

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2026, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 20250262.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250262
• Review • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Binghui1,2, ZHAO Chengji1( )
)
Received:2025-09-15
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2025-11-21
Contact:
ZHAO Chengji
E-mail:zhaochengji@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Binghui, ZHAO Chengji. Research Progress and Improvement Strategies of Phosphoric Acid-doped High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2026, 47(1): 20250262.
| Polymer type | Representative structure | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polybenzimidazoles |  | Excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties | Complex preparation process; poor solubility; severe phosphoric acid loss |
| Polyaryl ethers |  | Good mechanical strength; simple preparation process; high modifiability | Poor chemical stability |
| Polyphenyls |
| High chemical stability and excellent thermal stability | Metal⁃catalyzed process; poor solubility |
Phenylated polyphenylenes | 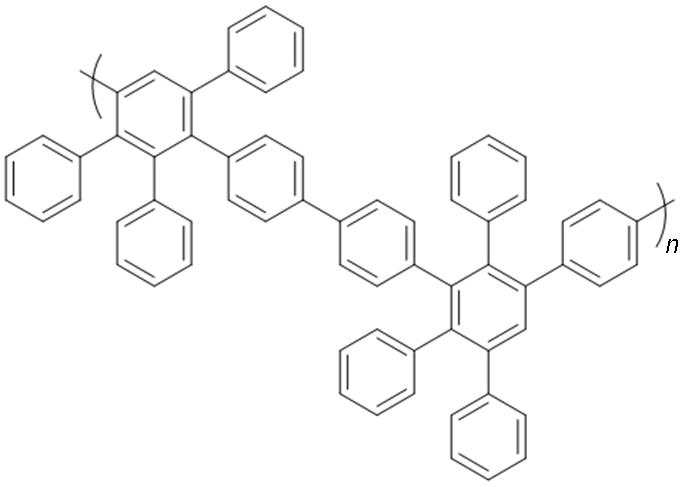 | Excellent chemical stability and mechanical properties; excellent solubility | Limited molecular design. |
| Poly(arylene⁃alkane)s | 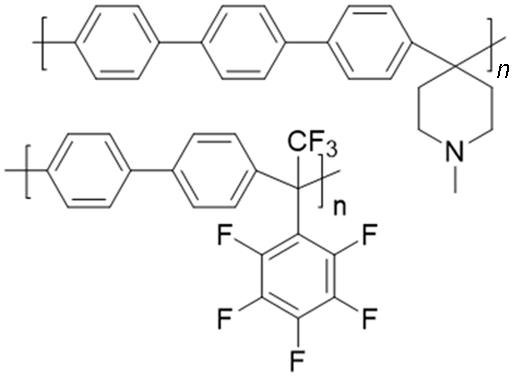 | No noble metal catalysts required; excellent thermal and chemical stability | The use of strong acid catalysts may cause environmental pollution |
| Polymers of intrinsic microporosity | 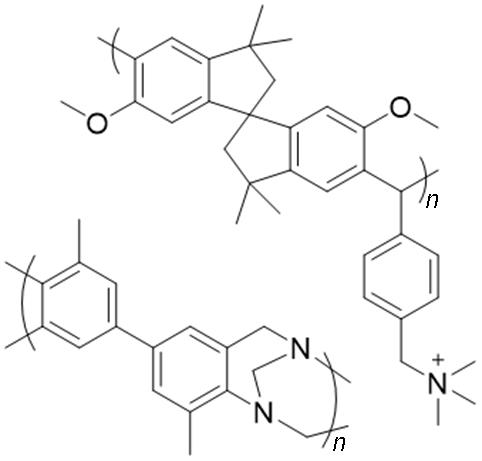 | Strong phosphoric acid retention capacity | Poor mechanical strength; Limited molecular design |
Table 1 Summary of the relevant properties of polymers with different backbone structures
| Polymer type | Representative structure | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Polybenzimidazoles |  | Excellent thermal stability and mechanical properties | Complex preparation process; poor solubility; severe phosphoric acid loss |
| Polyaryl ethers |  | Good mechanical strength; simple preparation process; high modifiability | Poor chemical stability |
| Polyphenyls |
| High chemical stability and excellent thermal stability | Metal⁃catalyzed process; poor solubility |
Phenylated polyphenylenes |  | Excellent chemical stability and mechanical properties; excellent solubility | Limited molecular design. |
| Poly(arylene⁃alkane)s |  | No noble metal catalysts required; excellent thermal and chemical stability | The use of strong acid catalysts may cause environmental pollution |
| Polymers of intrinsic microporosity |  | Strong phosphoric acid retention capacity | Poor mechanical strength; Limited molecular design |
| [1] | Thomas J., Edwards P., Dobson P., Owen G., J. Energy Chem., 2020, 51, 405—415 |
| [2] | Zhu Y. H., Liu Y., Zhang F., Fan Z. H., Kang Z. Y., Wan X. H., Wang G. X., Li J., Tian C., Lei H., Wang W. N., Tian X. L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2025, 41(3), 484—494 |
| [3] | Hou M., Yi B. L., J. Electrochem., 2012, 18(1), 1—13 |
