyun, WANG Xiaojiang, CAI Chao, HAO Jiejie, YU Guangli. Preparation, Characterization and Immunological Activity Evaluation of Low Anticoagulant Heparin Oligosaccharides† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(7): 1335. |
| [12] | WANG Donglong, ZHOU Jinghong, SUI Zhijun, ZHOU Xinggui, SCOTT L. Susannah. Synthesis and Characterization of Titanium-containing Periodic Mesoporous Organosilicas† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(6): 1042. |
| [13] | SHI Huimin, WANG Hui, YIN Jinwei, ZHU Qingyun, WU Ping, Tang Yawen, Zhou Yiming, Lu Tianhong. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of MWCNT@SiO2 Coaxial Nanocables† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(1): 175. |
| [14] | LI Jing, YANG Yong, CAO Xulong, ZHANG Jichao, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lu, ZHAO Sui. Interfacial Shear Rheological Properties of Enhanced Oil Recovery Polymers with Different Structures† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(4): 791. |
| [15] | ZHANG Hongtao, ZHU Li, ZHANG Shuang, ZHAN Xiaobei. Mechanism of Lentinan Hydrolysis Based on ESI-CID-MS/MS and Preparation of Full Series of Oligosaccharides† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(11): 2329. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||