

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 740.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180528
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Jian1,2, ZHU Zhaowu1,2,*( ), LEI Ze3, WANG Lina1,2, CHEN Desheng1,2, YI Aifei1,2, SU Hui1,2, QI Tao1,2,*(
), LEI Ze3, WANG Lina1,2, CHEN Desheng1,2, YI Aifei1,2, SU Hui1,2, QI Tao1,2,*( )
)
Received:2018-07-27
Online:2019-04-03
Published:2018-10-08
Contact:
ZHU Zhaowu,QI Tao
E-mail:zhwzhu@ipe.ac.cn;tqi@ipe.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Jian,ZHU Zhaowu,LEI Ze,WANG Lina,CHEN Desheng,YI Aifei,SU Hui,QI Tao. Preparation of Vanadium Oxalate by Solvent Extraction and Purification with P507 and Its Physicochemical Properties†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 740.
| V(A):V(O) | Vanadium concentration/ (g·L-1) | Oxalic concentration/ (mol·L-1) | V(A):V(O) | Vanadium concentration/ (g·L-1) | Oxalic concentration/ (mol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 20.75 | 1.59 | 1:4 | 76.31 | 0.50 |
| 1:2 | 38.77 | 1.24 | 1:5 | 81.61 | 0.40 |
| 1:3 | 58.70 | 0.85 | 1:10 | 105.37 | 0 |
Table 1 Vanadium concentration and residual oxalic acid in the loaded strip liquor(LSL) under various V(A):V(O)
| V(A):V(O) | Vanadium concentration/ (g·L-1) | Oxalic concentration/ (mol·L-1) | V(A):V(O) | Vanadium concentration/ (g·L-1) | Oxalic concentration/ (mol·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1:1 | 20.75 | 1.59 | 1:4 | 76.31 | 0.50 |
| 1:2 | 38.77 | 1.24 | 1:5 | 81.61 | 0.40 |
| 1:3 | 58.70 | 0.85 | 1:10 | 105.37 | 0 |
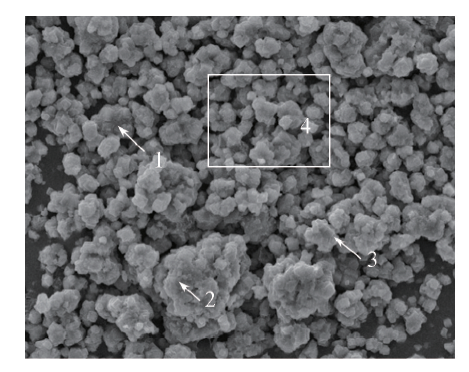
Fig.8 EDS analysis of vanadyl oxalate sampleSpots 1, 2 and 3 represent sample points seleeted during EDS point analysis; area 4 represents a sample area selected during EDS area analysis.
| Selected area | w(%) | m(V):m(C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | V | Total | ||
| Theoretical value | 15.48 | 51.61 | 32.91 | 100.00 | 2.12 |
| Spot 1 | 17.81 | 48.45 | 33.74 | 100.00 | 2.24 |
| Spot 2 | 16.11 | 51.70 | 32.19 | 100.00 | 2.13 |
| Spot 3 | 18.03 | 47.45 | 34.52 | 100.00 | 2.22 |
| Area 4 | 17.93 | 45.08 | 37.28 | 100.00 | 2.04 |
Table 2 EDS elemental composition analysis of vanadyl oxalate in Fig.8
| Selected area | w(%) | m(V):m(C) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | V | Total | ||
| Theoretical value | 15.48 | 51.61 | 32.91 | 100.00 | 2.12 |
| Spot 1 | 17.81 | 48.45 | 33.74 | 100.00 | 2.24 |
| Spot 2 | 16.11 | 51.70 | 32.19 | 100.00 | 2.13 |
| Spot 3 | 18.03 | 47.45 | 34.52 | 100.00 | 2.22 |
| Area 4 | 17.93 | 45.08 | 37.28 | 100.00 | 2.04 |
| [1] | Yang S. L., Peng F. C., Pan F. S., Gao S. Z., Mater.Rev.,2008, 22(4), 53—56 |
| (杨绍利, 彭富昌, 潘复生, 高仕忠. 材料导报, 2008, 22(4), 53—56) | |
| [2] | Gao Z. M., Zhang Y. F., Wang Q. S., Zhen J. Q., J. Chin. Ele. Micro. Soc.,2017, 36(2), 103—112 |
| (高占明, 张依福, 王秋实, 郑吉祺. 电子显微学报, 2017, 36(2), 103—112) | |
| [3] | Cao Y. L., Jia D. Z., Liu L., Xiao D. Q., Xin X. Q., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2005, 21(2), 134—136 |