| 侯明, 衣宝廉. 电化学, 2012, 18(1), 1—13 | |
| [4] | Meng H., Song J., Guan P., Wang H., Zhao W., Zou Y., Ding H., Wu X., He P., Liu F., Zhang Y., J. Power Sources, 2024, 602, 234205 |
| [5] | Cheng H. L., Han K. H., Li A., Tao L. J., Yi F. Y., Sun J. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(8), 20240217 |
| 程海龙, 韩康辉, 李奥, 陶璐静, 易飞扬, 孙娇娇. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(8), 20240217 | |
| [6] | Wang S., Jiang S. P., Natl. Sci. Rev., 2017, 4(2), 163—166 |
| [7] | Dong W. Y., Pan J. X., Guo W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(2), 20230397 |
| 董文雅, 潘建欣, 郭伟. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(2), 20230397 | |
| [8] | Gong L., Tao L., Wang L., Fu X., Wang S., Chinese J. Catal., 2025, 68, 155—176 |
| [9] | Aili D., Henkensmeier D., Martin S., Singh B., Hu Y., Jensen J. O., Cleemann L. N., Li Q., Electrochem. Energy Rev., 2020, 3(4), 793—845 |
| [10] | Wang Z. Q., Yang L. L., Sun H., Chem. Ind. Eng. Pro., 2020, 39(6), 20 |
| 王子乾, 杨林林, 孙海. 化工进展, 2020, 39(6), 20 | |
| [11] | Han S., Lv Y., Yang M. Y., Li Y. P., Tan C., Liu F., Yang H., Chu J. N., Liu M., Zhu C. Y., Gao R., Song Y. J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2025, 41(5), 1217—1224 |
| [12] | Adamski M., Peressin N., Holdcroft S., Mater. Adv., 2021, 2(15), 4966—5005 |
| [13] | Mauritz K. A., Moore R. B., Chem. Rev., 2004, 104(10), 4535—4585 |
| [14] | Amiinu I. S., Li W., Wang G., Tu Z., Tang H., Pan M., Zhang H., Electrochim. Acta, 2015, 160, 185—194 |
| [15] | Yang J., Xu H., Li J., Gong K., Yue F., Han X., Wu K., Shao P., Fu Q., Zhu Y., Xu W., Huang X., Xie J., Wang F., Yang W., Zhang T., Xu Z., Feng X., Wang B., Science, 2024, 385(6713), 1115—1120 |
| [16] | Ma W., Zhao C., Lin H., Zhang G., Ni J., Wang J., Wang S., Na H., J. Power Sources, 2011, 196(22), 9331—9338 |
| [17] | Ma W., Zhao C., Yang J., Ni J., Wang S., Zhang N., Lin H., Wang J., Zhang G., Li Q., Na H., Energy Environ. Sci., 2012, 5(6), 7617—7625 |
| [18] | Staiti P., Minutoli M., J. Power Sources, 2001, 94(1), 9—13 |
| [19] | Wu X., Scott K., Fuel Cells, 2012, 12(4), 583—588 |
| [20] | Li Q., Jensen J. O., Savinell R. F., Bjerrum N. J., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2009, 34(5), 449—477 |
| [21] | Wainright J. S., Wang J. T., Weng D., Savinell R. F., Litt M., J. Electrochem. Soc., 1995, 142(7), L121 |
| [22] | Melchior J. P., Majer G., Kreuer K. D., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, 19(1), 601—612 |
| [23] | Vogel H., Marvel C. S., Prog. Polym. Sci., 1961, 50(154), 511—539 |
| [24] | Seselj N., Aili D., Celenk S., Cleemann L. N., Hjuler H. A., Jensen J. O., Azizi K., Li Q., Chem. Soc. Rev, 2023, 52(12), 4046—4070 |
| [25] | Asensio J. A., Gómez⁃Romero P., Fuel Cells, 2005, 5(3), 336—343 |
| [26] | Wu A., Liu J., Wei G., Liu D., Wang L., J. Power Sources, 2022, 545, 231925 |
| [27] | Wang S., Zhao C., Ma W., Zhang G., Liu Z., Ni J., Li M., Zhang N., Na H., J. Membr. Sci., 2012, 411/412, 54—63 |
