

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (11): 1913.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170173
• Articles: Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Fangfang, WANG Hongbin, WANG Runwei, QIU Shilun, ZHANG Zongtao*( )
)
Received:2017-03-24
Online:2017-11-10
Published:2017-10-24
Contact:
ZHANG Zongtao
E-mail:zzhang@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Fangfang, WANG Hongbin, WANG Runwei, QIU Shilun, ZHANG Zongtao. Hydrothermal Synthesis and Electrochemical Li-storage Performances of NiCo2O4@C Nanocomposite†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1913.
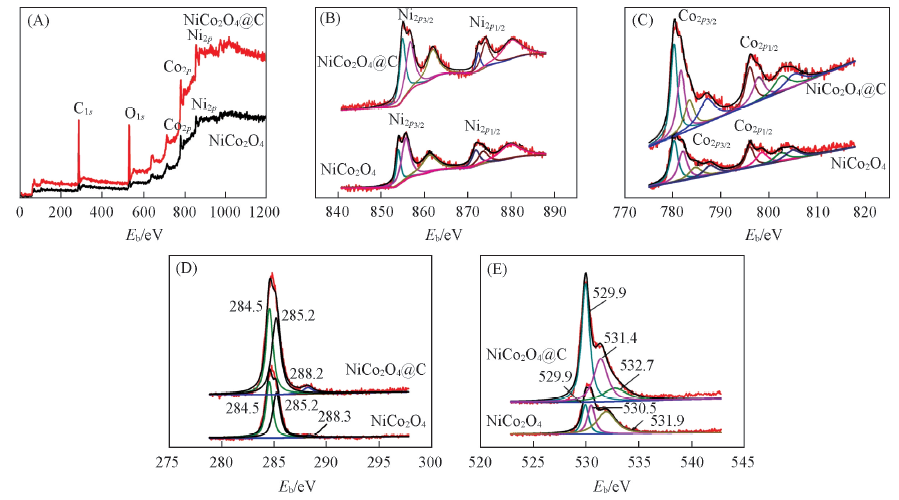
Fig.2 XPS spectra of NiCo2O4 material calcined in air at 400 ℃ and NiCo2O4/C material calcined in N2 at 400 ℃ (A) Full scan; (B) Ni2p; (C) Co2p; (D) C1s; (E) O1s.
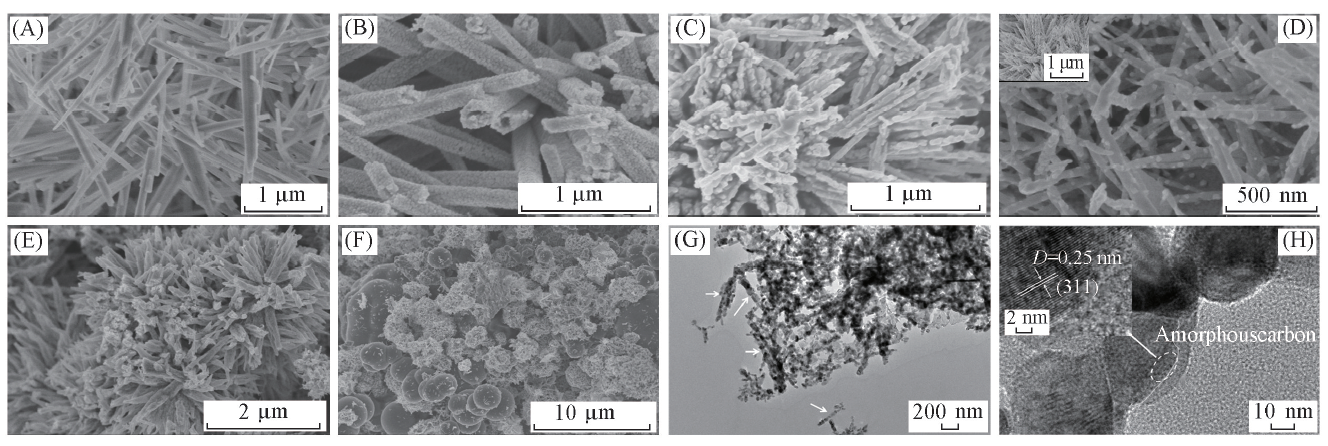
Fig.3 SEM images of the precursor(A), NiCo2O4(B, C) and NiCo2O4@C(D—F) and TEM(G),HRTEM(H) images of NiCo2O4@C-0.5(B) Calcined in air; (C) calcined in N2 atmosphere; (D) NiCo2O4@C-0.25; (E) NiCo2O4@C-0.5; (F) NiCo2O4@C-1.0.
