

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (9): 1695.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170019
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Zhiming1,2, DING Qiang1, GU Xiaojun2, XIN Hong3, BAI Binglian2,*( ), LI Min1,*(
), LI Min1,*( )
)
Received:2017-01-10
Online:2017-09-10
Published:2017-08-25
Contact:
BAI Binglian,LI Min
E-mail:baibinglian@jlu.edu.cn;minli@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Zhiming, DING Qiang, GU Xiaojun, XIN Hong, BAI Binglian, LI Min. Organogel and Photo-responsive Behaviour of Hydrazide Derivatives Containing Azobenzene Groups†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1695.
| Solvent | D7(CGC, mg/mL) | D8(CGC, mg/mL) | D10(CGC, mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclohexane | G(2.0) | G(2.0) | G(1.0) |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | S | G(17.5) | G(12.5) |
| DMSO | S | S | G(8.0) |
| Ethanol | P | P | P |
Table 1 Gelation properties of Dn*
| Solvent | D7(CGC, mg/mL) | D8(CGC, mg/mL) | D10(CGC, mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclohexane | G(2.0) | G(2.0) | G(1.0) |
| 1,2-Dichloroethane | S | G(17.5) | G(12.5) |
| DMSO | S | S | G(8.0) |
| Ethanol | P | P | P |
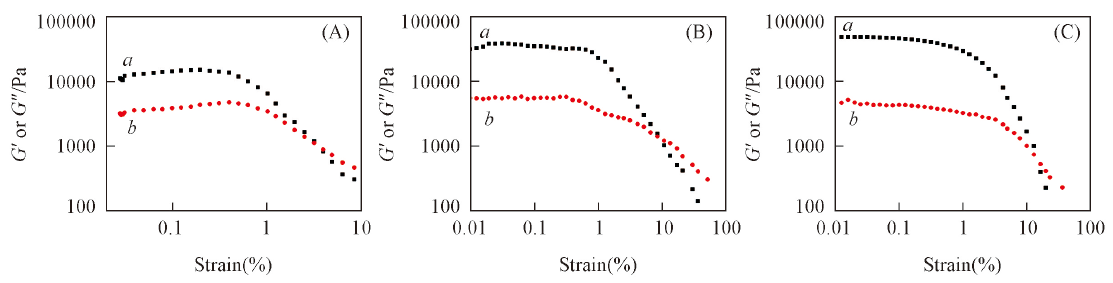
Fig.3 Amplitude dependencies of storage modulus(G', a) and lose moulus(G″, b) of D7(A), D8(B) and D10(C) gel in cyclohexane The frequency is 1 Hz and the strain is 0.1%, 10 mg/mL.
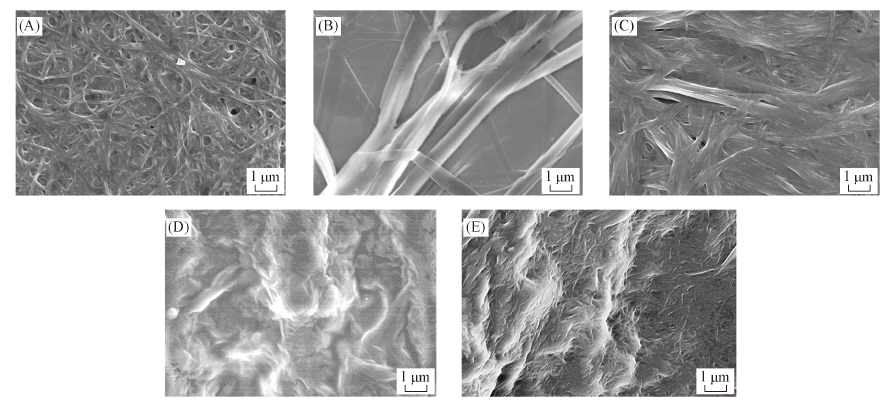
Fig.4 SEM images of D10(A—C), D7(D) and D8(E) xerogels in different solvents(A) Cyclohexane, 1 mg/mL; (B) DMSO, 8 mg/mL; (C) 1,2-dichloroethane, 13 mg/mL; (D, E)cyclohexane, 4 mg/mL.