| [28] | Luo Y., Yu D., Gao T., Bai W., Zhang S., Guan X., Wu W., Wang S., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 77, 784—794 |
| [29] | Cao K. Y., Peng J. W., Li H. B., Shi C. Y., Wang P., Liu B. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6), 2049—2055 |
| 曹凯悦, 彭金武, 李宏斌, 石埕荧, 王鹏, 刘佰军. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6), 2049—2055 | |
| [30] | Dai J., Zhang Y., Gong C., Wan Y., Zhuang Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 466, 143151 |
| [31] | Xu Z., Wang Q., Guo L., Li Y., Wang J., Yu S., Liao J., Xu Y., Shen J., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 34, 2310762 |
| [32] | Zhang N., Wang B., Zhao C., Wang S., Zhang Y., Bu F., Cui Y., Li X., Na H., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(34), 13996—14003 |
| [33] | Li Q., Liu L., Liang S., Li Q., Jin B., Bai R., Polym. Chem., 2014, 5(7), 2425—2432 |
| [34] | Wu W., Zou G., Fang X., Cong C., Zhou Q., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2017, 56(37), 10227—10234 |
| [35] | Zhao Y. Y., Tsuchida E., Choe Y. K., Wang J., Ikeshoji T., Ohira A., J. Membr. Sci., 2015, 487, 229—239 |
| [36] | Pang Y., Duan Y., Li Q., Liu B., Hu X., Liu Q., Zhao C., J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 686, 121999 |
| [37] | Yamamoto T., Hayashi Y., Yamamoto A., Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn, 2006, 51(7), 2091—2097 |
| [38] | Li T. T., Li H. B., Liu B. H., Zhao C. J., Li H. L., Prog. Chem., 2023, 35(11), 1559—1578 |
| 李婷婷, 李海宾, 刘炳辉, 赵成吉, 李昊龙. 化学进展, 2023, 35(11), 1559—1578 | |
| [39] | Bai Y., Xiao M., Wang C., Wang S., Meng Y., Miyatake K., Adv. Energy Mater., 2024, 14(33), 2400751 |
| [40] | Holmes T., Skalski T. J. G., Adamski M., Holdcroft S., Chem. Mater., 2019, 31(4), 1441—1449 |
| [41] | Peressin N., Adamski M., Schibli E. M., Ye E., Frisken B. J., Holdcroft S., Macromolecules, 2020, 53(8), 3119—3138 |
| [42] | Lee K., Spendelow J., Choe Y., Fujimoto C., Kim Y., Nat. Energy, 2016, 1(9), 16120 |
| [43] | Wang J., Zhao Y., Setzler B. P., Rojas⁃Carbonell S., Ben Yehuda. C., Amel A., Page M., Wang L., Hu K., Shi L., Gottesfeld S., Xu B., Yan Y., Nat. Energy, 2019, 4(5), 392—398 |
| [44] | Jin Y., Wang T., Che X., Dong J., Li Q., Yang J., J. Power Sources, 2022, 526, 231131 |
| [45] | Bai H., Peng H., Xiang Y., Zhang J., Wang H., Lu S., Zhuang L., J. Power Sources, 2019, 443, 227219 |
| [46] | Liu B., Duan Y., Li T., Pang Y., Liu Q., Li Q., Hu X., Zhao C., J. Membr. Sci., 2024, 692, 122273 |
| [47] | Liu B., Mu T., Liu Q., Pang Y., Lou J., Cao J., Zhao C., J. Membr. Sci., 2025, 733, 124327 |
| [48] | Feng X., Zhu J., Jin J., Wang Y., Zhang Y., van der Bruggen B., Prog. Mater Sci., 2024, 144, 101285 |
| [49] | Carta M., Malpass⁃Evans R., Croad M., Rogan Y., Jansen J C., Bernardo P., Bazzarelli F., Mckeown N. B., Science, 2013, 339(6117), 303—307 |
| [50] | Chen X., Wu L., Yang H., Qin Y., Ma X., Li N., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(33), 17875—17880 |
| [51] | Olvera L. I., Zolotukhin M. G., Hernández⁃Cruz O., Fomine S., Cárdenas J., Gaviño⁃Ramírez R. L., Ruiz⁃Trevino F. A., ACS Macro Lett., 2015, 4(5), 492—494 |