| Sample | N(%) | C(%) | H(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiCo2O4 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.123 |
| NiCo2O4@C-0.25 | 1.97 | 11.63 | 0.785 |
| NiCo2O4@C-0.5 | 3.59 | 23.44 | 1.179 |
| NiCo2O4@C-1.0 | 4.15 | 28.36 | 1.476 |
Table 1 CHN testing results(mass fraction) for different samples
| Sample | N(%) | C(%) | H(%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NiCo2O4 | 0.02 | 0.68 | 0.123 |
| NiCo2O4@C-0.25 | 1.97 | 11.63 | 0.785 |
| NiCo2O4@C-0.5 | 3.59 | 23.44 | 1.179 |
| NiCo2O4@C-1.0 | 4.15 | 28.36 | 1.476 |
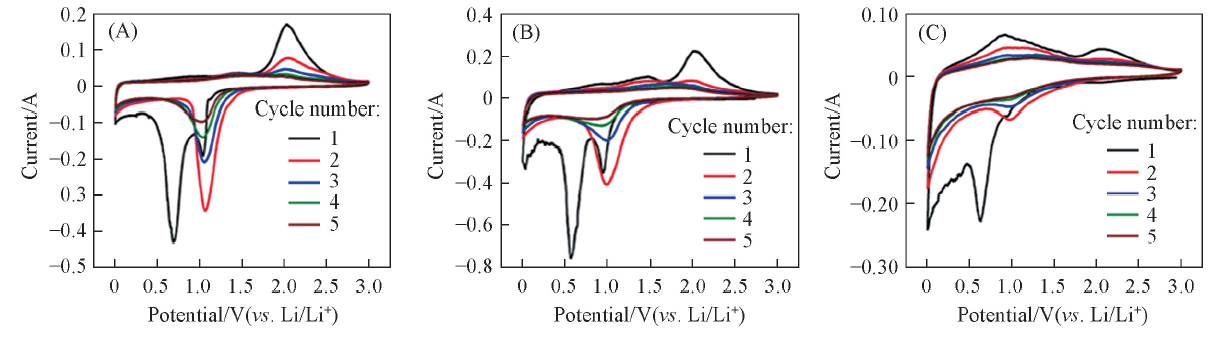
Fig.6 CV curves of NiCo2O4@C-0.25(A), NiCo2O4@C-0.5(B) and NiCo2O4@C-1.0(C) corresponding to the first five turns(voltage window was 0.01—3.0 V, scan rate was 0.05 mV/s)
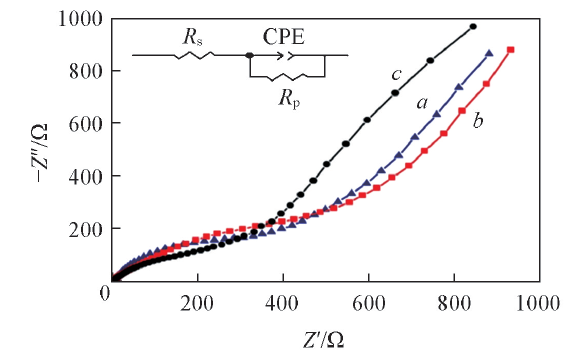
Fig.8 EIS spectra of NiCo2O4@C-0.25(a), NiCo2O4 @C-0.5(b) and NiCo2O4@C-1.0(c) after five cycles of charge/discharge at current density of 100 mA/gInset: equivalent circuit diagram.