| [4] | Lin H., Zou J., Li Q., Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium,2006, 27(1), 55—58, 63 |
| (林华, 邹建, 李庆. 钢铁钒钛, 2006, 27(1), 55—58, 63) | |
| [5] | Hao Q. L., Shao Q., Liu Q. Y., Mod. Chem.Ind.,2014, 34(11), 51—54 |
| (郝巧兰, 邵谦, 刘青云. 现代化工, 2014, 34(11), 51—54) | |
| [6] | Ren Z.Z., Huang W. G., J. Funct. Mater., 2007, 8, 2112—2113 |
| (任哲峥, 黄维刚 功能材料, 2007, 8 , 2112—2113) | |
| [7] | Wang A. R., Yuan J. F., Chin. J. Process Eng.,2017, 17(3), 558—564 |
| (王安仁, 袁吉峰. 过程工程学报, 2017, 17(3), 558—564) | |
| [8] | Li Z.T., Synthesis, Characterization and Electrochemical Performance of Vanadium-Based Materials, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, 2015 |
| (栗志同. 钒基材料的合成、 表征及其电化学性能研究, 广州: 华南理工大学, 2015) | |
| [9] | (栗志同, 王素清. 多孔五氧化二钒的制备及其电化学性能研究, 中国科技论文在线, |
| [10] | Ren D. X., Cao Y. Z., Chen C., Ying Y. H., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2012, 28(5), 768—774 |
| [11] | Huang W. G., Lin H., Tu M. J.,J. Funct.Mater.,2006, 3(37), 440—442 |
| (黄维刚, 林华, 涂铭旌. 功能材料, 2006, 3(37), 440—442) | |
| [12] | Wan L. F., Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(3), 56—60 |
| (万龙飞. 钢铁钒钛, 2016, 37(3), 56—60) | |
| [13] | Hao C. Z., Kong X. F., Yu M. A., A Method to Prepare Highly Pure Vanadyl Oxalate Solid Product, CP 201710340156.8,2017-08-18 |
| (郝承志, 孔祥风, 于明爱. 一种高纯草酸氧钒固体产品的制备方法, CP 201710340156.8, 2017-08-18) | |
| [14] | Cao P., Wan L. F., Shen B., Sun Z. H., Li Q. W., Pen Y., Hu L., A Method to Prepare Vanadyl Oxalate, CP 201200079205.4,2013-09-25 |
| (曹鹏, 万隆飞, 申彪, 孙朝晖, 李千文, 彭毅, 胡力. 一种草酸氧钒的制备方法,CP 201200079205.4, 2013-09-25) | |
| [15] | Bruyère V. I. E., Morando P. J., Blesa M. A., J. Colloid. Interf.Sci.,1999, 209, 207—214 |
| [16] | Bruyère V. I. E., Rodenas L. A. G., Morando P. J., Blesa M. A., J. Chem. Soc.Dalton.2001, 24(24), 3593—3597 |
| [17] | Zhang J., Zhu Z. W., Chen D. S., Wang L. N., Wang W. J., Lei Z., Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2018, 43(3), 303—311 |
| (张健, 朱兆武, 陈德胜, 王丽娜, 王伟菁, 雷泽. 稀有金属, 2018, 43(3), 303—311) | |
| [18] | Li L. J., Chang F. Z., Wang H. X., Bai R. G., Zhou X., Yan H., A Method to Prepare Vanadyl Oxalate, CP 201610775992.4,2017-02-08 |
| (李兰杰, 常福增, 王海旭, 白瑞国, 周欣, 闫浩. 一种草酸氧钒的制备方法, CP 201610775992.4, 2017-02-08) | |
| [19] | Zhang Y., Zhang T. A., Dreisinger D., Lv G. Z., Can. Metall.Quart.,2017, 56(5), 1—13 |
| [20] | Liu Y. H., Yang C., Hydrometallurgy of China,2010, 29(4), 263—266 |
| (刘彦华, 杨超. 湿法冶金,2010, 29(4), 263—266) | |
| [21] | Li X. B., Wei C., Wu J. N., Li C. X., Li M. T., Deng Z. G., Xu H. S., T. Nonferr. Metal.Soc.,2015, 25(10), 461—466 |
| [22] | Mehdi N., Fereshteh R., Ataollah B., Ehsan V., Sep. Purif.Technol.,2014, 136, 125—128 |
| [23] | Zhang G.Z., Study on the Recovery of V, Cr, and Fe form the Chloride Solution by Solvent Extraction, the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 2017 |
| (张国之. 酸性氯化物体系钒、 铬、 铁萃取分离基础研究,北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017) | |
| [24] | Li D., Preparation of Vanadyl Sulfate with High Purity form Vanadium Hydrochloride Solutions in Shorter Process, The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 2017 |
