

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (12): 2725.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180436
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Changqing1,4, YANG Dongjie1,4, XI Yuebin1,4, QIN Yanlin3, QIU Xueqing1,2,4,*( )
)
Received:2018-06-13
Online:2018-12-03
Published:2018-08-31
Contact:
QIU Xueqing
E-mail:cexqqiu@scut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Changqing,YANG Dongjie,XI Yuebin,QIN Yanlin,QIU Xueqing. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Silica/Porous Lignin Carbon Composites as Anode Materials for Lithium-ion Batteries†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2725.
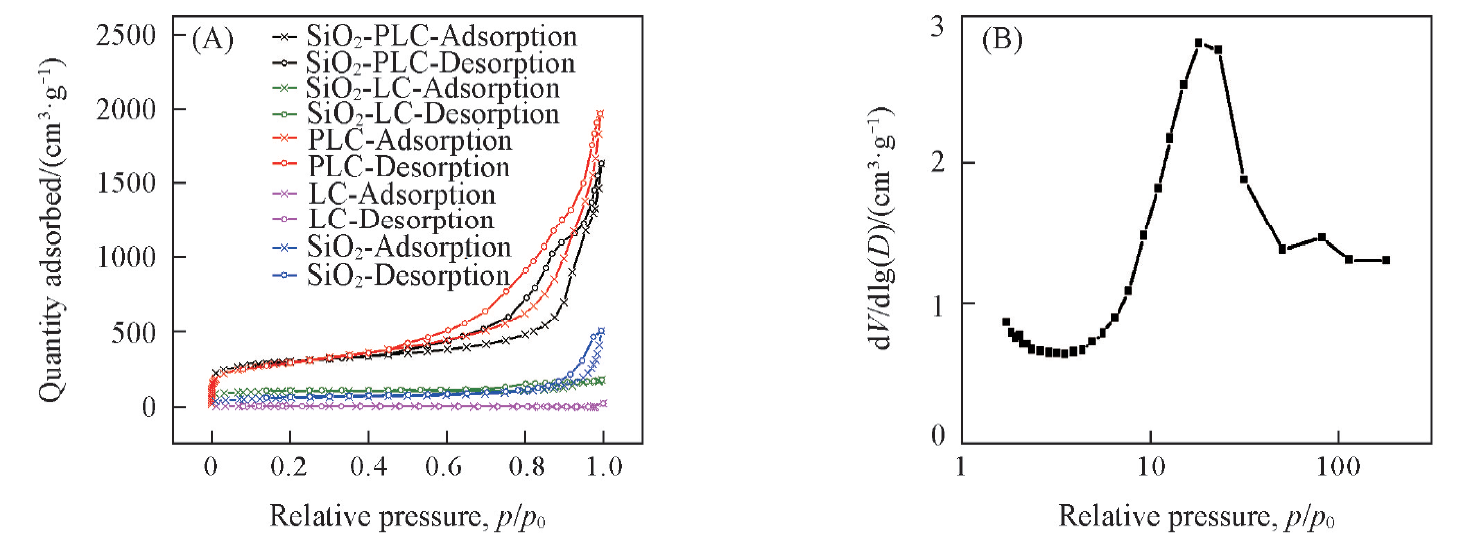
Fig.3 N2 Adsorption-desorption isotherms of the as-prepared samples(A) and the corresponding pore-size distribution of SiO2/PLC determined from the adsorption isotherm(B)
| Material | Carbon source | Carbonization temperature/℃ | Specific capacity (mA·h·g-1)/ Current density(mA·g-1) | Specific capacity (mA·h·g-1)/ Current density(A·g-1) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bimodal porous carbon-silica nanocomposites | Resol | ~50 | 850 | 611/200 | 300/3 | [ |
| H-SiO2/C composite | PAN | 50.4 | 1000 | 564/200 | 190/5 | [ |
| SiO2/C/graphene spheres | PVP and GO | 43 | 900 | 605/50 | - | [ |
| SiO2-coated graphite flake | Graphitc flake | 19 | 1000 | - | 480/2.5 | [ |
| Silica-carbon nanocomposite | Filter paper | 31 | 600 | 488/100 | 96/3 | [ |
| SiO2/PLC | Lignin | 21 | 600 | 820/100 | 235/5 | This work |
Table 1 Comparison of the lithium-storage performance between SiO2/PLC and previously reported SiO2/C anode materials
| Material | Carbon source | Carbonization temperature/℃ | Specific capacity (mA·h·g-1)/ Current density(mA·g-1) | Specific capacity (mA·h·g-1)/ Current density(A·g-1) | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bimodal porous carbon-silica nanocomposites | Resol | ~50 | 850 | 611/200 | 300/3 | [ |
| H-SiO2/C composite | PAN | 50.4 | 1000 | 564/200 | 190/5 | [ |
| SiO2/C/graphene spheres | PVP and GO | 43 | 900 | 605/50 | - | [ |
| SiO2-coated graphite flake | Graphitc flake | 19 | 1000 | - | 480/2.5 | [ |
| Silica-carbon nanocomposite | Filter paper | 31 | 600 | 488/100 | 96/3 | [ |
| SiO2/PLC | Lignin | 21 | 600 | 820/100 | 235/5 | This work |
| [1] | Zhang Y., Li Y., Li H., Zhao Y., Yin F., Bakenov Z., Electrochimica Acta,2016, 216, 475—483 |
| [2] | Li H., Wei Y., Zhang Y., Zhang C., Wang G., Zhao Y., Yin F., Bakenov Z., Ceramics International,2016, 42(10), 12371—12377 |
| [3] | Yan N., Wang F., Zhong H., Li Y., Wang Y., Hu L., Chen Q., Scientific Reports,2013, 3(3), 1568 |
| [4] | Chang W.S., Park C.M., Kim J.H., Kim Y.U., Jeong G., Sohn H.J., Energy & Environmental Science,2012, 5(5), 6895—6899 |
| [5] | Gao B., Sinha S., Fleming L., Zhou O., Advanced Materials,2010, 13(11), 816—819 |
| [6] | Tang C., Liu Y., Xu C., Zhu J., Wei X., Zhou L., He L., Yang W., Mai L., Advanced Functional Materials,2018, 28(3), 1704561 |
| [7] | Guo B., Shu J., Wang Z., Yang H., Shi L., Liu Y., Chen L., Electrochemistry Communications,2008, 10(12), 1876—1878 |
| [8] | Wang C.W., Liu K.W., Chen W.F., Zhou J.D., Lin H.P., Hsu C.H., Kuo P.L., Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers,2016, 3(11), 1398—1405 |
| [9] | Tenhaeff W.E., Rios O., More K., Mcguire M.A., Advanced Functional Materials,2013, 24(1), 86—94 |
| [10] | Xia H., Yin Z., Zheng F., Zhang Y., Materials Letters,2017, 205, 83—86 |