| [1] | Chen S. H., Wu J. F., Zhou R. H., Chen Y. Q., Song Y. H., Wang L., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(126), 104433-104440 |
| [2] | Wang C., Wang D. L., Wang Q. Y., Chen H. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(10), 2058-2062 |
| (王崇, 王殿龙, 王秋明, 陈焕俊. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(10), 2058-2062) | |
| [3] | Zou Q., Zai J. T., Liu P., Qian X. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 630-634 |
| (邹琼, 宰建陶, 刘萍, 钱雪峰. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(3), 630-634) | |
| [4] | Li Y., Han X. B., Liang J. C., Leng X. N., Ye K. Q., Hou C. M., Yu K. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 332-336 |
| [5] | Li L. L., Cheah Y. L., Ko Y. W., Teh P. F., Wee G., Wong C. L., Peng S. J., Srinivasan M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(36), 10935-10941 |
| [6] | Liu S.N., Wu J., Zhou J., Fang G. Z., Liang S. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 1-9 |
| [7] | Liu L., Zhang H. J., Yang J., Mu Y. P., Wang Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(44), 22393-22403 |
| [8] | Ma Y. C., Jiang H. Y., Liu Q. Z., Kang W. K., Shi J. S., New J. Chem., 2015, 39(9), 7495-7502 |
| [9] | Mo Y. D., Ru Q., Chen J. F., Song X., Guo L. Y., Hu S. J., Peng S. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(39), 19765-19773 |
| [10] | Mondal A. K., Su D., Chen S. Q., Xie X. Q., Wang G. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(17), 14827-14835 |
| [11] | Peng L., Zhang H. J., Bai Y. J., Yang J., Wang Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(44), 22094-22101 |
| [12] | Shen L. F., Yu L., Yu X. Y., Zhang X.G., Lou X. W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(6), 1868-1872 |
| [13] | Wu J., Mi R., Li S. M., Guo P., Mei J., Liu H., Lau W. M., Liu L. M., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(32), 25304-25311 |
| [14] | Zhang Y. F., Ma M. Z, Yang J., Su H. Q, Huang W., Dong X. C., Nanoscale,2014, 6(8), 4303-4308 |
| [15] | Zhou X. Y., Chen G. H., Tang J. J., Ren Y. P., Yang J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 97-103 |
| [16] | Li G. D., Xu L. Q., Zhai Y. J., Hou Y. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(27), 14298-14306 |
| [17] | Zhai Y. J., Mao H. Z., Liu P., Ren X. C., Xu L. Q., Qian Y. T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(31), 16142-16149 |
| [18] | Li J. F., Xiong S. L., Li X. W., Qian Y. T., Nanoscale,2013, 5(5), 2045-2054 |
| [19] | Guo L.Y., Ru Q., Song X., Hu S. J., Mo Y. D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(16), 8683-8692 |
| [20] | Guo L. Y., Ru Q., Song X., Hu S. J., Mo Y. D., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(25), 19241-19247 |
| [21] | Hu L. L., Qu B. H., Li C. C., Chen Y. J., Mei L., Lei D. N., Chen L. B., Li Q. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(18), 5596-5602 |
| [22] | Long C., Zheng M. T., Xiao Y., Lei B. F., Dong H. W., Zhang H. R., Hu H., Liu Y. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(44), 24419-24429 |
| [23] | Li T., Li X. H., Wang Z. X., Guo H. J., Li Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(22), 11970-11975 |
| [24] | Lei Y., Li J., Wang Y. Y., Gu L., Chang Y. F., Yuan H. Y., Xiao D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 1773-1780 |
| [25] | Jadhav H. S., Kalubarme R. S., Park C. N., Kim J., Park C. J., Nanoscale,2014, 6(17), 10071-10076 |
| [26] | Li B. S., Feng J. K., Qian Y. T., Xiong S. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(19), 10336-10344 |
| [27] | Nuli Y. N., Zhang P., Guo Z. P., Liu H. K., Yang J., Electrochem. Solid-State Lett., 2008, 11(5), A64-A67 |
| [28] | Huang L., Zhang W., Xiang J. W., Huang Y. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 248-255 |
| [29] | Zhang C. F., Yu J. S., Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22(13), 4422-4430 |