| [52] | Yang S., Li H., Zou W., Ling R., Ma X., Chen S., Yang Z., Xu T., JACS Au, 2024, 4(8), 3277—3283 |
| [53] | Guo Z., Perez⁃Page M., Chen J., Ji Z., Holmes S. M., J. Energy Chem., 2021, 63, 393—429 |
| [54] | Li J., Yang C., Zhang X., Xia Z., Wang S., Yu S., Sun G., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2023, 11(34), 18409—18418 |
| [55] | Tang H., Geng K., Wu L., Liu J., Chen Z., You W., Yan F., Guiver M. D., Li N., Nat. Energy, 2022, 7(2), 153—162 |
| [56] | Li J., Yang C., Lin H., Huang J., Wang S., Sun G., J. Energy Chem., 2024, 92, 572—578 |
| [57] | Liu B., Liu Q., Pang Y., Mu T., Zhao C., Macromolecules, 2024, 57(21), 10338—10348 |
| [58] | Kannan A., Aili D., Cleemann L. N., Li Q., Jensen J. O., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2020, 45(1), 1008—1017 |
| [59] | Li W., Liu W., Zhang J., Wang H., Lu S., Xiang Y., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2023, 33(6), 2210036 |
| [60] | Zeng L., Dong D., Lu J., He K., Liu X., Wang J., Wei Z., Gresil M., Ratcliffe J., Li Z., Wang H., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2025, 35(31), 2424662 |
| [61] | Zhang L., Liu M., Zhu D., Tang M., Zhu T., Gao C., Huang F., Xue L., Nat. Commun., 2024, 15(1), 3409 |
| [62] | Lee S., Seong J., Jo Y., Hwang S., Gwak G., Park Y., Kim Y., Lim K., Park H., Jang J., Kim H., Nam S., Lee S. Y., Nat. Energy, 2024, 9(7), 849—861 |
| [63] | Liao J., Li Q., Rudbeck H., Jensen J., Chromik A., Bjerrum N., Kerres J., Xing W., Fuel Cells, 2011, 11(6), 745—755 |
| [64] | Ju Q., Chao G., Wang Y., Lv Z., Geng K., Li N., J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 686, 121970 |
| [65] | Liu B., Duan Y., Pang Y., Li Q., Zhao C., Chem. Eng. J., 2023, 477, 146955 |
| [66] | Wang J., Dai Y., Wan R., Wei W., Xu S., Zhai F., He R., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 413, 127541 |
| [67] | Duan Y., Pang Y., Liu B., Wu L., Hu X., Li Q., Zhao C., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2023, 11(13), 5270—5283 |
| [68] | Bu F., Zhang Y., Hong L., Zhao W., Li D., Li J., Na H., Zhao C., J. Membr. Sci., 2018, 545, 167—175 |
| [69] | Hu X., Ao Y., Gao Y., Liu B., Zhao C., J. Membr. Sci., 2023, 687, 122102 |
| [70] | Liu B., Liu Q., Pang Y., Duan Y., Zhao C., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2025, 35(1), 2408291 |
| [71] | Yue Z., Cai Y. B., Xu S., Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2016, 41(24), 10421—10429 |
| [72] | Zhang W., Wang W., Xie D., Li J., Li H., Dai J., Tang Y., Yang T., Jin W., Zhou P., Gong C., J. Power Sources, 2024, 623, 235410 |
| [1] | CHENG Hailong, HAN Kanghui, LI Ao, TAO Lujing, YI Feiyang, SUN Jiaojiao. Preparation and Properties of Sulfonated Polystyrene/Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether ketone sulfone) Copolymer with Pendant Crosslinked Structure Composite Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(8): 20240217. |
