

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 1185.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170064
• Organic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIU Qin1, YU Yanhua2, CHEN Weida1, CHEN Chanyou1, ZHAO Yunjie3,4,*( ), ZENG Chen1,4,*(
), ZENG Chen1,4,*( )
)
Received:2017-01-26
Online:2017-07-10
Published:2017-05-23
Contact:
ZHAO Yunjie,ZENG Chen
E-mail:yjzhao.wh@gmail.com;chenz@gwu.edu
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LIU Qin, YU Yanhua, CHEN Weida, CHEN Chanyou, ZHAO Yunjie, ZENG Chen. Design of Common Bean Lectin Inhibitor and Its Hemagglutination Activity†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1185.
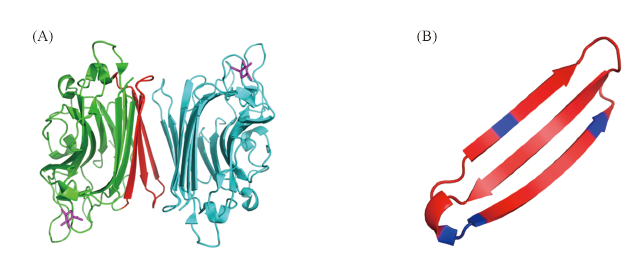
Fig.1 Structural analysis of common bean lectin dimer structure(A) Common bean lectin dimer structure(PDB code: 3WCR, chain A, chain B, β strand and NAG are colored in green, cyan, red and magenta, respectively); (B) β strand interface structure(GLU182-ASP217, less conserved or variable residues are colored in blue).
| Position | Residue | Conservation | Position | Residue | Conservation | Position | Residue | Conservation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 182 | GLU | 3 | 194 | THR | 7 | 206 | LEU | 2 |
| 183 | ASN | 5 | 195 | LYS | 6 | 207 | LYS | 2 |
| 184 | ALA | 7 | 196 | LEU | 5 | 208 | THR | 6 |
| 185 | GLU | 5 | 197 | LEU | 8 | 209 | SER | 6 |
| 186 | VAL | 8 | 198 | VAL | 7 | 210 | PHE | 4 |
| 187 | LEU | 3 | 199 | ALA | 8 | 211 | ILE | 6 |
| 188 | ILE | 9 | 200 | SER | 6 | 212 | VAL | 5 |
| 189 | THR | 6 | 201 | LEU | 7 | 213 | SER | 7 |
| 190 | TYR | 9 | 202 | VAL | 5 | 214 | ASP | 3 |
| 191 | ASP | 6 | 203 | TYR | 5 | 215 | THR | 4 |
| 192 | SER | 7 | 204 | PRO | 4 | 216 | VAL | 8 |
| 193 | SER | 5 | 205 | SER | 6 | 217 | ASP | 8 |
Table 1 Conservation analysis of the common bean lectin dimer interface residues
| Position | Residue | Conservation | Position | Residue | Conservation | Position | Residue | Conservation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 182 | GLU | 3 | 194 | THR | 7 | 206 | LEU | 2 |
| 183 | ASN | 5 | 195 | LYS | 6 | 207 | LYS | 2 |
| 184 | ALA | 7 | 196 | LEU | 5 | 208 | THR | 6 |
| 185 | GLU | 5 | 197 | LEU | 8 | 209 | SER | 6 |
| 186 | VAL | 8 | 198 | VAL | 7 | 210 | PHE | 4 |
| 187 | LEU | 3 | 199 | ALA | 8 | 211 | ILE | 6 |
| 188 | ILE | 9 | 200 | SER | 6 | 212 | VAL | 5 |
| 189 | THR | 6 | 201 | LEU | 7 | 213 | SER | 7 |
| 190 | TYR | 9 | 202 | VAL | 5 | 214 | ASP | 3 |
| 191 | ASP | 6 | 203 | TYR | 5 | 215 | THR | 4 |
| 192 | SER | 7 | 204 | PRO | 4 | 216 | VAL | 8 |
| 193 | SER | 5 | 205 | SER | 6 | 217 | ASP | 8 |
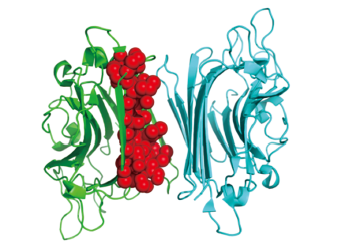
Fig.3 Potential binding pocket at the interface for inhibitor designPDB code: 3WCR, chain A, chain B and pocket are colored in green, cyan and red, respectively.