| [1] | Lehn J. M., Science, 1993, 260, 1762—1763 |
| [2] | Terech P., Weiss R. G., Chem. Rev., 1997, 97, 3133—3160 |
| [3] | George M., Weiss R. G., Accounts Chem. Res., 2006, 39, 489—497 |
| [4] | Yagai S., Karatsu T., Kitamura A., Chem. Eur. J., 2005, 11, 4054—4063 |
| [5] | Klajn R., Pure Appl. Chem., 2010, 82, 2247—2279 |
| [6] | Uchida K., Yamaguchi S., Yamada H., Akazawa M., Miyasaka H.,Chem. Commun., 2009, 4420—4422 |
| [7] | Matsuzawa Y., Tamaoki N., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2010, 114(4), 1586—1590 |
| [8] | Wang C., Chen Q., Sun F., Zhang D., Zhang G., Huang Y., Zhao R., Zhu D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132(9), 3092—3096 |
| [9] | Li X., Gao Y., Kuang Y., Xu B., Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 5364—5366 |
| [10] | Yang R. M., Dong G. X., Zhao D. J., Yang Y. L., Liu Y. H., Chem. Ind. Eng. Pro., 2015, 34(6), 1661—1671 |
| (杨润苗, 董观秀, 赵德建, 杨雁玲, 刘玉海.化工进展,2015, 34(6), 1661—1671) | |
| [11] | Ran X., Wang H. T., Zhang P., Bai B. L., Zhao C. X., Yu Z. X., Li M., Soft Matter, 2011, 7, 8561—8566 |
| [12] | Zhang X., Li M., J. Mol. Struct., 2008, 892, 490—494 |
| [13] | Zhang P., Wang H. T., Liu H. M., Li M., Langmuir,2010, 26(12), 10183—10190 |
| [14] | Zhao C. X., Wang H. T., Bai B. L., Qu S. N., Song J. X., Ran X., Zhang Y., Li M., New J. Chem., 2013, 37, 1454—1460 |
| [15] | Samanta S. K., Pal A., Bhattacharya S., Rao C., J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 20, 6881—6890 |
| [16] | Zhang Y., Wang H. T., Zhao C. X., Bai B. L., Li M., Soft Mater., 2014, 12, 230—236 |
| [17] | Bai B. L., Wei J., Kummetha R. R., Ozaki Y., Wang H. T., Li M., Vib. Spectrosc., 2014, 73, 150—157 |
| [18] | Bai B. L., Mao X. Y., Xi Z. H., Ma J., Lin X. L., Wang H. T., Li M., Liq. Cryst., 2014, 41, 214—221 |
| [19] | Xue C., Jin S., Weng X., Ge J. J., Shen Z., Shen H., Graham M. J., Jeong K. U., Huang H., Zhang D., Guo M., Harris F. W., Cheng S. Z. D., Li C. Y., Zhu L., Chem. Mater., 2004, 16, 1014—1025 |
| [20] | Bai B. L., Mao X. Y., Wei J., Wei Z. H., Li M., Sensors Actuat. B Chem., 2015, 211, 268—274 |
| [21] | Pritam C., Krishnendu D., Kumar D. P., Langmuir,2017, 33, 4500—4510 |
| [22] | Wang F. J., Hashimoto K., Tajima K., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 6014—6020 |
| [23] | Ghosh S., Li X. Q., Stepanenko V., Wurthner F., Chem. Eur. J., 2008, 14, 11343—11357 |
| [24] | Li H. M., Wang J., Ni Y. Z., Zhou Y. F., Yan D. Y., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2016, 74, 415—421 |
| (李惠梅, 王洁, 倪云洲, 周永丰, 颜德岳.化学学报, 2016, 74, 415—421) |
| [1] | LIU Suyu, DING Fei, LI Qian, FAN Chunhai, FENG Jing. Azobenzene-integrated DNA Nanomachine [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220122. |
| [2] | GAO Jian, FENG Yiyu, FANG Wenyu, WANG Hui, GE Jing, FENG Wei. Alkane Grafted Phase Change Azobenzene Materials Based on Low Temperature Heat Release [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220146. |