| [11] | Liu X., Chen Y., Liu H., Liu Z.Q., Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2017, 33(3), 239—245 |
| [12] | Hao S., Wang Z., Chen L., Materials & Design,2016, 111, 616—621 |
| [13] | Wang S., Zhao N., Shi C., Liu E., He C., He F., Ma L., Applied Surface Science,2018, 433, 428—436 |
| [14] | Wang H., Wu P., Qu M., Si L., Tang Y., Zhou Y., Lu T., Chemelectrochem,2015, 2(4), 508—511 |
| [15] | Zhang W., Yin J., Lin Z., Lin H., Lu H., Wang Y., Huang W., Electrochimica Acta,2015, 176, 1136—1142 |
| [16] | Etacheri V., Wang C., O’Connell M.J., Chan C.K., Pol V.G., Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015, 3(18), 9861—9868 |
| [17] | Xiong W., Qiu X., Yang D., Zhong R., Qian Y., Li Y., Wang H., Chemical Engineering Journal,2017, 326, 803—810 |
| [18] | Pan D., Wang S., Zhao B., Wu M., Zhang H., Wang Y., Jiao Z., Chemistry of Materials,2009, 21(14), 3136—3142 |
| [19] | Fey T.K., Lee D.C., Lin Y.Y., Kumar T.P., Synthetic Metals,2003, 139(1), 71—80 |
| [20] | Kim C., Park S., Cho J., Lee D., Park T., Lee W., Yang K., Journal of Raman Spectroscopy,2004, 35(35), 928—933 |
| [21] | Wenelska K., Ottmann A., Moszyński D., Schneider P., Klingeler R., Mijowska E., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2018, 511, 203—208 |
| [22] | Ji L., Lin Z., Alcoutlabi M., Zhang X., Energy & Environmental Science,2011, 4(8), 2682—2699 |
| [23] | Wang S.X., Yang L., Stubbs L.P., Li X., He C., ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013, 5(23), 12275—12282 |
| [24] | Dong J., Xue Y., Zhang C., Weng Q., Dai P., Yang Y., Zhou M., Li C., Cui Q., Kang X., Tang C., Bando Y., Golberg D., Wang X., Advanced Materials,2017, 29(6), 1603692 |
| [25] | Wang B., Wang Y., Peng Y., Wang X., Wang N., Wang J., Zhao J., Chemical Engineering Journal,2018, 348, 850—859 |
| [26] | Hou J., Cao C., Idrees F., Ma X., ACS Nano,2015, 9(3), 2556—2564 |
| [27] | Yu Y., Zhang J., Xue L., Huang T., Yu A., Journal of Power Sources,2011, 196(23), 10240—10243 |
| [28] | Qie L., Chen W.M., Wang Z.H., Shao Q.G., Li X., Yuan L.X., Hu X.L., Zhang W.X., Huang Y.H., Advanced Materials,2012, 24(15), 2047—2050 |
| [29] | Qiang Z., Liu X., Zou F., Cavicchi K.A., Zhu Y., Vogt B.D., Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2017, 121(31), 16702—16709 |
| [30] | Jiang Y., Mu D., Chen S., Wu B., Zhao Z., Wu Y., Ding Z., Wu F., Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018, 744, 7—14 |
| [31] | Xiang Z., Chen Y., Li J., Xia X., He Y., Liu H., Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry,2017, 21(8), 2425—2432 |
| [32] | Yang N.H., Wu Y.S., Chou J., Wu H.C., Wu N.L., Journal of Power Sources,2015, 296, 314—317 |
| [33] | Jia D., Wang K., Huang J., Chemical Engineering Journal,2017, 317, 673—686 |
| [34] | Wu X., Shi Z.Q., Wang C.Y., Jin J., Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2015, 746, 62—67 |
| [35] | Yuan Z., Zhao N., Shi C., Liu E., He C., He F., Chemical Physics Letters,2016, 651, 19—23 |
| [36] | Ren Y.R., Yang B., Wei H.M., Ding J.N., Solid State Ionics,2016, 292, 27—31 |
| [37] | Li J., Huang J., Chemical Communications,2015, 51(78), 14590—14593 |
| [38] | Zhou H., Zhu S., Hibino M., Honma I., Ichihara M., Advanced Materials,2003, 15(24), 2107—2111 |
| [39] | Wang M., Jia D., Li J., Huang J., RSC Advances,2014, 4(64), 33981—33985 |
| [40] | Li M., Li J., Li K., Zhao Y., Zhang Y., Gosselink D., Chen P., Journal of Power Sources,2013, 240(1), 659—666 |
| [41] | Ruffo R., Hong S.S., Chan C.K., Huggins R.A., Cui Y., Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2009, 113(26), 11390—11398 |