| [2] | JIA Linhan, YANG Daijun, MING Pingwen, MIN Junying, LENG Yu. Effect of Service Environment of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell on the Corrosion Behaviors of TA1 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(2): 20230436. |
| [3] | DONG Wenya, PAN Jianxin, GUO Wei. Study on Reverse Polarization of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell Stack Caused by Anode Starvation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(2): 20230397. |
| [4] | LI Shixuan, MENG Hua, YIN Xuehu, YI Jinfei, MA Lihong, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, YANG Wenrong, PANG Pengfei. A Double-Chamber Enzymatic Biofuel Cells-based Self-powered Glucose Biosensor Based on Graphene/Gold Nanoparticles/Titanium Carbide Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(12): 20240301. |
| [5] | ZHAO Qian, LI Shang, CHENG Kuangwei, WEN Zhiyong, ZHANG Xiaoyu, YI Shaojie, PAN Mu. Study on Nitrogen-doped PtCo/C Alloy Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(6): 20230016. |
| [6] | CHEN Yafeng, ZENG Liuli, GUO Wei. Effect of Water Flooding at Different Positions of Cathode Side on the Performance of Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(6): 20230003. |
| [7] | WANG Jun, DU Shiqian, TAO Li. Recent Progress of Catalysts in the High Temperature Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220722. |
| [8] | QIU Xinsheng, WU Qin, SHI Daxin, ZHANG Yaoyuan, CHEN Kangcheng, LI Hansheng. Preparation and High Temperature Fuel Cell Performance of Ionic Crosslinked Sulfonated Polyimides for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220140. |
| [9] | CHEN Changli, MI Wanliang, LI Yujing. Research Progress of Single Atom Catalysts in Electrochemical Hydrogen Cycling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220065. |
| [10] | LUO Bian, ZHOU Fen, PAN Mu. Study on Preparation and Accessibility of Hierarchical Porous Carbon Supported Platinum Catalyst [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210853. |
| [11] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [12] | JIA Hongjun, ZHANG Jiatao, MA Zhuoli, WANG Heng, YANG Xinyu, YANG Jiazhi. Preparation of PTFE/PAA/Nafion Composite Membrane by Aqueous Polymerization of Acrylic Acid and Its Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220350. |
| [13] | FU Zhinan, TAN Yunlong, XIAO Guyu, YAN Deyue. Synthesis and Properties of Sulfonated Poly(phthalazinone ether phosphine oxide)s with Perfluorobiphenyl Moieties for Proton Exchange Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2635. |
| [14] | PU Yangyang, NING Cong, LU Yao, LIU Lili, LI Na, HU Zhaoxia, CHEN Shouwen. Preparation and Characterizations of Cross-linked Sulfonated Poly(ether ether ketone)/Partially Fluorinated Sulfonated Poly(aryl ether sulfone) Blend Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2002. |
| [15] | CAO Kaiyue, PENG JinWu, LI Hongbin, SHI Chengying, WANG Peng, LIU Baijun. High-temperature Proton Exchange Membranes Based on Cross-linked Polybenzimidazole/hyperbranched-polymer Blends [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2049. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||