| [30] | Li D. L., Gong Y. N., Zhang Y. P., Luo C. Z., Li W. P., Fu Q., Pan C. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31, 12903-12910 |
| [31] | Mo Y. D., Ru Q, Song X, Guo L. Y., Chen J. F., Hou X. H., Hu S. J., Carbon,2016, 109, 616-623 |
| [32] | Li J. F., Xiong S. L., Liu Y. R., Ju Z. C., Qian Y. T., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 981-988 |
| [33] | Li H. H., Xu R. Y., Wang Y. P., Qian B. B., Wang H. B., Chen L., Jiang H. B., Yang Y. L., Xu Y. Y., RSC Adv., 2014, 4(94), 51960-51965 |
| [34] | Liu M., Jin H. Y., Uchaker E., Xie Z. Q., Wang Y., Cao G. Z., Hou S., Li J. Y., Nanotechnology,2017, 28, 155603-155611 |
| [1] | HOU Congcong, WANG Huiying, LI Tingting, ZHANG Zhiming, CHANG Chunrui, AN Libao. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH Composite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [2] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [3] | BAO Junquan, ZHENG Shibing, YUAN Xuming, SHI Jinqiang, SUN Tianjiang, LIANG Jing. An Organic Salt PTO(KPD)2 with Enhanced Performance as a Cathode Material in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2911. |
| [4] | LI Huiyang, ZHU Siying, LI Sha, ZHANG Qiaobao, ZHAO Jinbao, ZHANG Li. Influencing Factors and Promotion Strategies of the First-cycle Coulombic Efficiency of Silicon Suboxide Anodes in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2342. |
| [5] | LIU Tiefeng, ZHANG Ben, SHENG Ouwei, NAI Jianwei, WANG Yao, LIU Yujing, TAO Xinyong. Research Progress of the Binders for the Silicon Anode [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1446. |
| [6] | WANG Renheng, XIAO Zhe, LI Yan, SUN Yiling, FAN Shuting, ZHENG Junchao, QIAN Zhengfang, HE Zhenjiang. Synthesis of Li2FeP2O7 Cathode Material at Different Temperatures and Its Electrochemical Performance for Lithium Ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1299. |
| [7] | ZHANG Huishuang, GAO Yanxiao, WANG Qiuxian, LI Xiangnan, LIU Wenfeng, YANG Shuting. High-low Temperature Properties of Ni-rich LiNi0.6Co0.2Mn0.2O2 Cathode Material by Hydrothermal Synthesis with CTAB Assisted [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 819. |
| [8] | WANG Ye, ZHANG Xiaosi, SUN Lijing, LI Bing, LIU Lin, YANG Miao, TIAN Peng, LIU Zhongyi, LIU Zhongmin. Morphology Control of SAPO Molecular Sieves under the Assistance of Organosilane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 683. |
| [9] | HAN Muyao, ZHAO Lina, SUN Jie. Advances in Silicon and Silicon-based Anode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3547. |
| [10] | WANG Jianyu, ZHANG Qiang, YAN Wenfu, YU Jihong. Roles of Hydroxyl Radicals in Zeolite Synthesis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 11. |
| [11] | WU Qinming, WANG Yeqing, MENG Xiangju, XIAO Fengshou. Reconsideration of Crystallization Process for Aluminosilicate Zeolites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(1): 21. |
| [12] | XIANG Houzheng, XIE Hongxiang, LI Wenchao, LIU Xiaolei, MAO Aiqin, YU Haiyun. Synthesis and Electrochemical Performance of Spinel-type High-entropy Oxides [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1801. |
| [13] | ZHANG Chenyang,WEN Yuehua,ZHAO Pengcheng,CHENG Jie,QIU Jingyi,SUN Yanzhi. Effect of Organic Carbon Source on Performance of LiTi2(PO4)3/C Composite Electrodes in Aqueous Solutions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1352. |
| [14] | LIU Yabing,LI Mingyang,TIAN Ge,ALATENG Shaga,PEI Tonghe,NIE Jingsi. Syntheses, Structures and Catalytic Properties of Two Supramolecular Complexes Based on 2-Pyridylamine and Cluster † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 995. |
| [15] | JI Tianyi, LIU Xiaoxu, ZHAO Jiupeng, LI Yao. Synthesis and Lithium-storage Characteristics of Three-dimensional Cross-linked Graphene Nanofibers † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 821. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||