| [1] | HE Beibei, YANG Kuihua, LYU Rui. Construction of Mn-Cu Bimetal Containing Phyllosilicate Nanozyme and Evaluation of the Enzyme-like Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220150. |
| [2] | JIA Yanggang, SHAO Xia, CHENG Jie, WANG Pengpeng, MAO Aiqin. Preparation and Lithium Storage Performance of Pseudocapacitance-controlled Perovskite High-entropy Oxide La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3 Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| [3] | YAN Zhixuan, MA Ji, QU Jinlei, LIU Li, SUN Chong, LIU Jiwen, LIU Guangye, SUN Lishui, HE Lixia. Synthesis and Application of Modified Low Molecular Weight Polyisoprene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220066. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jie, YIN Bo, LIU Weixin, LIU Xingping, LIAN Wenxian, TANG Shaokun. Fabrication of Boehmite Fiber-reinforced Silica Aerogels and Their Performances [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220483. |
| [5] | LI Yichuan, ZHU Guofu, WANG Yu, CHAI Yongming, LIU Chenguang, HE Shengbao. Effects of Substrate Surface Properties and Precursor Chemical Environment on In⁃situ Oriented Construction of Titanium Silicalite Zeolite Membranes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2934. |
| [6] | BAO Junquan, ZHENG Shibing, YUAN Xuming, SHI Jinqiang, SUN Tianjiang, LIANG Jing. An Organic Salt PTO(KPD)2 with Enhanced Performance as a Cathode Material in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2911. |
| [7] | WU Zhuoyan, LI Zhi, ZHAO Xudong, WANG Qian, CHEN Shunpeng, CHANG Xinghua, LIU Zhiliang. A Highly Efficient One-step Preparation Method of Nano-silicon and Carbon Composite for High-performance Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2500. |
| [8] | TIAN Runsai, LU Qian, ZHANG Hongbin, ZHANG Bo, FENG Yuanyuan, WEI Jinxiang, FENG Jijun. Design and Construction of N-Doping Carbon in⁃situ Coated Cu2O/Co3O4@C Heterostructured Composite Material for Highly Efficient Lithium-ion Storage [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2592. |
| [9] | YI Conghua, SU Huajian, QIAN Yong, LI Qiong, YANG Dongjie. Preparation of Lignin Nanocarbon and Its Performance as a Negative Electrode for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1807. |
| [10] | WANG Yuxiang, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LYU Jiamin, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. One-step Synthesis of Amorphous Silica Aluminum Support Materials with Controllable Acidity and Porosity and Catalytic Performance of Their Pd-based Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1826. |
| [11] | MAO Eryang, WANG Li, SUN Yongming. Advances in Alloy-based High-capacity Li-containing Anodes for Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1552. |
| [12] | WANG Yimeng, LIU Kai, WANG Baoguo. Coating Strategies of Ni-rich Layered Cathode in LIBs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1514. |
| [13] | HAN Yandong, HAN Mingyong, YANG Wensheng. Sol-gel Construction of Mesoporous Silica Nanomicrostructures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 965. |
| [14] | SUN Quanhu, LU Tiantian, HE Jianjiang, HUANG Changshui. Advances in the Study of Heteratomic Graphdiyne Electrode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 366. |
| [15] | ZHOU Zhan, MA Lufang, TAN Chaoliang. Preparation of Layered (NH4)2V6O16·H2O Nanosheets as an Anode for Li-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 662. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||