| [3] | WANG Gaobo, MA Jing. Binding Selectivity Between Diazobenzene and Different Nucleophilic Reagents: Covalent and Noncovalent Interactions [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2238. |
| [4] | LI Shanshan, ZHAO Wenjuan, LI Hui, FANG Qianrong. A Photoresponsive Azobenzene-functionalized Covalent Organic Framework † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1384. |
| [5] | TANG Yucai,QU Huang,ZHANG Wenxi,WANG Feifei,WANG Gang. Synthesis of α-Sulfonyl Ketones via I2/TBHP Promoted Radical Sulfonylation of Silyl Enol Ethers with Sulfohydrazides under Mild Conditions † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 118. |
| [6] | ZHAO Ruiyang,YU Chunyan,HAN Jishu,FU Yunlei,LI Ming,HU Dehua,LIU Fusheng. Preparation of Photo-responsive Film by Electrochemical Deposition Method and the Application in Optical Information Storage† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 358. |
| [7] | LIU Dahai, ZHANG Xueyan, FENG Yusha, DU Xianlong, XUE Longqi, DU Jianshi, ZHANG Guirong, YANG Qingbiao, LI Yaoxian. Synthesis of Novel Fluorescein-Thiospirolactams Hg2+ Fluorescent Probes and Its Application in vivo† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1412. |
| [8] | XIA Meng, PENG Xiongwei, GAO Hongfei, YAN Chao, CHEN Huiru, CHENG Xiaohong. Synthesis and Properties of Barbituric Acid Based Taper Shaped Rodlike Liquid Crystal Compound and Hydrogen Bonded Complex with Triazine Derivative† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1203. |
| [9] | WANG Xiaochuang, ZHANG Jie, XIE Jianwei. Copper/Dodecyl Substituted Hydrazide-pyridine-N-oxide Catalyzed N-Arylation of Imidazoles with Aryliodides in Water† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1178. |
| [10] | WU Juan, ZHAO Bowen, HUANG Chao, CHEN Dongmei, ZHU Bixue. Supramolecular Design of Coordination Complexes of Zn(Ⅱ) and Vapor Adsorption for MeOH† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1069. |
| [11] | YANG Chuanxiao, YU Mengwen, SONG Duoduo, SUN Xiangying. Determination of Cr(Ⅵ) by Ratiometric and Visual Fluorescence Method Based on Formaldehyde Functionalized Polyethyleneimine-rhodamine B Hydrazide System† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 852. |
| [12] | YAN Chao, XIAO Yulong, DAI Heng, CHENG Xiaohong. Synthesis and Properties of Symmetric Azobenzene Derivative† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 475. |
| [13] | WANG Xiao, YANG Xinguo, SHEN Qili. Synthesis and Gel Properties of a Novel Amide Gelator with Melamine Moieties and Rationalizing Gelation Behavior by Hansen Solubility Parameters† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 2068. |
| [14] | WANG Yehai, KONG Yifu, CHEN Chenchen, LI Yiming. Chemical Synthesis of K33 Acetylated SUMO Protein† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(11): 1987. |
| [15] | MI Xiaolong, JIAO Xiaojie, LIU Chang, HE Song, ZENG Xianshun. Rhodamine-based Cell Permeable Fluoresecent Turn-on Probes for Cupric Ion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(10): 1784. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||