| [1] | Wang P., Ren S. C., Wang G. L., Food Res. Dev., 2009, 30(12), 171—174 |
| (王鹏, 任顺成, 王国良.食品研究与开发, 2009, 30(12), 171—174) | |
| [2] | Wilson R.F., Stalker H. T.M, Brummer E. C., Legume Crop Genomics, AOCS Press, Champaign, 2004, 60—82 |
| [3] | Xiao J., Li B., Shi X. H., E C. L., Guan H. B ., Feng T.,Nor. Horticul., 2016, (15), 194—198 |
| (肖靖, 李斌, 石晓华, 鄂成林, 管洪波, 凤桐. 北方园艺, 2016, (15), 194—198) | |
| [4] | Wang R., Ding F., Gao Y. J., Wang X. Y., Li Q., Chin. J. Food Hygi., 2016, 28(5), 580—584 |
| (王锐, 丁凡, 高永军, 王霄晔, 李群.中国食品卫生杂志, 2016, 28(5), 580—584) | |
| [5] | Li J. N., Yang W., Peng N., Chen C. Y., Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2015, 48(4), 727—734 |
| (李佳楠, 杨薇, 彭娜, 陈禅友.中国农业科学, 2015, 48(4), 727—734) | |
| [6] | Shang R., Wu H., Guo R., Liu Q., Pan L., Li J. N., Hu Z. H., Chen C. Y., Acta Horticulturae Sunica,2015, 42(11), 2163—2173 |
| (尚蕊, 吴华, 郭瑞, 刘琴, 潘磊, 李佳楠, 胡志辉, 陈禅友.园艺学报, 2015, 42(11), 2163—2173) | |
| [7] | Yin X. L., Li T. T., Liu D. L., Wang Y., Sun S. R., J. Chin. Biotechnol., 2011, 31(7), 133—139 |
| (殷晓丽, 李婷婷, 刘东亮, 王燕, 孙素荣.中国生物工程杂志, 2011, 31(7), 133—139) | |
| [8] | Teixeira-Sa D. M., Reicher F., Braga R. C., Beltramini L. M., de Azevedo M. R., Phytochemistry,2009, 70(17/18), 1965—1972 |
| [9] | Rouge P., Culerrier R., Granier C., Rancé F., Barre A., Molecular Immunology,2010, 47(14), 2359—2366 |
| [10] | Li X. M., Food Science, 2008, 29(11), 328—331 |
| (李笑梅. 食品科学, 2008,29(11), 328—331) | |
| [11] | Zhao Y. J., Liu Z. C., Liu Q., Chen G., Chen C. Y., Zeng C., World J.Complex Medicine,2015, 1(1), 34—39 |
| (赵蕴杰, 刘志超, 刘琴, 陈高, 陈禅友, 曾辰.世界复合医学, 2015, 1(1), 34—39) | |
| [12] | Banerjee N., Senqupta S., Roy A., Ghosh P., Das K., Das S., PLoS One,2011, 6(4), e18593 |
| [13] | Jimenez M., Saiz J. L., Andre S., Gabius H. J., Solis D., Glycobiology,2005, 15(12),1386—1395 |
| [14] | Menard S., Cerf-Bensussan N., Heyman M., Mucosal. Immunol., 2010, 3(3), 247—259 |
| [15] | Nagae M., Soga K., Morita-Matsumoto K., Hanashima S., Ikeda A., Yamamoto K., Yamaguchi Y., Glycobiology,2014, 24(4), 368—378 |
| [16] | UniProt C., Nucleic Acids Res., 2010, 38(Database issue), D142—D148 |
| [17] | Angermuller C., Biegert A., Soding J., Bioinformatics,2012, 28(24), 3240—3247 |
| [18] | Biegert A., Soding J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,2009, 106(10), 3770—3775 |
| [19] | Duan Y., Wu C., Chowdhury S., Lee M. C., Xiong G., Zhang W., Yang R., Cieplak P., Luo R., Lee T., Caldwell J., Wang J., Kollman P., J. Comput. Chem., 2003, 24(16), 1999—2012 |
| [20] | Mahoney M. W., Jorgensen W. L., J. Chemical Physics,2000, 112(20), 8910—8922 |
| [21] | Pronk S., Pall S., Schuiz R., Larsson P., Bjelkmar P., Apostolov R., Shirts M. R., Smith J. C., Kasson P. M., van der Spoel D., Hess B., Bioinformatics,2013, 29(7), 845—854 |
| [22] | Volkamer A., Kuhn D., Rippmann F., Rarey M., Bioinformatics,2012, 28(15), 2074—2075 |