| (李丹. 含钒氯化物溶液短流程制备高纯硫酸氧钒研究,,北京: 中国科学院大学, 2017) |
| [1] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [2] | LI Yanyan, DUAN Linrui, LUO Jingshan. Moisture-assisted Crystallization of Inorganic Perovskite CsPbI3 Film [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1785. |
| [3] | MIAO Weijun, WU Feng, WANG Yong, WANG Zongbao. In⁃situ Study of the Epitaxial Crystallization of PCL/RGO at High Shear Rate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 910. |
| [4] | WANG Juan, WANG Linying, ZHU Dali, CUI Wenhao, WANG Yifeng, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongmin. Progress in Direct Synthesis of High Silica Zeolite Y [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 1. |
| [5] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [6] | ZHANG Xin, ZHAO Fulai, WANG Yu, LIANG Xuejing, FENG Yiyu, FENG Wei. Preparation and Electrical Properties of Germanium Telluride Field Effect Transistor [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2032. |
| [7] | WANG Yang, WANG Sidi, TANG Shaokun. Synthesis and Characterization of Imine-based Covalent Organic Framework(COF-LZU1) in Supercritical Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1792. |
| [8] | HE Zhechao, XIA Kun, WANG Jing, ZHOU Dan, LU Xinhuan, XIA Qinghua. Controllable Synthesis of SAPO-5 Molecular Sieves and Exploration of the Crystallization Process † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1224. |
| [9] | WANG Yuyao, ZHANG Qiang, YU Jihong. Synthesis of Hierarchical NaX Zeolite and Its CO2 Adsorption Performance † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 616. |
| [10] | LUO Dongxia, LI Bing, WANG Quanyi, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Study on Crystallization Process of SAPO-5 Molecular Sieve [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2442. |
| [11] | FANG Xijie,LIU Ruiyun,LIN Sen,SHI Lei,WANG Runwei,LI Yi,LI Junying. Synthesis of STW-zeotype Germanosilicate via Steam-assisted Crystallization† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 867. |
| [12] | HAN Jiahui,HUANG Hanxiong,HUANG Yuxiao. Improving Crystallization Behavior and Melt Strength of Poly(lactic acid) via Adding Talc and PLA-g-MAH† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2089. |
| [13] | ZHANG Wu,JI Yanyan,PENG Han,DAI Shaoying,LIU Ying,ZHANG Jimei,WANG Dongmei. High Efficiency Synthesis of FeY Type Zeolite and Its Heterogeneous Fenton Catalytic Degradation† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1985. |
| [14] | XIA Kun, ZHOU Dan, YANG Yun, YANG Shuijin, XIA Qinghua. Efficient Synthesis of Highly Uniform AlPO4-11 Microcrystalline and Study on the Crystallization Process† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1624. |
| [15] | YANG Qian, YANG Canyu, SUN Kongchun, HOU Wenqing, WU Leyan, SHEN Baochun. Synthesis and Application of Chiral Polyaniline/Silica Dioxide Core/Shell Composite† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1587. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||