| [23] | Chang C. D., Waki M., Ahmad M., Meienhofer J., Lundell E. O., Haug J. D., European Journal of Allergy & Clinical Immunology,2009, 15(1), 59—66 |
| [24] | Sun C., Zhu Z., Mo Q.H., Lectin, Science Press, Beijing, 1988, 117—130 |
| (孙册, 朱政, 莫庆汉. 凝集素,北京:科学出版社, 1988, 117—130) | |
| [25] | Zhao C., Xia C.G., Yu M., Pan Y., Wang L., Chin. J.Antibiotics,2015, 40(3), 234—240 |
| (赵晨, 夏春光, 于敏, 潘月, 王辂.中国抗生素杂志, 2015, 40(3), 234—240) | |
| [26] | Huang Y. L., Gao X. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universites,2016, 37(5), 928—931 |
| (黄义玲, 高雪峰, 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(5), 928—931) | |
| [27] | Zhu Q. K., Zhu M. L., Zou J. X., Feng P. C., Fan G. T., Liu Z. B., Wang W. J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2013, 29(6), 1153—1158 |
| [28] | Li W. Z., Meng W., Tian P., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2015, 31(1), 149—155 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [3] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [4] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [5] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [6] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [7] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [8] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [9] | QU Siying, XU Qin. Different Roles of Some Key Residues in the S4 Pocket of Coagulation Factor Xa for Rivaroxaban Binding † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| [10] | MA Yucong, FAN Baomin, WANG Manman, YANG Biao, HAO Hua, SUN Hui, ZHANG Huijuan. Two-step Preparation of Trazodone and Its Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism for Carbon Steel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| [11] | ZHANG Zhang,WANG Dong,WANG Xiaolei,XU Yan. Regulation of Ester Synthesis Activity of Rhizopus chinensis Lipase† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 747. |
| [12] | MA Lan,RONG Jingjing,ZHU Youliang,HUANG Yineng,SUN Zhaoyan. Simulation on the Dynamic Process of Formation of Particle Cluster by Generalized Exponential Model† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 195. |
| [13] | WU Hongmei,LI Huiting,LI Yongcheng,WANG Hongqing,WANG Meng. Using Group Contribution Method and Molecular Dynamics to Predict the Glass Transition Temperature of Poly(p-phenylene isophthalamide)† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 180. |
| [14] | ZHU Jingxuan,YU Zhengfei,LIU Ye,ZHAN Dongling,HAN Jiarui,TIAN Xiaopian,HAN Weiwei. Exploration of Increasing the Non-specificity Substrates Activity for the Phosphotriesterase-like Lactonase Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 138. |
| [15] | LIU Yanfang, YANG Hua, ZHANG Hui. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on the Orientation of Alkane Mixture on Graphene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1729. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||